Your company just greenlit a major cloud migration. Exciting, right? But here’s the reality check: 60% of organizations lose data or face downtime during these moves. That “quick weekend migration” can turn into Monday morning chaos with customer records exposed, systems down, and executives demanding answers. Secure Data Migration isn’t just IT jargon. It’s the difference between a smooth transition and a $4.45 million breach, according to IBM’s report. Yet companies keep making the same mistake: treating security like the last item on a checklist.
Think about what’s actually moving during migration. Customer payment details. Employee health records. Proprietary algorithms powering your AI models. This isn’t just data but it’s your business reputation packaged in vulnerable file transfers.
The stakes keep rising. Cloud platforms, analytics dashboards, and AI tools now run critical operations. Meanwhile, hackers specifically target migration windows when security controls are weakest. Regulators aren’t sympathetic either. GDPR fines, HIPAA violations, and PCI-DSS penalties don’t care if you were “in the middle of migrating.”
So what’s the solution? Stop bolting security on afterward. Build it into every phase like planning, transfer, and validation. Your customers, compliance officers, and CFO will thank you.
Key Learnings
- Security must be embedded throughout the migration lifecycle – Secure data migration is not a one-time activity. Data must be protected before, during, and after migration to prevent leaks, loss, and unauthorized access.
- Data movement is one of the highest-risk phases for breaches – Sensitive enterprise data is most vulnerable while in transit or transformation. Strong encryption, access controls, and monitoring are essential to reduce risk.
- Governance and compliance drive secure migration success – Clear data ownership, audit trails, and regulatory alignment ensure secure and compliant migrations, especially in regulated industries.
- Automation improves both security and reliability – Automated validation, reconciliation, and security checks reduce human error and provide consistent protection at enterprise scale.
- Secure data migration builds long-term trust and resilience – A security-first migration approach enables reliable analytics, regulatory confidence, and future digital innovation without compromising data integrity.
Simplify Your Decision Between Informatica and Databricks
Work with Kanerika to Build Scalable AI Solutions
What Is Secure Data Migration?
Secure data migration refers to the process of transferring data from one system to another while maintaining strict protection measures throughout the entire journey. Simply put, it means moving your information safely without exposing it to risks like theft, loss, or unauthorized access.
Notably, security does not only involve a point of check. Instead, it can be used throughout the overall migration life cycle starting with initial planning and ending with final validation. These involve pre-migration tests, encrypted data transmission, confidential storage, and post-migration audit.
As a result, companies that engage in secure data migration practices safeguard customer data, keep the organization compliant, and avoid expensive breaches. Businesses must never therefore consider security as a luxury, but a must have to any successful data migration plan.
