BI Migration for Healthcare is becoming increasingly important as health systems modernize. Hospitals and clinics are adopting electronic health records, expanding telemedicine, connecting medical devices, and using more advanced diagnostic systems than ever before. But with this evolution comes an explosion of data. In fact, global healthcare data is expected to grow at over 36% CAGR through 2025, according to IDC.
Since clinical, operational, financial, imaging, claims and patient-interaction data is on the rise, the legacy BI systems are unable to keep pace. Their interoperability, performance and scalability are a problem as well as their rigid compliance requirements such as HIPAA and HITRUST. Thus, healthcare leaders are resorting to the modern BI to provide real-time insights, reduce reporting gaps, better management of population health, and better patient experience.
This blog addresses all the aspects of healthcare BI transformation key drivers, modern architecture, migration road map, tools and platforms, best practices, real-world case studies, and future trends that are shaping analytics in healthcare.
Key Learnings
- Modern BI migration is essential for healthcare due to rising data volumes from EHRs, imaging systems, telemedicine, and operational workflows.
- Cloud-native platforms like Fabric, Databricks, and Snowflake offer the scalability, compliance, and real-time processing legacy BI tools cannot provide.
- A strong migration strategy must prioritize HIPAA/HITECH security, PHI protection, semantic consistency, and robust governance.
- High-value dashboards such as patient flow, infection control, and readmission analytics deliver quick wins and support clinical operations.
- Future BI will integrate AI, LLM copilots, real-time hospital analytics, and multi-cloud architectures to enable proactive, data-driven healthcare.
Elevate Your Enterprise Reporting by Migrating to Power BI!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Migration Services
Why Healthcare Enterprises Need BI Migration
Healthcare organizations are generating more data than ever before, and this rapid growth is one of the primary reasons BI migrations has become essential. EHR and EMR systems now produce large volumes of clinical, operational, and administrative data every second. As a result, modern platforms are required to process, analyze, and visualize this information quickly and accurately.
Additionally, the demand for predictive analytics is rising fast. Hospitals and health systems must forecast readmission risk, identify chronic disease patterns, and anticipate resource needs. However, traditional BI tools such as Cognos, SSRS, SAP BO, and Qlik often struggle because they are not cloud-native and cannot scale to meet these advanced requirements.
In addition, healthcare businesses have to comply with stringent compliance requirements such as HIPAA, HITRUST, GDPR, and ICD-10 reporting standards. Consequently, they require BI systems that enhance effective governance, auditing, lineage, and data protection.
Meanwhile, the current care models demand cross-functional dashboards, which unite clinical, operational, financial, and infection-control awareness. However, legacy BI systems have difficulties in combining the information between EHR, PACS, LIS, RIS, pharmacy, billing and claims systems.
Real time visibility is also important in healthcare operations such as monitoring the ER wait time, ICU occupancy, bed turnaround and shortage of supplies. The older BI systems are too slow to provide such responsiveness.
Finally, cloud and AI technologies are becoming central to healthcare transformation. Moving to modern BI platforms enables organizations to leverage advanced analytics, AI-driven insights, and scalable infrastructure.
