What if your factory could make decisions on its own? What if machines, systems, and software agents worked together to predict issues, fix problems, and optimize production without waiting for human intervention? This is the promise of Agentic AI in Manufacturing, emerging as the next major leap in Industry 4.0.
Today’s factories face growing pressure: labor shortages, rising operational costs, stricter quality expectations, and unpredictable supply chain disruptions. At the same time, AI adoption is accelerating. Over 72% of manufacturers are already using or planning to use AI-driven automation to improve operations, according to Deloitte.
However, traditional AI focuses on predictions, not actions. This is where Agentic AI changes the game. Moreover, Agentic AI combines reasoning, planning, memory, and tool usage to perform autonomous multi-step tasks such as scheduling, quality control, inventory optimization, and maintenance.
In simple terms, Agentic AI acts like a digital teammate that can monitor systems, make decisions, and execute workflows across the factory.
In this blog, we will explore the full landscape of Agentic AI in manufacturing its architecture, real-world use cases, benefits, challenges, and the future of autonomous industrial operations.
Key Learnings
- Agentic AI transforms manufacturing by enabling machines and software systems to make autonomous, multi-step decisions instead of relying only on human intervention.
- Real-world use cases span predictive maintenance, quality control, scheduling, supply chain coordination, safety monitoring, and compliance automation.
- A strong architecture covering data layers, intelligence models, orchestration engines, integrations, and execution workflows is essential for successful deployment.
- Manufacturers must address challenges such as legacy systems, data governance, model accuracy, regulatory compliance, and workforce readiness.
- The future will bring autonomous factories, multi-agent ecosystems, self-healing systems, and real-time optimisation across plants, making agentic AI a core part of Industry 4.0.
Boost Your Business Efficiency with Intelligent AI Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Why Manufacturing Needs Agentic AI
Manufacturing operations are becoming more complex than ever. Every production line involves machines, people, materials, safety rules, and tight compliance standards. As factories grow more connected, even small delays or errors can create major disruptions. Therefore, manufacturers need systems that can understand what is happening in real time and make decisions without waiting for human intervention.
In traditional environments, teams handle issues manually approving work orders, checking machine data, coordinating logistics, or resolving quality problems. However, these tasks take time, and slow responses often lead to equipment downtime, production loss, or inventory gaps. Agentic AI changes this by making autonomous decisions that help prevent breakdowns, maintain quality, and keep the flow of materials running smoothly.
At the same time, modern factories are witnessing a strong convergence of OT and IT systems. Sensor data, MES updates, ERP transactions, and supply chain signals now move across the factory floor every second. Yet many manufacturers still struggle with fragmented data, manual coordination, and disconnected tools.
Agentic AI directly solves these challenges. Removes manual bottlenecks by automating multi-step tasks. Additionally, connects disconnected systems to create a unified view of operations. As well as, cuts slow decision cycles by analyzing data instantly. It reduces quality issues by identifying deviations early. It prevents inventory mismatches by monitoring stock in real time. Most importantly, Agentic AI works at machine speed, not human speed, ensuring faster responses and smoother production.
