Databricks Unity Catalog implementation is becoming essential for enterprises struggling with fragmented data governance across multiple clouds and workspaces. Disconnected policies, inconsistent permissions, and data duplication create security and compliance risks that slow down analytics and decision-making. In fact, a Gartner survey found that 60% of organizations face management and compliance challenges due to siloed data systems and lack of centralized oversight.
To address these issues, Databricks Unity Catalog acts as a unified governance layer that brings together centralized access control, metadata management, and data lineage tracking within the Databricks Lakehouse Platform. It simplifies how organizations secure, organize, and audit their data across teams and environments.
This blog explains what Unity Catalog is, why it matters, its architecture, step-by-step implementation process, and best practices for achieving consistent, secure, and scalable enterprise data control.
Key Learnings
- Databricks Unity Catalog provides a single, unified management layer that centralizes access control, metadata management, and data lineage across all Databricks workspaces.
- Centralized management ensures easier reviewing, faster permission management, and improved regulatory compliance with frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA.
- The architecture integrates smoothly with identity systems (Azure AD, AWS IAM), cloud storage (ADLS, S3, GCS), and BI tools (Power BI, Tableau, Looker).
- Adopting best practices such as minimal access, naming conventions, automatic setup with Terraform, and regular audits improves efficiency and security.
- Integrating Unity Catalog with enterprise ecosystems (Collibra, Alation, or Informatica) enhances data to be easily found and controls access systems.
- With effective Databricks Unity Catalog implementation, companies can achieve secure collaboration, data democratization, and reliable insights at scale.
What is Databricks Unity Catalog?
Databricks Unity Catalog is a unified management solution that helps organizations manage all their data, analytics, and AI assets from one central place. It simplifies how companies handle permissions, track data usage, and maintain compliance across multiple Databricks workspaces.
The main goal of Unity Catalog is to centralize access control, metadata management, and data lineage, giving teams a single view of all data assets, whether they are tables, files, or machine learning models. It eliminates the complexity of managing permissions separately in each workspace, making governance easier and more consistent.
Key Features of Databricks Unity Catalog:
- Centralized metadata storage: Keeps information about all data assets, such as tables, files, models, and dashboards in one secure location.
- Fine-grained access control: Allows administrators to set precise permissions at the catalog, schema, and table levels, making sure that right people have the right access.
- Automated data lineage tracking: Records how data moves and transforms across SQL queries, notebooks, and workflows, helping users understand the full data journey.
- Integration with cloud identity providers: Works with services like Azure AD, AWS IAM, and Google Cloud IAM for seamless authentication and role management.
Organizations use Unity Catalog to achieve consistency, compliance, and better data discoverability. It supports efficient collaboration, reduces duplication, and builds trust in enterprise data by providing full transparency into how data is stored, accessed, and used across the Databricks platform.

Why Unity Catalog Matters for Enterprises
Managing data security and compliance across multiple Databricks workspaces is a growing challenge for companies. Each workspace often runs with its own set of permissions and management rules, leading to siloed management, duplicate policies, and inconsistent data access. This fragmentation not only increases risk but also slows down analytics and collaboration.
Databricks Unity Catalog helps solve this by providing a centralized governance framework that simplifies how organizations control access, maintain compliance, and monitor data usage. It creates a single source of truth for data governance, making it easier to manage security at scale.
Importance of Unity Catalog:
- Centralized security: Offers one governance model across all data, models, and ML assets, reducing the need for separate configurations per workspace.
- Simplified compliance: Makes it easier to align with regulatory standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, ensuring secure and auditable data practices.
- Cross-cloud flexibility: Operates consistently across AWS, Azure, and GCP, allowing enterprises to maintain governance across multi-cloud environments.
- Enhanced discoverability: Provides a unified search and metadata view, enabling teams to quickly find and understand data assets.
A Databricks report highlights that enterprises using Unity Catalog have reduced time spent managing data permissions by up to 40%, while improving audit readiness and governance consistency.
Overall, Unity Catalog delivers clear business value by enabling secure collaboration, faster audits, and data democratization which empowers teams to access and use data confidently within controlled boundaries.
