Last quarter, a Fortune 500 retailer lost $2.3 million because their inventory system couldn’t talk to their sales platform. Orders went through. Stock numbers didn’t update. Customers got angry. The fix took three weeks. This wasn’t a tech failure. It was a data integration failure. Most enterprises run 900+ applications. As organizations collect data from ERP systems, CRMs, SaaS tools, IoT devices, and external APIs, building a unified and reliable ecosystem has become harder than ever. This is why Data Integration Best Practices are now essential for every modern enterprise.
According to Gartner, poor data quality and ineffective integration cost organizations an average of $12.9 million per year due to inefficiency and bad decisions. Therefore, following strong data integration practices is critical, not only for performance and governance but also for unlocking the full value of analytics, AI, and automation.
In this blog, we will explore modern architectures, integration patterns, governance frameworks, essential tools, real-world use cases, and actionable best practices that help enterprises build a scalable and future-ready data integration ecosystem.
Key Learnings
1. Unified data is essential – Integrating ERP, CRM, SaaS, and streaming systems remove silos and creates a single source of truth for analytics and AI.
2. Modern architectures matter – Using Lakehouse platforms, real-time ingestion, and governed semantic layers ensures scalability, reliability, and flexibility.
3. Standardisation drives quality – Consistent schemas, metadata, and data models improve trust, reduce errors, and simplify downstream analytics.
4. Automation and governance are critical – Automated pipelines, lineage, RBAC, and data quality controls strengthen compliance and reduce operational risk.
5. Continuous optimization is required – Monitoring SLAs, tracking costs, and refining integration patterns ensure long-term efficiency as data grows.
Enhance Data Accuracy and Efficiency With Expert Integration Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
Why Data Integration Matters?
Data integration is a critical foundation for modern organizations because it enables consistent, reliable, and unified data across all business systems. Below are the key reasons why it matters, explained clearly and simply.
1. Eliminates Data Silos Across Systems
To begin with, enterprises use many disconnected systems such as ERP, CRM, HRMS, SaaS platforms, and legacy databases. Data integration breaks these silos and brings information together into a unified, accessible structure.
2. Supports Analytics, Machine Learning, and BI Dashboards
Integrated data powers for advanced analytics, predictive models, and reporting tools like Power BI, Tableau, and Looker. Without clean integrated data, insights become slow, inconsistent, or unreliable.
3. Enables Customer 360 and Operational Use Cases
Next, integration is essential for building customer 360 views, improving operations, enhancing fraud detection, and optimizing supply chain processes. It connects customer behaviors, transactions, and operational signals into a single, business-ready dataset.
4. Ensures Data Quality, Trust, and Compliance
Data integration helps organizations maintain data accuracy, consistency, and completeness. When data flows through governed pipelines with validation rules and metadata, it becomes more trustworthy. It also supports compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
5. Improves Decision-Making Speed Across the Organization
Integrated and consistent data accelerates decision-making by giving business users real-time visibility. Moreover, it reduces manual reconciliations and prevents teams from working with conflicting datasets.

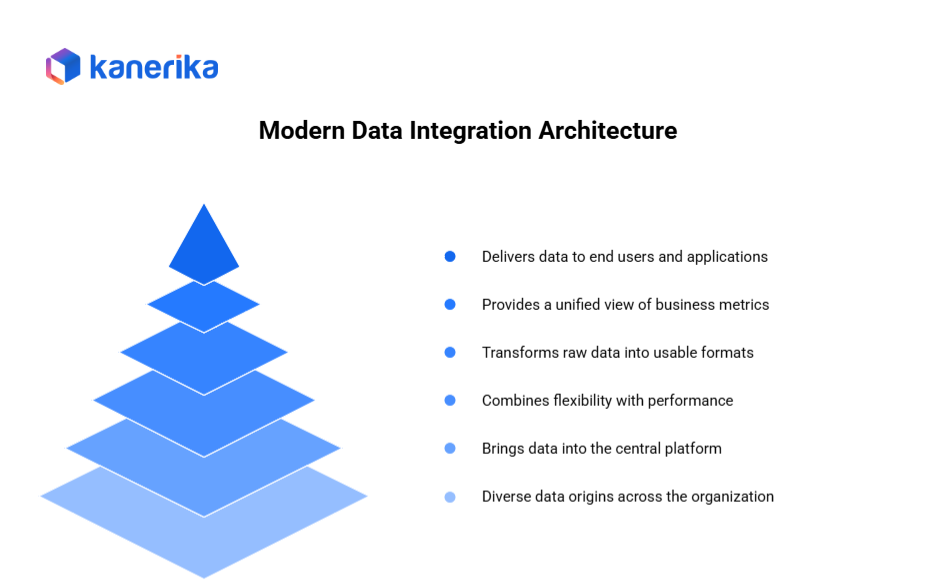
Modern Data Integration Architectures
Modern data integration architectures connect diverse systems and enable data flow through multiple layers. Understanding these components helps organizations build effective data platforms.