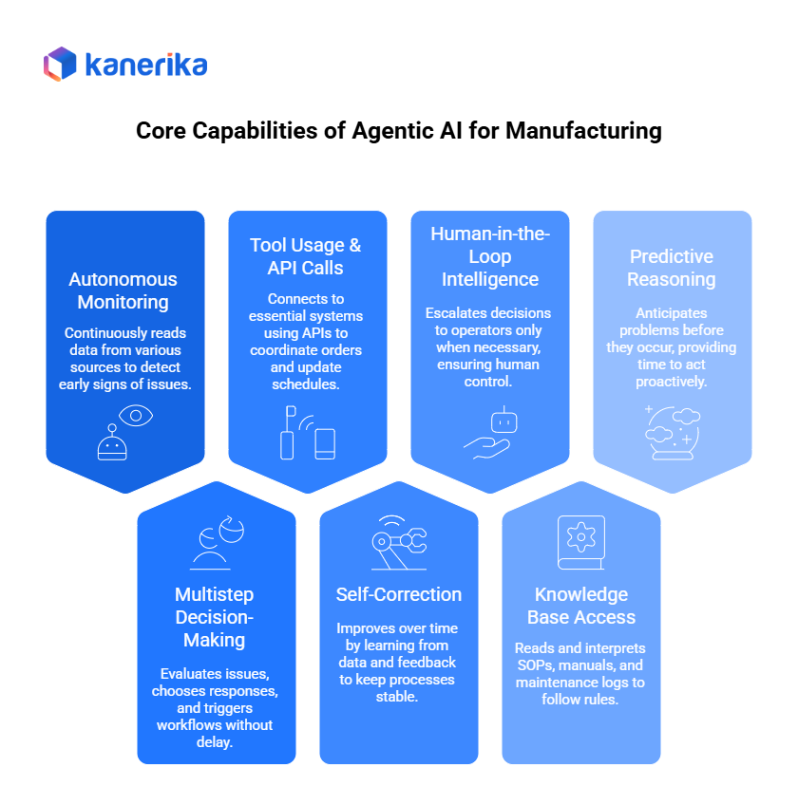
Core Capabilities of Agentic AI for Manufacturing
Agentic AI brings a powerful set of capabilities that fit naturally into modern factory operations. These capabilities allow systems to think, act, and improve much like an experienced operator, but with far greater speed and accuracy.
1. Autonomous Monitoring
To begin with, agentic AI continuously reads data from IoT sensors, machine logs, MES updates, and QMS records. It watches temperature, vibration, cycle times, defects, and energy use in real time. This always-on monitoring helps detect early signs of failure or quality issues before they escalate.
2. Multistep Decision-Making
Instead of stopping at detection, agentic AI evaluates the issue, chooses the most suitable response, and triggers the required workflow. For example, if a machine overheats, the agent can slow the cycle, schedule maintenance, alert a technician, and reroute production—all without delay.
3. Tool Usage & API Calls
Moreover, agentic AI connects to all essential systems across the factory. It interacts with ERP, MES, PLM, WMS, CMMS, and even RPA bots using APIs. This allows it to coordinate orders, check inventory, update schedules, and initiate work orders automatically.
4. Self-Correction
Agentic AI improves over time. It learns from historical data, past outcomes, and operator feedback. When patterns change, the agent adjusts parameters like maintenance thresholds or inspection frequency—to keep the process stable.
5. Human-in-the-Loop Intelligence
Even with strong automation, some decisions need operator approval. In such cases, the agent evaluates the scenario and escalates only when necessary, ensuring humans stay in control where it matters most.
6. Knowledge Base Access
The agent can also read and interpret SOPs, manuals, digital instructions, BOMs, and maintenance logs. This helps it follow rules consistently and guide workers during exceptions.
7. Predictive Reasoning
Finally, agentic AI anticipates problems before they occur. It predicts machine failures, demand shifts, supply delays, and process deviations—providing enough time to act proactively.
Real-World Use Cases of Agentic AI in Manufacturing
Agentic AI is already reshaping factories across the world. It automates decision-making, optimizes workflows, and brings a new level of intelligence to daily operations. Below are the most impactful real-world applications, explained with clarity and industry relevance.
1. Predictive Maintenance Agents
To begin with, predictive maintenance agents continuously monitor machine sensors vibration, temperature, pressure, RPM, and energy consumption. They detect anomalies early and classify them as potential bearing failures, lubrication issues, or alignment problems.
Once an issue is confirmed, the agent automatically creates a work order in the CMMS, assigns the right technician, and recommends spare parts. It also adjusts production loads to avoid machine stress.
This significantly reduces unplanned downtime, increases asset lifespan, and prevents costly shutdowns.
2. Quality Control Agents
Next, quality agents analyze inspection images, sensor outputs, process parameters, and defect logs in real time. They quickly identify deviations such as surface defects, incorrect dimensions, or temperature fluctuations.
