Healthcare data breaches skyrocketed in the US over the past three years, with a staggering 133 million records compromised in 2023 alone. This represents a concerning increase from 45.9 million breaches in 2021 and 51.9 million in 2022, highlighting the urgent need for stricter data governance in the healthcare industry.
In the healthcare sector, governance of data is not just a regulatory requirement but a critical foundation for patient safety and treatment efficacy. Effective enterprise data governance in healthcare ensures that every piece of information—from patient records to clinical studies—is accurate, accessible, and secure. This commitment not only supports compliance with stringent regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. but also allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions, enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.
Table of Contents
Importance of Data Governance in Healthcare
The healthcare industry often deals with enormous data that includes patient medical history, records, medications, and other information. This increase in data is primarily driven by three factors:
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
The transition from paper-based records to EHRs has captured a vast amount of clinical data, including patient demographics, medical histories, medications, and treatment plans.
2. Wearables and Medical Devices
The growing popularity of wearable health trackers and connected medical devices generates a continuous stream of real-time patient data, like heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels.
3. Other Technologies
Technologies like genetic testing, imaging advancements, and remote monitoring further contribute to the ever-growing data pool.
While this data holds immense potential for improving patient care, research, and personalized medicine, managing its sheer volume presents significant challenges:
1. Data Silos
Different healthcare systems and devices often operate with incompatible formats, creating data silos that hinder comprehensive patient care and data analysis.
2. Data Quality
Ensuring data accuracy and completeness across diverse sources can be difficult. Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to misdiagnosis, wrong treatment decisions, and wasted resources.
3. Security and Privacy
Protecting sensitive patient data from cyberattacks and unauthorized access requires robust security measures and compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
4. Data Management Costs
Storing, analyzing, and managing massive datasets can be expensive, placing a strain on healthcare organizations’ budgets.
5. Data Overload for Clinicians
The sheer volume of data can overwhelm healthcare professionals, hindering their ability to efficiently extract meaningful insights for patient care.
Case Study: Enhancing Data Governance and Compliance Management
Business Context
The client is a leading automobile manufacturer in Germany. They were struggling to identify and manage sensitive information across diverse sources, leading to potential breaches in customer privacy. Kanerika resolved their issues by:
- Establishing a Governance system to identify and track PHI and PCI-sensitive data, enhancing security and compliance
- Developing mechanisms for connecting various data types, ensuring comprehensive sensitive information management
- Customizing data patterns to monitor sensitive data, tailored to organizational needs, supporting enhanced data analytics

Advantages of Effective Data Governance in Healthcare
Improved Patient Care
1. Informed Clinical Decision-Making
Complete Patient Picture
The unification of data from multiple sources, such as wearables, test findings, and EHRs, into a single patient record is made easier by data governance. Based on a patient’s whole medical history, this holistic view enables medical practitioners to make well-informed treatment decisions.
Data-Driven Insights
Healthcare providers can spot trends and patterns in patient populations by examining massive databases. This may result in the creation of more individualized care plans, more efficient treatment regimens, and better methods for illness prediction and prevention.
Reduced Medical Errors
By ensuring data consistency and accuracy, data governance reduces the possibility of medication errors, incorrect diagnoses, and other missteps that could endanger patients.
2. Enhanced Care Coordination
Seamless Communication
Data governance promotes data interoperability between different healthcare systems, allowing for seamless communication and information sharing between providers. This is especially crucial for patients with complex medical conditions who require care coordination across different specialties.
Reduced Duplication of Services
Data governance lowers costs and enhances the patient experience by preventing needless tests and procedures and offering a consolidated view of a patient’s medical history.
Improved Continuity of Care
Healthcare practitioners may guarantee continuity of care during transitions, such as hospital admissions and discharges, when patient data is easily available across various care locations.
3. Personalized Medicine
Tailored Treatment Plans
Healthcare practitioners can create individualized treatment regimens that have a higher chance of success for each patient by using data governance to analyze genetic and other patient-specific data.
Proactive Care
Healthcare professionals can identify patients who are at risk of contracting specific diseases and take preventive action to enhance their overall health outcomes by evaluating patient data.