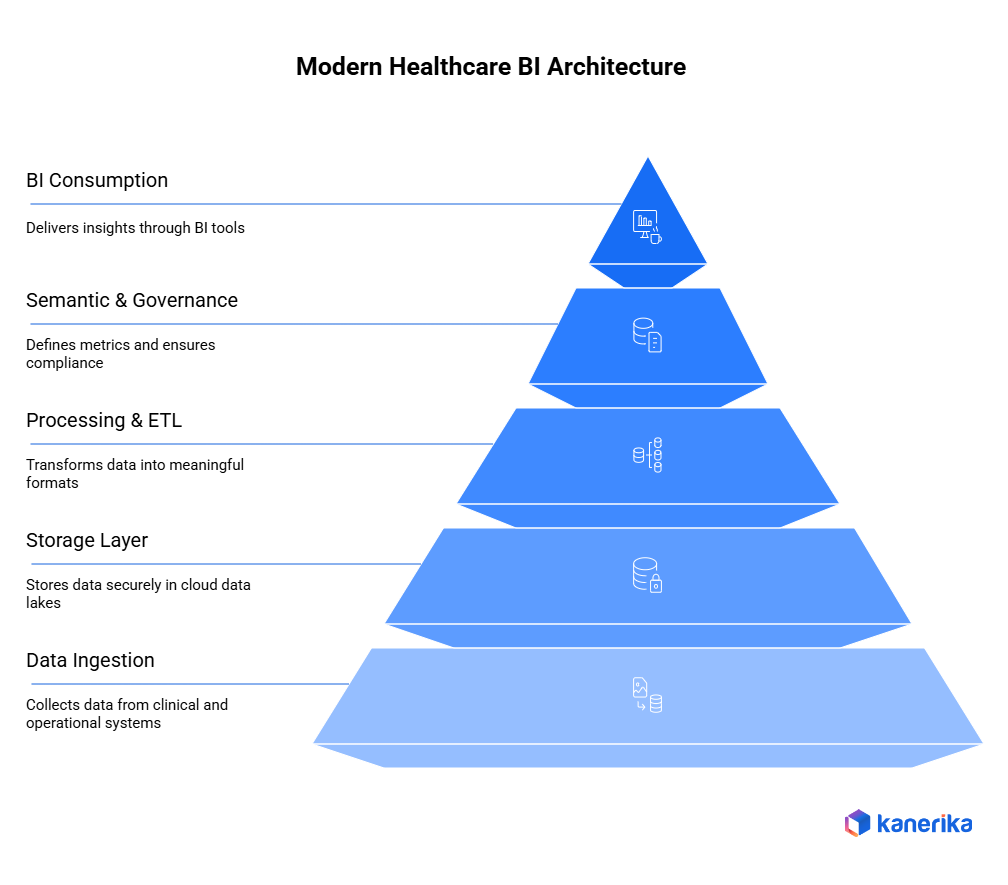
Modern BI Architecture for Healthcare
The modern healthcare analytics demands the architecture able to process various types of data, rigid guidelines, and real-time decision-making. In order to accomplish this, healthcare enterprises employ stratified BI architecture that is secure, scaled, as well as clinical accuracy.
1. Data Ingestion Layer
The first layer focuses on collecting data from many clinical and operational systems. Healthcare professionals use the EHR systems like the Epic and Cerner that exchange data with the help of an HL7 and FHIR API that should be incorporated into the BI environment.
Besides this, hospitals absorb the information of PACS imaging systems, laboratory information systems (LIS), radiology information systems (RIS), insurance clearinghouses, pharmacy systems, and claims processors. Both batch and streaming ingestion are essential batch for historical data and streaming for real-time events such as bed availability, vitals monitoring, and ER triage updates.
2. Storage Layer
Once data is ingested, it must be stored in a secure and scalable environment. Modern healthcare enterprises use cloud data lakes that support structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Lakehouse platforms such as Databricks, Snowflake, and Microsoft Fabric unify storage and analytics, enabling advanced queries across massive datasets.
Healthcare imaging introduces additional needs, including support for DICOM files and large file optimization. Moreover, storage systems must comply with strict regulations by applying encryption, role-based access control (RBAC), and secure key management.
3. Processing & ETL Layer
Next, the data is transformed into clinically meaningful formats. ETL/ELT pipelines normalize and clean data from multiple sources, including HL7, CCD, and FHIR records. Standardization is critical, so data is mapped to common clinical vocabularies such as SNOMED, LOINC, and ICD-10. Some use cases require real-time processing, such as monitoring critical care alerts, sepsis indicators, or operating room workflows.
4. Semantic & Governance Layer
This layer defines the metrics and ensures compliance. Healthcare teams use semantic models to standardize key clinical KPIs such as length of stay (LOS), readmission rate, and infection rate. Operational metrics such as patient throughput, room utilization, and scheduling efficiency are also defined here. Governance ensures PHI/PII protection using masking, lineage, and access auditing, all aligned with HIPAA, HITECH, and GDPR guidelines.
