Your team has been preparing for months. The database migration is scheduled, stakeholders are aligned, and everything seems on track. Then, the first migration reports come in.
Some records don’t match. Key fields are missing. Dashboards that worked perfectly before are now throwing errors.
The IT lead scrambles to diagnose the issue while leadership demands answers. “Where’s the customer data?” “Why are transactions missing?”
This wasn’t hypothetical for TSB Bank in 2018. What should’ve been routine turned into one of the most significant IT disasters in UK banking history. And here’s the thing—it didn’t happen because the technology was bad. It happened because the basics got missed.
Look, migrations seem simple on paper. You’re just moving data from point A to point B, right? In reality? You’re juggling massive data volumes, legacy systems that talk in completely different languages, compliance rules that won’t forgive mistakes, and dependencies you didn’t even know existed. One field maps wrong, one timestamp gets corrupted, one validation rule gets skipped—and suddenly customer accounts are broken.
I’ve looked at the numbers. Gartner says nearly 83% of data migration projects miss their targets. You know what I’ve seen across those failed projects? It’s rarely the big dramatic stuff. It’s the small assumptions. The “surely this will work the same way” thinking. The validation that didn’t happen because everyone was already overconfident.
The stakes aren’t small either. When data goes wrong during a migration, you’re not just dealing with technical cleanup. You’re looking at compliance violations, customers who can’t access their accounts, operations grinding to a halt. That costs real money and real trust.
So what actually goes wrong, and more importantly—how do you avoid it? That’s what this blog covers.
TL;DR
- Data migration is high‑stakes work: get it wrong and you risk data loss, downtime, compliance issues, and months of painful cleanup; get it right and you unlock faster analytics and smoother operations.
- The biggest risks are almost never just “tools”; they come from poor planning, unclear scope, weak testing, and underestimating how messy legacy data really is.
- Look, even a tiny amount of data loss or corruption can break critical reports, distort forecasts, and quietly damage customer trust long after the migration is “done.”
- Security and compliance are non‑negotiable: during migration your data is more exposed than usual, so encryption, masking, audit logs, and role‑based access are your safety net, not a nice‑to‑have.
- Downtime is where things get real—if your CRM, payment systems, or EMR are offline, every extra minute costs money, reputation, or, in some industries, actual safety.
- Honestly, manual, spreadsheet‑driven migrations just do not scale; automation, CDC, and modern accelerators like Kanerika FLIP are what keep projects predictable, auditable, and on schedule.
- Don’t get me wrong—technology matters—but the teams that win at migration pair good tools with strong governance, clear ownership, realistic timelines, and obsessive testing.
- If you are staring at a high‑risk migration and feeling uneasy, that’s normal; this guide walks through the top risks and shows how Kanerika’s specialists use automation, governance, and real‑world playbooks to de‑risk the entire journey.