1. Source Systems
Data originates from various systems across the organization. SaaS applications like Salesforce and Workday provide cloud-based business data. ERP systems handle financial and operational information. CRM platforms store customer interactions and sales data.
Legacy databases contain historical records accumulated over decades. Additionally, IoT devices generate sensor readings and telemetry data. Streaming data flows continuously from applications, websites, and mobile devices.
2. Ingestion Layer
The ingestion layer brings data from sources into the central platform using different approaches. Batch ingestion uses ETL/ELT tools to load data on schedules like hourly or daily.
Real-time ingestion leverages technologies like Apache Kafka, Azure Event Hubs, and AWS Kinesis to capture streaming data immediately. Furthermore, API-based pipelines pull data from REST or GraphQL endpoints on demand or through scheduled calls.
3. Storage Layer
Modern storage architectures combine flexibility with performance. Lakehouse platforms like Databricks, Snowflake, Microsoft Fabric, and Google BigQuery unify data lake and warehouse capabilities.
Traditional data warehouses continue serving structured analytics needs. Organizations separate hot storage for frequently accessed data from cold storage for archival information, optimizing costs while maintaining accessibility.
4. Processing Layer
The processing layer transforms raw data into usable formats. ETL/ELT workflows clean, validate, and structure data for analysis. Stream processing engines like Apache Flink, Spark Streaming, and Kafka Streams handle real-time data transformation.
These technologies enable transformation at scale, processing millions of records efficiently across distributed computing clusters.
5. Semantic Layer
The semantic layer provides a unified view of business metrics and definitions. It creates governed datasets ensuring everyone uses consistent calculations and terminology. This layer abstracts technical complexity, allowing business users to access data using familiar business language rather than understanding underlying table structures.
6. Consumption Layer
Finally, the consumption layer delivers data to end users and applications. Business intelligence tools like Power BI, Looker, and Tableau visualize data through dashboards and reports.
Machine learning platforms including Azure ML and AWS SageMaker use data for training and deploying models. Moreover, reverse ETL pushes insights back to operational systems, closing the loop between analytics and action.
Data Integration Best Practices
Building a reliable, scalable, and future-ready data integration ecosystem requires thoughtful design and disciplined execution. The following best practices offer a comprehensive guide to help organizations ensure that their integration pipelines are efficient, maintainable, and aligned with business goals. Each practice is explained clearly and in simple language, so teams across all levels can adopt them effectively.
1. Start with a Clear Integration Strategy
To begin with, every data integration initiative must be guided by a well-defined strategy.
- Identify your goals: speed, accuracy, data volume, or real-time insights.
- Understand business priorities and what outcomes the integration must support.
- Map business processes to data flows so that every integration task aligns with real use cases.
This step ensures that teams avoid unnecessary complexity and focus on what truly matters.
2. Standardize Data Models & Schemas
Consistency is key for smooth integration.
- Use canonical data models so that different systems speak a unified “language.”
- Enforce consistent naming conventions, data types, and formats.
- Implement schema validation rules to prevent errors downstream.
This standardization improves data quality, reduces confusion, and simplifies maintenance.
3. Choose the Right Integration Pattern
Different use cases require different integration approaches.
- Use batch processing for daily or hourly data that doesn’t need real-time updates.
- Use streaming architecture (Kafka, Event Hubs, Kinesis) for events and real-time needs like fraud detection.
- Use API-driven pipelines for microservices and SaaS systems that require instant, transactional connectivity.
Choosing the right pattern prevents latency issues and unnecessary operational load.
4. Use ETL/ELT Intelligently
Modern cloud systems require flexible transformation strategies.
- Use ELT for cloud warehouses like Snowflake, BigQuery, and Fabric, where compute can scale on demand.
- Use ETL for on-premise, legacy, or regulated environments.
- Always push compute to the most scalable and cost-efficient platform available.
This ensures your pipelines remain both fast and cost-effective.
5. Ensure High Data Quality
Data quality is the backbone of meaningful analytics.
- Validate source data at ingestion time.
- Apply cleansing, deduplication, standardization, and transformation rules.
- Monitor metrics like null counts, drift, and freshness.
High-quality data builds trust and deliver more accurate insights.
6. Build Scalable, Modular Pipelines
A well-designed pipeline should be easy to extend and maintain.