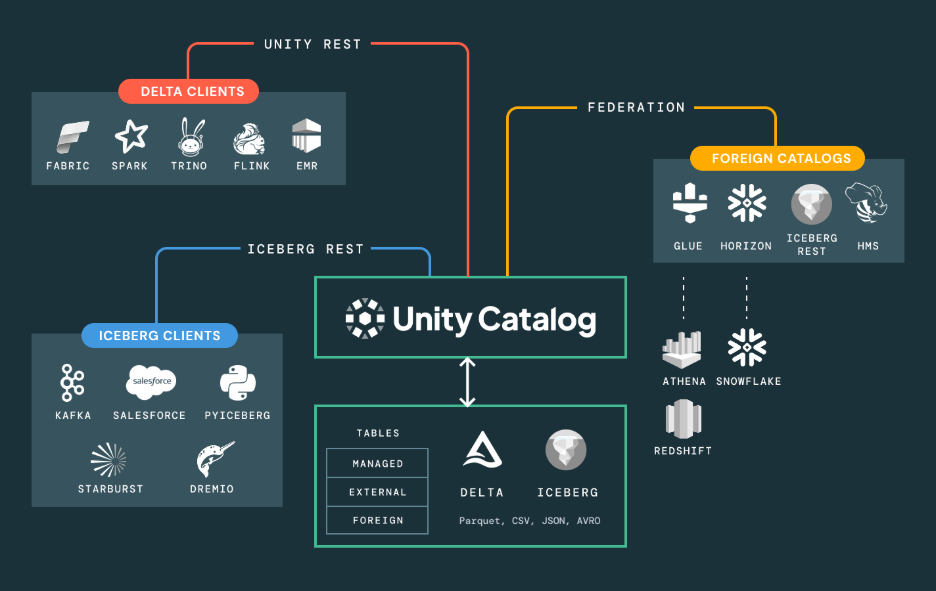
Core Components of Unity Catalog
Unity Catalog organizes data through a hierarchy of components. Each component serves a specific purpose in managing data access, governance, and metadata.
1. Metastore
The metastore acts as the central metadata repository. It stores information about all data objects including tables, views, schemas, and catalogs. Organizations typically create one metastore per region or cloud account. Moreover, the metastore sits at the top of the Unity Catalog hierarchy and contains all metadata for workspaces attached to it.
2. Catalog
Catalogs provide the top-level container defining access boundaries. Each catalog holds schemas, tables, and managed data within a single organizational unit. However, organizations create separate catalogs for production of data, development environments, or different business units. Catalogs help isolate data and control who can access specific datasets.
3. Schemas (Databases)
Schemas provide logical grouping for related data assets. They sit inside catalogs and organize tables by business domain or department. As well as a finance catalog might contain schemas for accounts_payable, accounts_receivable, and general_ledger. Schemas help segregate data while maintaining it within the same catalog boundary.
4. Tables and Views
Tables and views represent the actual data assets users query and analyze. Unity Catalog supports both managed tables stored in Unity Catalog’s storage and external tables pointing to data in other locations. Moreover, Delta Lake tables receive special support for ACID transactions, time travel, and scalability. Views provide logical representations of data without storing it separately.
5. Data Lineage
Unity Catalog automatically captures data lineage showing how data moves through your system. Lineage tracking works at both column level and table level. Also, users see which upstream sources feed their tables and which downstream systems consume their data. Hence, this visibility helps understand data transformations and dependencies without reading code or documentation.
6. Permissions and Roles
Unity Catalog implements role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) for fine-grained security. Permissions control who can create, read, update, or delete specific data objects. Additionally, the system supports privileges on catalogs, schemas, tables, views, and even individual columns. Moreover, users receive only the minimum access needed for their work. Permissions apply across data assets and machine learning models, providing unified security management.
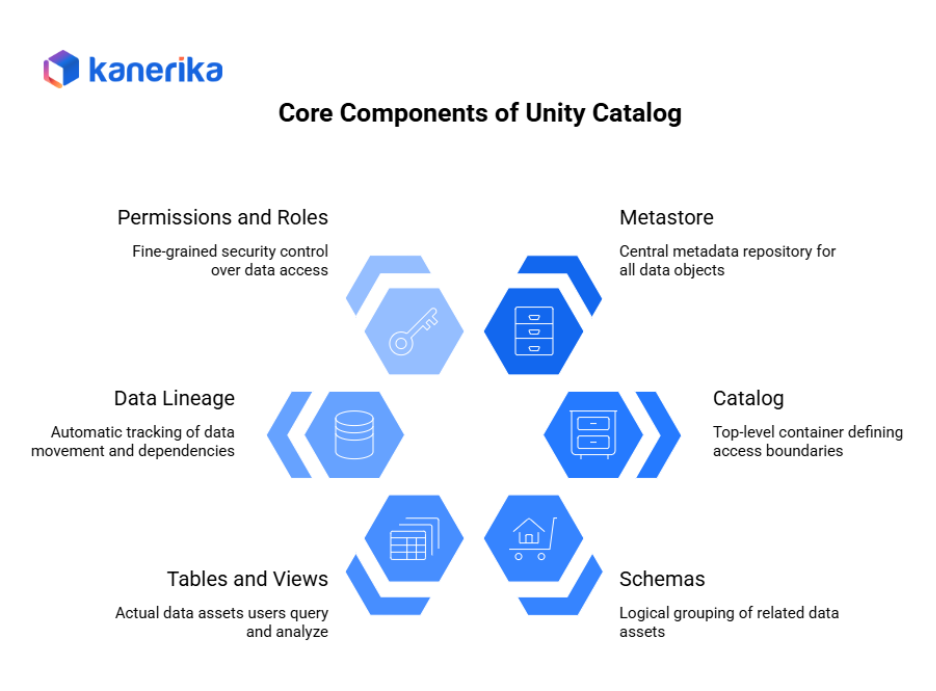
Architecture Overview of Databricks Unity Catalog
Databricks Unity Catalog architecture forms the backbone of secure and centralized data governance in the Databricks Lakehouse Platform. It provides a unified layer that manages metadata, access control, and data lineage tracking across all workspaces and environments.