Beyond detection, these agents suggest corrective actions—like adjusting weld speed or resetting mould pressure and can trigger a root-cause analysis workflow.
By integrating with QMS platforms, they ensure faster issue resolution and consistent production quality.
3. Production Scheduling & Optimization Agents
Traditional scheduling is rigid and slow. However, agentic AI updates schedules dynamically based on machine health, labor availability, and material delays.
For instance, if a machine shows early signs of overheating, the agent automatically reassigns jobs to another line. If a shipment is delayed, it rearranges production orders to minimize idle time.
It synchronizes this data across MES and ERP to keep all teams aligned and production flowing smoothly.
4. Supply Chain Coordination Agents
Agentic AI also plays a major role outside the factory floor. It monitors vendor performance, shipment status, weather risks, and production forecasts.
If a delay is detected, the agent triggers backup supplier workflows, adjusts reorder points, or suggests alternative routes.
This proactive coordination reduces material shortages, improves on-time delivery, and stabilizes production.
Agentic AI Vs Generative AI: The Ultimate Comparison Guide
Explore key differences between Agentic AI and Generative AI, and their business impacts.
5. Autonomous Process Control Agents
Another powerful use case is real-time process optimization. These agents read sensor inputs from ovens, presses, CNC machines, and chemical tanks.
They then fine-tune parameters—such as torque, temperature, pressure, or feed rate—to keep the process within target limits.
This reduces scrap, improves product consistency, and ensures compliance with engineering standards.
6. Inventory Management Agents
Inventory agents forecast material consumption based on demand, BOM usage, and production patterns. They detect upcoming stockouts, mismatches, or excess inventory.
When needed, the agent automatically triggers replenishment of workflows through WMS and procurement systems.
This prevents line stoppages and reduces carrying costs.
7. Worker Safety Agents
Safety-focused agents analyze incident reports, sensor alerts, CCTV insights, and SOP violations.
They identify unsafe behavior, detect hazardous patterns, and generate real-time alerts for supervisors.
The agent can also create automated risk assessments and suggest training or corrective actions, improving overall workplace safety.
8. Document & Compliance Automation Agents
Manufacturing requires strict documentation batch records, quality logs, audit trails, and compliance reports.
Agentic AI automates this process by generating accurate ISO, OSHA, FDA, or industry-specific documentation. It validates traceability logs, checks missing fields, and flags compliance risks.
This reduces manual effort and ensures audit readiness at all times.
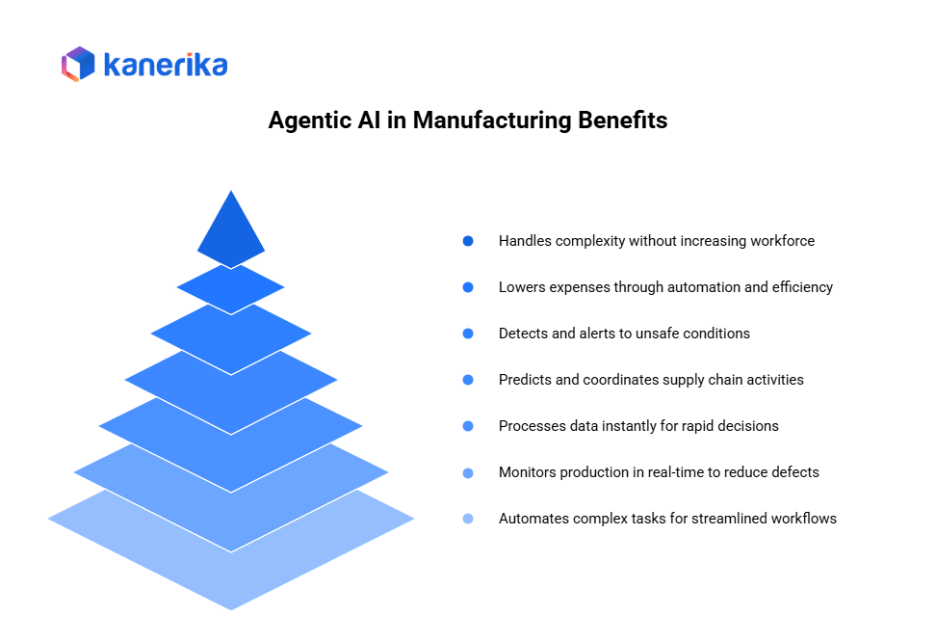
Benefits of Agentic AI in Manufacturing
Agentic AI delivers significant value across the entire manufacturing lifecycle. By combining real-time intelligence with autonomous decision-making, it helps factories operate with greater speed, accuracy, and reliability. Below are the key benefits manufacturers experience today:
- Higher uptime through proactive and autonomous maintenance – Agents monitor equipment continuously, detect early warning signs, and trigger maintenance before breakdowns occur.
