Ever launched a “successful” migration only to have users revolt the next morning? “The customer addresses are wrong!” “Half the inventory is missing!” “Why do we have three John Smiths with the same ID?” Welcome to the $12.9 million problem that’s what Gartner says poor data quality costs organizations yearly.
Here’s the dirty secret about migration projects: technology rarely fails. Your data does. Ensuring Data Quality During Data Migration sounds boring until your CFO can’t close quarterly books because revenue numbers don’t match.
Picture this: Sales calls a customer using the migrated CRM. Wrong phone number. They try the email. Bounces back. The shipping address? That’s actually their old office from 2019. One bad record wastes 15 minutes. Multiply that across thousands of records and hundreds of employees.
Think of it like photocopying. One smudge on the original creates thousands of flawed copies. Similarly, migration amplifies existing data problems. IBM research shows that 27% of business leaders doubt their data accuracy during migrations.
But wait, it gets worse. Regulators don’t accept “we were migrating” as an excuse for compliance failures. Board members don’t care about technical success when business reports show garbage.
The fix isn’t buying expensive tools at the last minute. Start with quality checks on day one. Profile your data. Clean as you go. Validate continuously. Treat data quality like security and build it into every phase, not something you test at the end.
Key Learnings
- Data quality determines migration success – Most data migration failures are caused by poor data quality, not technology. Accurate, complete, and consistent data is essential for trusted outcomes after migration.
- Data quality issues surface during migration, not after – Migration exposes hidden problems such as duplicates, missing values, and broken relationships. Identifying these early prevents costly rework later.
- Data profiling and cleansing must start before migration – Pre-migration profiling establishes baselines and reveals quality gaps. Cleansing and standardization ensure only reliable data is migrated.
- Validation and reconciliation ensure accuracy during and after migration – In-flight checks and post-migration reconciliation confirm source-to-target accuracy. This builds confidence for business sign-off and reporting.
- Automation and governance improve data quality at scale – Automated data quality checks and strong governance reduce manual errors and maintain consistency across large enterprise migrations.
Accelerate Your Data Transformation by Migrating!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Migration Services
What Does “Data Quality” Mean in Data Migration?
Data quality means your information is accurate, complete, consistent, and timely. Accuracy ensures records match reality as customer addresses are correct, not outdated. Completeness means no missing fields like blank phone numbers. Consistency guarantees information matches across all systems. Timeliness confirms data reflects current situations, not last year’s status.
Four Pillars of Data Quality :
- Accuracy means your data represents reality correctly. Customer names match actual identities, addresses point to real locations, and prices reflect current rates. Inaccurate data causes wrong shipments, billing errors, and poor decisions.
- Completeness ensures all required fields contain values. Missing phone numbers prevent customer contact. Empty product descriptions hurt sales. Complete data supports full business operations without gaps.
- Consistency maintains uniform formats and values across systems. Date formats stay standardized. “California” doesn’t appear as “CA” in one place and “Calif.” elsewhere. Consistent data integrates smoothly and prevents confusion.
- Timeliness keeps information current and relevant. Customer addresses update when people move. Product availability reflects actual inventory. Outdated data leads to failed deliveries and frustrated customers. Fresh data enables accurate reporting and effective decision-making.
Operational vs Migration Data Quality
Operational data quality focuses on daily business activities within stable systems. However, migration data quality addresses unique challenges during system transfers. Operational issues might stay hidden in existing systems. Migration exposes every flaw when moving data between different platforms and formats.
Migration Amplifies Existing Issues
Here’s the problem: migration acts like a magnifying glass for data problems. That duplicate customer record you ignored? It becomes three duplicates in the new system. Inconsistent date formats? They cause import failures. Moreover, poor quality data slows migration timelines and increases costs significantly.
A single incorrect customer record becomes hundreds after migration. Inconsistent date formats crash import scripts. Missing required fields halt entire transfers. Therefore, cleaning data before migration isn’t optional as it prevents costly failures and ensures your new system starts with reliable, trustworthy information.
