Modernization has become a strategic data priority for every organization, yet many still struggle with ageing systems, technical debt, frequent downtime, data inconsistencies, and rising migration costs. Moreover, as enterprises push toward cloud, analytics, and AI-driven architectures, the need for faster and safer transformation is stronger than ever. This is where Migration Accelerators for Enterprises play a critical role.
These accelerators help simplify complex migrations and reduce the risks that commonly derail large programs. Research shows that over 70% of digital transformation failures are tied to poor migration planning and execution. Consequently, with such high failure rates, enterprises cannot rely on manual processes alone.
This guide explains what migration accelerators are, where they help, and how to build an enterprise‑ready roadmap.
From Legacy to Modern Systems—We Migrate Seamlessly!
Partner with Kanerika for proven migration expertise.
Key Takeaways
- Migration accelerators package automation, templates, and tested workflows together so you’re not starting from scratch every time
- They solve the problems that actually kill migrations: messy legacy systems, human mistakes, and plans that fall apart on contact with reality
- You’ll want automated discovery, connectors to your existing systems, validation tools, and dashboards that show what’s broken before it becomes a crisis
- Pick accelerators that fit your specific situation—cloud moves need different tools than BI migrations
Why Most Migrations Go Sideways
Here’s something nobody wants to talk about in planning meetings: somewhere between 70% and 90% of digital transformation projects fail to meet their goals. McKinsey’s been tracking this for years. BCG looked at over 850 companies and found only about a third actually got what they were hoping for.
That’s a brutal success rate for projects that cost millions.
The reasons aren’t mysterious. Legacy systems turn out to be way more tangled than anyone thought. The scope keeps growing because someone discovers another integration nobody documented. Manual processes work fine until they don’t, and then you’ve got bad data sitting in production while everyone points fingers.
Timelines slip because everything connects to everything else. Touch one system and three others break. The architect who built half of it left two years ago. The documentation exists but hasn’t been updated since 2017.
Most teams try to muscle through with consultants, spreadsheets, and incessant hours spent on problem-solving. Sometimes that works. But if you’re trying to get to cloud-native architecture or stand up real-time analytics, you need something faster and reliable.
That’s the gap migration accelerators fill. Not magic—just tools that have seen this movie before.
What Is a Migration Accelerator
Strip away the marketing language and you’ve got a toolkit. Scripts, templates, connectors, documented processes—stuff that’s already been built and tested so you don’t have to figure it out yourself.
The difference between an accelerator and a regular migration tool? Scope. A single tool might handle data extraction or schema conversion. An accelerator handles discovery, mapping, transformation, validation, and monitoring as one connected process. You’re not stitching together five different products and hoping they play nice with each other.
Picture renovating a kitchen. You could source every cabinet, countertop, and fixture separately from different suppliers. Or you could buy a package where someone’s already figured out what fits together. Both approaches get you a kitchen eventually. One takes three times longer and leaves a lot more room for expensive mistakes. Using migration accelerator for enterprise migration are like getting the package.