Transform Your Business with Ultimate Data Migration Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for data migration services
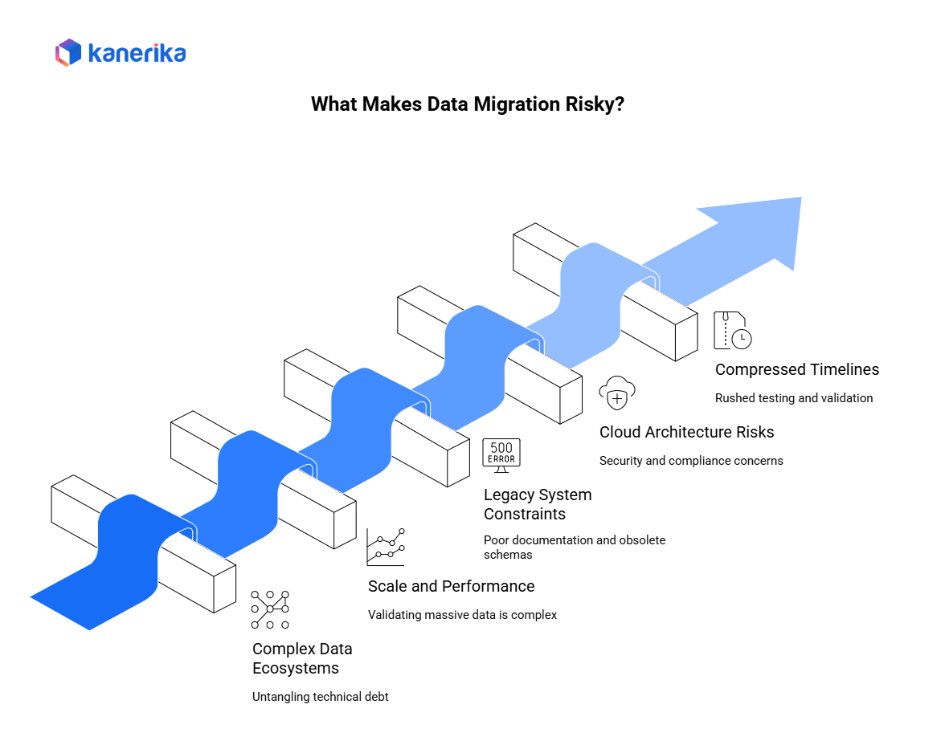
What Makes Data Migration Risky?
Data migration carries significant risks that can derail digital transformation initiatives and impact business continuity. Understanding these underlying causes helps organizations prepare more effectively.
1. Complexity of Modern Data Ecosystems
Today’s enterprises manage intricate data landscapes with multiple formats (CSV, JSON, XML, Parquet), systems (CRM, ERP, databases), and interdependencies across applications. Legacy data migration often involves untangling decades of accumulated technical debt, where data relationships aren’t clearly documented, and business logic exists only in legacy code.
2. Scale and Performance Challenges
Organizations now handle massive data volumes ranging from terabytes to petabytes, with continuous data velocity requiring near-zero downtime migrations. ETL risks multiply exponentially as data size increases, making validation and reconciliation increasingly complex and time-consuming.
3. Legacy System Constraints
Outdated systems present critical cloud migration challenges including poor documentation, obsolete data schemas, inconsistent data quality, and unstructured information stored across file systems. Many legacy databases lack modern APIs or integration capabilities, forcing custom extraction methods that introduce additional failure points.
4. Cloud and Hybrid Architecture Risks
Transitioning to cloud environments introduces new security vulnerabilities, data sovereignty concerns, network latency issues, and regulatory compliance requirements across jurisdictions. Hybrid models compound these challenges by requiring seamless synchronization between on-premise and cloud systems.
5. Business Pressure and Compressed Timelines
Organizations face intense pressure for rapid digital transformation, often compressing critical testing and validation phases. This rushed approach increases the likelihood of data loss, corruption, or incomplete migration.
Example: When migrating from on-premise ERP to SAP S/4HANA, mismatched data structures can delay go-live by months. One manufacturing company experienced a six-month setback when customer master data fields didn’t align between systems, requiring extensive custom mapping and validation.
Without proper planning, risk assessment, and phased validation, data migration projects risk catastrophic failures that compromise data integrity and business operations.
Top Risks in Data Migration
1. Data Loss and Corruption
Risk: Missing, incomplete, or altered data during transfer represents one of the most critical threats in any migration project. Data can be lost due to network interruptions, incompatible formats, or transformation errors during the ETL process.
Impact: Loss of customer records creates immediate operational challenges, while financial inaccuracies can trigger compliance issues and auditing problems. Operational downtime resulting from corrupted data can cost enterprises thousands of dollars per hour in lost productivity and revenue.
