Databricks security best practices have become essential as enterprises face rising threats and increasing regulatory pressure. According to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average global data breach now costs $4.45 million, making strong data protection a business necessity rather than an option.
As organizations adopt modern data and AI platforms, the risks multiply, from misconfigurations and identity leaks to weak governance and unsecured multi-cloud networks. Many teams deploy Databricks for its scalability and performance but often overlook foundational security and compliance measures during implementation.
Databricks Security Best Practices provide a clear roadmap to build a secure, compliant, and resilient Lakehouse environment. By focusing on access control, encryption, governance, and continuous monitoring, enterprises can manage data responsibly, reduce risk, and accelerate innovation safely.
This blog explores what security means in the context of Databricks — why it matters, the key best practices, architecture overview, implementation checklist, and common pitfalls to avoid.
Modernize Your Data Infrastructure For Real-Time Insights And Agility.
Partner With Kanerika To Simplify And Speed Up Your Migration.
Key Takeaways
- Databricks security best practices provide strong protection across key domains — identity, data encryption, network isolation, governance, and continuous monitoring.
- The Lakehouse architecture allows organizations to scale analytics and AI securely across multi-cloud environments and global regions.
- Success depends on aligning security with business priorities, building a solid governance foundation, and embedding controls from day one.
- Security is not a single event but a continuous process involving regular audits, automation, and proactive monitoring.
- Following Databricks’ proven framework ensures compliance readiness, reduces operational risks, and builds lasting data trust across the enterprise.
Why Security Matters in Databricks?
Enterprises today manage massive volumes of data spread across multiple clouds, streaming systems, and AI workloads. This growing complexity expands their risk surface — exposing vulnerabilities such as unauthorized access, data leakage, misconfiguration, and governance gaps. Without a strong security foundation, even the most advanced analytics platforms can become points of failure rather than innovation.
Databricks helps address these risks through its built-in security and governance capabilities. It provides tools for fine-grained access control, encryption, compliance monitoring, and secure collaboration — all integrated within its Lakehouse architecture. However, the real advantage comes when organizations implement these features strategically, aligning them with their data governance and compliance frameworks.
By applying Databricks security best practices, enterprises can ensure compliance with global standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, while maintaining visibility and control over their entire data landscape. The result is a secure, scalable, and compliant environment that fosters innovation without compromising trust.
Strong security controls in Databricks not only reduce the risk of breaches and compliance penalties but also enhance data reliability — enabling faster decision-making and greater confidence in enterprise analytics.
(Source: Databricks Security Best Practices Guide)
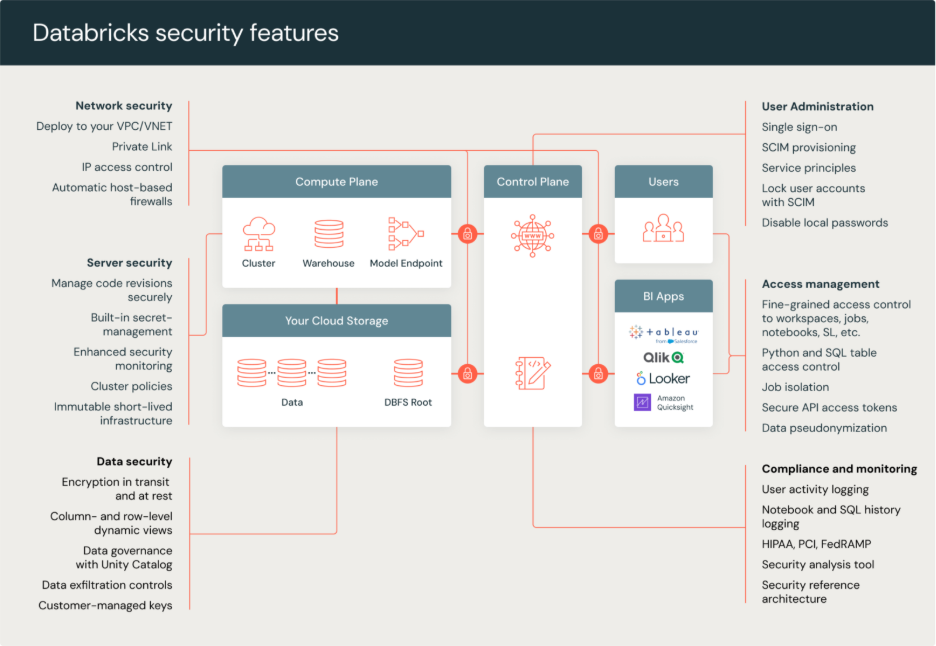
Core Security Pillars & Best Practices
Securing Databricks requires a layered approach across multiple domains. Each layer — identity, data, network, governance, and operations — plays a vital role in creating a resilient and compliant Lakehouse environment.