- Reuse transformation logic instead of rewriting code.
- Separate ingestion, staging, and production layers for cleaner architecture.
- Modularize your pipelines to simplify updates and testing.
This approach reduces technical debt and speeds up enhancements.
Data Integration Services in the California
Explore Kanerika’s data integration services in California, designed to seamlessly connect diverse data sources, streamline workflows, and enhance data accessibility.
7. Adopt Metadata-Driven & Declarative Integration
Metadata brings intelligence and automation to integration.
- Use metadata catalogues like Azure Purview, Collibra, or Alation.
- Enable auto-documentation, data lineage, and schema tracking.
- Drive transformations using metadata instead of hardcoded logic.
This improves governance, transparency, and long-term maintainability.
8. Prioritize Governance & Compliance
To keep data secure and compliant, strong governance is essential.
- Use role-based access control and audit trails.
- Apply PII masking, encryption, and tokenization wherever needed.
- Ensure alignment with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
Governed data pipelines protect organizations from risk and strengthen trust.
9. Automate Everything Possible
Automation accelerates development and improves reliability.
- Use orchestration tools like Airflow, Azure Data Factory, Prefect, or Dagster.
- Automate error handling, retries, notifications, and rollbacks.
- Standardize reusable templates for ingestion and transformation.
This reduces manual effort and ensures consistent execution.
10. Test Integration Workflows Rigorously
Testing prevents issues from reaching production.
- Use unit tests, integration tests, schema tests, and regression tests.
- Test both data and logic to catch edge cases early.
- Validate upstream and downstream impacts of changes.
Strong testing practices make your pipelines more predictable and error-resistant.
11. Monitor, Measure & Optimize
Finally, continuous improvement is crucial.
- Track pipeline SLAs, throughput, and latency.
- Use performance dashboards and cost monitoring tools.
- Identify bottlenecks and re-architect when workloads grow.
Ongoing optimization ensures that pipelines stay efficient as data volumes and business demands increase.
Key Tools for Data Integration
Building an effective data integration ecosystem requires the right set of tools across ingestion, transformation, governance, and activation. Each category serves a unique purpose, and choosing the right combination ensures smooth, scalable, and reliable data flow across the enterprise. Below is a clear breakdown of essential tools used in modern data integration.
1. Integration Platforms
To begin with, these platforms simplify the movement of data across SaaS apps, databases, ERP systems, and cloud platforms.
- Informatica, Talend, Matillion, Fivetran, Stitch, Azure Data Factory (ADF), and MuleSoft
They offer pre-built connectors, low-code transformations, and strong governance features, making them suitable for enterprise-grade workloads.
2. Streaming Systems
For real-time analytics and event-driven applications, streaming tools are crucial.
- Apache Kafka, Apache Pulsar, Azure Event Hubs, Amazon Kinesis
These systems support continuous ingestion, high-throughput pipelines, and real-time data processing across microservices and analytics layers.
3. Cloud Data Engines
Next, cloud-native engines act as the core processing and storage platforms.
- Databricks, Snowflake, Google BigQuery, Microsoft Fabric
They enable scalable ETL/ELT, SQL analytics, ML workflows, and unified lakehouse architectures.
4. Governance Tools
Governance ensures trust, security, and compliance across integrated data.
- Collibra, Alation, Azure Purview
They provide metadata catalogs, lineage tracking, access control, and policy enforcement.
5. Orchestration & Automation
These tools manage workflow scheduling, dependencies, and automated execution.
- Apache Airflow, dbt, Prefect, Dagster
They help teams build modular, testable, and repeatable pipeline workflows.
6. Reverse ETL & Activation
Finally, activation tools push clean, enriched data back into business apps.
- Hightouch, Census
They sync warehouse data to CRM, marketing, finance, and support platforms, enabling operational analytics.
Data Ingestion vs Data Integration: How Are They Different?
Uncover the key differences between data ingestion and data integration, and learn how each plays a vital role in managing your organization’s data pipeline.
Real-World Use Cases
Modern data integration delivers real business value by connecting fragmented systems and enabling faster, smarter decisions. The following real-world examples show how organizations across different industries use data integration to transform their operations. Each example highlights both the technical flow and the business outcomes enabled by seamless data movement.
1. Customer 360 for Retail
To begin with, retailers rely heavily on personalized engagement, but customer data is spread across CRM systems, e-commerce platforms, loyalty programs, POS systems, and mobile apps.
By integrating these sources into a unified pipeline, retailers can:
- Build complete Customer 360 profiles
- Understand buying behavior in real time
- Deliver personalized offers and dynamic pricing
- Increase customer lifetime value
This level of integration enables relevance, higher conversion rates, and improved retention.