Mitigation:
- Implement checksum validation and automated reconciliation reports to verify data integrity at every stage
- Perform trial runs with smaller representative datasets to identify potential issues early
- Maintain comprehensive backups and clearly defined rollback plans with documented recovery procedures
- Use row counts, hash comparisons, and field-level validation to ensure completeness
Example: A 2% data loss in CRM migration can distort customer segmentation models, leading to misdirected marketing campaigns and inaccurate sales forecasting that impacts quarterly revenue projections.
2. Poor Data Quality
Risk: Migrating inconsistent, duplicate, or invalid data into the target system perpetuates existing data quality issues and often amplifies them. Legacy systems frequently contain decades of accumulated data inconsistencies, null values, and conflicting records.
Impact: Business users lose trust in analytics and reporting when data quality issues surface post-migration. Poor data quality leads to compliance failures, incorrect business decisions, and increased manual data correction efforts that negate migration benefits.
Mitigation:
- Apply comprehensive data profiling and cleansing pre-migration to identify quality issues early
- Implement automated validation rules and metadata checks that flag anomalies before migration
- Involve business subject matter experts in data mapping and validation to ensure business logic integrity
- Establish data quality metrics and thresholds that must be met before proceeding
- Use data quality tools to standardize formats, deduplicate records, and enrich missing information
3. Inadequate Planning and Scoping
Risk: Undefined objectives, unclear migration scope, or missing dependency mapping creates chaos during execution. Many projects fail because teams underestimate complexity or overlook critical system interdependencies.
Impact: Cost overruns frequently exceed 50% of original budgets, project delays extend timelines by months, and failed cutovers force emergency rollbacks that damage stakeholder confidence.
Mitigation:
- Define clear, measurable success metrics including data accuracy targets, performance benchmarks, and business continuity requirements
- Develop a detailed migration roadmap with defined milestones, decision points, and rollback triggers
- Conduct thorough impact analysis before execution, mapping all data dependencies and downstream system effects
- Create a comprehensive project charter with documented assumptions, constraints, and risk registers
4. Security and Compliance Risks
Risk: Unauthorized access, data breaches, or non-compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, or SOC2 during migration can expose organizations to severe consequences. Data is particularly vulnerable during transit and temporary storage phases.
Impact: Legal penalties can reach millions of dollars, while reputational damage causes customer churn and loss of competitive advantage. Data breaches during migration have ended careers and forced executive resignations.
Mitigation:
- Encrypt data both in transit using TLS/SSL and at rest using AES-256 encryption standards
- Mask or tokenize sensitive fields (PII, PHI, payment data) during migration testing and validation
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) with least-privilege principles and maintain comprehensive audit trails
- Conduct compliance checks specific to cloud migrations, ensuring data residency requirements are met
- Perform security assessments and penetration testing before and after migration
- Document data lineage and maintain chain of custody for regulated industries
5. Downtime and Business Disruption
Risk: Extended downtime during cutover or data synchronization failures can halt critical business operations. Even planned maintenance windows often overrun due to unexpected complications or performance issues.
Impact: Lost productivity affects thousands of employees, missed transactions result in direct revenue loss, and business interruption damages customer relationships and service level agreements.
Mitigation:
- Plan migrations during low-traffic periods using historical usage analytics to identify optimal windows
- Use incremental or parallel migration techniques that allow systems to run simultaneously during transition
- Test rollback and failover systems extensively before go-live to ensure rapid recovery capability
- Implement real-time monitoring dashboards that track migration progress and alert on anomalies
- Use phased migration approaches that move data in stages rather than “big bang” cutovers
- Maintain warm standby systems that can take over if migration encounters critical issues
6. Integration Failures
Risk: Data not syncing correctly between legacy and new systems creates disconnected information silos. API mismatches, incompatible data formats, and timing issues cause integration breakdowns.
Impact: Broken business processes force manual workarounds, data duplication creates reconciliation nightmares, and incomplete data transfer leaves critical information stranded in legacy systems.