Why Data Quality Issues Surface During Migration
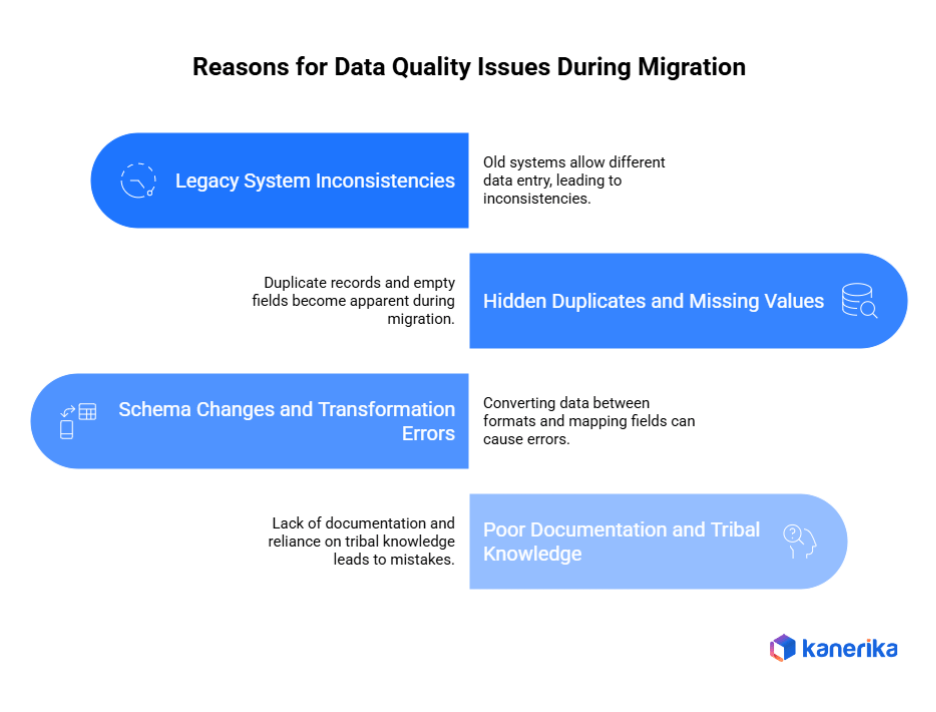
Migration acts like a spotlight, revealing data quality problems hidden in your systems for years. Here’s why these issues suddenly appear during transfers.
1. Legacy System Inconsistencies
Legacy system data issues accumulate over decades of operations. Old systems allowed users to enter data differently like some typed “New York,” others used “NY” or “nyc.” Additionally, outdated validation rules permitted impossible dates or negative quantities. These inconsistencies work fine within familiar systems but break during migration when strict rules apply.
2. Hidden Duplicates and Missing Values
Duplicate data records often hide in plain sight. Customer “John Smith” appears three times with slight variations as different spellings, addresses, or account numbers. Moreover, missing data values scatter throughout databases. Empty fields that seemed harmless suddenly become critical when new systems require complete information. Migration tools flag these problems immediately, stopping transfers until resolved.
3. Schema Changes and Transformation Errors
Data transformation errors occur when converting information between different formats. Your old system stored phone numbers as text; the new one requires specific numeric formats. Furthermore, schema mapping mistakes happen when fields don’t align perfectly. A 50-character name field must fit into a 30-character space, causing data truncation and loss.
4. Poor Documentation and Tribal Knowledge
Many organizations lack proper data documentation. Only longtime employees understand what certain codes mean or why specific fields exist. This tribal knowledge disappears during migration when those experts aren’t available. Consequently, teams make incorrect assumptions about data meaning, leading to mapping errors and quality problems downstream.
Common Data Quality Challenges in Migration Projects
Data quality challenges plague most migration projects, causing delays and errors. Understanding these common issues helps organizations prepare effective solutions.
1. Duplicate and Inconsistent Records
Duplicate data problems occur when the same customer, product, or transaction appears multiple times with slight variations. One system shows “Robert Smith” while another has “Bob Smith.” Additionally, inconsistent formats create chaos like phone numbers as (555) 123-4567 versus 5551234567. These discrepancies multiply during migration, creating serious accuracy issues.