- Reduced scrap and defects with continuous quality monitoring – Real-time inspection, anomaly detection, and automated corrections keep production within acceptable limits.
- Faster decision-making through real-time reasoning – Agents process thousands of data points instantly and make decisions at machine speed.
- Improved operational efficiency by automating complex tasks – Workflows related to scheduling, routing, approval, procurement, and reporting run automatically.
- Better supply chain performance through predictive coordination – Agents track supplier reliability, shipment delays, and material consumption, enabling proactive adjustments.
- Safety improvements using anomaly detection and automated risk alerts – Unsafe conditions, SOP violations, and hazard patterns are identified early and addressed quickly.
- Cost reduction across maintenance, labor, and quality operations – Fewer breakdowns, less scrap, and lower manual effort reduce operational costs significantly.
- Scalable operations with minimal incremental workforce – Autonomous agents allow factories to handle more complexity without increasing headcounts.
Architecture of Agentic AI in Manufacturing
Agentic AI in manufacturing relies on a well-designed architecture that connects machines, data systems, and decision engines into one intelligent ecosystem. This architecture ensures agents can sense, think, and act across the factory floor. Below is a breakdown of the key layers and how they work together.
1. Data Layer
Every agent begins with strong, real-time data. This layer gathers information from:
- IoT sensors and edge devices
- PLCs and machine controllers
- ERP systems
- MES and SCADA platforms
- QMS and WMS applications
The data flows through both streaming pipelines (for real-time control) and batch pipelines (for analysis and optimization). Together, these systems give agents a complete view of production, quality, inventory, and equipment health.
2. Intelligence Layer
Once data is available, the intelligence layer processes it. This layer includes:
- LLMs and SLMs that interpret instructions, read documents, summarize logs, and support complex reasoning
- Vision models for analyzing images, detecting defects, or interpreting video feeds
- Predictive analytics algorithms for forecasting failures, demand shifts, or supply delays
These models enable the agent to understand context, predict outcomes, and evaluate multiple action paths.
3. Agent Orchestration Layer
This layer forms the “brain” of agentic AI. It includes:
- A planning engine that decides the next action
- A memory store for short-term and long-term operational knowledge
- A tool-calling system for interacting with external systems
- A self-correction loop that allows the agent to learn and adjust based on feedback and results
Together, these components allow agents to make decisions autonomously, execute multi-step workflows, and improve over time.
4. Integration Layer
Agents need to interact with existing manufacturing systems, and this layer ensures that. It includes:
- API gateways for ERP, MES, CMMS, WMS, PLM, and QMS
- RPA connectors for older systems without APIs
With these integrations, agents can check inventory, schedule maintenance, update orders, and sync data across platforms.
5. Execution Layer
Finally, the execution layer allows agents to perform actions. Examples include:
- Triggering work orders in CMMS
- Submitting purchase orders in ERP
- Adjusting production schedules in MES
- Initiating workflows through automation tools
This layer ensures decisions lead to real operational impact across the factory floor.