1. Identity & Access Management (IAM)
Managing who can access what is the first line of defense. Organizations should follow the least privilege principle, granting users only the permissions they need.
- Enforce Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to strengthen user verification.
- Use SCIM integration for automated user and group synchronization.
- Limit the number of admin accounts and implement service principals for automation.
- Apply compute policies to control who can create clusters and what configurations are allowed.
2. Data Protection: Encryption & Key Management
Databricks protects data both at rest and in transit through strong encryption standards.
- Use Customer-Managed Keys (CMKs) for encryption on S3, ADLS, or GCS storage.
- Enable TLS encryption for all data transfers.
- Restrict public access to storage buckets and enable versioning and automatic backups for resilience.
3. Network & Endpoint Security
Network security ensures that data never leaves trusted boundaries.
- Use private networks (VPC/VNet) for workspace isolation.
- Apply IP access lists and PrivateLink endpoints to secure communication paths.
- Isolate sensitive workloads and restrict egress traffic to trusted destinations only.
4. Governance, Compliance & Monitoring
Governance ensures visibility and control across the data landscape.
- Use Unity Catalog to apply fine-grained permissions, manage lineage, and enforce access policies.
- Implement audit logs and system tables to monitor data activity.
- Conduct regular security reviews and compliance audits to maintain readiness.
5. Operational Security & DevSecOps
Security extends beyond configuration — it’s a continuous operational effort.
- Use infrastructure-as-code (IaC) to standardize deployment and enforce configurations.
- Implement CI/CD pipelines with integrated security checks.
- Restrict unapproved libraries and monitor system logs for unusual activity.
- Adopt DevSecOps to embed security throughout data and ML workflows.
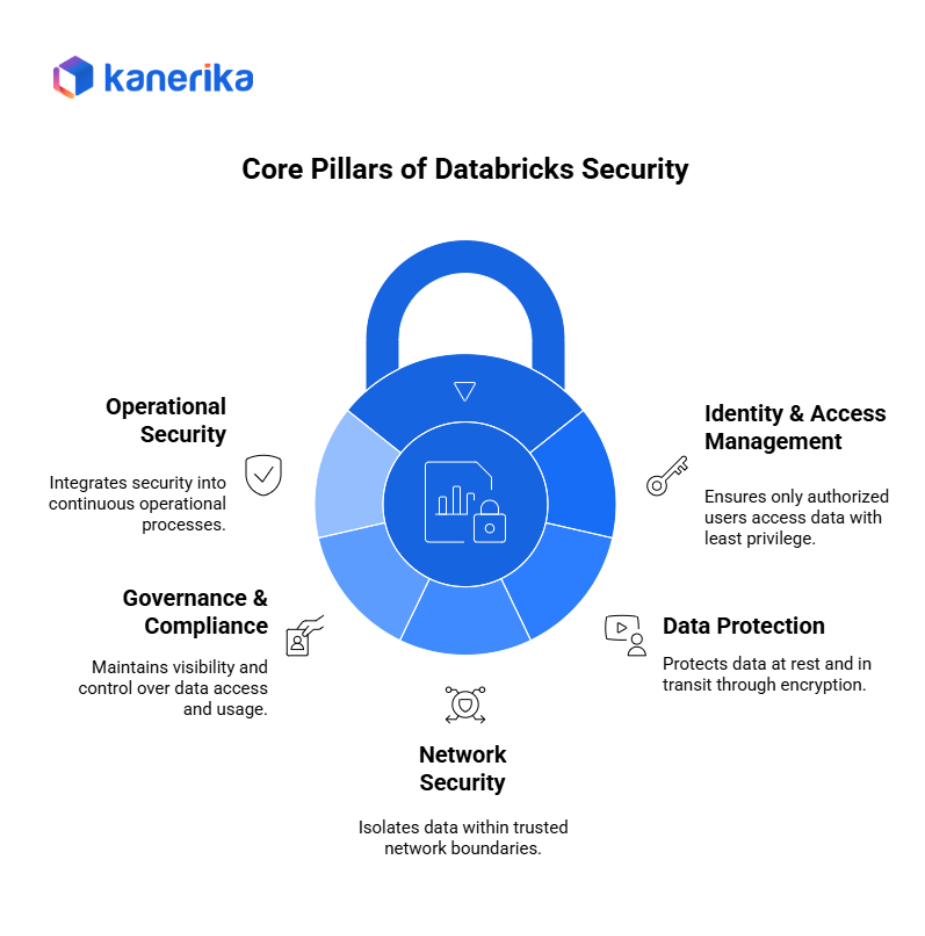
Security Architecture Overview