2. Invalid or Outdated Data
Outdated data loses value over time. Customer addresses change, products get discontinued, and pricing updates regularly. Moreover, invalid entries like fake email addresses or impossible dates cause import failures. Consequently, migrating stale information wastes storage and confuses users.
3. Broken Relationships and Keys
Data relationship issues emerge when connections between tables break. Foreign keys that linked orders to customers suddenly point nowhere. Parent-child relationships get scrambled. Furthermore, reference data mismatches prevent systems from functioning correctly after migration.
4. Mismatched Business Rules
Different systems follow different business logic rules. Source systems might allow negative inventory while target systems don’t. Date formats, currency codes, and validation rules vary between platforms. Therefore, data passing old rules fails new system requirements.
5. Data Loss During Transformation
Data transformation errors happen when converting between formats. Text truncates because field sizes differ. Decimal precision gets lost. Special characters become garbled. These losses often go unnoticed until users report missing information.
6. Manual Validation Limitations
Manual data validation simply can’t keep pace with millions of records. Human reviewers miss patterns, get tired, and introduce inconsistencies. Additionally, manual checks delay projects significantly.
Addressing these migration data quality issues early prevents costly fixes after go-live and ensures reliable information reaches target systems.
Role of Data Profiling Before Migration
Data profiling before migration reveals hidden problems in your source systems before they cause expensive failures. This critical first step saves time and money throughout the entire project.
1. Data Profiling Is the First Step to Quality
Data profiling examines your existing information to understand its actual condition. Think of it like a health checkup before surgery. You discover what’s broken before attempting fixes. Without profiling, you’re migrating blindly, hoping problems won’t surface later.
2. Identifying Anomalies, Nulls, and Outliers
Profiling tools scan millions of records quickly, finding data anomalies humans would miss. They spot empty fields where data should exist, unusual values that break patterns, and extreme outliers indicating errors. For instance, finding birth dates in the future or prices listed as negative amounts.
3. Establishing Data Baselines
Data quality baselines document your starting point. Record how many duplicates exist, percentage of null values, and format inconsistencies. Additionally, measure completeness rates for critical fields. These metrics help track improvement and justify cleanup investments.
4. Linking Profiling Insights to Cleansing Plans
Profiling results drive your data cleansing strategy. If profiling reveals 30% duplicate customers, prioritize deduplication efforts. High null rates in important fields require fill strategies. Therefore, profiling findings directly shape your remediation roadmap.
Smart organizations invest in automated data profiling tools that analyze data faster and more accurately than manual reviews, ensuring clean migrations.
Partner with Kanerika for help.
Move Your Azure Workloads to Microsoft Fabric for a Unified Setup.
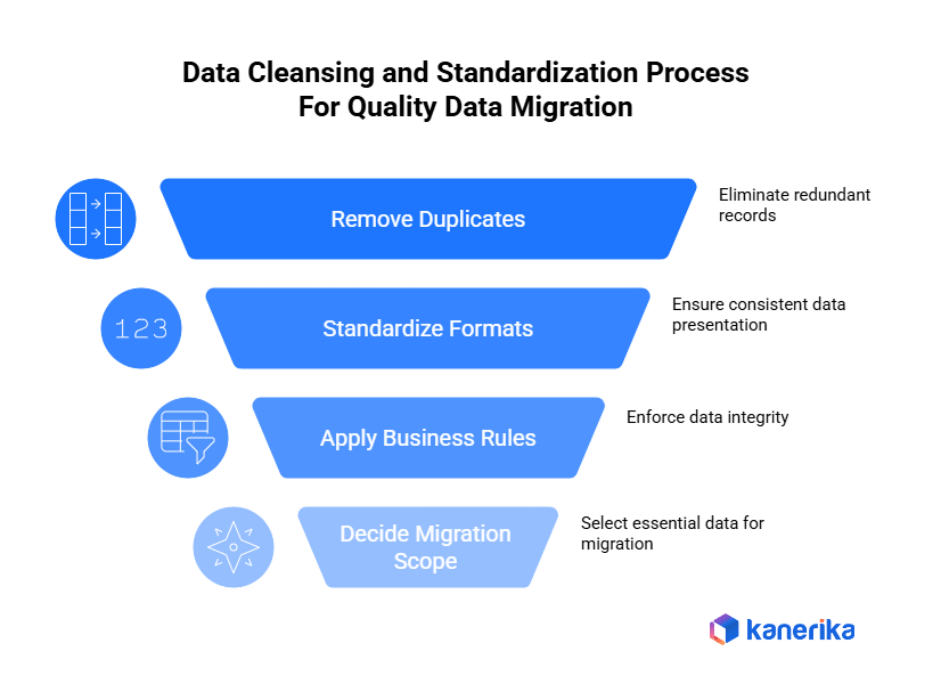
Data Cleansing and Standardization Strategies
Data cleansing strategies transform messy information into clean, reliable data ready for migration. Implementing these techniques prevents quality problems in your new systems.
