Databricks Data Lineage plays a crucial role in ensuring trust, transparency, and accountability across complex data ecosystems. As data travels through pipelines—being transformed, aggregated, and shared across systems, lack of visibility can lead to compliance risks and inaccurate insights. According to a recent survey, 70% of enterprises struggle with incomplete or outdated lineage, impacting their ability to trace data origins and maintain governance standards.
Built into Unity Catalog, Databricks’ unified governance layer, Databricks Data Lineage automatically tracks data movement, transformations, and dependencies across workspaces, notebooks, jobs, and dashboards. It provides real-time visibility into data flows from ingestion to analytics, creating a trusted foundation for governance and compliance.
This blog explores what Databricks Data Lineage is, why it matters, how it works, and the best practices to implement it effectively in enterprise environments.
Key Takeaways
- Databricks Data Lineage provides complete visibility of data movement, transformations, and connections within the Databricks environment.
- Integrated into Unity Catalog, it offers automatic lineage tracking for tables, views, notebooks, and workflows without manual setup.
- It supports multiple languages — SQL, Python, Scala, and R — and works smoothly across Delta Live Tables, ETL pipelines, and BI dashboards.
- Lineage data is stored in Unity Catalog’s central control layer, accessible via the Databricks UI or REST APIs.
- The solution enables easy audits, impact analysis, and compliance, helping companies meet regulatory standards such as GDPR and HIPAA.
- By connecting technical lineage with business context, organizations can improve data trust, traceability, and collaboration across teams.
- Best practices include adopting Unity Catalog early, automating lineage validation, and integrating with enterprise data catalogs for richer governance.
- Addressing common challenges—like incomplete lineage capture or visualization overload—ensures consistent, reliable insights.
- With Databricks Data Lineage, enterprises build a transparent, governed, and future-ready data ecosystem that strengthens both analytics and AI initiatives.
What is Databricks Data Lineage?
Databricks Data Lineage is an automated framework that tracks how data moves, transforms, and is used across the Databricks environment. It is built into Unity Catalog, Databricks’ unified governance layer, and gives organizations a clear view of their data flow from source to consumption. The system captures lineage information for tables, views, notebooks, workflows, and dashboards without manual setup.
It records relationships between datasets at different levels, showing how data transforms throughout its lifecycle. The framework supports multiple programming languages and connects across ETL, analytics, and machine learning workloads.
Key Capabilities:
- Automatically captures table-to-table, column-level, and notebook-level lineage.
- Supports SQL, Python, Scala, and R operations within the Databricks workspace.
- Integrates lineage across ETL pipelines, Delta Live Tables, and BI dashboards.
- Enables end-to-end traceability from raw ingestion to final business consumption.
- Stores lineage metadata within Unity Catalog’s governance layer for centralized management.
- Provides visualization through the Databricks UI and programmatic access via REST APIs.
This built-in automation enables organizations to trace data flow, verify accuracy, and ensure compliance with governance standards. It simplifies troubleshooting, improves data trust, and strengthens overall transparency across the data ecosystem. By combining automated lineage capture with unified governance, Databricks delivers a scalable and auditable foundation for enterprise data management.
How Databricks Data Lineage Works
Databricks Unity Catalog automatically captures data lineage as queries run across your data platform. The system tracks where data comes from, how it changes, and where it goes.
Architecture Flow
1. Data Ingestion
When data enters through Delta tables or pipelines, Unity Catalog starts capturing metadata and dependencies immediately. The system records source information without requiring manual setup or configuration.
2. Transformation Tracking
Unity Catalog tracks lineage whether you use SQL queries, notebooks, or Delta Live Tables. The system captures relationships at both table level and column level. Every transformation gets recorded automatically as queries execute.
3. Storage
Lineage metadata stores in Unity Catalog’s centralized metastore. This provides global visibility across all workspaces attached to the same metastore. Teams in different workspaces see the same lineage information for shared data.