A secure Databricks deployment follows a clear flow: data ingestion layer (secure pipelines and connectors) → metadata & governance layer (Unity Catalog for catalogs/schemas/tables, lineage, and policies) → compute & storage layer (hardened workspaces, private networking, encryption, CMKs) → consumption layer (analytics/AI, Databricks SQL, notebooks, dashboards) protected by fine-grained access controls. Each layer adds defense-in-depth while keeping performance high.
1. How best practices map to the architecture
- Identity & access (IAM): SSO, MFA, RBAC, service principals applied across Unity Catalog and workspaces to enforce least privilege at every hop.
- Data protection: Encryption in transit (TLS) and at rest (S3/ADLS/GCS) with customer-managed keys; storage firewalls and private endpoints at the storage boundary.
- Network security: Private VPC/VNet, IP allowlists, PrivateLink/PE to isolate traffic; egress controls on clusters; workspace separation for sensitive workloads.
- Governance & monitoring: Unity Catalog policies, lineage, system tables and audit logs feed SIEM/SOAR; scheduled reviews validate compliance posture.
- Operational security (DevSecOps): IaC and CI/CD standardize cluster policies, runtime versions, and library controls; continuous scanning detects drift.
2. Multi-cloud and global scale
Databricks runs on AWS, Azure, and GCP, so you can standardize controls while meeting regional rules. Use the same reference architecture—private networking, CMKs, Unity Catalog policies—then adapt storage accounts, key vaults, and endpoints per cloud/region to satisfy data residency.
3. Shared responsibility model
Security is a team effort:
- Cloud provider secures the physical/host infrastructure and native services.
- Databricks secures the platform control plane and offers features like workspace hardening, cluster policies, audit logs, and Unity Catalog.
- You (the customer) secure configurations and data: IAM, network design, CMKs, catalog policies, job code, monitoring, and incident response.
Together, these layers create a resilient, compliant, and scalable security posture for the Databricks Lakehouse.