Top AI Agent Development Companies You Should Know in 2025
Explore the top 10 AI agent development companies in 2025, driving automation and innovation
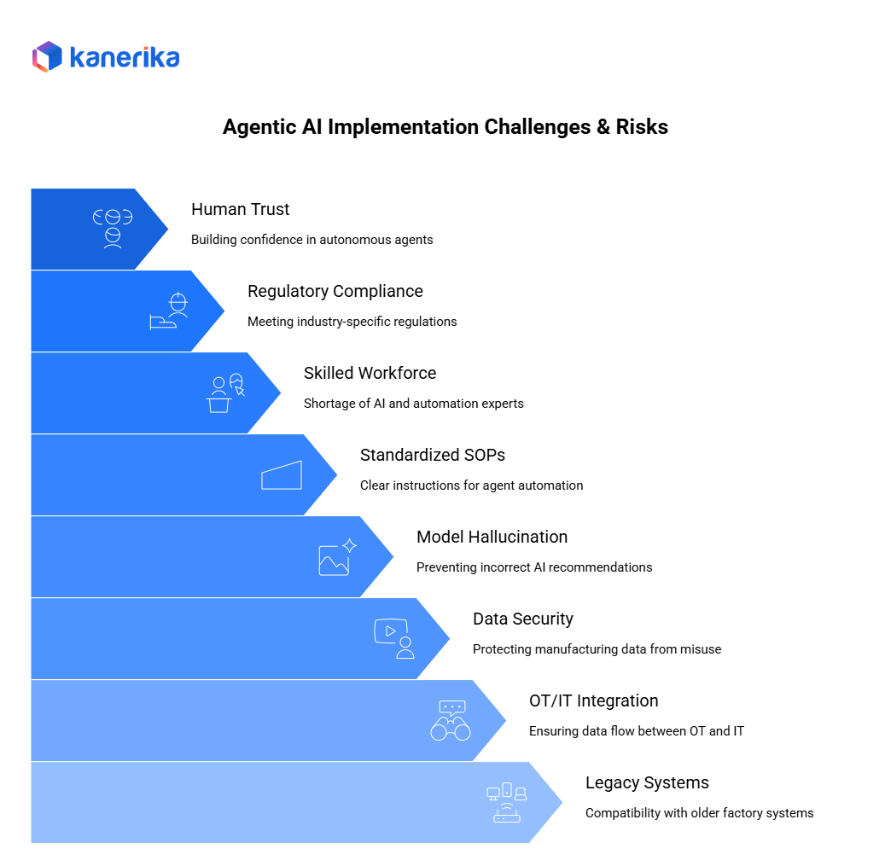
Challenges & Risks of Agentic AI in Manufacturing
Although agentic AI brings major advantages, manufacturers must also navigate several risks and challenges. These issues can slow adoption or reduce impact if not managed well.
1. Legacy System Compatibility
Many factories still run older PLCs, SCADA systems, or proprietary software. As a result, connecting these systems to modern APIs or AI agents becomes difficult and may require custom integration or edge gateways.
2. OT/IT Integration
Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) often operate in silos. Therefore, ensuring smooth data flow between machines, sensors, ERP, MES, and cloud systems is one of the biggest barriers to building reliable agents.
3. Data Security & Governance
Manufacturing data includes machine logs, production metrics, and sometimes customer or supplier information. Strong encryption, access control, and governance policies are essential to prevent leaks or misuse.
4. Model Hallucination Risks
Since LLM-based agents may generate incorrect recommendations, factories must implement guardrails, validation logic, and human approvals for critical decisions.
5. Lack of Standardized SOPs
Agents rely on clear instructions. However, many factories still use outdated or inconsistent SOPs, making automation difficult.
6. Skilled Workforce Shortage
AI engineers, data scientists, and automation experts are in short supply. This slows deployment and scaling.
7. Regulatory Compliance
Industries like automotive, aerospace, food, and pharma follow strict compliance rules. Every AI-driven action must be traceable and audit-ready.
8. Human Trust and Adoption
Finally, operators may hesitate to rely on autonomous agents. Clear communication, training, and human-in-the-loop workflows help build confidence.
Future of Agentic AI in Manufacturing
The future of manufacturing is moving rapidly toward autonomy, and agentic AI will play a central role. Below are the key trends shaping the next decade.