Mitigation:
- Conduct comprehensive pre-migration system compatibility testing to identify integration gaps early
- Use modern APIs or middleware platforms for live synchronization during transition periods
- Validate integration logic post-migration with end-to-end transaction testing across all connected systems
- Implement data reconciliation processes that continuously verify synchronization accuracy
- Document all integration points, data flows, and transformation rules for troubleshooting
- Test error handling and exception management scenarios thoroughly
7. Lack of Stakeholder Alignment
Risk: Business and IT teams misaligned on scope, priorities, or success criteria create conflicting objectives that undermine project success. Communication breakdowns between technical and business stakeholders are common.
Impact: Conflicting goals lead to wasted effort, miscommunication causes rework and delays, and project fatigue sets in as teams lose confidence in leadership direction.
Mitigation:
- Establish a cross-functional steering committee with executive sponsorship and clear decision-making authority
- Define explicit roles, responsibilities, and escalation protocols using RACI matrices
- Maintain transparent communication through real-time dashboards and regular status updates
- Conduct stakeholder workshops to align on priorities and manage expectations
- Implement formal change management processes that require approval for scope modifications
8. Inadequate Testing and Validation
Risk: Migrated data fails in production environments due to incomplete or insufficient testing coverage. Many organizations rush through testing phases under business pressure, only to discover critical issues after go-live.
Impact: Critical reports and dashboards break in production, errors surface during high-stakes business processes, and emergency fixes damage team morale and stakeholder trust.
Mitigation:
- Perform comprehensive end-to-end testing including unit tests, integration tests, regression tests, and user acceptance testing
- Validate data accuracy (correctness), volume (completeness), and referential integrity (relationships) systematically
- Create detailed data validation checklists that require business user sign-off before production deployment
- Test under realistic load conditions that simulate peak business volumes
- Establish clear test exit criteria with defined acceptance thresholds
- Document all test cases, results, and defect resolutions for audit trails
Cognos vs Power BI: A Complete Comparison and Migration Roadmap
A comprehensive guide comparing Cognos and Power BI, highlighting key differences, benefits, and a step-by-step migration roadmap for enterprises looking to modernize their analytics.
9. Tool and Technology Limitations
Risk: Using generic or outdated migration tools unsuited for complex transformations limits automation potential and introduces manual errors. Legacy ETL tools often lack cloud-native capabilities and modern data format support.
Impact: Partial automation increases manual intervention requirements, low performance causes extended migration windows, and limited functionality requires costly custom development.
Mitigation:
- Evaluate specialized migration accelerators like Kanerika FLIP, Informatica Cloud, AWS DMS, Azure Data Factory, or Talend Stitch
- Conduct pilot migrations to test tool compatibility with source and target systems
- Assess tools for scalability, transformation capabilities, and monitoring features
- Consider cloud-native migration services for cloud destinations
- Invest in modern ETL modernization rather than perpetuating legacy tool dependencies
10. Skill Gaps and Resource Constraints
Risk: Limited expertise in target platforms, modern cloud architectures, or specialized migration tools creates execution bottlenecks. The shortage of experienced data engineers and cloud architects compounds this challenge.
Impact: Increased dependency on expensive external vendors, delayed timelines due to learning curves, and quality issues from inexperienced implementation decisions.
Mitigation:
- Upskill internal teams on new ETL platforms and cloud services through structured training programs
- Build hybrid teams combining internal subject matter experts with external partner specialists
- Leverage migration-as-a-service models for large-scale projects requiring specialized expertise
- Create knowledge transfer plans that ensure internal teams can support systems post-migration
- Use managed services and platform-as-a-service offerings to reduce operational complexity
How to Mitigate Data Migration Risks
Data migration doesn’t have to be a gamble — adopting a structured, four-pillar approach turns risk into a controlled journey of transformation.
1. Assessment & Planning
Begin by mapping all data dependencies, types (structured, unstructured), and risk categories (e.g., critical systems, regulated data). Develop a roadmap and define success metrics — like zero-data loss or < 1 hour downtime — before execution begins.