4. Visualization
The Databricks user interface provides an interactive lineage graph. Users view upstream datasets feeding into their tables and downstream systems consuming their data. The graph shows connections with visual arrows and expandable nodes.
Image Source: Databricks Blog – Unity Catalog Data Lineage
5. Integration
Lineage data connects with enterprise governance systems through REST APIs. Organizations query lineage information programmatically for compliance reporting, impact analysis, or custom tooling.
Supported Environments
Databricks tracks lineage across multiple execution environments:
- Databricks SQL – Queries run through SQL editor or SQL warehouses
- Delta Live Tables – Declarative pipeline definitions
- Notebooks – Python, SQL, Scala, and R code
- Unity Catalog assets – Tables, views, volumes, and dashboards
Image Source: Databricks Blog – Column Level Lineage
Real Example
Consider a Delta Live Table pipeline in production:
- Source data: A raw customer_orders Delta table contains order transactions from your e-commerce system.
- Transformation: Your pipeline reads this raw data, applies business logic removing test orders, calculates sales totals, and joins customer demographics.
- Output: The pipeline creates a curated sales_insights table used by business reports and dashboards.
Unity Catalog automatically creates lineage links between these tables. Users viewing sales_insights see it originates from customer_orders. Column-level lineage shows how total_revenue in the insights table derives from order_amount and quantity in the raw orders table.
When someone modifies the customer_orders table schema, lineage shows all downstream tables and reports affected by the change. This prevents breaking reports by revealing dependencies before making changes.
How It Captures Lineage
Unity Catalog captures lineage through runtime query analysis:
- Query execution monitoring – The system watches queries as they run and extracts data flow information.
- Metadata extraction – Databricks reads which tables appear in FROM clauses and which tables receive INSERT or CREATE operations.
- Column mapping – The system tracks how columns transform through SELECT statements, joins, and calculations.
- Relationship building – Unity Catalog builds a graph connecting sources, transformations, and destinations.
This happens automatically without the need of code changes or special annotations. Lineage captures for all supported languages and execution modes.
Access Methods
Users access lineage information three ways:
- Visual Interface – Navigate to any table in Catalog Explorer and click the Lineage tab. View interactive graphs showing data flow.
- System Tables – Query lineage system tables using SQL for programmatic access to lineage metadata.
- REST API – Call lineage APIs to retrieve dependency information for automation or integration with other tools.
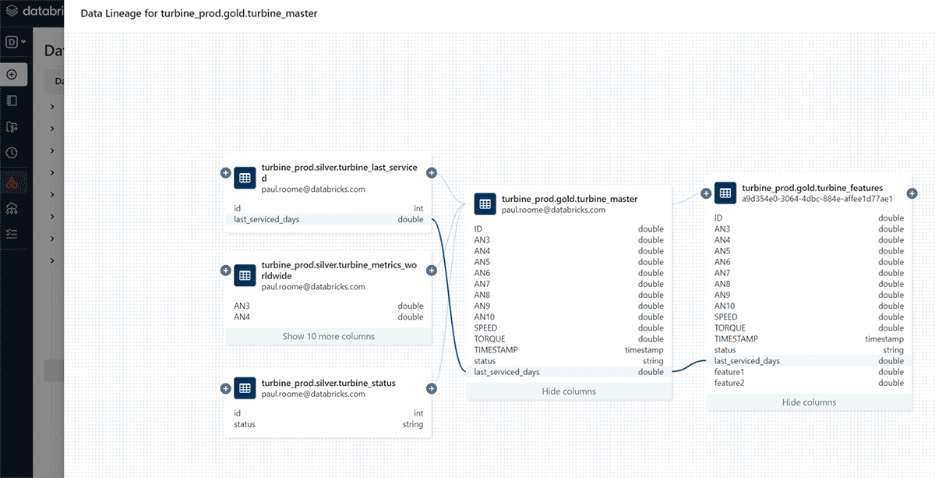
Image Source: https://www.databricks.com/blog/announcing-general-availability-data-lineage-unity-catalog
Key Features
- Real-time updates – Lineage appears immediately after query execution without delays.