1. Autonomous Factories
Manufacturing plants will increasingly operate with minimal human intervention. Agents will monitor machines, adjust parameters, and make real-time decisions to optimize production.
2. Multi-agent Factory Ecosystems
Instead of a single AI system, factories will run multiple specialized agents maintenance agents, quality agents, scheduling agents working together and coordinating decisions across the plant.
3. AI-driven Robots Collaborating with Digital Agents
Physical robots on the shop floor will interact with digital agents that guide tasks, plan workflows, and provide instructions. This collaboration will improve precision, speed, and safety.
4. Closed-loop Manufacturing
Manufacturing cycles will become fully automated. Agents will detect deviations, run diagnostics, correct issues, and validate outcomes without waiting for human involvement.
5. Real-time Optimization Across Plants
Companies with multiple plants will use agents to coordinate production loads, manage capacity, and balance resources in real time across global locations.
6. Predictive Supply Networks
Agentic AI will help predict demand changes, supplier risks, and logistics delays, adjusting procurement and inventory workflows automatically.
7. Self-healing Factories
Factories will become capable of resolving issues autonomously. Agents will identify failures, trigger corrective actions, and restore processes before downtime occurs.
Meet Karl: Kanerika’s AI Data Insights Agent
Karl – Kanerika’s AI agent for data analysis is built to make data accessible for everyone in your organization. With Karl, you don’t need to write SQL or rely on analysts—just ask your question in plain English, and get instant answers in the form of charts, summaries, or tables. It uses advanced AI to understand what you’re asking, fetch the right data, and explain it clearly.
From exploring trends to generating reports, Karl handles it all with ease. Whether you’re in marketing, sales, or leadership, Karl helps you make faster, smarter decisions without the technical hassle.
Become an Industry Leader with Kanerika’s Cutting-edge AI Solutions
Kanerika is a top-rated AI implementation company known for building custom AI models and solutions that align perfectly with each client’s unique business needs. With deep expertise in AI, we empower businesses across industries like banking and finance, retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics to seamlessly integrate AI into their operations. Our tailored AI solutions are designed to elevate operational efficiency, reduce costs, and drive impactful outcomes.
By developing advanced, industry-specific models, we help businesses automate complex processes, make data-driven decisions, and gain competitive advantages. Whether it’s optimizing financial forecasting, enhancing customer experiences in retail, streamlining manufacturing workflows, or advancing patient care, Kanerika’s AI solutions adapt to diverse requirements and challenges. Our commitment to client success has established us as a leader in the AI space, trusted by companies to transform their operations and realize measurable improvements through intelligent automation and analytics.
Elevate Organizational Productivity by Integrating Agentic AI!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
1. What is Agentic AI in Manufacturing?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems that can autonomously monitor data, reason, plan actions, use tools, and execute multi-step workflows across manufacturing operations.
2. How is Agentic AI different from traditional AI?
Traditional AI makes predictions, while Agentic AI takes actions. It can trigger work orders, adjust machine parameters, update schedules, or escalate issues without manual steps.
3. What manufacturing processes benefit most from Agentic AI?
Predictive maintenance, quality inspection, production scheduling, inventory optimization, supply chain coordination, and safety monitoring benefit significantly.
4. Does Agentic AI replace human workers?
No. It augments workers by automating repetitive decisions and tasks. Humans remain essential for oversight, strategy, high-risk approvals, and complex judgement.
5. Is Agentic AI safe to use on the factory floor?
Yes—when combined with proper governance, human-in-the-loop controls, and validation steps. Safety frameworks ensure accurate and reliable automated actions.
6. What systems can Agentic AI integrate with?
Agentic AI connects with ERP, MES, SCADA, PLCs, CMMS, WMS, QMS, and RPA tools through APIs, gateways, and industrial protocols.
7. What are the main challenges in deploying Agentic AI?
Key challenges include legacy system compatibility, data security, regulatory compliance, skilled workforce gaps, integration complexity, and building trust in AI-driven decisions.