1. Removing Duplicates and Obsolete Records
Duplicate data removal starts with defining matching rules. Decide whether similar names, addresses, or IDs indicate the same record. Use automated deduplication tools to merge or eliminate copies efficiently. Additionally, delete obsolete records like inactive customers from five years ago or discontinued products. This reduces migration volume and improves system performance.
2. Standardizing Formats and Values
Create consistent data formats for dates, addresses, phone numbers, and categorical values across all systems. Therefore, establish standardized naming conventions and value mappings that eliminate confusion. Moreover, implement automated validation rules that enforce format consistency during data ingestion processes.
3. Applying Business Rules Consistently
Implement data validation rules that reflect current business requirements. Ensure mandatory fields contain values. Check that numerical ranges make sense. Verify relationships between connected data elements. Furthermore, enforce naming conventions and coding standards across all datasets.
4. Deciding What Data Not to Migrate
Smart data migration planning includes leaving behind unnecessary information. Archive historical data that regulatory rules no longer require. Eliminate test records and temporary entries. Therefore, migrating only essential data speeds transfers and reduces costs.
Effective data quality improvement through cleansing delivers accurate, consistent information that users can trust immediately after go-live.
Ensuring Data Quality During Migration Execution
Mobility of data needs to be monitored actively during the migration process, rather than in advance or post one. Instant validation helps in the detection of issues when they can be easily corrected.
1. In-Flight Validation and Checkpoints
The quality of in-flight data checks is made during data transfer across systems. Install checkpoints at critical points- after extraction, during transformation and before loading. Such quality gates prevent the movement of bad data. Also, automated notifications inform the teams of emerging problems as they occur, and minor problems do not get out of control.
2. Aggregate and Row-Level Checks
Use both comprehensive and high level validations. Row-level data checks are checks that are conducted to verify the completeness of individual records, compliance with formatting and compliance with business rules. Concurrently, aggregate validation is the method used to compare the number of records, the number of sum totals, and statistical patterns of source and target. As an illustration, assuming that there are 10,000 customers under the existing system, then there should be 10,000 customers in the new system.
3. Specialist Tracking of Accuracy of Transformation
Monitor the data transformations on the information during migration. Ensure that data conversion of dates, currency calculation, and formatting change are yielding desired outcomes. Furthermore, sample transformed records at regular intervals to ensure the logic was correct in various data situations.
4. Eliminating Late-Stage Surprises
Projects are shot and budgets blown out. Continuous quality monitoring occurs at an early point in time when it is less expensive to fix. Skip run validation scripts until the end of every batch of migration.
The use of these migration quality controls is to provide clean and accurate data to target systems that returns immediate business value once go-live.