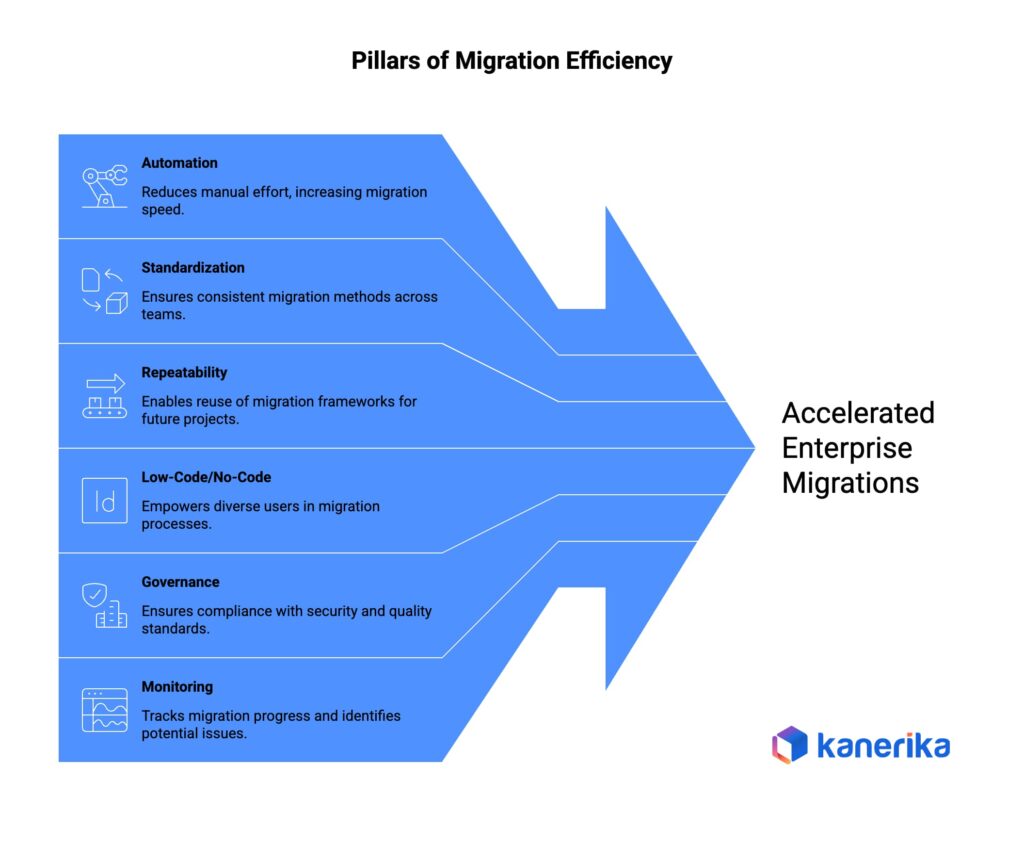
Good accelerators share a few traits:
- Automation that actually works without constant babysitting. Consistent processes so your migration in Q2 looks like your migration in Q4. Governance baked in from the start—not bolted on later when audit shows up asking questions. Dashboards that tell you what’s happening right now, not what happened last week when it’s too late to fix.
- Low-code options matter too. Your business analysts shouldn’t need to file a ticket and wait three days every time they want to check on something.
- The best accelerators also learn. They capture what worked, what didn’t, and make the next migration smoother than the last one.
Why Migration Accelerators for Enterprises is a Must?
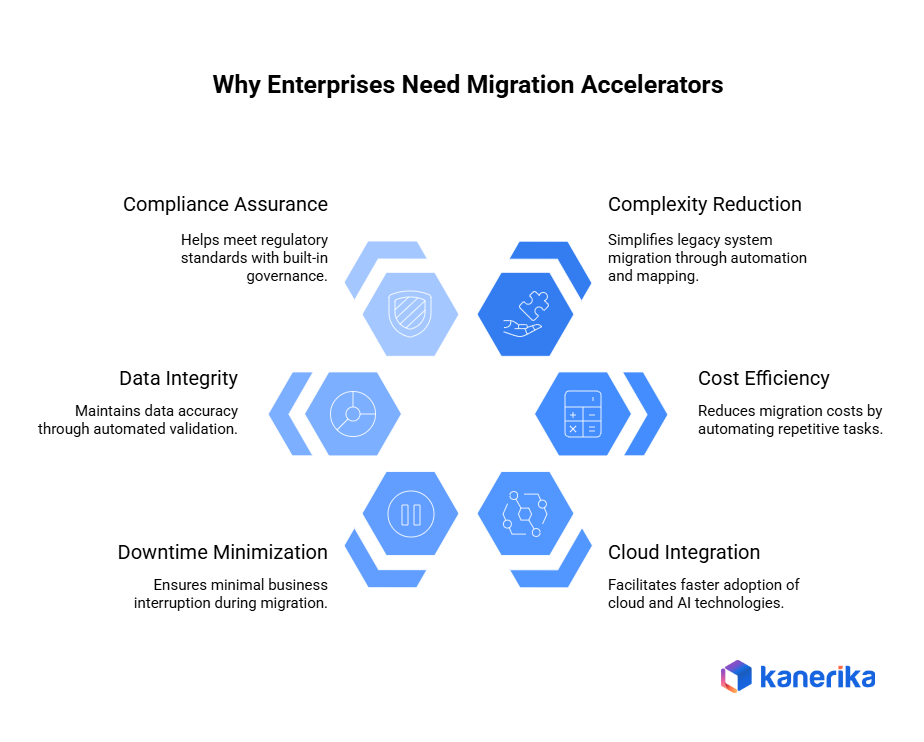
A few things have changed in the last decade that make the old approaches obsolete.