5. BI Consumption Layer
Finally, insights are delivered through BI tools such as Power BI, Tableau, and Looker. Clinicians use dashboards for patient outcomes, ER performance, radiology throughput, and care quality. Executives access dashboards for cost, utilization, revenue cycle, and financial performance. Additionally, embedded analytics integrates insights directly into clinician workflows, improving decision-making at the point of care.
Tools & Platforms for BI Migration in Healthcare
The migration of BI systems used in the healthcare sector needs the tools to be able to process clinical data, address the rigid regulatory requirements, and provide high-level analytics in scale. Contemporary BI migration patterns incorporate frameworks of both analytics systems, information engineering tools, governance systems, and accelerators tailored at the healthcare setting.
1. Modern BI Tools
Healthcare organizations increasingly prefer cloud-first BI tools that support governed datasets and secure access.
- Power BI is widely adopted due to its strong governance, integration with Microsoft Fabric, and ability to manage PHI through row-level security and compliance controls.
- Tableau remains popular for rich clinical visualizations, especially in hospitals focused on quality improvement and operational analytics.
- Looker offers a semantic modeling layer that helps define consistent clinical KPIs across departments.
2. Cloud Data Platforms
As hospitals shift to cloud-native analytics, several platforms support secure storage and real-time insights.
- Microsoft Fabric provides unified analytics, governance, and pipelines built for regulated industries.
- Databricks Lakehouse is ideal for handling large PHI datasets, imaging data, and machine learning workflows such as predicting readmissions or sepsis.
- Snowflake Healthcare Data Cloud supports secure data collaboration with payers, labs, and partners while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
- Google BigQuery is preferred for high-speed analytics and integration with imaging AI models for radiology and pathology workflows.
3. Healthcare Integration Tools
Connecting clinical systems is often the hardest part of BI migration.
- Enterprise-grade ETL tools like Informatica and Talend support complex transformations and healthcare-specific validations.
- FHIR/HL7 engines, including Mirth Connect, help integrate EHR data from systems such as Epic and Cerner.
- Cloud ingestion tools like Fivetran and Matillion simplify ingestion from SaaS, claims processors, and administrative systems.
4. Governance Tools
Because healthcare data contains PHI, strong governance is essential.
- Azure Purview offers automated PHI scanning, lineage tracking, and compliance controls.
- Collibra provides enterprise-level metadata cataloging for clinical and operational datasets.
- Alation supports governance frameworks across clinical, finance, and operational teams.
5. Migration Accelerators
To reduce migration timelines, organizations use accelerators such as:
- Tableau to Power BI, Cognos to Power BI, SSRS to Power BI converters
- Legacy warehouse → Fabric, Databricks, Snowflake
- Automated clinical code conversions (ICD-10, SNOMED)
- AI-driven frameworks that map reports, rebuild visuals, and validate metrics
Step-by-Step BI Migration Roadmap for Healthcare
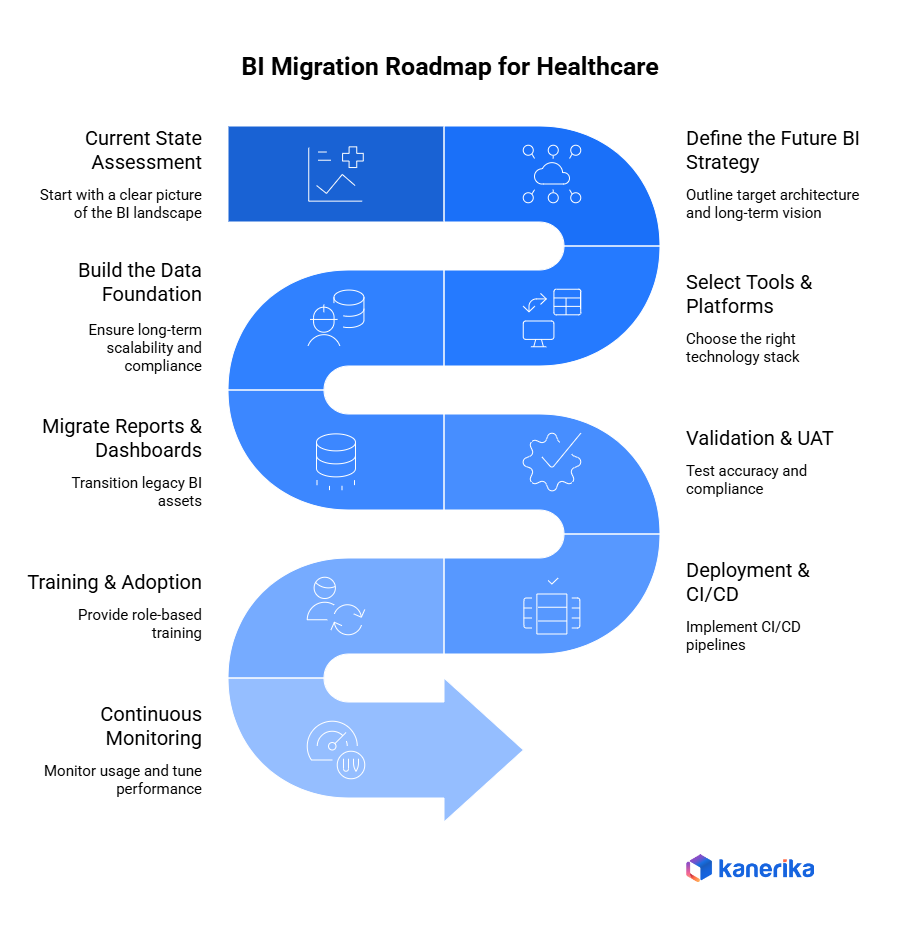
An effective BI migration within the healthcare sector needs to be well-organized, repeatable, and guard clinical information, maintain regulatory adherence, and enable real-time decision-making. The path ahead presents the critical actions that healthcare enterprises need to follow when transitioning over to new cloud-native and modern analytics systems that support their legacy BI systems.
Step 1: Current State Assessment
It starts by having a clear picture of the current BI landscape.
- List all the reports, dashboards, OLAP cubes, scripts and data sources that are being used.
- Assess the data flow of EHR/EMR systems, PACS, LIS, RIS, billing, and claims management tools.
- Determine data silos which do not support the ability to do unified analytics.
- Review compliance gaps related to HIPAA, SOC 2, HITRUST, and internal audit requirements.
This assessment helps create a complete inventory and identifies high-risk areas.
Step 2: Define the Future BI Strategy
Next, healthcare organizations must outline their target architecture and long-term vision.
- Decide on a cloud-first, AI-ready BI architecture that supports predictive analytics and operational intelligence.
- Determine needs for real-time reporting, such as ER wait times, ICU capacity, bed occupancy, infection trends, and command-center visibility.
- Prioritize clinical, financial, and operational BI use cases to align the migration with organizational goals.
Step 3: Select Tools & Platforms
Choosing the right technology stack is a critical decision.
- Select the BI tool: Power BI, Tableau, or Looker, depending on governance, visualization, and embedded analytics needs.
- Choose the data platform: Databricks, Microsoft Fabric, Snowflake, or BigQuery to handle structured and unstructured clinical data securely.
- Define the governance model to support PHI protection, role-based access, lifecycle management, and lineage tracking.
Step 4: Build the Data Foundation
A strong foundation ensures long-term scalability and compliance.
- Ingest data using HL7/FHIR APIs, EHR interfaces, DICOM imaging transfers, and claims/insurance connectors.
- Build structured data layers: staging → curated → gold for clear separation of duties.
- Normalize clinical vocabulary using SNOMED, LOINC, ICD-10, CPT, and RxNorm to ensure consistency across reports.
Step 5: Migrate Reports & Dashboards
Once the foundation has been established, legacy BI assets are set back or reinvented.
- Use accelerators to map Tableau, Cognos, SSRS, or Qlik dashboards into modern BI tool equivalents.
- Redesign dashboards to fit clinical workflows for example, clinician summaries, patient flow visualizations, infection monitoring, or financial KPIs.