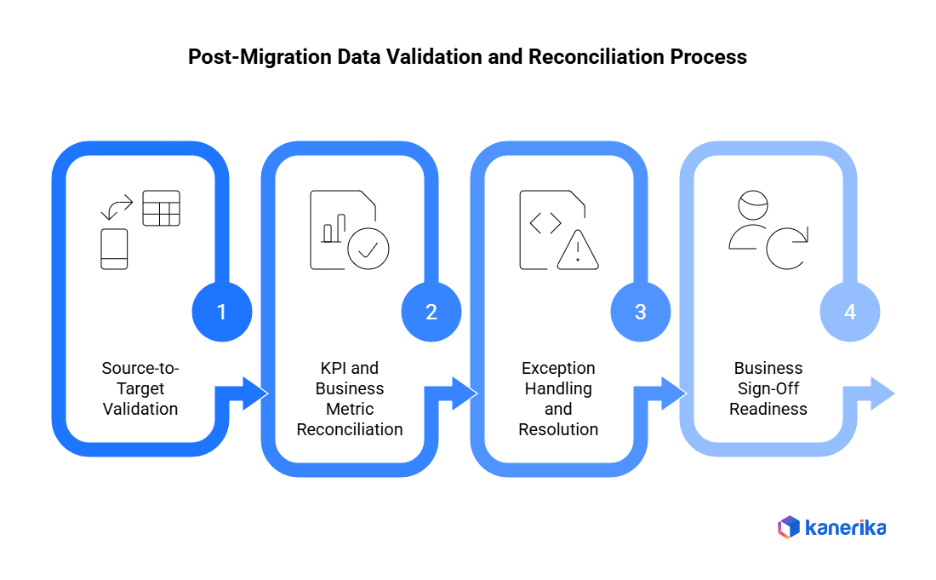
Post-Migration Data Validation and Reconciliation
Post-migration data validation confirms that information transferred correctly and systems function properly. This final quality checkpoint determines whether migration truly succeeded.
1. Source-to-Target Validation
Source-to-target reconciliation compares original data against migrated information. Check record counts match exactly between systems. Verify key fields contain identical values. Additionally, validate that relationships between tables remained intact. Automated comparison tools handle this faster than manual spot-checks, especially with millions of records.
2. KPI and Business Metric Reconciliation
Beyond raw data, validate that business metrics reconciliation produces correct results. Do revenue totals match? Are customer counts accurate? Check that calculated fields like year-to-date sales align between old and new systems. Moreover, run standard business reports in both environments and compare outputs side-by-side.
3. Exception Handling and Resolution
Document every discrepancy found during validation. Create an exception resolution process that prioritizes issues by business impact. Critical errors blocking operations need immediate fixes. Minor formatting differences can wait. Furthermore, track resolution status transparently so stakeholders understand progress.
4. Business Sign-Off Readiness
Migration sign-off requires business user approval, not just IT confirmation. Have department leaders validate that their data looks correct and supports daily operations. Test real workflows with actual users. Therefore, obtain formal acceptance demonstrating the system meets business requirements.
Thorough data validation processes build confidence that migrated information supports reliable business operations from day one.
Tools That Help Ensure Data Quality During Migration
Data quality tools automate processes of quality management which would require months of manual effort. Selecting the appropriate technology stack will speed up the migration process, and will also enhance accuracy.
1. Data Profiling Tools
Profiling software such as Informatica Data Quality, Talend and IBM InfoSphere is used to analyze source data automatically. These tools are able to scan millions of records within a short period and detect patterns, anomalies, and quality problems. Moreover, they produce statistical reports including completeness rates, duplicate rates and format inconsistency among datasets.
2. Data Quality and Cleansing Tools
Data cleansing platforms such as Trifacta, Alteryx, and Microsoft Power Query standardize formats, remove duplicates, and fix inconsistencies. They apply transformation rules consistently across entire datasets. Moreover, these tools validate data against business rules before migration begins.
3. Data Reconciliation and Validation Tools
Automatic comparisons between source and target systems are done using data reconciliation software such as QuerySurge, iCEDQ and Datagaps. They checked the number of records, verified the field values and detected discrepancies. In addition, automated comparison removes human error during the validation processes.
4. Automated Testing Frameworks
Testing tools create repeatable validation scripts that run throughout migration. They check data integrity at multiple checkpoints, ensuring consistent quality from start to finish.
5. AI-Assisted Data Quality Platforms
Current AI-driven data quality software such as Ataccama and Precisely apply machine learning to identify anomalies, propose remedies, and estimate problems with quality. Such platforms are pattern learners and become more precise with time.