How Unity Catalog Fits within the Databricks Lakehouse Architecture:
- Central governance layer: Unity Catalog acts as a shared governance layer that sits above all Databricks workspaces, linking them to a single metastore for consistent data control.
- Metadata management: The metastore stores details of catalogs, schemas, tables, and views, ensuring that data assets are uniformly registered and tracked across regions.
- Data lineage tracking: Automatically records how data moves across pipelines, notebooks, and queries, providing full visibility into transformations and dependencies.
- Integration with Delta Lake: Works seamlessly with Delta tables for ACID compliance, scalability, and version control.
Key Integrations:
- Identity systems: Connects with Azure Active Directory, AWS IAM, and other identity providers to enforce user authentication and role-based access.
- Data storage layers: Integrates with cloud storage systems like Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS), Amazon S3, and Google Cloud Storage (GCS) to manage structured and unstructured data securely.
- BI and ML tools: Ensures unified governance for analytics and AI platforms such as Power BI, Tableau, and Databricks’ own MLflow and AutoML tools.
Unity Catalog also supports secure data sharing through Delta Sharing, allowing organizations to collaborate safely with external partners while maintaining strict control over shared assets.
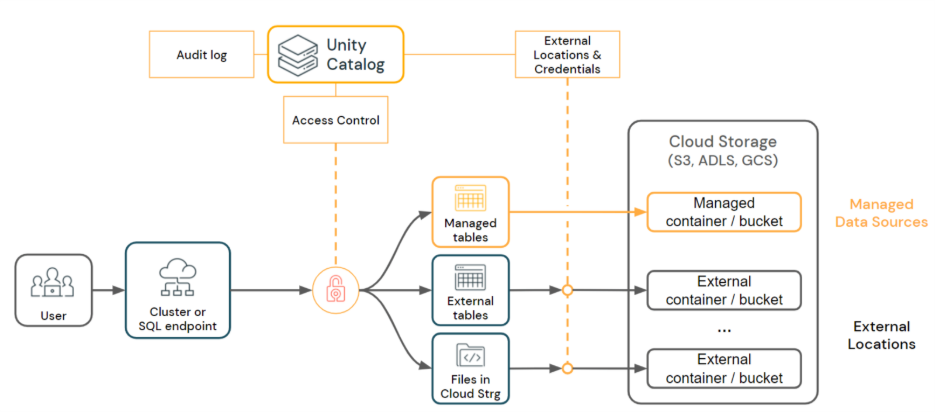
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Implementing Databricks Unity Catalog helps organizations build a unified data governance framework across all workspaces. Below is a step-by-step approach to plan, configure, and validate your setup efficiently.
Step 1: Prerequisites and Planning
Before starting the implementation, clearly define your data governance objectives. Identify the data domains, access models, and compliance requirements your organization follows.
Ensure you have account-level access in Databricks and that your workspaces are properly connected.
Set up identity integrations by defining users, groups, and authentication through your preferred cloud identity provider, such as Azure Active Directory, AWS IAM, or Okta.
Step 2: Create a Metastore
The metastore is the central repository that stores metadata about all data assets. You can create it through the Databricks UI or using the REST API.
Assign storage credentials (S3, ADLS, or GCS) and define a default storage location where metadata and managed tables will reside.
Example (Databricks UI):
- Go to the Account Console → Data Governance.
- Select Create Metastore.
- Provide a name, region, and storage location path.
- Assign appropriate storage credentials.

Step 3: Assign Workspaces to Metastore
Once your metastore is created, link all workspaces that need centralized governance. Each workspace can only be connected to one metastore per region.