Patient Empowerment
Patients can be empowered to take a more active role in their treatment decisions through data governance frameworks that prioritize patient access to their own health information.
Compliance and Regulatory Aspects
1. Regulatory Requirements
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
This is the cornerstone of healthcare data privacy in the US, requires particular security measures to protect patient health information (PHI). It requires data governance techniques including strong security standards, data encryption, and access controls.
HITECH Act (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act)
By mandating safe electronic transmission of PHI and breach reporting procedures in the event of a data breach, this act enhances HIPAA.
Other Regulations
Healthcare companies may also need to abide by state-specific privacy laws or other rules, such as the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in the European Union, depending on where they are located.
2. How Data Governance Helps with Compliance
Data Classification and Access Controls
Data governance facilitates the categorization and identification of sensitive PHI, enabling the deployment of suitable access controls. By doing this, the chance of data breaches or illegal access is reduced.
Data Retention and Disposal Policies
The amount of time healthcare institutions are allowed to keep patient data is frequently regulated. In order to comply with these laws, data governance frameworks guarantee appropriate data preservation procedures and safe disposal techniques.
Audit Trails and Accountability
Robust data governance procedures create transparent audit trails that monitor patient data access and utilization. This makes compliance easier to prove and makes inquiries into possible infractions easier.
Data Breach Response Plans
Developing a strong data breach response strategy is a crucial part of data governance. In addition to maintaining regulatory compliance with notification requirements, this guarantees a prompt and efficient reaction to data breaches, reducing the impact on patients.
Implementing Data Governance in Healthcare
1. Assessing the Current Landscape
Data Management Audit
To assess current data management procedures, do a thorough audit. Data collection, storage, access, security, and quality are just a few of the areas that need to be evaluated.
Gap Analysis
Analyze the audit results to detect any flaws in your present data governance procedures. You can then customize your data governance plan and target areas for development.
Stakeholder Involvement
Throughout the assessment process, involve important stakeholders from various departments, such as IT, healthcare personnel, and legal teams. This guarantees a comprehensive comprehension of the data management requirements of the firm.
2. Developing a Data Governance Plan
Define Goals and Objectives
Clearly state your goals for implementing data governance. This can entail strengthening data security, promoting greater care coordination, or improving data quality.
Develop a Roadmap
Make a thorough plan that outlines the actions you must take to accomplish your data governance objectives. There should be precise tasks, deadlines, and resource allocation in this roadmap.
Prioritize Initiatives
Not all data governance projects must be done simultaneously. Sort your priorities according to the extent of the gaps that now exist and how they might affect your overall objectives.
3. Fostering a Data-Centric Culture
Raising Awareness
Inform employees at all levels of the value of data governance and their specific responsibilities for maintaining the security, privacy, and quality of data.
Data Stewardship
Create a data stewardship program that designates teams or individuals to be in charge of particular data assets. The accuracy, integrity, and accessibility of the data that has been assigned to these data stewards will be their responsibility.
Training and Communication
Provide employees with continual training so they may acquire the skills and information required for efficient data management procedures. Share updates on data governance projects and the significance of data stewardship on a regular basis.