The right migration quality tools will save manual work and produce more accurate findings, as compared to the conventional methods.
How to Migrate from SSRS to Power BI: Enterprise Migration Roadmap
Discover a structured approach to migrating from SSRS to Power BI, enhancing reporting, interactivity, and cloud scalability for enterprise analytics.
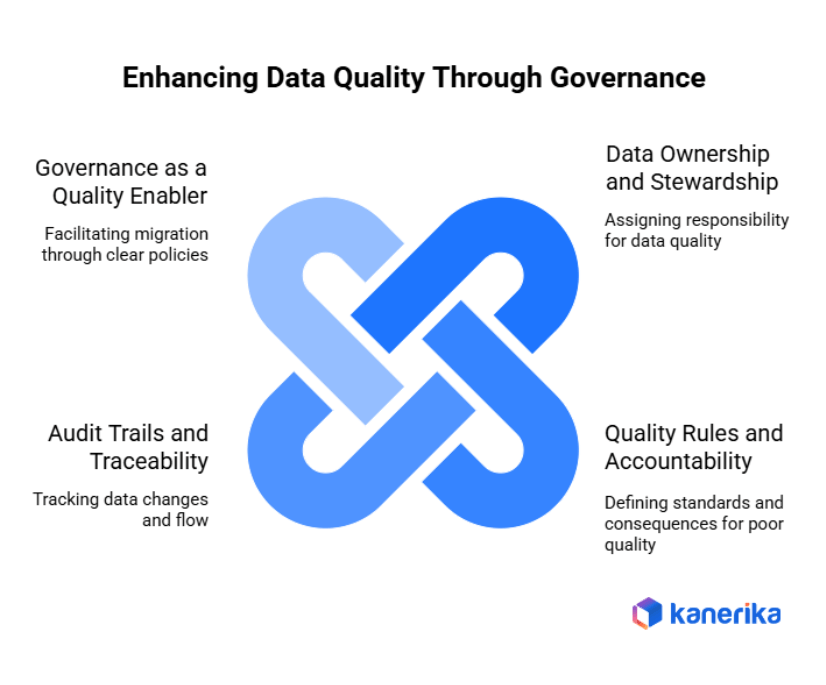
Role of Data Governance in Migration Data Quality
Migration data governance sets explicit rules, accountability and responsibility of ensuring quality in the transfer process. Effective governance systems can ensure there are no problems with quality even before they arise.
1. Data Ownership and Stewardship
Data ownership gives certain persons the charge of data quality in their arenas. Customer billing information is owned by finance. HR manages employee records. Moreover, quality standards are maintained by the data stewards on a daily basis, where they review and accept exceptions. Without proper ownership, quality issues will slip under the carpet.
2. Quality Rules and Accountability
Governance frameworks define data quality standards that everyone follows. They specify acceptable formats, mandatory fields, and validation requirements. Moreover, accountability measures ensure teams face consequences for poor quality data. Regular quality scorecards track performance and drive improvement.
3. Audit Trails and Traceability
The detailed audit records all the changes in data during the migration. Monitor and identify those who have altered the records, the time and the reason why they made changes. Besides, data lineage demonstrates the flow of information between the source and target systems. The compliance requirements are supported by this traceability and ease of troubleshooting.
4. Governance as a Quality Enabler
Good data governance models cannot slow migration, but can facilitate it. Defined policies remove misunderstanding of quality expectations. There are predefined procedures that make sure that they are subject to the same treatment on a team-to-team basis. As such, governance offers the system necessary in ensuring quality on an enterprise level.
Strong migration governance practices used will change quality as an after-thought to a strategic advantage during the whole project lifecycle.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Quality During Migration
Data quality best practices transform chaotic migrations into controlled, successful projects. Following these proven strategies protects your information investment.
1. Start Quality Checks Early
Begin early data quality assessment during planning phases, not just before go-live. Profile source data immediately to understand current conditions. Additionally, identify quality issues months before migration starts. Early detection provides time for proper remediation rather than rushed last-minute fixes.