- Column-level detail – Track individual column transformations and dependencies.
- Cross-workspace visibility – See lineage across all workspaces sharing the same metastore.
- Security integration – Lineage respects Unity Catalog permissions. Users only see lineage for data they can access.
- External lineage – Connect lineage from sources like Salesforce or destinations like Tableau for end-to-end visibility.
Databricks data lineage works automatically behind the scenes, requiring no setup beyond enabling Unity Catalog. The system captures comprehensive lineage as your data pipelines run.
Key Features of Databricks Data Lineage
Databricks data lineage provides comprehensive tracking capabilities built directly into Unity Catalog. These features work together to give organizations complete visibility into data flow across their platforms.
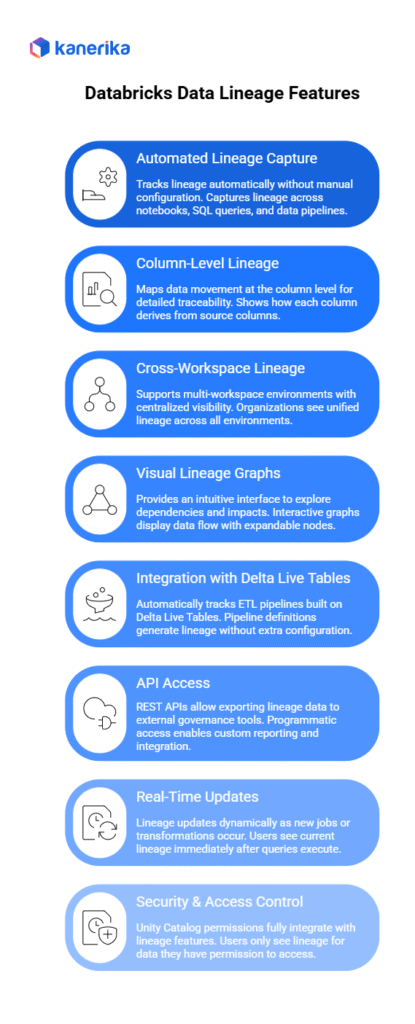
1. Automated Lineage Capture
The system tracks lineage automatically without needing manual setup or code changes. Moreover, lineage captures across notebooks, SQL queries, and data pipelines as they execute. Users write queries normally while Unity Catalog records links between datasets in the background. Hence, no special notes, markers, or tags are needed.
2. Column-Level Lineage
Databricks maps data movement at the column level for detailed tracking. Additionally, users see exactly how each column in destination tables derives from source columns. When total_revenue appears in a report, column-level lineage shows it comes from price * quantity calculations in source tables. This detailed tracking helps identify exactly which source fields affect specific business metrics.
3. Cross-Workspace Lineage
The system supports multiple workspace environments with central version through Unity Catalog. Consequently, organizations running separate workspaces for development, testing, and production see unified lineage across all environments. Data flowing between workspaces maintains lineage tracking. Teams in different departments view the same lineage information for shared data tables.
4. Visual Lineage Graphs
Databricks provides an intuitive interface to explore dependencies and impacts. Interactive graphs display data flow with expandable nodes and connection arrows. Users click on tables to see upstream sources feeding them and downstream consumers using them. The visual format makes complex data relationships easy to understand without reading code or documentation.
5. Integration with Delta Live Tables
Unity Catalog automatically tracks ETL pipelines built on Delta Live Tables framework. Pipeline definitions written declaratively generate lineage without extra configuration. Each transformation step appears in lineage graphs showing how raw data becomes refined business tables. Correspondingly, this integration eliminates gaps in lineage tracking across different pipeline types.
6. API Access
REST APIs allow exporting lineage data to external governance tools like Collibra, Alation, or Informatica. Organizations integrate Databricks lineage with enterprise metadata repositories. Moreover, programmatic access enables custom reporting, compliance automation, and integration with existing data catalogs. Teams query lineage information to build impact analysis tools or automated change notifications.