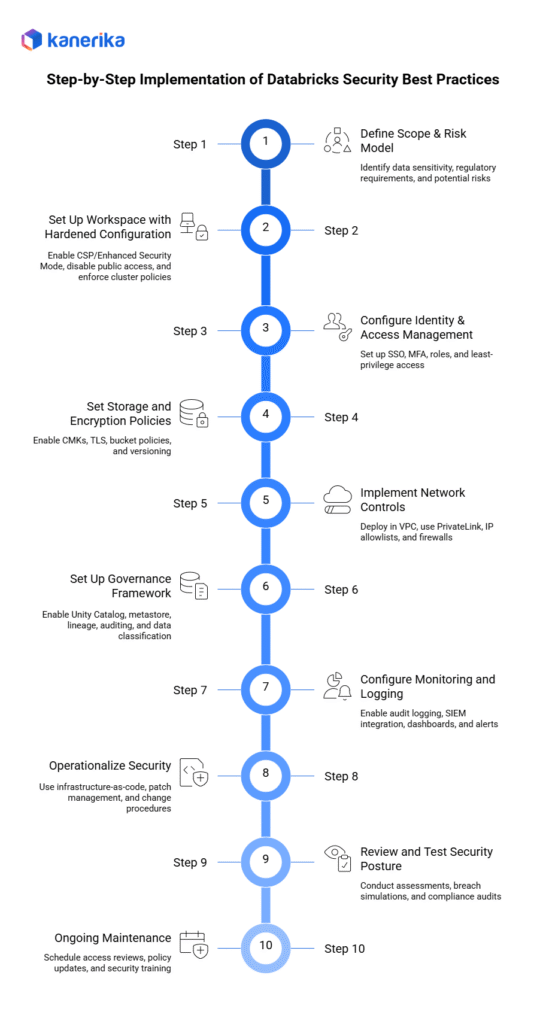
Step-by-Step Implementation of Secure Databricks Environment
Implementing secure Databricks environments requires careful planning and execution. This practical checklist guides organizations through each critical step to build a hardened, compliant platform.
Step 1: Define Scope & Risk Model
Begin by identifying which data and workloads require protection. Classify data by sensitivity levels such as public, internal, confidential, and highly confidential. Also, maps regulatory requirements like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or GDPR to specific workloads.
Assess potential risks including data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance violations. Moreover, document security requirements for each risk category. Hence, this foundation informs all subsequent security decisions.
Step 2: Set Up Workspace with Hardened Configuration
Create your Databricks workspace using security-focused settings from the start. Enable the Compliance Security Profile (CSP) or Enhanced Security Mode depending on your requirements. Thus, these profiles apply baseline security controls automatically.
Configure workspace settings to disable public access and require private connectivity. Set default cluster policies that enforce security standards. Restrict notebook exports to prevent data exfiltration. Additionally, starting with hardened configurations is easier than retrofitting security later.
Step 3: Configure Identity & Access Management
Set up single sign-on (SSO) connecting Databricks to your identity provider like Azure AD, Okta, or AWS IAM Identity Center. Next, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users accessing sensitive data. Create roles matching your organizational structure such as data engineers, analysts, and admins.
Assign users to appropriate groups based on job functions. Apply least-privilege principles by granting only minimum necessary permissions. However, regularly review access permissions to remove unnecessary privileges as roles change.
Step 4: Set Storage and Encryption Policies
Configure customer-managed keys (CMKs) to control encryption of data at rest. This ensures your organization maintains direct control over encryption keys rather than relying solely on cloud provider keys. Also, enables encryption for data in transit by enforcing TLS connections.
Set bucket policies restricting access to authorized services and users only. Enable versioning on storage buckets to protect against accidental deletions or malicious changes. Moreover, document key rotation procedures and test recovery processes.
Step 5: Implement Network Controls
Establish network isolation by deploying Databricks in your own Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) or Virtual Network. Configure AWS PrivateLink, Azure Private Link, or GCP Private Service Connect to keep traffic off the public internet. Set IP allowlists restricting which networks can access your workspace.
Conswquenyly, disables public IP addresses on compute clusters. Configure firewall rules controlling inbound and outbound traffic. Use network security groups to segment environments and limit lateral movement. These controls significantly reduce attack surface.
Build, Train, and Deploy AI Models Seamlessly with Databricks Mosaic AI
Discover how Databricks Mosaic AI unifies analytics and AI for smarter, faster data-driven decisions.
Step 6: Set Up Governance Framework
Enable Unity Catalog as your central governance layer. Create a metastore to store metadata about all data assets. Establish catalog structures organizing data logically by domain, environment, or sensitivity. Configure data lineage tracking to show how information flows through systems.
As well as, enable access auditing to record who accesses what data and when. Set up data classification tags marking sensitive information. Create policies for data retention and deletion meeting regulatory requirements.