2. Automate Wherever Possible
Manual quality checks don’t scale effectively. Implement automated data validation tools that scan millions of records consistently. Automation eliminates human error, speeds validation, and frees teams for complex problem-solving. Moreover, automated scripts run repeatedly throughout migration without additional cost.
3. Prioritize Business-Critical Data
Not all data deserves equal attention. Focus quality efforts on business-critical information first—customer records, financial transactions, and regulatory data. Apply stricter validation rules to high-impact datasets. Therefore, allocate resources where quality matters most to operations.
4. Involve Business Users in Validation
IT teams can’t validate business logic alone. Engage business user validation throughout the process. Department leaders understand what “good data” looks like for their functions. Furthermore, user acceptance confirms data supports actual workflows correctly.
5. Treat Quality as Continuous, Not One-Time
Continuous data quality management monitors information before, during, and after migration. Quality isn’t a checkpoint but it’s an ongoing commitment. Regular assessments catch degradation early and maintain standards long-term.
Implementing these migration quality practices delivers clean, trustworthy data that drives business value immediately.
Accelerate Your Data Transformation by Migrating!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Migration Services
Case Study 1: Healthcare Data Migration with Enhanced Governance
Client: Large Healthcare Network (32 terabytes of legacy records)
Challenge: The healthcare organization faced massive data governance challenges while migrating from legacy Cerner systems to Epic. They needed to maintain HIPAA compliance, preserve patient data integrity, and ensure clinical staff could access critical information without interruption. The system contained 32 terabytes of legacy records, 75 terabytes of medical images, and 34 million scanned documents that all required careful governance during migration.
Kanerika’s Solution: We implemented a comprehensive governance framework using our FLIP migration accelerators. Our approach included automated data classification to identify sensitive patient information, role-based access controls to maintain HIPAA compliance, and complete data lineage tracking from source to target systems. The migration preserved all user access levels and external system dependencies while providing an intuitive interface that required minimal staff training.
Results:
- 100% of reports successfully migrated on time and budget
- Zero HIPAA compliance violations during migration
- 30% reduction in duplicate patient records
- Significant cost savings on system maintenance redirected to Epic implementation
- Complete audit trail documentation for regulatory compliance
This project demonstrated how strong governance doesn’t slow down migration – it actually makes it more reliable and successful.
Case Study 2: Manufacturing Data Modernization with Microsoft Fabric
Client: Global Manufacturing Company
Challenge: The manufacturing client struggled with fragmented data across multiple legacy systems that made governance nearly impossible. Different departments used inconsistent data definitions, quality standards varied across plants, and regulatory compliance was difficult to maintain. They needed to modernize to Microsoft Fabric while establishing unified governance across their global operations.
Kanerika’s Solution: Using our FLIP migration accelerators, we automated the transition from Azure Data Factory and legacy SSIS packages to Microsoft Fabric. Our governance approach included establishing clear data ownership roles, implementing quality checks at every pipeline stage, and creating centralized metadata management. We leveraged Microsoft Purview for unified data discovery and classification while ensuring all governance policies applied consistently across workspaces.
Results:
- 30% improvement in data processing speeds
- 40% reduction in operational costs
- 80% faster insight delivery to business teams
- 95% reduction in report generation time
- Centralized governance policies across all global manufacturing sites
- Real-time data quality monitoring and automated alerts
The client now operates with a single source of truth for manufacturing data while maintaining strict quality and compliance standards across all locations.
How Kanerika Ensures Data Quality Through Data Governance in Migration
Kanerika stands out as a leading data and AI consulting company that transforms how enterprises approach data governance during migration projects. We’ve helped businesses across healthcare, manufacturing, retail, financial services, and logistics achieve seamless data modernization while maintaining strict governance standards.
Our FLIP Migration Platform Makes Governance Automatic
At the heart of our approach is FLIP, our AI-powered migration accelerator that automates up to 80% of the migration process. But FLIP isn’t just about speed – it’s built with governance at its core. The platform automatically maintains data lineage, enforces quality checks, and preserves business logic during migration. This means your governance policies stay intact while your data moves to modern platforms like Microsoft Fabric, Azure Synapse, or Databricks.