7. Real-Time Updates
Lineage updates dynamically as new jobs or transformations occur. Users see current lineage immediately after queries execute rather than waiting for batch processing. Additionally, this real-time capability ensures lineage information stays accurate as pipelines evolve. Teams make decisions based on up-to-date dependency information.
8. Security & Access Control
Unity Catalog permissions fully integrate with lineage features. Users only see lineage for data they have permission to access. As well as, audit logs record who views lineage information and when. Hence, this security integration ensures lineage features respect existing data governance policies without requiring separate permission management.
| Feature | Description |
| Automated Lineage Capture | Tracks lineage without manual configuration across notebooks, SQL, and pipelines |
| Column-Level Lineage | Maps data movement at the column level for detailed traceability |
| Cross-Workspace Lineage | Supports multi-workspace environments with centralized visibility via Unity Catalog |
| Visual Lineage Graphs | Provides an intuitive interface to explore dependencies and impacts |
| Integration with Delta Live Tables | Automatically tracks ETL pipelines built on Databricks’ managed Delta Live framework |
| API Access | REST APIs allow exporting lineage data to governance tools like Collibra or Alation |
| Real-Time Updates | Lineage updates dynamically as new jobs or transformations occur |
| Security & Access Control | Fully integrated with Unity Catalog permissions and audit logs |
Step-by-Step Guide of Implementing Data Lineage in Databricks
Setting up data lineage in Databricks requires enabling Unity Catalog and following specific steps to register datasets and build pipelines.
Step 1: Enable Unity Catalog
Unity Catalog provides the foundation for data lineage tracking in Databricks.
- Set up metastore
Create a Unity Catalog metastore in your Databricks account console. The metastore acts as the top-level container for all your data. You need one metastore per region where you operate.
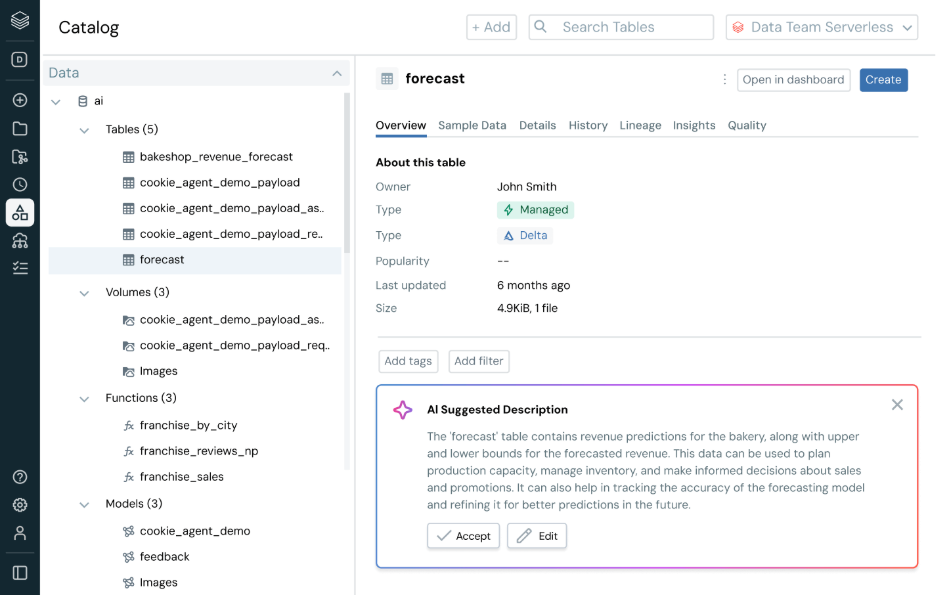
Image Source: https://www.databricks.com/product/unity-catalog
- Assign workspaces
Link your Databricks workspaces to the metastore. This enables Unity Catalog features including lineage tracking across all attached workspaces.