2. Automation & Tools
Leverage modern migration accelerators and platforms (for example Kanerika FLIP, AWS DMS, Azure Data Factory) to extract, convert, and validate data automatically. Automation reduces human error, speeds up transfers, and provides audit logs for traceability.
3. Governance & Testing
Implement data governance protocols—role-based access, encryption, audit trails—and build a comprehensive testing plan: unit tests, regression tests, UAT, and reconciliation. Logs and checkpoints help ensure integrity and accountability throughout the migration.
4. Continuous Monitoring
Once live, migration isn’t done: monitor KPIs such as data-latency, error-rates, and rollback events. For example, a global retailer cut migration downtime by 65% using automated validation pipelines integrated with Azure Data Factory.
By following these four pillars — rigorous assessment, smart automation, strong governance, and ongoing monitoring; organizations can mitigate risk, accelerate timelines, and build a future-ready data environment.
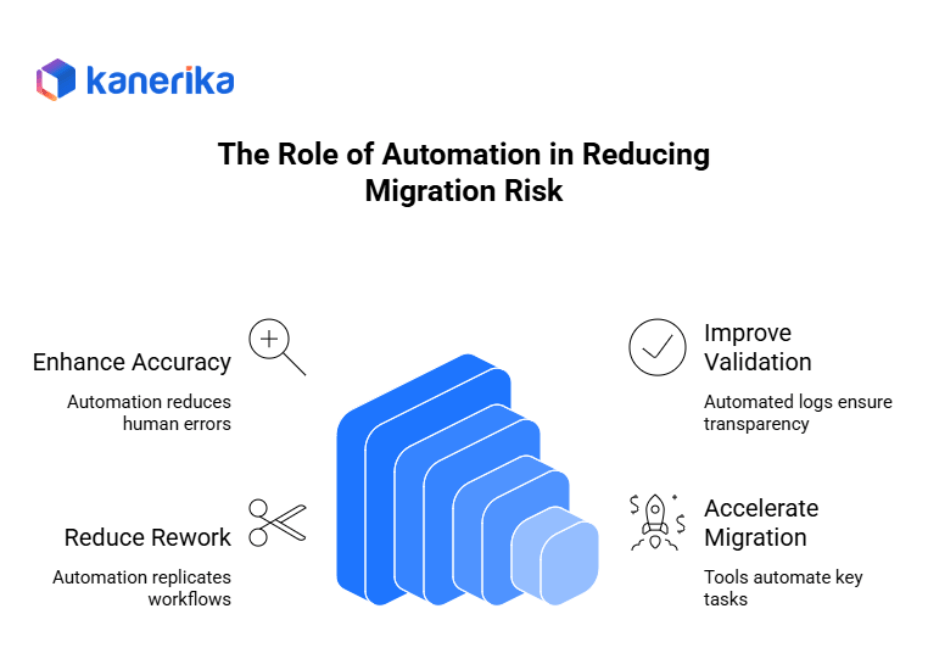
The Role of Automation in Reducing Migration Risk
1. Accelerates Accuracy and Consistency
Automation ensures every dataset, mapping, and transformation follows the same validated logic — minimizing human error and improving data accuracy.
2. Enhances Validation and Traceability
Automated pipelines create validation logs, audit trails, and reconciliation reports, enabling full transparency and compliance throughout the migration lifecycle.
3. Reduces Manual Rework
Instead of rebuilding mappings or workflows one by one, automation tools replicate them programmatically, cutting down repetitive manual effort.
4. Leverages Migration Accelerators
Tools like Kanerika FLIP, AWS DMS, and Azure Data Factory automate metadata parsing, code generation, and schema conversion for faster, more reliable migrations.
Example in Action
Kanerika’s FLIP automates Informatica → Talend or SSIS → Fabric migrations — extracting repository metadata, converting logic, and validating results — reducing manual rework and human dependency.
Compares Manual vs. Automated Approaches
Manual: Prone to errors, inconsistent logic, time-intensive validation.