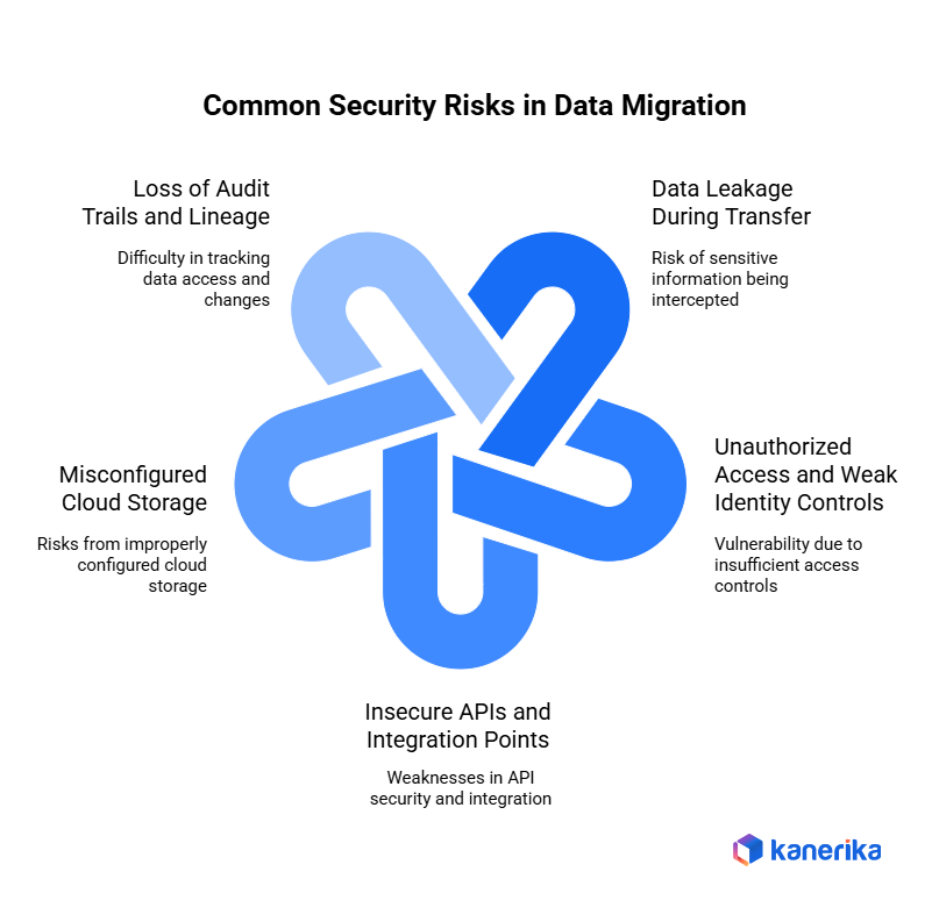
Common Security Risks in Data Migration
Knowledge on the security risks of data migration assists companies to safeguard confidential information in transfers. These are the most important threats to consider whenever undertaking a cloud data migration project.
1. Data Leakage During Transfer
One of the greatest threats of migration security is data leakage. Information transferred among systems is prone to being intercepted. Hackers can get hold of sensitive information over the wire without adequate encryption. As such, all data transfers should be done using secure protocols such as SSL/TLS by organizations.
2. Unauthorized Access and Weak Identity Controls
Lack of sufficient access control during data migration poses a great vulnerability. Unprotected passwords, lack of the multi-factor authentication, and excess user permissions enable unauthorized people to access or alter the information. This makes it necessary to incorporate effective authentication of identity in securing information during the migration process.
3. Insecure APIs and Integration Points
Migration API vulnerabilities are not typically detected. Most organizations have integrated systems using APIs without ensuring security. Attackers find these integration points easy to attack. Also, the old versions of API could have reported security vulnerabilities that can be used by hackers.
4. Misconfigured Cloud Storage
Among the most frequent errors, there are cloud storage misconfigurations. Data are vulnerable to intruders through publicly available storage containers, weak permission, and non-functioning encryption. In addition, default security controls hardly offer proper protection to sensitive business information.
5. Loss of Audit Trails and Lineage
Organizations are incapable of tracking who accessed what data and when changes have been made without appropriate data audit trails. This invisibility complicates the breach detection. In addition to this, the lost data lineage will add complexity to compliance reporting and recovery of the incidents will practically be impossible.
These data migration risks cannot be effectively handled without a thorough planning, regular monitoring, and professional advice of the whole process.
Key Principles of Secure Data Migration
The practice of high-quality secure data migration principles would make sure your data is secure during the whole process of transferring it. These are the basic practices that all organizations need to embrace.
1. Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit
Data encryption forms the foundation of secure migration. Encrypt information both when stored (at rest) and during transfer (in transit). This means using AES-256 encryption for stored data and TLS/SSL protocols for data movement. Consequently, even if intercepted, encrypted data remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Robust identity and access management controls who can access your migration environment. Implement multi-factor authentication for all users. Additionally, integrate with enterprise identity providers to maintain consistent security policies. This prevents unauthorized individuals from accessing sensitive systems during migration.