- Configure permissions
Set up access policies for teams and users. Define who can create catalogs, manage schemas, and access specific tables. Unity Catalog uses these permissions to control lineage visibility.
Step 2: Register Datasets
Unity Catalog needs your data registered to track lineage.
- Create catalogs and schemas – Organize data using the three-level namespace: catalog.schema.table. Create catalogs for different business domains or environments like production and development.
- Register tables – Create tables in Unity Catalog using SQL commands or notebooks. Tables can reference data stored in Delta Lake or external locations.
- Use Delta Lake – Store data in Delta Lake format for version control and ACID compliance. Delta Lake tables automatically integrate with Unity Catalog lineage tracking.
Example SQL command:
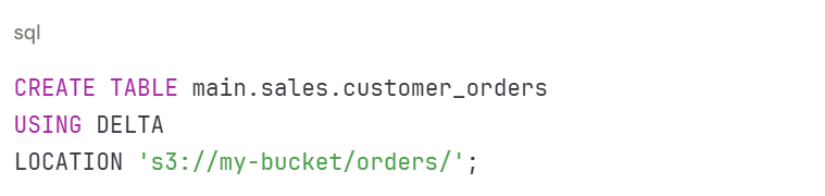
Step 3: Develop Pipelines and Workflows
Build your data transformation pipelines using any supported method.
- Databricks SQL – Write SQL queries in the SQL editor or notebooks. Unity Catalog captures lineage automatically when queries reference Unity Catalog tables.
- PySpark and notebooks – Develop transformations using Python, Scala, or R in notebooks. Read from Unity Catalog tables and write results back to Unity Catalog.
- Delta Live Tables – Build declarative pipelines using Delta Live Tables framework. Define transformations and dependencies. Unity Catalog tracks the entire pipeline lineage automatically.
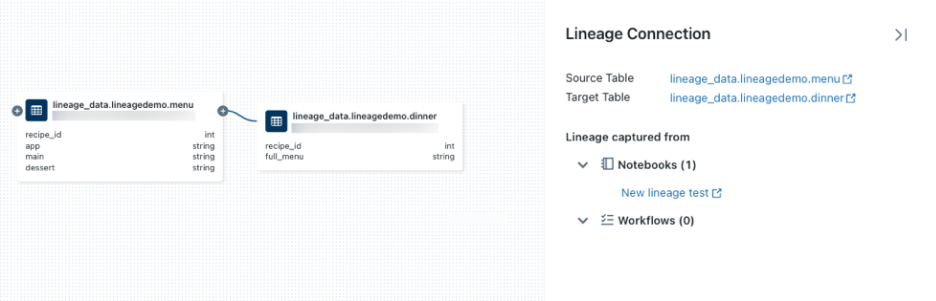
Image Source: https://docs.databricks.com/sap/en/data-lineage
Unity Catalog captures lineage as pipelines execute. No special code or configuration needed.
Step 4: View and Explore Lineage
Access lineage information through the Databricks interface.
Navigate to Catalog Explorer – Click Catalog in the workspace sidebar. Search or browse for your table.
Open Lineage tab – Select the table you want to investigate. Click the Lineage tab to see immediate dependencies.
Explore interactive graph – Click “See Lineage Graph” to view the full visual representation. The graph shows upstream tables feeding your dataset and downstream consumers using it.