2. Fraud Detection in Banking
Fraud detection requires both speed and accuracy. Banks often integrate data from payment gateways, core banking systems, device telemetry, user behavior logs, and geolocation services.
With real-time data integration:
- Fraud scoring systems analyze events instantly
- Machine learning models receive up-to-date behavioral signals
- False positives reduce significantly
- High-risk cases trigger automated alerts
This helps financial institutions protect customers while improving trust and compliance. As customers move money across accounts constantly, banks also refine fraud controls around routine transfers, for example, advising on the best way to transfer money between banks helps customers pick safer, properly authenticated methods that reduce the risk of interception or account-takeover attempts.
3. Supply Chain Visibility
Supply chains depend on precise, timely information. By integrating data from ERP systems, warehouse management systems (WMS), shipment tracking platforms, and IoT sensors, companies achieve:
- End-to-end visibility of goods
- Accurate forecasting of delays
- Optimized inventory levels
- Reduced downtime across warehouses and plants
This integration helps prevent costly disruptions and supports proactive decision-making.
4. Healthcare Interoperability
Healthcare systems often struggle with siloed EMRs, lab systems, imaging platforms, pharmacy systems, and insurance databases.
Data integration allows:
- Unified patient histories
- Faster diagnosis and treatment
- Improved care coordination
- Compliance with standards such as HL7 and FHIR
As a result, hospitals enhance both patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
5. AI/ML Feature Pipelines
Finally, advanced analytics and machine learning models depend on clean, unified data. Integration pipelines connect raw data from multiple systems into structured feature stores. This helps organizations:
- Train models on consistent, high-quality datasets
- Reduce data drift and maintain model accuracy
These pipelines unlock reliable AI-driven decision-making at a scale.
Maximizing Efficiency: The Power of Automated Data Integration
Discover the key differences between data ingestion and data integration, and learn how each plays a vital role in managing your organization’s data pipeline.
Common Data Integration Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the right tools and architecture, data integration can fail if core mistakes are not addressed. These mistakes often lead to slow pipelines, inaccurate insights, and costly rework. Below are the most common pitfalls and how to avoid them, explained simply and clearly.
1. Missing Business Alignment
To begin with, many teams rush into building pipelines without understanding the business purpose. When integration work is not aligned with clear outcomes, it leads to low adoption and wasted effort.
2. Overcomplicated Pipelines
Some organizations build overly complex workflows with unnecessary transformations and branching logic. This increases maintenance costs and makes troubleshooting harder. Simplicity and modular design are always better.
3. Inconsistent Schemas
A common issue is mismatched column names, data types, or formats across systems. Without schema standardization, teams face frequent breaks, reconciliation errors, and unreliable reporting.
4. Manual Processes Without Automation
Manual ingestion, validation, and deployment slow down development. Moreover, they introduce human error. Automating ingestion, transformations, testing, and monitoring ensures consistent and repeatable execution.
5. Ignoring Data Quality
If data is not validated or cleaned early, errors propagate across pipelines. Missing values, duplicates, and incorrect formats reduce the accuracy of analytics and AI models. Data quality checks must be embedded into each stage.
6. No Governance or Lineage
Without governance, it becomes hard to track who owns which dataset, how data flows, or where sensitive information resides. Lack of lineage makes audits and debugging difficult.
7. Over-Reliance on Batch When Streaming Is Needed
In many cases, teams continue using batch pipelines even when real-time requirements exist. This creates latency issues in fraud detection, customer analytics, and operations.

Data Integration Roadmap for Enterprises
A structured roadmap helps enterprises implement data integration in a predictable, scalable, and low-risk way. The following step-by-step guide outlines how organizations can move from scattered data sources to a unified, governed, and automated data ecosystem.
1. Assess Current State & Data Maturity
To begin with, evaluate existing systems, data quality, integration methods, and team capabilities. Identify silos, pain points, and bottlenecks.
2. Define Integration Goals and SLAs
Next, clarify what the organization wants to achieve—real-time insights, improved data quality, cost reduction, or regulatory compliance. Set clear SLAs for latency, freshness, and availability.
3. Identify Source Systems and Integration Needs
Document ERP, CRM, SaaS apps, databases, IoT sources, and streaming systems. Understand formats, volumes, and update frequency.
4. Select Architecture (Batch, Streaming, Hybrid)
Choose the right pattern based on business needs.
- Batch for periodic ingestion
- Streaming for real-time decisions
- Hybrid for complex enterprises
5. Choose Tools & Platforms
Select integration tools, cloud platforms, storage engines, and orchestration frameworks that fit your architecture and scale needs.