Step 7: Configure Monitoring and Logging
Enable audit logging in the Account Console to capture all user activities and administrative actions. Moreover, configure log delivery to your SIEM system for centralized monitoring and alerting. Query system tables regularly to identify suspicious patterns or policy violations.
Create dashboards showing security metrics like failed login attempts, permission changes, and data access patterns. Additionally, set up alerts for critical events such as privilege escalations or unusual data exports. Establish procedures for investigating and responding to security incidents.
Step 8: Operationalize Security
Implement infrastructure-as-code using Terraform or ARM templates to deploy consistent, secure configurations. Hence, this approach prevents configuration drift and enables version control for security settings. Establish patch management processes ensuring timely application of security updates.
Configure automatic runtime version updates for clusters to receive security patches quickly. Create change management procedures requiring security review before modifications. As well as, document standard operating procedures for common security tasks.
Step 9: Review and Test Security Posture
Conduct regular security assessments to identify gaps and weaknesses. Simulate breach scenarios testing how well controls prevent or detect attacks. Perform penetration testing to validate network and access controls. Correspondingly, run compliance audits verifying adherence to required standards.
Review access logs identifying anomalous patterns. Test backup and recovery procedures ensuring data can be restored after incidents. Document findings and create remediation plans addressing identified issues.
10. Ongoing Maintenance
Security implementation is not a one-time project but an ongoing practice. Schedule quarterly access reviews removing unnecessary permissions. Update security policies as regulations evolve.
Monitor for new threats and vulnerabilities affecting your environment. Provide security training to users on data handling and threat awareness. Therefore, maintain documentation reflecting current configurations and procedures.
Databricks Security Best Practices & Pitfalls to Avoid
Building a secure Databricks environment requires a disciplined and continuous approach. Below are key best practices to strengthen your data security framework — and common pitfalls that organizations should avoid.
Best Practices Summary
- Align security with business risk: Start by mapping your Databricks security controls to your organization’s risk model, focusing on regulatory, operational, and reputational impact.
- Prioritize high-impact controls first: Begin with identity and access management (SSO, MFA, least privilege) and encryption before expanding to network and monitoring layers.
- Build a strong data foundation: Establish governance using Unity Catalog early. Apply fine-grained access, lineage tracking, and data classification from day one to prevent future security gaps.
- Leverage pre-built frameworks: Use Databricks’ Compliance Security Profile and partner accelerators to save time and ensure configuration consistency across workspaces.
- Embed automation: Implement infrastructure-as-code (IaC) for provisioning, patching, and monitoring to maintain consistent and repeatable security practices.
Pitfalls to Avoid
- Overextending efforts: Launching too many parallel initiatives dilutes focus and delays measurable progress. Start small, secure critical workloads first, and expand gradually.
- Ignoring non-traditional assets: Many teams overlook security for notebooks, ML models, and unstructured data, which can expose vulnerabilities if left unmanaged.
- Underestimating complexity: Data quality issues, multiple integrations, and unmanaged shadow IT can create backdoors into your environment if not identified early.
- Deploying AI without security operations: Machine learning pipelines require the same rigor as data pipelines—apply governance, version control, and monitoring.
Security in Databricks is not a one-time configuration but a continuous lifecycle. Regular reviews, monitoring, and adaptation to new risks are key to maintaining resilience, compliance, and trust. Source
Real-World Use Cases
Several global enterprises have strengthened their data protection and compliance posture by adopting Databricks security best practices. These organizations span sectors such as energy, healthcare, and finance, proving the platform’s adaptability for high-stakes data environments.
1. Shell – Securing Multi-Cloud Energy Analytics
Shell, a global leader in energy, leverages Databricks on Azure to unify its data analytics while maintaining tight control over access and compliance. Using PrivateLink, Customer-Managed Keys (CMKs), and strict egress policies, Shell ensures that sensitive operational data never leaves its controlled network. The integration of Unity Catalog provided central governance and simplified audit tracking across regions.
As a result, Shell achieved improved compliance readiness and minimized the risk of misconfiguration across its multi-cloud landscape.