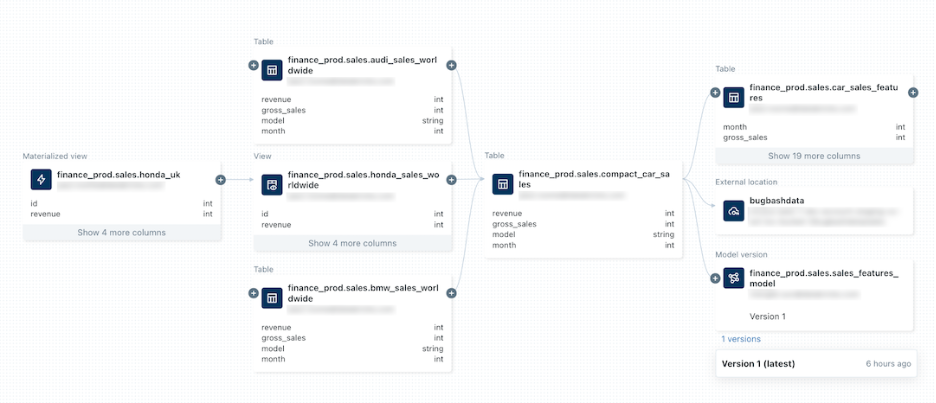
Image Source: https://docs.databricks.com/aws/en/data-governance/unity-catalog/data-lineage
Expand nodes – Click the plus icon on table boxes to expand and see more connections. Explore step by step through your data pipeline.
View column-level lineage – Expand table nodes to see individual columns. Track how specific columns transform from source to destination.
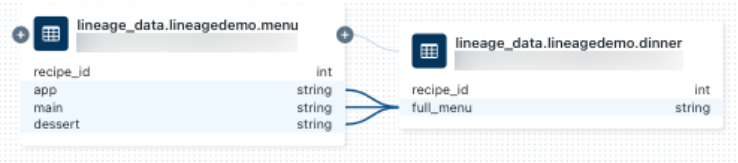
Image Source: https://docs.databricks.com/aws/en/data-governance/unity-catalog/data-lineage
Check notebook and job dependencies – Click on connections between tables to see which notebooks or jobs performed the transformations.
Step 5: Integrate and Automate
Connect lineage data with external systems for advanced use cases.
1. Use REST APIs – Extract lineage metadata programmatically using Databricks REST APIs. Query lineage endpoints to retrieve upstream and downstream dependencies.
Example API call:
GET /api/2.0/lineage-tracking/table-lineage
2. Query system tables – Access lineage information through SQL queries on system tables:
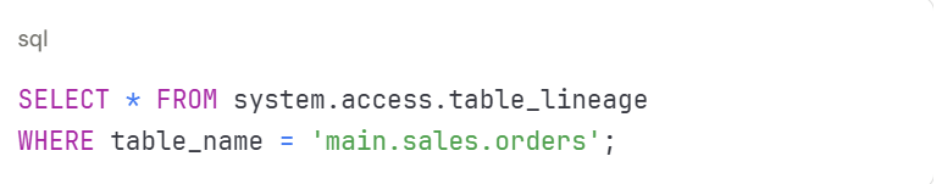
3. Build governance dashboards – Combine lineage data with other governance metrics. Create custom dashboards showing data usage patterns, access frequency, and dependency maps.
4. Integrate with governance tools – Export lineage metadata to external governance platforms like Collibra or Alation. Use APIs to sync lineage information regularly.
5. Combine with audit logs – Join lineage data with audit logs showing who accessed what data and when. Build comprehensive data oversight systems.
6. Automate monitoring – Set up automated checks that alert teams when critical data dependencies change or when lineage breaks.
Key Implementation Tips
- Start small – Begin with critical datasets before expanding to entire data platform.
- Test permissions – Verify that lineage respects Unity Catalog access controls correctly.
- Document dependencies – Use lineage to create documentation showing data flows automatically.
- Train teams – Help users understand how to read and interpret lineage graphs.
- Monitor regularly – Check lineage information regularly to ensure accurate capture.
Lineage tracking works automatically once Unity Catalog is enabled and data is registered. The system captures dependencies as queries execute without requiring code changes or special configuration.