3. Least Privilege and Role-Based Access
Follow the least privilege principle by granting users only the minimum access they need. Use role-based access control to assign permissions based on job functions. For instance, developers shouldn’t access production data unnecessarily. Therefore, limiting access reduces potential security breaches significantly.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Logging
Implement continuous security monitoring throughout the migration lifecycle. Track all data access, changes, and system activities in real-time. Moreover, maintain comprehensive logs for compliance and incident investigation. This visibility helps detect suspicious activities immediately.
5. Secure Rollback and Recovery Planning
Migration should always be prepared by developing safe rollback procedures. Make encrypted backup and recovery drills. More so, have clear procedures of going back to older systems in case of problems. This provides continuity of the business as well as upholding the security standards.
Adhering to the best practices of data migration safeguards important data, ensures compliance, and establishes customer trust during the process of your migration.
Secure Data Migration Approaches
Various data migration processes need specific security approaches. These approaches assist in the selection of the appropriate secure migration strategy by the organizations.
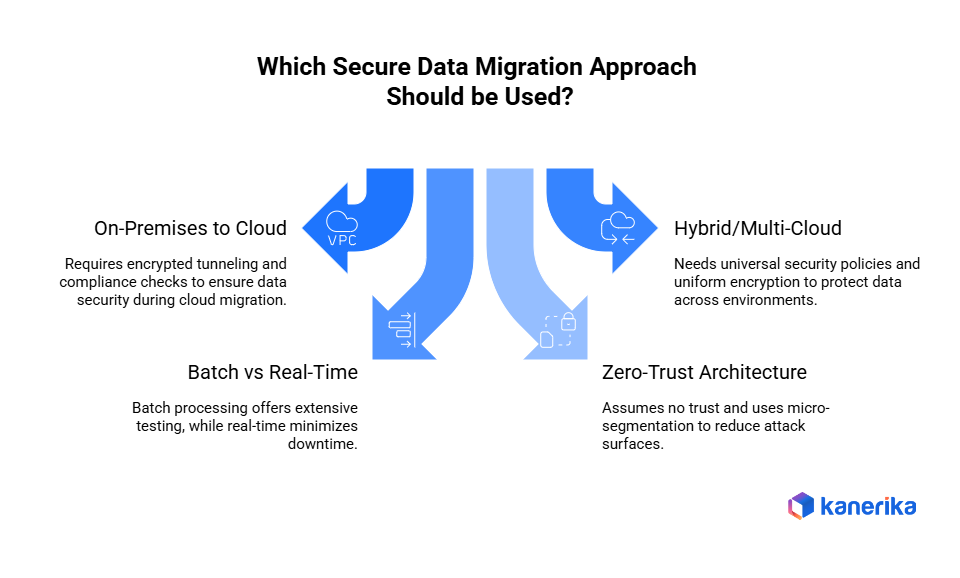
1. On-Premises to Cloud Security Considerations
Security of cloud migration requires additional concern when migrating off-premises systems. Create encrypted tunneling with VPNs or direct. Also, check cloud provider certifications and compliance criteria. In addition, determine the data residency criteria to comply with the regulatory requirements before transmitting sensitive data.
2. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Migration Security
When data is distributed in several environments, the hybrid cloud security is complicated. Enact universal security policies. In addition, apply uniform encryption key and identity tools. This guarantees protection in spite of the location of data in the course of migration.
3. Secure Batch vs Real-Time Migration
Security of batch migration can be done extensively on large datasets prior to their migration. Nevertheless, the migration in real-time needs to be monitored and threats detected immediately. Select batch processing of sensitive data that needs high testing. On the other hand, real time is more convenient when the downtime is important to be reduced.
4. Zero-Trust Architecture in Migration Workflows
Zero-trust migration presupposes that no user/system can be trusted. Check all access requests on an ongoing basis, independent of whether the network is in place or not. Also, use micro-segmentation on transfers and segment networks. This will greatly minimize attack surfaces.