6. Build the Ingestion Layer
Create connectors, pipelines, and ingestion workflows with proper error handling and retries.
7. Standardize Schemas & Metadata
Apply common data models, consistent naming, and metadata catalogs to maintain trust and traceability.
8. Implement Governance
Set up role-based access, lineage tracking, quality checks, and compliance controls.
9. Automate Pipelines
Use orchestration tools to automate scheduling, alerts, documentation, and scaling.
10. Test & Validate
Run unit tests, schema tests, reconciliation checks, and regression tests to ensure reliability.
11. Deploy, Monitor & Optimize
Move production, monitor performance and cost, and refine pipelines based on metrics.
12. Scale Across More Domains
Finally, extend integration to new departments, new sources, and more advanced AI/ML workflows.
Simplify Your Data Management With Powerful Integration Services!!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
Case Studies: Kanerika’s Successful Data Integration Projects
1. Unlocking Operational Efficiency with Real-Time Data Integration
The client is a prominent media production company operating in the global film, television, and streaming industry. They faced a significant challenge while upgrading its CRM to the new MS Dynamics CRM. This complexity in accessing multiple systems slowed down response times and posed security and efficiency concerns.
Kanerika has reolved their problem by leevraging tools like Informatica and Dynamics 365. Here’s how we our real-time data integration solution to streamline, expedite, and reduce operating costs while maintaining data security.
- Implemented iPass integration with Dynamics 365 connector, ensuring future-ready app integration and reducing pension processing time
- Enhanced Dynamics 365 with real-time data integration to paginated data, guaranteeing compliance with PHI and PCI
- Streamlined exception management, enabled proactive monitoring, and automated third-party integration, driving efficiency
2. Enhancing Business Performance through Data Integration
The client is a prominent edible oil manufacturer and distributor, with a nationwide reach. The usage of both SAP and non-SAP systems led to inconsistent and delayed data insights, affecting precise decision-making. Furthermore, the manual synchronization of financial and HR data introduced both inefficiencies and inaccuracies.
Kanerika has addressed the client challenges by delvering follwoing data integration solutions:
- Consolidated and centralized SAP and non-SAP data sources, providing insights for accurate decision-making
- Streamlined integration of financial and HR data, ensuring synchronization and enhancing overall business performance
- Automated integration processes to eliminate manual efforts and minimize error risks, saving cost and improving efficiency
Kanerika: The Trusted Choice for Streamlined and Secure Data Integration
At Kanerika, we excel in unifying your data landscapes, leveraging cutting-edge tools and techniques to create seamless, powerful data ecosystems. Our expertise spans the most advanced data integration platforms, ensuring your information flows efficiently and securely across your entire organization.
With a proven track record of success, we’ve tackled complex data integration challenges for diverse clients in banking, retail, logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing. Our tailored solutions address the unique needs of each industry, driving innovation and fueling growth.
We understand that well-managed data is the cornerstone of informed decision-making and operational excellence. That’s why we’re committed to building and maintaining robust data infrastructures that empower you to extract maximum value from your information assets.
Choose Kanerika for data integration that’s not just about connecting systems, but about unlocking your data’s full potential to propel your business forward.
Empower Your Data-Driven Workflows With Data Integration Best Practices!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
FAQs
1. What is data integration and why is it important?
Data integration connects information from multiple systems like ERP, CRM, SaaS, databases, into a unified view. It improves data quality, enables analytics, supports AI, and reduces operational inefficiencies.
2. What are the most common challenges in data integration?
Typical challenges include siloed systems, inconsistent schemas, poor data quality, legacy platforms, lack of governance, and high latency in pipelines.
3. What is the best architecture for modern data integration?
A Lakehouse or cloud-native architecture works best, combining real-time ingestion, scalable storage, ELT processing, a semantic layer, and governed consumption tools.
4. How do I choose between ETL and ELT?
Choose ETL for legacy or regulated systems needing strict control. Choose ELT when using cloud engines like Snowflake, Databricks, BigQuery, or Fabric that can scale compute efficiently.
5. What tools are commonly used for data integration?
Popular tools include Informatica, Talend, ADF, MuleSoft, Fivetran, Kafka, Databricks, Snowflake, Collibra, Airflow, dbt, and Hightouch.
6. How can I ensure high data quality during integration?
Implement validation rules, cleansing, deduplication, schema checks, profiling metrics, and automated alerts to catch anomalies early.
7. What governance practices should be included in integration projects?
Use RBAC, lineage tracking, metadata catalogues, audit logs, PII masking, and regulatory frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.