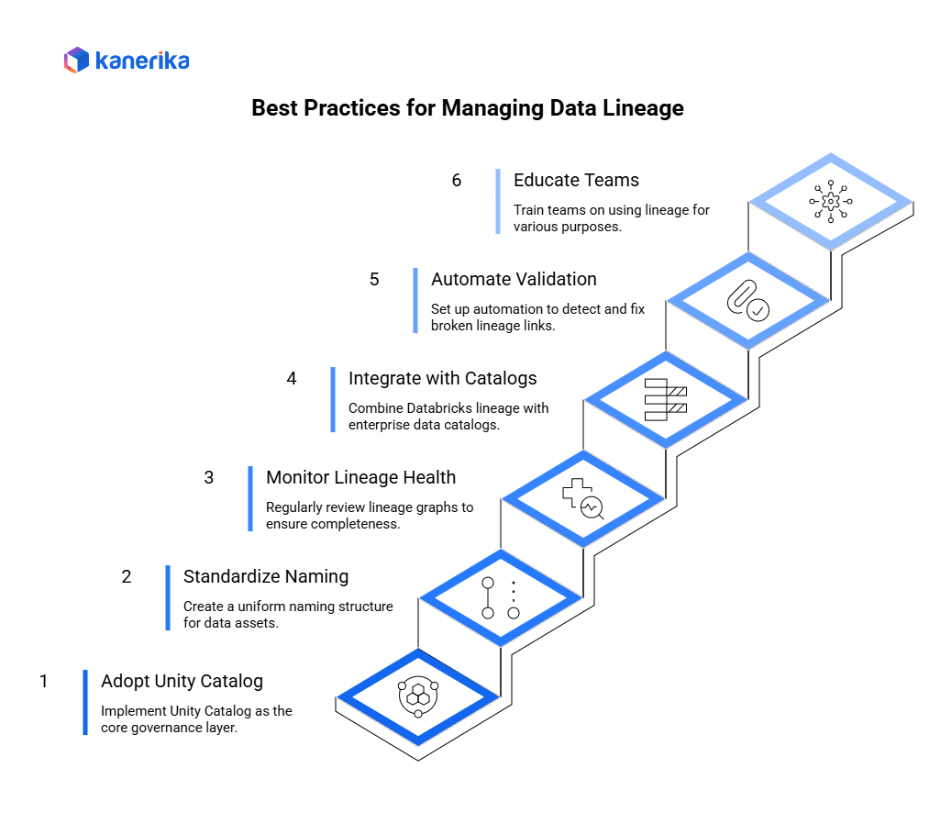
Best Practices for Managing Data Lineage
Implementing Data Lineage in Databricks requires structure, consistency, and monitoring. Following these practices ensures reliable tracking and supports long-term data governance.
1. Adopt Unity Catalog Early
Enable Unity Catalog as the core governance layer. Centralizing data access and lineage in one environment simplifies management and enforces consistent permissions across all teams.
2. Standardize Naming Conventions
Create a uniform naming structure for datasets, pipelines, and notebooks. Clear naming helps users identify data sources quickly and reduces confusion during audits.
3. Monitor Lineage Health Regularly
Review lineage graphs and ensure all jobs, tables, and assets are properly registered. Consistent monitoring prevents missing or incomplete lineage tracking.
4. Integrate with Enterprise Data Catalogs
Combine Databricks lineage with tools like Collibra or Alation to add business context and enable enterprise-wide visibility into data assets.
5. Automate Lineage Validation
Set up automation to detect and fix broken lineage links after schema changes or pipeline updates. This maintains data accuracy and reduces manual checks.
6. Educate Teams and Promote Use
Train data engineers, analysts, and governance teams on how to use lineage for debugging, auditing, and compliance. Encourage adoption across departments to ensure shared accountability.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Managing data lineage in Databricks can become complex as systems scale and data flows expand. Addressing common issues early helps maintain accuracy and reliability across all environments.
1. Incomplete Lineage Capture
Lineage gaps often occur when some processes run outside Databricks-managed contexts. To prevent this, ensure all jobs and assets are executed within Databricks and that every dataset is properly registered in Unity Catalog. This guarantees complete lineage tracking across pipelines and workspaces.