2. Regeneron – Protecting Genomic and Clinical Data
Regeneron, a biotechnology company, uses Databricks Lakehouse for genomic data analysis and drug discovery. Handling sensitive healthcare data required robust security measures, including encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access control, and workspace isolation under HIPAA compliance. By adopting Databricks’ Compliance Security Profile, Regeneron secured patient data while accelerating AI-driven insights in medical research.
The company reports faster compliance audits and more secure cross-team collaboration in research environments.
Key Lessons Learned
- Early governance alignment ensures consistent enforcement of access controls.
- Implementing data classification and lineage tracking improves compliance transparency.
- Continuous monitoring and logging prevent small misconfigurations from escalating into security incidents.
By following Databricks security best practices, these enterprises reduced operational risk, improved audit readiness, and strengthened trust in their data ecosystem — enabling innovation without compromising compliance or security.
Kanerika and Databricks: Building Secure Data Ecosystems Through Proven Best Practices
At Kanerika, we partner with Databricks to help enterprises implement industry-leading security best practices across their data and AI environments. Our collaboration unites Kanerika’s expertise in data governance, AI, and cloud security with Databricks’ Lakehouse Platform, enabling organizations to operate in a secure, compliant, and scalable way.
We know that today’s enterprises face rising risks — from data breaches and compliance violations to governance gaps across multi-cloud environments. That’s why our joint approach focuses on embedding Databricks Security Best Practices from the ground up, covering every layer from identity management to encryption and monitoring.
As a Microsoft Data & AI partner and a Databricks implementation specialist, Kanerika ensures that security is not just reactive but proactive. Our solutions follow compliance-by-design principles, aligned with ISO 27001, ISO 27701, and SOC II standards — ensuring every data operation meets global security benchmarks.
Through this partnership, we help enterprises:
- Strengthen data protection with role-based access controls, CMKs, and private networking.
- Enable real-time monitoring through unified audit logging and lineage visibility.
- Simplify compliance operations with secure, automated governance frameworks.
- Minimize risk exposure while enabling scalable data innovation.
Across industries — from healthcare to financial services — our clients rely on Kanerika and Databricks to build secure Lakehouse architectures that balance innovation with governance. Together, we help organizations transform security from an operational challenge into a strategic advantage.
Secure Your Organization With Databricks Security Best Practices.
Partner With Kanerika To Secure Your Data.
FAQs
1. What are Databricks Security Best Practices?
Databricks Security Best Practices are a set of guidelines designed to help enterprises protect their Lakehouse environments. They cover identity management, encryption, network isolation, governance, and continuous monitoring — ensuring compliance and reducing data risks.
2. How does Databricks ensure data security?
Databricks provides built-in security features such as Customer-Managed Keys (CMKs) for encryption, PrivateLink for network isolation, Unity Catalog for governance, and audit logs for monitoring. These features align with major compliance standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2.
3. Why is governance important in Databricks security?
Governance provides visibility and control over data usage. With Unity Catalog, Databricks enables fine-grained access controls, data lineage tracking, and consistent policies across all workspaces — ensuring secure collaboration and regulatory compliance.
4. What are the main security layers in Databricks?
Security in Databricks is built across multiple layers:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Data Encryption (at rest and in transit)
- Network Security (PrivateLink, VPC/VNet)
- Governance and Monitoring (Unity Catalog, audit logs)
- Operational Security (DevSecOps practices)
5. How can enterprises monitor security in Databricks?
Enterprises can use audit logs, system tables, and SIEM integrations to monitor user activity, data access, and policy changes in real time — improving detection and response to potential threats.
6. What common mistakes should teams avoid?
Avoid deploying Databricks without enabling MFA, CMKs, or governance tools. Ignoring unstructured data, skipping access reviews, and not isolating production workloads are frequent missteps that weaken security.
7. How do Databricks Security Best Practices support compliance?
By applying encryption, RBAC, lineage tracking, and automated audit logging, Databricks helps enterprises meet compliance mandates such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and FedRAMP, ensuring secure data management across multi-cloud environments.