These secure means of data transfer protect the organizations against breaches and free the way to the transition. Hence, it is necessary to choose the correct method depending on your needs in order to successfully migrate.
Role of Data Governance and Compliance in Secure Migration
Data governance in migration ensures organizations maintain control and compliance throughout the transfer process. Strong governance frameworks protect sensitive information while meeting regulatory requirements.
1. Data Classification and Ownership
Classification of data determines the level of protection that is required on certain information. Classify label data as public, internal, confidential, or restricted. Another one is ensuring that there is ownership of data by holding certain teams accountable. This transparency avoids security loopholes in the process of migration.
2. Audit Trails and Traceability
Extensive audit trails record all the activities that occurred during migration. Monitor people who accessed information and dates of the change and the alteration. Additionally, keep data lineage to demonstrate the flow of information between systems. Such traceability becomes absolutely critical in compliance reporting and investigating incidents.
3. Regulatory Requirements
Various industries have defined the requirements of data migration. Strict privacy regulations in GDPR safeguard the data of European citizens. The HIPAA regulations protect the information in the healthcare sector through encryption and controls. Moreover, SOX compliance guarantees that financial data is intact, whereas the standards of the PCI-DSS secure payment card data. Breaking these laws attracts harsh punishment.
4. Aligning Governance with Migration Security
Effective data governance systems are directly incorporated with security. Determine the policies prior to migration. Also, perform frequent compliance audits during the process. Such alignment provides a guarantee that security requirements, as well as regulatory requirements are met.
Having good migration compliance practices ensures that organizations are not confronted with legal risks and also instill confidence in customers about the capability of data management.
Secure Data Migration Best Practices for Enterprises
By using the best practices of enterprise data migration, you will surely secure sensitive information in the entire process of information transfer. These are some of the key implementation strategies.
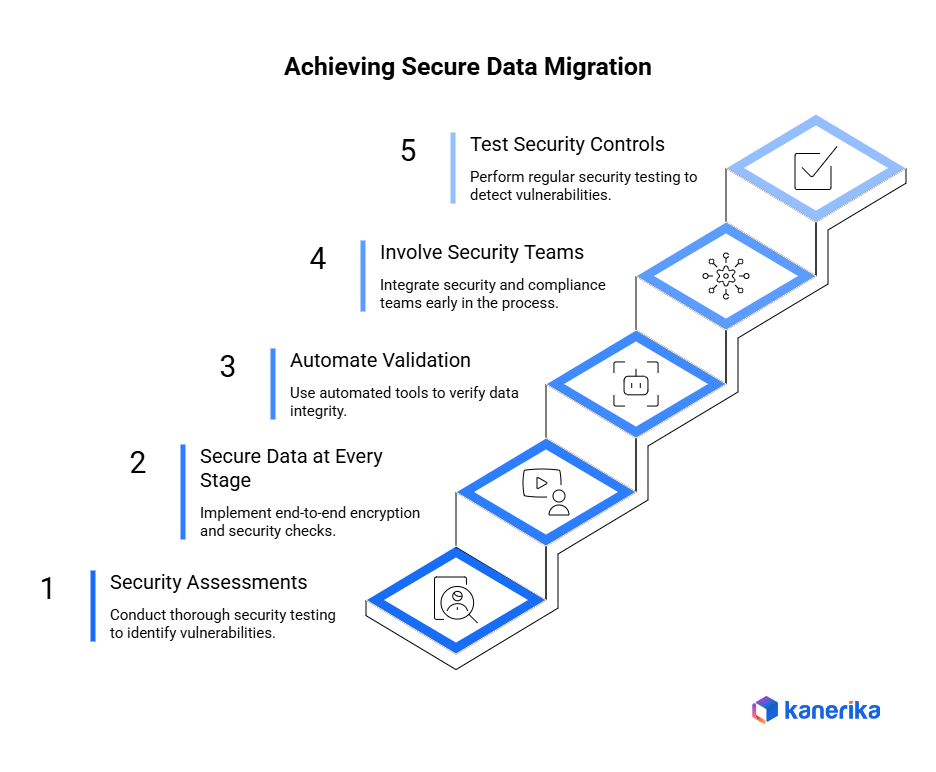
1. Perform Security Assessments Before Migration
Always ensure proper data migration security testing is done prior to the commencement of any project. Find weaknesses of existing systems and possible threats in target environments. Also, assess levels of data sensitivity and compliance. This preliminary study helps to avoid expensive security breaches in the future.