Step 6: Validation & UAT
There should be accuracy and compliance testing.
- Verify such clinical outcomes like LOS, readmission rates, the number of infections, and throughput.
- Test PHI/PII masking, row level security and access policies.
- Compare output to source EHR, billing, and financial systems to identify 100 percent integrity.
Step 7: Deployment & CI/CD
Once validated, the solution is ready for enterprise rollout.
- Implement CI/CD pipelines for BI artifacts.
- Publish certified datasets, semantic models, and governed metrics.
Step 8: Training & Adoption
User adoption determines long-term success.
- Provide role-based training for clinicians, administrators, finance teams, and operations managers.
- Run change-management workshops to ease the transition from legacy tools.
Step 9: Continuous Monitoring
Finally, continuous improvement keeps BI effective.
- Monitor usage analytics to identify valuable and underused reports.
Best Practices for BI Migration in Healthcare
A tradeoff between clinical precision, regulatory requirements, technical scalability, and acceptance by the users is necessary when migrating Business Intelligence systems in the healthcare sector. Thus, an ordered sequence of best practices will guarantee that the legacy BI tools are easily changed to new and cloud-native analytics systems. The following are the key principles that healthcare institutions should use in BI migration.
1. Prioritize Compliance and Patient Data Security
Because healthcare data contains highly sensitive PHI, compliance must lead every design and migration decision.
- Align BI architecture with HIPAA, HITECH, HITRUST, GDPR, and regional healthcare privacy standards.
- Implement PHI masking, tokenization, and differential privacy where required.
- Enforce role-based access control (RBAC) so users only see the data necessary for their roles.
- Maintain detailed audit logs for every access and transformation to support regulatory reviews.
By doing so, healthcare enterprises reduce compliance risks while enabling safe data use.
2. Build a Healthcare Semantic Layer
A unified semantic layer improves trust, consistency, and interoperability across clinical and operational reporting.
- Standardize definitions for core metrics such as Length of Stay (LOS), mortality rate, ALOS, OR utilization, readmission rate, infection rate, and throughput metrics.
- Create a clinical and financial glossary that aligns with coding systems like ICD-10, DRG, SNOMED, and CPT.
- Ensure all BI tools reference the same governed datasets so teams analyze consistent data.
3. Use a Cloud-Native Foundation
Modern BI in healthcare depends on scalable, compliant infrastructure.
- Use columnar storage formats like Parquet and governed Lakehouse tables like Delta for both structured and unstructured data.
- Apply smart partitioning to support faster queries on PHI-heavy datasets such as claims, EHR events, and lab results.
- Choose platforms designed for healthcare data workloads—Databricks, Snowflake Healthcare Data Cloud, or Microsoft Fabric.
4. Adopt Metadata-Driven Pipelines
Metadata-driven approaches reduce manual work and improve auditability.
- Enable automated documentation during ingestion, transformation, and reporting.
- Use lineage tracking to map data journeys from EHR → Lakehouse → BI dashboards.
- Automate schema drift handling and validation to maintain long-term reliability.
5. Focus on High-Value Dashboards First
To deliver quick wins and ensure adoption, prioritize the dashboards that impact daily operations.
- Readmission dashboards to support risk scoring and intervention.
- Infection control dashboards for real-time surveillance.
- Patient flow dashboards covering ER wait times, ICU occupancy, and bed management.
6. Implement a Strong Governance Framework
Governance ensures accuracy, security, and consistent data use.
- Form a centralized governance committee including clinical, IT, and compliance leaders.
- Enforce automated policies for data retention, PHI masking, and access permissions.
- Certify datasets to build user trust.
7. Enable Self-Service BI for Clinicians and Managers
Finally, empowering healthcare teams with safe, intuitive analytics increases BI adoption.
- Provide pre-defined, governed datasets tailored to clinical, operational, and financial roles.
- Apply guardrails that prevent PHI exposure or unauthorized data combinations.
Crystal Reports to Power BI Migration 2025: Key Considerations
Learn how to migrate from Crystal Reports to Power BI for modern, interactive analytics.