To assign:
- In the Databricks Account Console, navigate to Workspaces.
- Select the workspace and click Assign Metastore.
- Choose your created metastore and confirm the assignment.
This step ensures that all governance settings—such as access control and lineage—apply consistently across workspaces.
Step 4: Set Up Catalogs, Schemas, and Tables
After linking your workspaces, define the data organization structure. Unity Catalog follows a three-level hierarchy:
Catalog → Schema → Table.
Use Databricks SQL or REST APIs to create these entities.
Example SQL commands:

This structure ensures that datasets are logically grouped and access permissions are easy to manage.
Step 5: Configure Access Controls
Unity Catalog allows fine-grained access control using SQL-based GRANT statements. You can define access at the catalog, schema, or table level.
Example:
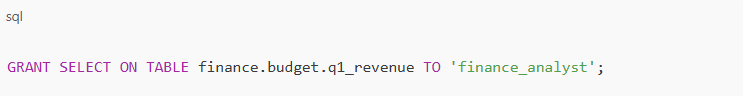
This ensures users and groups only have access to the data they need, improving data security and compliance.
Step 6: Enable Lineage and Auditing
Unity Catalog automatically captures data lineage for all SQL queries, notebooks, and workflows. You can view data flow from source to destination tables in the Databricks UI under the Lineage tab.
Enable auditing by integrating with Databricks audit logs or exporting metadata via REST APIs. This helps in compliance tracking and change management.
Step 7: Validate and Test
Finally, validate the entire setup.
- Run test queries to verify that permissions and access rules are enforced.
- Check lineage tracking for accuracy.
- Confirm that workspace assignments and catalogs are synchronized.
Document your governance policies, approval workflows, and escalation processes for future reference.
This validation phase ensures a stable, secure, and scalable Unity Catalog environment ready for enterprise data operations.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Workspace not seeing metastore – Verify the workspace is in the same region as the metastore. Check workspace assignment in account console.
- Permission errors – Verify users have USE CATALOG on catalog, USE SCHEMA on schema, and appropriate table privileges.
- Storage access errors – Check that storage credentials have correct permissions. Verify bucket or storage account access from Databricks.
- Lineage not appearing – Ensure queries of reference Unity Catalog tables using three-level namespace. Lineage only captures for Unity Catalog objects.
Unity Catalog implementation requires careful planning but delivers unified governance, access control, and data discovery across your entire organization. The setup time invested pays off through simplified data management and improved security.
Integration with Enterprise Ecosystem
Databricks Unity Catalog integrates easily with enterprise systems, ensuring consistent data governance, lineage tracking, and secure access across the business environment. It supports smooth connections with identity systems, BI tools, and enterprise data catalogs to create a unified governance framework.
Key Integration Points:
- Enterprise Identity Systems:
Integrates with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), Okta, and other identity providers to manage authentication and user access. Role-based access control ensures that only authorized users can view or modify data assets.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics Tools:
Connects with Power BI, Tableau, and Looker, allowing users to query data directly from governed tables in Unity Catalog. This ensures that all reports and dashboards use trusted, consistent data sources.
- Data Catalog and Governance Tools
Exports lineage and metadata through REST APIs to connect with enterprise governance platforms like Collibra, Alation, or Informatica EDC. This integration helps maintain business context, ownership, and traceability of data.
- Data Sharing and Collaboration
Uses Delta Sharing, an open protocol built into Databricks, to share data securely with external partners, vendors, and clients without data duplication or file transfers.
- Monitoring and Auditing
Tracks all data activity and access through Databricks Audit Logs and the Events API. These logs help monitor user behavior, detect policy violations, and maintain compliance.
By integrating with identity, analytics, and governance systems, Unity Catalog becomes the central control point for managing, monitoring, and protecting data across the enterprise.
Best Practices for Unity Catalog Implementation
Implementing Databricks Unity Catalog successfully requires the following structured governance and operational practices. These best practices help ensure consistent security governance, efficient access management, and reliable lineage monitoring across all workspaces.
1. Adopt the Least-Privilege Access Model
Grant users only the permissions they need for their tasks. This reduces risks from accidental changes or data misuse and helps maintain stronger security.
2. Standardize Catalog and Schema Naming Conventions
Use consistent and clear naming patterns for catalogs, schemas, and tables. Standard naming improves clarity and prevents confusion in large, multi-team environments.
3. Group Users by Functional Roles
Manage permissions based on roles such as data engineer, analyst, or administrator. Role-based access simplifies permission changes and keeps governance consistent across projects.