2. Secure Data at Every Stage
Data security needs to be end-to-end and be safeguarded before, at the time of, and after the migration. Encrypt the data in source systems. Second, keep it encrypted when transferring it with secure protocols. Lastly, ensure security checks in the target environment. As such, the constant protection removes the security gaps in the process.
3. Automate Validation and Reconciliation
Implement automated data validation to verify information integrity after migration. Use reconciliation tools to compare source and destination datasets automatically. Moreover, automated checks detect discrepancies faster than manual reviews. This approach reduces human error while improving accuracy.
4. Involve Security and Compliance Teams Early
Incorporate security teams into the migration planning. Involve compliance officers at the beginning of a conversation on regulatory requirements. Moreover, engage risk management teams to evaluate the risks. Early cooperation will eliminate security oversights and guarantee compliance with the organizational policies.
5. Test Security Controls Continuously
Security testing should be done periodically during migration to detect possible vulnerabilities before they become issues. Perform penetration testing on migration environments. Also, conduct vulnerability tests as the process goes on. Conduct disaster recovery exercise to ensure that rollback procedures are operating as intended.
These data migration security strategies can help safeguard the assets of the enterprise, preserve compliance, and sustain business continuity in times of necessary system migrations.
Secure Data Migration for Cloud Platforms
Cloud data migration security involves specific challenges when moving data to platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Here’s what you need to know for safe cloud transfers.
1. Shared Responsibility Model
The cloud shared responsibility model splits security tasks between you and your provider. Your cloud vendor secures physical infrastructure and base services. However, you must protect your data, applications, and user access. Many breaches happen because organizations assume the cloud provider handles everything. Understanding who does what prevents dangerous gaps in protection.
2. Cloud-Native Security Features
Major cloud platforms offer built-in security tools. AWS provides KMS for encryption keys. Azure has Security Center for threat alerts. Google Cloud offers IAM for managing permissions. Use these cloud-native security tools instead of building everything from scratch. They work seamlessly with other platform services and receive regular updates.
3. Securing Storage, Networking, and Access
Start with cloud storage security by reviewing bucket permissions carefully. Check that storage isn’t publicly accessible unless absolutely necessary. Set up virtual private clouds to keep network traffic isolated. Use private connections for sensitive data transfers rather than the public internet. Enable multi-factor authentication for everyone who accesses cloud systems.
4. Avoiding Common Cloud Migration Security Mistakes
Many companies make the same errors during cloud moves. Leaving storage buckets open to the public tops the list. Others forget to turn on encryption or skip security testing before going live. Review all settings manually don’t trust defaults.
Smart secure cloud migration requires using both provider tools and your own security practices together effectively.
Partner With Kanerika for Risk Free Data Warehouse Migration
Partner with Kanerika Today!
Real-World Success Stories: How Kanerika Migration Accelerators Simplify Complex Data Migrations
Case Study 1: Transforming Retail Reporting and Analytics with SQL to Microsoft Fabric Migration
Client Challenge: A big retail company had messy reporting systems spread across different SQL databases. Getting sales reports took hours because data lived in separate places. Their IT team spent too much time fixing broken reports instead of helping the business grow. Monthly reports often had wrong numbers because data didn’t match up.