Real-World Case Studies
Already, modern BI migration is bringing significant benefits to the real-world healthcare organizations. These are some of the ways in which migration to cloud-native analytics platforms alters clinical, operational, and financial performance.
Case Study 1: Cleveland Clinic – Migrated to Microsoft Azure for BI
Cleveland Clinic is one of the world’s leading healthcare systems, and it needs a modern way to manage its growing volume of clinical and research data. Therefore, the organization migrated to Microsoft Azure to support advanced BI and analytics workloads.
The migration improved data accessibility across departments, enabled faster reporting, and strengthened research capabilities by offering centralized, scalable storage and compute. Thanks to Azure’s integration with Power BI, researchers and clinicians gained quick access to dashboards and insights supporting patient care and medical studies.
Case Study 2: Kaiser Permanente – Adopted Cloud Analytics for BI Modernization
One of the biggest healthcare providers in the U.S., Kaiser Permanente, migrated its analytics services to Google Cloud to aid in advancing BI and population health analytics. It also helped in the improved operation reporting, real-time analytics and better patient care insights across its network due to this migration.
Using cloud-based BI, Kaiser Permanente is now able to process the large-scale healthcare data including the claims, EHR events, and imaging and operational metrics to be processed more quickly and with improved precision. The relocation also contributed to the improvement of patient experience due to timely information about clinicians and administrators.
Case Study 3: Mount Sinai – Uses Databricks Lakehouse for Unified BI
Mount Sinai Health System adopted the Databricks Lakehouse Platform to integrate clinical, operational, genomic, and research data into a unified analytics ecosystem. This has allowed the organization to now drive AI-based models, disease prediction, patient risk score, and clinical decision support.
This Databricks allowed Mount Sinai to minimize its data silos, speed up the pace of research, and develop BI dashboards that unify both real-time hospital operations and long-term clinical trends.
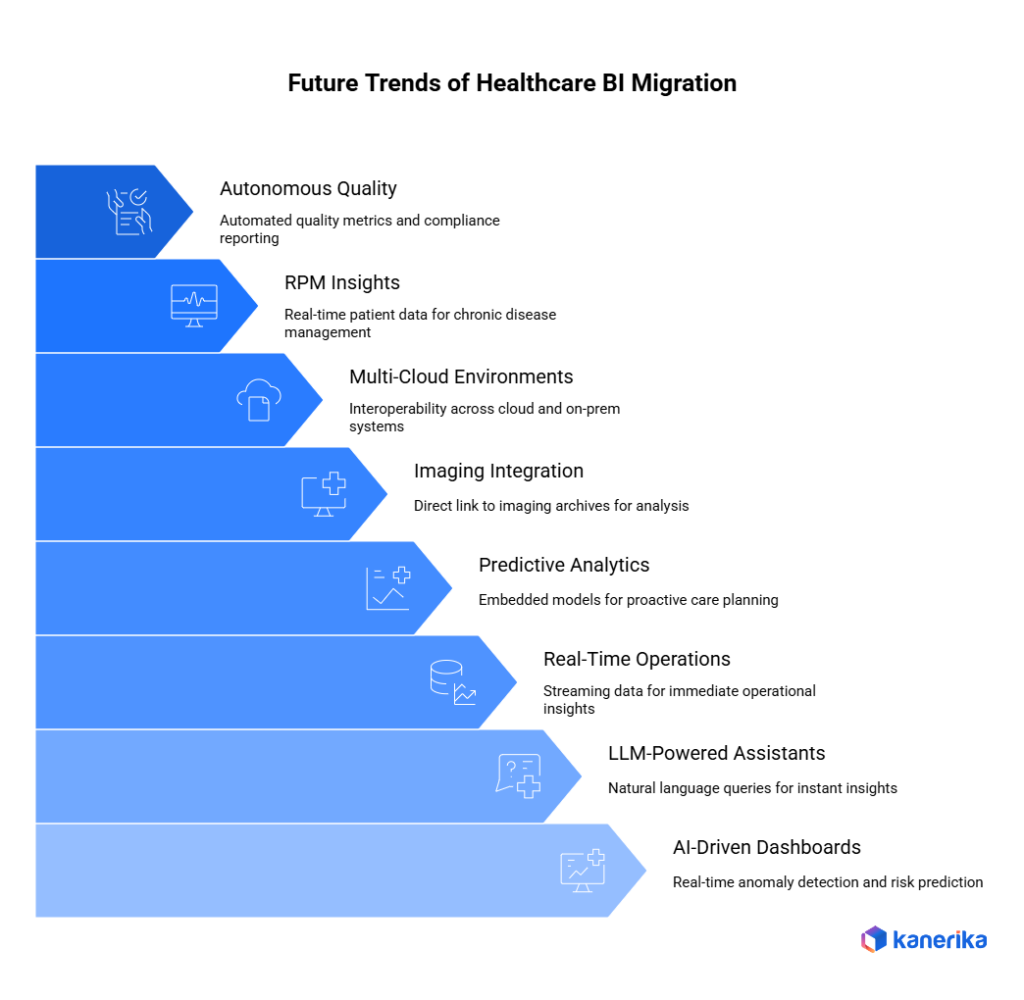
Future Trends in BI Migration for Healthcare
Along with the current trends of moving healthcare organizations towards cloud-native analytics, there are some strong trends defining the future of BI migration. These trends will redefine how hospitals, clinics, and payers use data to improve patient care, operational efficiency, and clinical decision-making.
1. AI-Driven Clinical Dashboards