2. Cross-System Dependencies
External data sources and third-party tools can break end-to-end visibility. Use REST APIs or connectors to extract lineage metadata from external systems and merge it into the Databricks governance layer for unified traceability.
3. Access Control Conflicts
Multiple teams using shared datasets can create governance risks. Implement role-based access control (RBAC) through Unity Catalog to manage permissions, ensuring users only access data relevant to their roles.
4. Visualization Overload
Extensive lineage graphs can be overwhelming in large-scale environments. Simplify visualization by grouping related datasets, pipelines, or domains. Use filters to focus on specific data flows or key business processes.
Struggling to choose between Cloudera and Databricks? We simplify the journey.
Partner with Kanerika for expert data strategy and implementation.
Kanerika’s Partnership with Databricks: Enabling Smarter Data Solutions
We at Kanerika are proud to partner with Databricks, bringing together our deep expertise in AI, analytics, and data engineering with their robust Data Intelligence Platform. Furthermore, our team combines deep know-how in AI, data engineering, and cloud setup with Databricks’ Lakehouse Platform. Together, we design custom solutions that reduce complexity, improve data quality, and deliver faster insights. Moreover, from real-time ETL pipelines using Delta Lake to secure multi-cloud deployments, we make sure every part of the data and AI stack is optimized for performance and governance.
Our implementation services cover the full lifecycle—from strategy and setup to deployment and monitoring. Additionally, we build custom Lakehouse blueprints aligned with business goals, develop trusted data pipelines, and manage machine learning operations using MLflow and Mosaic AI. We also implemented Unity Catalog for enterprise-grade governance, ensuring role-based access, lineage tracking, and compliance. As a result, our goal is to help clients move from experimentation to production quickly, with reliable and secure AI systems.
We solve real business challenges, such as breaking down data silos, enhancing data security, and scaling AI with confidence. Furthermore, whether it’s simplifying large-scale data management or speeding up time-to-insight, our partnership with Databricks delivers measurable outcomes. We’ve helped clients across industries—from retail and healthcare to manufacturing and logistics—build smarter applications, automate workflows, and improve decision-making using AI-powered analytics.
Make the most of Databricks Data Lineage with Unity Catalog
Partner with Kanerika to build scalable, future-ready data solutions.
FAQs
1. What is Databricks Data Lineage?
Databricks Data Lineage is an automated tracking framework built into Unity Catalog, Databricks’ unified governance layer. It records how data moves, transforms, and is consumed across tables, views, notebooks, workflows, and dashboards — providing full visibility and traceability across the data ecosystem.
2. Why is Data Lineage important in Databricks?
Data lineage is essential for governance, compliance, and data trust. It helps teams understand where data originates, how it changes, and which systems rely on it. This visibility supports root cause analysis, impact assessments, and regulatory audits such as GDPR or HIPAA compliance.
3. How does Databricks capture Data Lineage?
Databricks automatically captures lineage through Unity Catalog as data flows through notebooks, SQL queries, and Delta Live Tables. It records relationships at both table and column levels, without requiring manual configuration.
4. What can I view in the Lineage Graph?
The Lineage tab in the Databricks UI displays interactive graphs showing upstream and downstream dependencies. Users can explore how specific columns or tables connect across workflows, helping identify data sources and usage paths.
5. Can Databricks Data Lineage integrate with other governance tools?
Yes. Databricks provides REST APIs to extract lineage metadata, allowing integration with third-party governance and cataloging tools like Collibra, Alation, or Informatica EDC for unified enterprise data management.
6. What environments support Databricks Data Lineage?
Lineage is supported in Databricks SQL, Delta Live Tables, and notebooks using Python, SQL, or Scala. It also covers Unity Catalog assets such as tables, views, and dashboards.
7. How can enterprises benefit from Databricks Data Lineage?
Enterprises gain end-to-end data transparency, simplified governance, and faster debugging. Automated lineage improves collaboration between engineering, analytics, and compliance teams — ensuring decisions are based on accurate, traceable data.