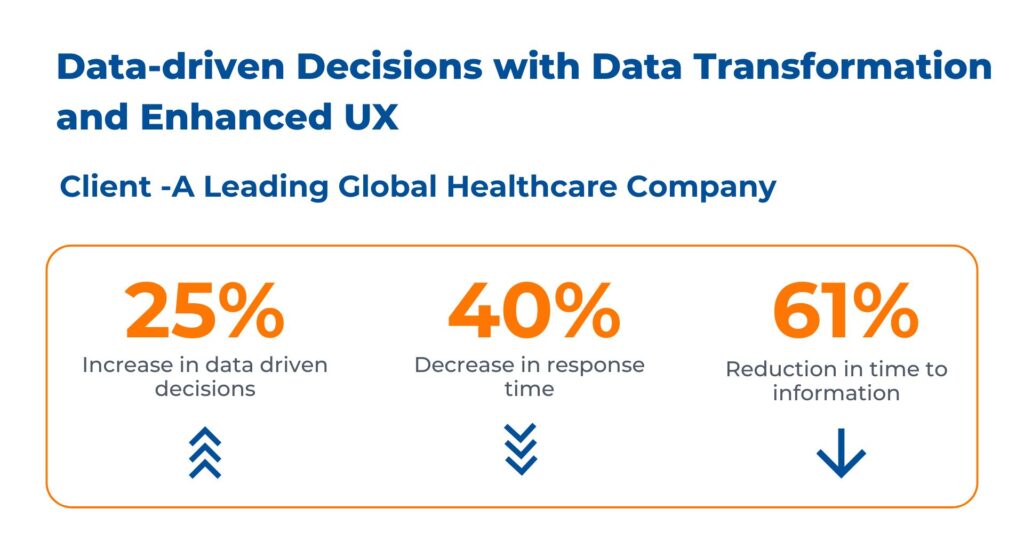
Case study: Transforming Healthcare Through Data-Driven Insights in Healthcare
Business Context
The client is a global healthcare company. They faced difficulties with disparate, siloed data sources and missing data mapping created inefficiencies and hindered decision-making. They wanted to seamlessly link sales, financial, and customer services data and elevate service quality, responsiveness, and overall operational agility through insightful data enabled by healthcare dashboards.
Kanerika addressed their data management challenges by offering the following solutions:
- Leveraged Snowflake for centralized and global data mapping, eliminating silos and providing a unified view across verticals
- Implemented Power BI in this healthcare project with a user-friendly and intuitive UI/UX design, enabling data exploration and data-driven decisions
- Facilitated quick and comprehensive analysis via dashboards and reports, reducing the time to obtain valuable insights
Best Practices for Implementing Data Governance in Healthcare
Building a successful data governance program requires a well-defined framework, effective strategies, and the right technological tools.
1. Frameworks and Strategies
Data Governance Institute (DGI) Framework
The six main components of this framework—data strategy, data quality, data architecture, data security, data privacy, and metadata management—offer an organized method. These categories can be modified by healthcare institutions to solve certain patient data management concerns.
Health Information Management Systems Society (HIMSS) Data Governance Framework
The four key domains of this framework are information security, data lifecycle management, data quality, and data access. It highlights the significance of data lineage—tracing data throughout its lifecycle for accountability and auditability—and complies well with healthcare laws.
2. Strategies for Effective Implementation
Start Small, Scale Up
Start with a pilot project that focuses on a particular data domain, like access restrictions or data quality. This makes it possible for staggered distribution throughout the organization and permits early success.
Focus on Business Value
Clearly state how data governance efforts will help the firm achieve its objectives. This aids in prioritizing activities and gaining support from stakeholders.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Evaluate the success of your data governance program on a regular basis and make any modifications. This guarantees that the program stays current as it adapts to meet changing needs.
3. Technology and Tools
Data Management Platforms (DMPs)
DMPs offer a single platform for managing data quality, access control, and storage. They make data more accessible to authorized users and simplify data governance chores.
Data Catalogs
These tools generate an inventory of all the data assets present in an organization, along with metadata describing the usage, content, and origin of the data. This makes data discovery easier and encourages data stewardship.
Data Security and Privacy Tools
To protect patient data, use security solutions including access control systems, firewalls, and data encryption. Use solutions that facilitate the automation of data privacy compliance chores as well.
Data Analytics Tools
To identify problems with data quality, track data access trends, and learn more about how data is used within the company, employ advanced analytics technologies.
Safeguard Sensitive Healthcare Data with Kanerika’s Robust Data Governance Solutions
Kanerika is a leading provider of robust data governance solutions, leveraging advanced technologies and tools to implement efficient frameworks that safeguard sensitive healthcare data. With extensive expertise in data management and analytics, we help healthcare organizations ensure the security, integrity, and compliance of their patient data.
Our comprehensive approach includes data cataloging, data lineage, data quality management, and data security features such as access controls, encryption, and data masking. By streamlining data governance, we enable healthcare providers to make informed decisions, improve patient care, and maintain trust with their patients.
We offer solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of healthcare organizations, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. With Kanerika, healthcare providers can rest assured that their patient data is secure and protected from unauthorized access and breaches.