Legacy systems got older and weirder:
That mainframe from 1998? Still running. The guy who understood the custom COBOL modules retired in 2019. Nobody documented half the integrations because they were supposed to be temporary. Accelerators can scan your environment and tell you what you’ve actually got before you start moving things around. Surprises during migration are expensive. Surprises during discovery are just information.
Deadlines got tighter:
Executives read about Microsoft Fabric, Databricks, and Snowflake. They see competitors moving faster. They want results by next quarter, not next year. Those platforms deliver real value, but only if you can get clean, governed data there quickly. Ready-made connectors and proven migration patterns help teams move at the speed leadership expects.
Mistakes got more expensive:
One bad record in a manual process can cascade through your whole data pipeline. A typo in a mapping spreadsheet corrupts reports for weeks before anyone notices. Validation tools catch problems early, before they hit production and wake someone up at 3 AM with an angry email chain.
Downtime tolerance dropped to zero:
Customers expect systems to work around the clock. Partners need real-time data feeds. The business can’t afford to take everything offline for a maintenance weekend while you hope the migration goes smoothly. Phased migrations and automated cutovers let you transition piece by piece without bringing everything down. Try coordinating that with spreadsheets and prayers.
Compliance requirements multiplied:
GDPR, CCPA, industry-specific regulations—the rules keep expanding. You need audit trails showing exactly what data moved where and when. Manual processes struggle to provide that level of traceability. Accelerators generate documentation as they work.
Types of Migration Accelerators
Migration accelerators are pre-built tools, templates, and frameworks that speed up technology transitions while reducing risks and costs. Moreover, organizations leverage these accelerators to avoid starting from scratch and benefit from proven migration patterns.
1. Cloud Migration Accelerators
Cloud migration accelerators help organizations move workloads from on-premises infrastructure to cloud platforms efficiently.
- Lift-and-shift templates – Provide pre-configured patterns for moving existing applications to the cloud with minimal changes, enabling quick migrations while preserving current architectures
- Infrastructure-as-code provisioning – Tools like Terraform, ARM templates, and CloudFormation automate resource creation through code, ensuring consistent deployments and eliminating manual configuration errors
- Cloud architecture blueprints – Offer reference designs for common scenarios like three-tier applications, microservices, or data platforms, providing proven patterns that organizations can adapt to their specific needs
These accelerators dramatically reduce the time required to establish cloud environments. Moreover, they incorporate security best practices, compliance controls, and cost optimization strategies from the beginning.
2. Data Migration Accelerators
Data migration accelerators focus on moving data between systems while maintaining quality and integrity.
- Schema mapping tools – Automatically analyze source and target databases, identifying relationships and suggesting appropriate mappings between different data models
- ETL/ELT automation – Generate transformation code based on mapping rules, eliminating manual coding for common transformation patterns
- Data validation scripts – Verify that migrated data matches source data through automated comparison checks, catching discrepancies before they affect business operations
- Incremental & CDC migration frameworks – Enable continuous synchronization between old and new systems by tracking changes in source systems and applying only those changes to target systems
Furthermore, these frameworks allow organizations to maintain both environments during transition periods. Consequently, this approach minimizes downtime and provides rollback options if issues arise.
What Are The Top 5 Microsoft Fabric Use Cases In 2026?
Explore what are the top use cases organizations are using Microsoft Fabric
3. Application Modernization Accelerators
Application modernization accelerators help transform legacy applications into modern architectures.
- App refactoring toolkits – Analyze existing code and suggest improvements, identifying technical debt and providing automated refactoring for common patterns
- API enablement frameworks – Add API layers to legacy applications, allowing modern systems to integrate without rewriting entire applications
- Containerization accelerators – Convert traditional applications into Docker containers and generate Kubernetes deployment configurations, enabling applications to run in cloud-native environments
These tools bridge the gap between legacy and modern architectures. Hence, instead of requiring complete rewrites, they enable gradual modernization where organizations improve applications incrementally while maintaining business continuity.