FLIP helps businesses avoid the common governance failures that plague manual migrations. Instead of losing track of data ownership or breaking security controls, our accelerator ensures every piece of information is properly classified, tracked, and protected throughout the journey.
Microsoft Partnership Validates Our Expertise
Kanerika recently earned Microsoft’s Data Warehouse Migration to Microsoft Azure Specialization – a recognition that requires documented success in migrating enterprise data warehouses while maintaining data integrity and business continuity. This achievement validates our proven methodology for handling complex governance challenges during large-scale migrations.
Our multiple Microsoft credentials include Analytics on Microsoft Azure Advanced Specialization and Solutions Partner designations for Data & AI, Infrastructure, and Digital & App Innovation. This rare combination means we can handle every aspect of your Microsoft implementation while ensuring governance remains strong from start to finish.
Industry-Specific Governance Solutions
We understand that different industries face unique governance challenges. Healthcare organizations need HIPAA compliance and patient data protection. Financial services require SOX adherence and audit trails. Manufacturing companies must track supply chain data and maintain quality standards. Our team brings deep vertical expertise to ensure your governance framework meets industry-specific requirements during migration.
Real Results Through Proven Methodologies
Our IMPACT methodology drives successful governance-led migration projects by focusing on tangible outcomes. We start with thorough assessment of your current systems, followed by detailed planning to ensure seamless transition. Our certified experts use cutting-edge tools to execute migration while minimizing downtime and maintaining your governance standards throughout the process.
Reliable Data Migration Supports Better Operations
Kanerika will help you move your data the right way.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is data quality in the context of migration?
Data quality in migration refers to ensuring information remains accurate, complete, consistent, and valid throughout the transfer process. It means your data works correctly in the new system and supports business operations without errors. Quality encompasses both technical accuracy (correct formats, no corruption) and business relevance (meaningful, current information).
2. When should data quality checks begin in a migration project?
Quality checks should start during the planning phase, not just before go-live. Begin with data profiling to understand current conditions. Early assessment reveals issues when you have time for proper fixes. Additionally, continuous validation throughout extraction, transformation, and loading catches problems at each stage. Waiting until the end creates expensive, rushed remediation efforts.
3. What are the most common data quality issues during migration?
The most frequent data quality problems include duplicate records with slight variations, missing values in critical fields, inconsistent formats across datasets, broken relationships between tables, and outdated information. Moreover, data loss during transformation, invalid entries that fail business rules, and mismatched data types between source and target systems cause significant issues.
4. How do you measure data quality during migration?
Measure quality using specific data quality metrics like completeness rates (percentage of required fields populated), accuracy scores (how many values are correct), consistency checks (matching formats and standards), and validity percentages (compliance with business rules). Additionally, track duplicate rates, error counts, and reconciliation match percentages between source and target systems.
5. What tools help automate data quality validation?
Data quality automation tools include profiling software like Informatica and Talend, cleansing platforms such as Trifacta and Alteryx, and reconciliation tools like QuerySurge and iCEDQ. Furthermore, ETL platforms often include built-in validation capabilities. Modern AI-powered solutions like Ataccama detect anomalies automatically and suggest corrections based on learned patterns.
6. Who is responsible for data quality during migration?
Data quality responsibility requires collaboration across multiple roles. Data owners from business departments define quality requirements. Data stewards enforce standards daily. IT teams implement technical validation. Moreover, migration leads coordinate quality activities, while business users validate results. Executive sponsors provide resources and resolve conflicts. Quality succeeds only with clear accountability at every level.
7. How do you handle data quality issues found during migration?
Address discovered issues through a structured exception management process. First, log and categorize each problem by severity and business impact. Next, prioritize critical issues blocking operations for immediate resolution. Additionally, establish clear escalation paths for complex problems. Create remediation plans with assigned owners and deadlines. Furthermore, track resolution progress and communicate status to stakeholders regularly throughout the project.