Healthcare BI is shifting from static reporting to AI-supported dashboards that highlight anomalies, predict risks, and suggest clinical interventions in real time. Moreover, these dashboards will be constantly updated once the new data are received. This translates into faster and more confidence in the actions of clinicians. This helps in providing prompt and proactive care to the patients.
2. LLM-Powered BI Assistants for Clinicians
Large Language Models (LLMs) integrated into BI platforms will allow clinicians to ask natural-language questions such as “Showsepsis risk for ICU patients today” and instantly receive insights. This minimizes the reliance on data teams and speeds up decision making. In addition, this eliminates the learning aspect of using complex BI tools. This way, physicians and nurses will have the ability to spend more time attending to patients as opposed to documents.
3. Real-Time Hospital Operations BI
BI systems will increasingly process streaming data from EHR, IoT sensors, bed-tracking systems, and patient flow tools. This will support real-time insights for ER congestion, operating room usage, ICU strain, and supply shortages. This will support real-time insights for ER congestion, operating room usage, ICU strain, and supply shortages. Consequently, hospital administrators will be able to react to problems before they get out of control.
4. Predictive Analytics Embedded in BI
Hospitals will embed predictive models readmission risk, LOS forecasting, infection spread, and staffing demand directly into BI dashboards, making analytics more actionable and proactive. Moreover, the insights will be presented together with the current performance metrics. This helps care teams plan ahead and reduce operational stress.
5. DICOM + Imaging Analytics Integration
The BI systems of the future will be linked to the imaging archives directly, so the radiology throughput dashboards, AI-based anomaly detection, and imaging-aligned clinical outcomes will also be available. Besides, the imaging information will be connected with patient records to be analyzed further. This enhances the rapidity in diagnosing and coordinating care.
6. Multi-Cloud BI Environments
Multi-cloud strategies will be implemented in healthcare systems to meet regional requirements, connect with payer systems, and be resilient. BI systems will be able to interoperate across AWS, Azure, GCP and on-prem environments. BI systems will be able to interoperate across AWS, Azure, GCP and on-prem environments. Consequently, the flexibility of organizations is achieved without compromising on compliance or performance.
7. BI + Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Insights
Remote patient monitoring will deliver real-time patient vital and device information, which will be delivered directly to BI dashboards to manage chronic disease and virtual care. Besides, patient status can be monitored remotely by care teams and acted upon at an early stage. This will aid in improved results and decrease hospital readmission.