Data Conversion vs Data Migration: Which Approach Suits Your Project?
Explore the differences between data conversion and migration, and how Kanerika handles both.
4. BI & Reporting Migration Accelerators
Business intelligence migration accelerators automate transitions between reporting platforms.
- Tableau to Power BI – Convert dashboards, extract data connections, and recreate visualizations in the target platform, preserving business logic while adapting to Power BI’s capabilities
- SSRS to Fabric or Power BI – Migrate SQL Server Reporting Services reports to modern cloud platforms, converting report definitions and maintaining report functionality
- Cognos to Power BI – Handle IBM Cognos migrations, converting reports and analytics to Microsoft’s platform
- Crystal Reports to Modern cloud BI – Move legacy Crystal Reports to contemporary platforms with updated visualization and distribution capabilities
Thus, these accelerators address the significant challenge of recreating hundreds or thousands of reports manually. They preserve report logic, data connections, and user customizations while upgrading to modern platforms. However, organizations should expect some manual adjustments since platforms differ in capabilities and design philosophies.
5. AI & Analytics Migration Accelerators
AI and analytics migration accelerators facilitate movement of advanced analytics workloads to modern platforms.
- ML model migration toolkits – Convert machine learning models between frameworks, translating trained models from older platforms to contemporary tools while preserving model accuracy
- Databricks/Fabric modernization accelerators – Migrate data engineering workflows, notebooks, and analytics code to these unified platforms, handling syntax conversions, library mappings, and architectural adjustments
These accelerators recognize that rebuilding sophisticated analytics pipelines and retraining models from scratch proves extremely time-consuming. Instead, they enable organizations to preserve existing investments while gaining benefits of modern platforms like improved scalability, better collaboration tools, and unified governance.
Key Components of a Migration Accelerator
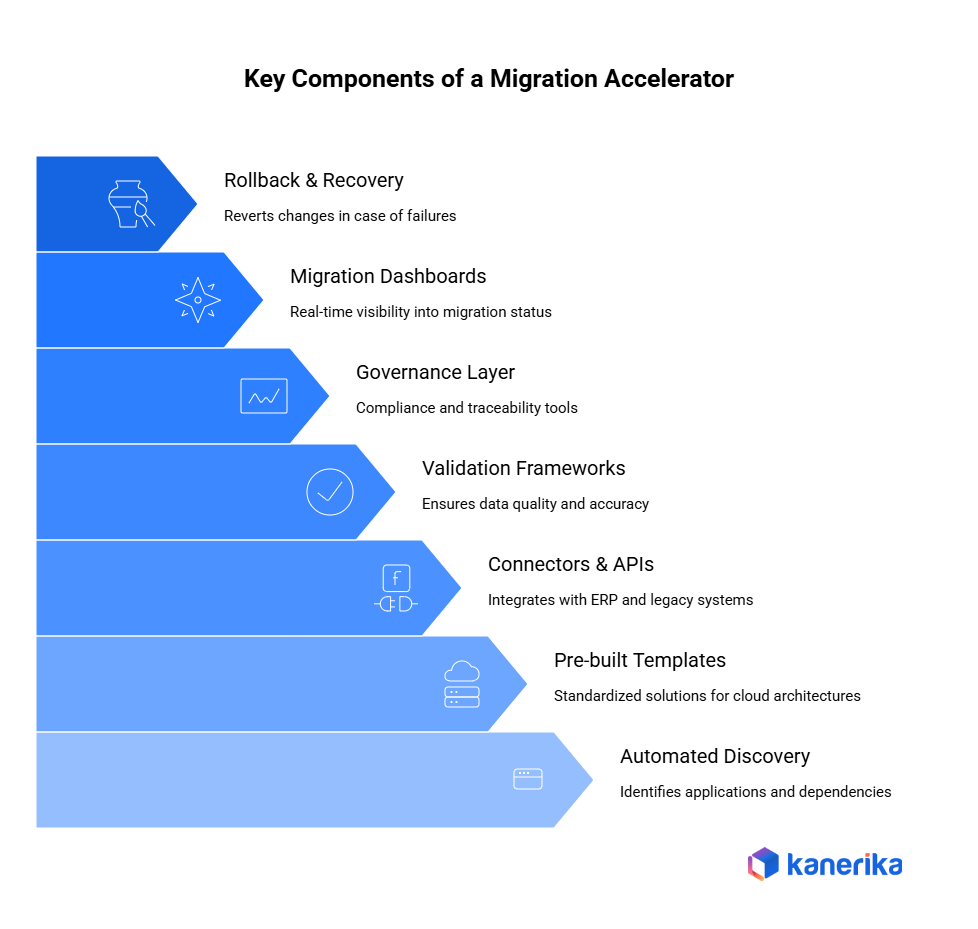
A strong migration accelerator is built on several essential components that work together to make enterprise modernization faster, safer, and more predictable. Below are the key elements explained in simple and clear terms.