4. Audit Data Access and Lineage Regularly
Schedule periodic audits to review who accessed which datasets and how they were used. Use lineage tracking to confirm that data transformations and usage align with governance rules.
5. Automate Provisioning and Policy Management
Use Terraform scripts or Databricks REST APIs to automate catalog creation, workspace configuration, and permission assignments. Automation reduces manual errors and speeds up setup.
6. Educate Teams on Governance and Data Responsibility
Conduct training sessions to help users understand data security practices, access protocols, and compliance requirements. Awareness ensures data is used responsibly and securely.

Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
When setting up Databricks Unity Catalog, teams may face several migration challenges, governance gaps, and configuration issues. Being aware of these pitfalls helps ensure a smooth and secure implementation.
1. Missing Workspace Linkage
Forgetting to link workspaces to the same metastore leads to inconsistent governance. Always verify workspace assignments before rollout.
2. Poor Naming Conventions
Unclear or inconsistent catalog and schema names cause confusion in large teams. Use standardized naming across all environments.
3. Over-Granting Permissions
Assigning broad roles can lead to data misuse. Apply the least-privilege principle to restrict unnecessary access.
4. Ignoring Lineage Validation
Skipping lineage verification after migration can hide data flow errors. Always review lineage views to confirm data accuracy.
5. Incomplete Identity Sync
Failure to synchronize users and groups from the identity provider may block access. Regularly update and validate identity mappings.
Kanerika’s Partnership with Databricks: Enabling Smarter Data Solutions
We at Kanerika are proud to partner with Databricks, bringing together our deep expertise in AI, analytics, and data engineering with their robust Data Intelligence Platform. Furthermore, our team combines deep know-how in AI, data engineering, and cloud setup with Databricks’ Lakehouse Platform. Together, we design custom solutions that reduce complexity, improve data quality, and deliver faster insights. Moreover, from real-time ETL pipelines using Delta Lake to secure multi-cloud deployments, we make sure every part of the data and AI stack is optimized for performance and governance.
Our implementation services cover the full lifecycle—from strategy and setup to deployment and monitoring. Additionally, we build custom Lakehouse blueprints aligned with business goals, develop trusted data pipelines, and manage machine learning operations using MLflow and Mosaic AI. We also implemented Unity Catalog for enterprise-grade governance, ensuring role-based access, lineage tracking, and compliance. As a result, our goal is to help clients move from experimentation to production quickly, with reliable and secure AI systems.
We solve real business challenges, such as breaking down data silos, enhancing data security, and scaling AI with confidence. Furthermore, whether it’s simplifying large-scale data management or speeding up time-to-insight, our partnership with Databricks delivers measurable outcomes. We’ve helped clients across industries—from retail and healthcare to manufacturing and logistics—build smarter applications, automate workflows, and improve decision-making using AI-powered analytics.
Make the most of Databricks Data Lineage with Unity Catalog
Partner with Kanerika to build scalable, future-ready data solutions.
FAQs
1. What is Databricks Unity Catalog?
Databricks Unity Catalog is a unified data governance solution that centralizes access control, metadata management, and data lineage across all Databricks workspaces. It helps teams manage permissions, monitor usage, and maintain compliance within a single governance layer.
2. Why is Unity Catalog important for enterprises?
Enterprises use Unity Catalog to solve governance issues caused by multiple workspaces and data silos. It ensures consistent security policies, centralized access control, and easier compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
3. How do you implement Unity Catalog in Databricks?
Implementation involves several steps — creating a metastore, assigning workspaces, setting up catalogs and schemas, configuring access permissions, and enabling data lineage tracking. Databricks provides tools and REST APIs to simplify this process.
4. What cloud platforms does Unity Catalog support?
Unity Catalog supports multi-cloud environments, including AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud (GCP). It integrates with cloud identity systems such as Azure AD, AWS IAM, and Okta for unified authentication and role-based access.
5. Can Unity Catalog integrate with BI and data catalog tools?
Yes. It connects with Power BI, Tableau, and Looker for analytics, and integrates with governance tools like Collibra and Alation using REST APIs to share metadata and lineage information.
6. How does Unity Catalog handle data lineage tracking?
Unity Catalog automatically tracks data movement across SQL queries, notebooks, Delta Live Tables, and ETL pipelines. The lineage graph in the Databricks UI helps users trace data origins and transformations for audits and debugging.
7. What are some best practices for Unity Catalog implementation?
Adopt a least-privilege access model, use consistent naming conventions, automate provisioning with Terraform, and regularly audit lineage and permissions. These practices ensure security, scalability, and reliable governance across the enterprise.