Automated: Predictable, scalable, and auditable with built-in governance and performance checks.
- Business Impact:
Automation shortens migration timelines, strengthens data integrity, and empowers teams to focus on optimization instead of repetitive execution.
Kanerika : Your Trusted Partner for Risk Free Data Migrations
Kanerika is a trusted partner for organizations looking to modernize their data platforms efficiently and securely. Modernizing legacy systems unlocks enhanced data accessibility, real-time analytics, scalable cloud solutions, and AI-driven decision-making. Traditional migration approaches can be complex, resource-intensive, and prone to errors, but Kanerika addresses these challenges through purpose-built migration accelerators and our FLIP platform, ensuring smooth, accurate, and reliable transitions.
Our accelerators support a wide range of migrations, including Tableau to Power BI, Crystal Reports to Power BI, SSRS to Power BI, SSIS to Fabric, SSAS to Fabric, Cognos to Power BI, Informatica to Talend, and Azure to Fabric. Additionally, by leveraging automation, standardized templates, and deep domain expertise, Kanerika helps organizations reduce downtime, maintain data integrity, and accelerate adoption of modern analytics platforms. Moreover, with Kanerika, businesses can confidently future proof their data infrastructure and maximize the value of every migration project.
FAQs
1. What are the main risks involved in data migration?
Main risks involved in data migration are data loss, corruption, downtime, and compliance breaches. They happen because validation gets skipped, transformation rules misalign, or source data is messier than expected. At Kanerika, we’ve seen transaction records vanish because checksum validation wasn’t running. The pattern we consistently find? Organizations understand the tech risks but underestimate operational complexity. Our framework addresses this upfront.
2. Why do most data migration projects fail or exceed timelines?
According to Gartner, nearly 83% of data migrations face delays due to underestimated complexity, unclear scope, and insufficient testing. A well-defined roadmap and automation can help avoid these pitfalls. Kanerika worked with a client who thought “move the database” will be easy until they discovered three systems were pulling from it. Kanerika’s FLIP Migration Accelerator prevents this with structured planning and pre-built automation that catches scope issues early.
3. How can data loss be prevented during migration?
Use checksum validation at every stage, run reconciliation reports comparing source and target, maintain complete backups, and pilot with smaller datasets first. Kanerika’s approach includes automated validation at transformation and post-completion stages. The teams that actually catch missing records verify data instead of assuming it worked. Our acceleration framework validates in real-time.
4. What role does automation play in mitigating migration risks?
Automation reduces human error by 70-80% because it eliminates manual mapping and validation. Kanerika’s FLIP Migration Accelerators automate extraction, transformation, and reconciliation so your team oversees instead of executing manually. Our clients typically see 70-80% automation rates, which means faster timelines and fewer firefighting moments at go-live.
5. How can organizations ensure compliance and data security during migration?
Encrypt data in transit, use role-based access controls, mask sensitive information, and run pre- and post-migration audits. Kanerika builds audit trails into every migration—you document every change so when regulators ask “how do you know your data is intact?” you show proof. Kanerika’s compliance-first modernization approach protects healthcare, financial, and regulated industries.
6. What are the signs of poor data migration governance?
Fuzzy accountability, incomplete audit logs, inconsistent validation reports, and misaligned stakeholders. When nobody can trace why a field got corrupted, that’s poor governance. Kanerika implements governance frameworks with clear roles, documented procedures, and traceability at every step—turning migrations from political projects into controlled, auditable processes.
7. How can companies reduce the overall risk in data migration projects?
Plan thoroughly, automate everywhere, test in multiple stages, and monitor post-migration KPIs continuously. The difference? Starting with a proven framework instead of inventing from scratch. Kanerika’s FLIP Accelerators come with built-in quality gates, pre-configured rules, and automated discovery. Organizations move faster with significantly less risk because we’ve already solved common migration problems.