1. Automated Discovery Tools
To begin with, discovery tools identify existing applications, data sources, and dependencies. They create an application inventory and perform dependency mapping, which helps teams understand what needs to be migrated and how systems are connected.
2. Pre-built Templates
Migration accelerators include ready-made templates for cloud architectures, data pipelines, dashboards, and security policies. These templates ensure standardization and reduce the time spent designing solutions from scratch.
3. Connectors & APIs
Enterprises often rely on ERP, CRM, databases, and legacy systems. Accelerators provide connectors and APIs to integrate with these systems easily, reducing manual setup and enabling faster data movement.
4. Validation Frameworks
Reliable migration requires verified and accurate data. Validation frameworks offer data quality checks, reconciliation scripts, and transformation logs to ensure that migrated data matches source data and meets defined standards.
5. Governance Layer
Governance is essential in regulated industries. A strong accelerator includes tools for data lineage, access control, and audit logs, ensuring compliance and traceability across the entire migration process.
6. Migration Dashboards
These dashboards provide real-time visibility into migration status, progress, errors, and performance metrics. They help teams make informed decisions quickly and track overall project health.
7. Rollback & Recovery Mechanisms
Finally, rollback and recovery tools allow teams to revert changes safely in case of failures. This reduces migration risk and ensures business continuity.
Architecture of an Enterprise Migration Accelerator
A well-designed enterprise migration accelerator follows a structured and modular architecture. This architecture ensures that every stage of the migration process is efficient, reliable, and easy to manage. Below are the key architectural layers, each playing a crucial role in delivering smooth modernization.
1. Discovery & Assessment Layer
To begin with, this layer scans existing systems to create a complete inventory of applications, databases, schemas, and dependencies. It helps teams understand the current state and identify risks early.
2. Planning & Mapping Engine
Next, the accelerator uses a mapping engine to define source-to-target mappings, standards, and migration rules. It determines how data, logic, and configurations will move to the new platform.
3. Automation Execution Layer
Once planning is complete, the automation engine executes tasks such as extraction, loading, schema creation, pipeline generation, and configuration updates using scripts, workflows, or templates.
4. Data Transformation Layer
This layer applies to required transformations—such as cleansing, formatting, restructuring, or converting data types, ensuring that the target platform receives clean and compatible data.
5. Validation & Testing Layer
After transformation, validations are performed. The system conducts data quality checks, record comparisons, reconciliation, and functional testing to verify accuracy and completeness.
6. Monitoring & Reporting Layer
Finally, this layer provides dashboards for real-time monitoring, error tracking, and progress reporting. It keeps teams updated throughout the migration.
Modern Architectural Principles
Using microservices, an API-first design, and cloud-native infrastructure helps accelerators scale easily, integrate smoothly with enterprise systems, and support parallel migrations significantly speeding up modernization efforts.
Real-World Use Cases
Migration accelerators are widely used across industries to modernize systems faster, reduce project risk, and improve long-term performance. Below are some of the most common and impactful enterprise use cases, explained with clear benefits.
1. Cloud Modernization
Many enterprises still run critical workloads on on-premise servers. Migration accelerators help move these workloads to AWS, Azure, or GCP much faster by using automated discovery, infrastructure templates, and pre-built scripts.
Business Value: Lower infrastructure cost, faster scaling, improved security.