8. Autonomous Quality-of-Care Dashboards
The automation of quality metrics will be provided by agentic AI, its deviations will be detected, and compliance-ready reports prepared to be submitted to CMS, Joint Commission, and other regulators. In addition, these dashboards will automatically update with the change of regulations. This will minimize reporting load and also provide a continuous level of compliance.
Kanerika: Accelerating BI Migration for Healthcare Enterprises
Kanerika assists healthcare organizations to upgrade their BI and analytics systems by providing expedited, secure, and clinically-focused approaches to migration. The aging BI systems fail to match the increasing amounts of clinical, operational, imaging and claims data being produced by hospitals and health networks. Their performance, interoperability and compliance requirements like HIPAA, HITECH and CMS reporting are problematic. Kanerika assists healthcare teams in transitioning on modern BI systems without disturbing the patient care or daily operations.
We support the migration of such tools as Tableau, Cognos, SSRS, SAP BO, and Qlik to the cloud-native platforms, including Power BI and Microsoft Fabric. This change will enable clinicians, administrators, and executives to have access to real-time clinical dashboards, operational metrics, revenue cycle analytics, and population health insights. Along with the modernization of BI, we help to move to Lakehouse based on Fabric, Databricks, and Snowflake, and provide the integration of HL7/FHIR data, EHR/EMR exports, and imaging data, including DICOM documents.
We also deal with cloud migration to Azure or AWS, modernize ETL pipelines to process clinical data, and upgrades workflow automation (omitting claims processing and compliance reporting). The proprietary platform named FLIP by Kanerika allows the migration process to proceed faster with up to 80% being automated so that data accuracy is maintained, clinical logic is preserved, and operational continuity is not lost.
Compliant with international standards, ISO 27001, ISO 27701, SOC 2, and GDPR Kanerika will make all the migrations secure, compliant, and reliable. We work with providers to develop a more efficient clinical process, better decisions, and a future-proof BI environment through a profound understanding of the role of healthcare data, cloud engineering, and AI automation.
Migrate to Power BI for Smarter Analytics and Real-Time Insights!
Partner with Kanerika for Seamless Migration Services.
FAQs
1. What is BI migration in healthcare?
BI migration in healthcare involves moving reporting and analytics from legacy BI tools to modern platforms. This includes dashboards for clinical, operational, and financial data. The goal is to improve reporting speed, accuracy, and accessibility. In 2026, BI migration is critical to support data-driven patient care and compliance.
2. Why are healthcare organizations migrating their BI platforms ?
Healthcare data volumes are growing rapidly due to digital health records, claims systems, and connected devices. Legacy BI tools struggle with performance, scalability, and security. Migrating to modern BI platforms enables real-time insights and supports advanced analytics. It also helps reduce operational and infrastructure costs.
3. What data is typically included in healthcare BI migration?
Healthcare BI migration usually includes clinical records, claims data, billing information, and operational metrics. Data from EHR, EMR, finance, and compliance systems is consolidated. Historical data is also migrated for trend analysis and audits. Accurate data handling is essential due to regulatory requirements.
4. How does BI migration improve patient care and operations?
Modern BI platforms deliver faster access to reliable data for doctors and administrators. This improves care coordination, resource planning, and operational efficiency. Real-time dashboards help identify risks early and improve outcomes. Better insights lead to smarter clinical and business decisions.
5. What are the biggest challenges in healthcare BI migration?
Common challenges include poor data quality, system integration issues, and strict compliance requirements. Managing sensitive patient data securely is a major concern. Downtime during migration can also disrupt operations. A well-planned migration strategy helps address these risks.
6. How does healthcare BI migration ensure compliance and security?
BI migration includes strong data governance, encryption, and access controls. Platforms are designed to meet regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. Audit trails and data lineage ensure transparency. This helps healthcare organizations maintain compliance during and after migration.
7. What should healthcare organizations look for in a BI migration partner?
Healthcare organizations should choose partners with proven migration experience and domain expertise. The partner should understand healthcare data standards and compliance needs. Automation and accelerators can reduce risk and timelines. A strong partner ensures a smooth, secure, and future-ready BI migration.