Kanerika’s Solution : We used Kanerika’s migration accelerator to move all their old SQL reports to Power BI on Microsoft Fabric, making everything run faster and more reliably. We automated all the manual data prep work by putting business rules into Fabric pipelines so teams didn’t have to do boring data checks anymore. We replaced their messy old reporting systems with one clean Microsoft Fabric setup that answers questions much quicker.
Impact Delivered:
- Sales teams now see live inventory numbers instead of day-old data
- IT team freed up 20 hours per week to work on new business projects
- 74% Faster Reporting Cycles
Case Study 2: Moving from Informatica to Talend with Smart Automation
Client Challenge : The company had a big Informatica system that cost too much and was hard to maintain. License costs kept going up every year. Their data workflows were complicated, and any changes required lots of manual work. They couldn’t modernize because migrations would take forever.
Kanerika’s Solution : We used FLIP technology to automatically convert Informatica mappings and business rules into Talend format. Our FIRE tool pulled out all the repository data so we could create new Talend jobs without rebuilding everything by hand. We tested all outputs carefully and set everything up to work in the cloud.
Impact Delivered:
- 70% reduction in manual migration effort
- 60% faster time to delivery
- Better stability through accurate logic preservation
Kanerika : Your Trusted Partner for Risk Free and Secure Data Migrations
Kanerika is a trusted partner for organizations looking to modernize their data platforms efficiently and securely. Modernizing legacy systems unlocks enhanced data accessibility, real-time analytics, scalable cloud solutions, and AI-driven decision-making. Traditional migration approaches can be complex, resource-intensive, and prone to errors, but Kanerika addresses these challenges through purpose-built migration accelerators and our FLIP platform, ensuring smooth, accurate, and reliable transitions.
Our accelerators support a wide range of migrations, including Tableau to Power BI, Crystal Reports to Power BI, SSRS to Power BI, SSIS to Fabric, SSAS to Fabric, Cognos to Power BI, Informatica to Talend, and Azure to Fabric. Additionally, by leveraging automation, standardized templates, and deep domain expertise, Kanerika helps organizations reduce downtime, maintain data integrity, and accelerate adoption of modern analytics platforms. Moreover, with Kanerika, businesses can confidently future proof their data infrastructure and maximize the value of every migration project.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is secure data migration?
Secure data migration is the process of moving data between systems while protecting it from unauthorized access, loss, or corruption. It ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability throughout the migration lifecycle. Security controls are applied before, during, and after migration. This is critical for enterprise and regulated environments.
2. Why is secure data migration important for enterprises?
During migration, data is most vulnerable to breaches and misuse. Enterprises handle sensitive customer, financial, and operational data that must remain protected. Secure migration reduces business risk, ensures compliance, and maintains trust. It also prevents costly post-migration security incidents.
3. What are the common security risks during data migration?
Common risks include data leakage during transfer, weak access controls, insecure APIs, and misconfigured cloud storage. Loss of audit trails and improper encryption are also major concerns. Without proper controls, these risks can lead to compliance violations and data breaches.
4. How can enterprises ensure data security during migration?
Enterprises should use encryption for data at rest and in transit, apply role-based access controls, and monitor activity continuously. Security testing and validation should be performed at every stage. Involving security and compliance teams early improves outcomes.
5. Does secure data migration support regulatory compliance?
Yes, secure data migration helps meet regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and PCI-DSS. Audit trails, data lineage, and access logs provide proof of compliance. Proper governance ensures regulatory requirements are met even while data is in motion.
6. What role does automation play in secure data migration?
Automation reduces manual errors and ensures consistent security checks. Automated validation, reconciliation, and monitoring help detect issues early. This improves both security and reliability, especially for large-scale enterprise migrations.
7. How do organizations measure the success of secure data migration?
Success is measured by zero data breaches, accurate data validation, compliance readiness, and minimal downtime. Reduced security incidents and strong audit results are key indicators. Ultimately, business confidence in migrated data defines success.