Impact: Migration timelines reduce from months to weeks, with minimal disruption.
2. Data Warehouse Modernization
Enterprises often need to shift from legacy warehouses like Netezza, Teradata, or Oracle to modern cloud warehouses such as Snowflake, BigQuery, Microsoft Fabric, or Databricks. Accelerators provide schema converters, ELT templates, and validation scripts.
Business Value: Better performance, lower storage cost, support for AI workloads.
Impact: Reduced risk and fast cutover with high data accuracy.
3. BI Reporting Migration
Organizations often migrate from Tableau, Cognos, or SSRS to Power BI. Migration accelerators automate report mapping, metadata extraction, and visual conversion.
Business Value: Standardized reporting, unified analytics, lower licensing costs.
Impact: Faster migration with consistent dashboards across teams.
4. Application Transformation
Enterprises modernize old systems by breaking monoliths into microservices or converting legacy applications into containerized, API-enabled services.
Business Value: Improved scalability, faster deployments, and easier updates.
Impact: Reduced refactoring time and smoother application upgrades.
5. ERP/CRM Migration
Accelerators support migrations from SAP or Oracle to cloud-based versions with automated data extraction, mapping, and validation.
Business Value: Better integration, enhanced performance, future-ready architecture.
Impact: Lower transition risk and fewer business interruptions.
6. AI & Analytics Migration
Machine learning pipelines and analytics workloads are moved to cloud AI platforms. Accelerators automate pipeline conversion, model deployment, and testing.
Business Value: Faster experimentation, real-time insights, support for LLM and AI agents.
Impact: Reduced engineering effort and quicker adoption of advanced analytics.
Data Ingestion vs Data Integration: Which One Do You Need?
Understand data ingestion vs integration: key differences & Kanerika’s approach to seamless data handling.
How AI, LLMs & Automation Enhance Migrations?
AI, LLMs, and automation have transformed the way enterprises execute migrations. They make the entire process faster, smarter, and far more reliable. Below are the key ways these technologies enhance modernization efforts.
1. NLP for Schema Mapping & Code Conversion
To begin with, Natural Language Processing helps interpret legacy schemas, column descriptions, and code logic. AI models can automatically generate target mappings and even convert SQL, ETL scripts, or config files into modern formats.
2. AI Agents for Multi-Step Migration Tasks
AI agents can execute end-to-end migration workflows by planning tasks, running scripts, validating results, and escalating issues. They also help monitor pipelines and self-correct errors when needed.
3. LLMs for Documentation Generation & Validation
Large Language Models create migration documents, data dictionaries, runbooks, and user guides automatically. They can also validate logic by summarizing differences, checking inconsistencies, and highlighting missing components.
4. Predictive Analytics for Risk Scoring
AI models analyze patterns in legacy systems to identify risks such as data quality gaps, dependency conflicts, or performance issues. This lets teams address problems early.
5. Intelligent Dependency Detection
LLMs and AI tools detect connections between tables, APIs, applications, and workflows—something highly error-prone when done manually.
6. Automated Test Case Generation
AI can create unit tests, integration tests, reconciliation scripts, and test datasets automatically, reducing manual QA effort.

Data Migration Case Study: Global Spend Management Leader
A global leader in spend management partnered with Kanerika to migrate their customer service operations from legacy systems to a modern, cloud-native platform. The client operated across North America, Latin America, Asia, and Europe, and needed a seamless transition that wouldn’t disrupt customer experience.
Challenges
- Managing two separate platforms (legacy and modern)
- Complex business rules and high-volume data flows
- Risk of downtime and data loss during migration
Enterprise Data Modernization: A Complete Roadmap for 2026
Explore how enterprises are modernizing their data infrastructure to outpace competitors by 2× in decision-making speed and agility.
Kanerika’s Solution
We used our cloud migration expertise to move the client’s applications and data to a multi-node, distributed cloud platform. Our team preserved all functionalities, validated business rules, and ensured data integrity throughout the process.
Impact
- 32% reduction in infrastructure costs
- 46% improvement in application performance
- 60% faster error resolution
- Streamlined onboarding and reduced maintenance costs
Kanerika : Your Trusted Partner for Data Migrations
Kanerika is a trusted partner for organizations looking to modernize their data platforms efficiently and securely. Modernizing legacy systems unlocks enhanced data accessibility, real-time analytics, scalable cloud solutions, and AI-driven decision-making. Traditional migration approaches can be complex, resource-intensive, and prone to errors, but Kanerika addresses these challenges through purpose-built migration accelerators and our FLIP platform, ensuring smooth, accurate, and reliable transitions.
Our accelerators support a wide range of migrations, including Tableau to Power BI, Crystal Reports to Power BI, SSRS to Power BI, SSIS to Fabric, SSAS to Fabric, Cognos to Power BI, Informatica to Talend, and Azure to Fabric. Additionally, by leveraging automation, standardized templates, and deep domain expertise, Kanerika helps organizations reduce downtime, maintain data integrity, and accelerate adoption of modern analytics platforms. Moreover, with Kanerika, businesses can confidently future proof their data infrastructure and maximize the value of every migration project.
Simplify Your Migration Journey with Experts You Trust!
Partner with Kanerika for smooth, error-free execution.
FAQs
1. What are migration accelerators for enterprises?
A migration accelerator is a set of tools, frameworks, and automation assets designed to speed up large-scale data or platform migrations. It reduces manual effort by automating assessment, code conversion, validation, and testing. For enterprises, accelerators help minimize risk, ensure consistency, and shorten migration timelines. They are especially valuable for complex, multi-system environments.
2. How do migration accelerators reduce enterprise migration risk?
Migration accelerators enforce standardized migration patterns and proven workflows. They include built-in checks for data accuracy, schema consistency, and dependency mapping. By automating validation and reconciliation, they reduce human error. This ensures data integrity and business continuity during enterprise migrations.
3. What types of migrations benefit most from accelerators?
Accelerators are highly effective for migrations involving legacy systems such as SQL Server, Informatica, on-prem data warehouses, and BI platforms. They are also useful for cloud migrations to platforms like Microsoft Fabric, Azure Databricks, and cloud data lakes. Enterprises with high data volumes and complex dependencies see the greatest value. Repeatable workloads benefit the most.
4. How do migration accelerators improve migration speed and efficiency?
Accelerators automate repetitive tasks such as code translation, pipeline creation, and test case execution. This significantly reduces manual development and rework. As a result, migration cycles are faster and more predictable. Enterprises can move from planning to production in shorter timelines without compromising quality.
5. Do migration accelerators support validation and post-migration testing?
Yes, enterprise-grade migration accelerators include automated validation, reconciliation, and performance testing. They compare source and target results to ensure accuracy after migration. Post-migration testing confirms that reports, dashboards, and analytics perform as expected. This builds confidence in the migrated environment.
6. Can migration accelerators be customized for enterprise needs?
Most accelerators are designed to be flexible and configurable. Enterprises can adapt them to specific business rules, compliance requirements, and system architectures. Customization ensures alignment with industry regulations and internal standards. This makes accelerators suitable for healthcare, retail, finance, and logistics enterprises.
7. How do migration accelerators support long-term value beyond migration?
Beyond initial migration, accelerators help standardize architecture, improve governance, and enable scalability. They create reusable migration patterns that support future modernization initiatives. Enterprises benefit from lower technical debt and faster onboarding of new workloads. This ensures sustained value long after migration is complete.
8. What's the difference between a migration tool and a migration accelerator?
A tool handles one task—data extraction, schema conversion, that kind of thing. An accelerator covers the whole journey from discovery through validation and monitoring. Kanerika’s FLIP platform connects these stages so you’re not stitching together separate products and hoping they work together.
9. How do accelerators handle data validation during migration?
Automated reconciliation compares source and target data throughout the process. Row counts, checksums, business rule validation, sample comparisons. Kanerika’s FLIP platform generates validation reports automatically so teams can verify accuracy without manual spot-checking.
10. What should we look for when evaluating migration accelerator vendors?
Coverage for your specific migration path, integration with your existing systems, governance and compliance features, and proven experience in your industry. Kanerika offers pre-built accelerators for the most common enterprise migrations plus the flexibility to handle custom scenarios through the FLIP platform.










