As organizations modernize their analytics stacks, the comparison between Microsoft Fabric vs Tableau is becoming more relevant. In 2025, Microsoft expanded Fabric with deeper Copilot integration, real-time analytics, and unified governance across data engineering and BI. At the same time, Tableau continued enhancing its visualization and embedded analytics capabilities, reinforcing its position as a leading tool for interactive data exploration.
The market reflects this shift. The global business intelligence and analytics software market is expected to exceed $50 billion by 2028, driven by demand for AI-assisted insights and self-service analytics. Organizations now evaluate platforms not only on dashboards but also on data integration, governance, and scalability, where the differences between Microsoft Fabric and Tableau become clear.
Continue reading this blog to understand how Microsoft Fabric vs Tableau compare across features, use cases, and business needs, and which platform fits your analytics strategy best.
Key Takeaways
- One approach offers an end-to-end analytics platform covering data ingestion, engineering, governance, AI, and BI, while the other is primarily focused on visualization and exploration.
- Platform consolidation helps reduce data movement, simplify governance, and create a single source of truth for analytics teams.
- Visualization-first tools enable faster ad hoc analysis and storytelling, especially for analysts who need flexibility and quick insights.
- Unified storage and shared semantic models support consistent metrics, real-time reporting, and easier collaboration across teams.
- Cost structures vary widely, making user scale, workload intensity, and viewer volume key factors in platform selection.
- The right choice depends on whether the priority is enterprise-wide analytics modernization or fast, design-led business intelligence.
Transform your Data with Microsoft Fabric!
Work with Kanerika to Simplify Your Adoption Journey
Microsoft Fabric vs Tableau: Key Differences Explained
Fabric and Tableau serve overlapping business intelligence needs but take fundamentally different approaches. Microsoft Fabric is an end-to-end analytics platform built around a unified lakehouse architecture with native Azure integration and comprehensive data engineering, data science, and BI capabilities. Tableau is a specialized data visualization and dashboarding product known for its intuitive design experience and extensive connector ecosystem.
Core Practical Differences to Understand
- Platform Scope Fabric delivers a complete analytics stack with storage, compute, pipelines, and BI in one unified ecosystem. Tableau focuses on visualization and analytics, typically paired with separate data engineering and storage solutions.
- Integration Model Fabric integrates natively with Azure services, including Power BI, Microsoft Purview, Synapse, and Azure Data Factory. Tableau connects broadly to numerous data sources but usually requires external data preparation or pipelines for large-scale data engineering tasks.
- Governance and Security Fabric provides lakehouse-native governance and enterprise cataloging built into the platform. Tableau offers strong governance features but typically depends on underlying data platforms for unified lineage and storage governance.
- Primary User Focus Fabric suits teams wanting platform consolidation and tight cloud integration. Tableau suits analysts and data storytellers who prioritize fast, flexible visualization with rich UI capabilities.
- Latest Updates Worth Noting In January 2026, Microsoft acquired Osmos to bring autonomous data engineering into Fabric, reducing manual data preparation effort by 50%. Tableau 2026 introduced Tableau Agent, an AI-powered assistant for natural language queries, and enhanced Pulse integration for embedded metrics in dashboards.
Quick Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microsoft Fabric | Tableau |
| Core Focus | End-to-end analytics platform | Data visualization and dashboards |
| Best For | Platform consolidation, large-scale analytics | Fast, flexible data exploration |
| Data Engineering | Built-in pipelines and lakehouse | Relies on external ETL tools |
| Visualization | Strong via Power BI integration | Industry-leading visuals |
| Integration | Deep Azure and Microsoft ecosystem | Broad connectors across vendors |
| Governance | Centralized and built-in | Strong, often tied to data platform |
| Ease of Use | Familiar for Microsoft users | Very intuitive for analysts |
| Pricing Model | Capacity and consumption-based | Per-user licensing |
| Ideal Choice | If you want one analytics platform | You prioritize visualization depth |
Features Comparison: Data Visualization and Analytics Capabilities
This section compares visualization, analytics, modeling, and advanced capabilities that matter when evaluating adoption, developer productivity, and business impact.
1. Visualization and Dashboarding
Fabric delivers visualization through Power BI experiences with modern dashboards, interactive visuals, and parameter-driven reporting. Tableau is widely recognized for visualization polish, custom charting capabilities, and ad-hoc exploration freedom. The 2026 Tableau release improved the Show Me feature to display all visualization types upfront, making exploration easier for new users. Power BI in Fabric focuses on integrated semantic models and enterprise distribution at scale.
If pixel-perfect visual storytelling and rapid exploratory analysis are core requirements, Tableau maintains an edge. If governed, repeatable reporting and single-model distribution matter most; Fabric wins. Direct Lake mode in Fabric provides real-time dashboard updates without scheduled refreshes, connecting directly to OneLake for continuously fresh insights.
2. Data Modeling and Semantic Layers
Tableau relies on data extracts, published data sources, or external semantic layers created in upstream platforms. Organizations typically build semantic layers in data warehouses or dedicated tools before connecting to Tableau.
Fabric centralizes semantic modeling as part of the platform via OneLake and shared datasets, supporting consistent metrics across the organization and reducing duplication. This approach favors organizations requiring a single source of truth across many reports and teams.
3. Data Preparation, ETL, and Pipelines
Tableau Prep provides basic data preparation capabilities with visual workflows for cleaning and shaping data. The 2026 release added spatial calculations, including MakePoint, MakeLine, and Buffer functions. However, complex transformations and large-scale data engineering typically require third-party ETL tools or cloud pipelines.
Fabric includes integrated pipeline and ETL capabilities through Data Factory, Dataflow Gen2, and lakehouse-native transforms. Data engineering, transformation, and BI can be managed in one place, reducing handoffs and simplifying end-to-end automation. The January 2026 High Concurrency mode reduced Spark operation startup from 3-5 minutes to under 5 seconds for subsequent jobs.
4. Advanced Analytics and AI
Tableau 2026 features Tableau Agent, an AI assistant built on Einstein Copilot that helps users create calculations and receive visualization recommendations via natural language. Tableau Pulse provides automated insights explaining metric changes. Enhanced Q&A capabilities allow conversational questions about data with intelligent responses.
Fabric ties analytics to Azure Machine Learning, notebook experiences, and Microsoft Copilot integrations for model-driven insights and operationalization. Fabric IQ, introduced at Microsoft Ignite, provides a semantic data layer with Ontology capabilities for mapping data to business meaning. The Osmos acquisition brings autonomous AI agents that manage end-to-end data workflows and automatically generate production-grade PySpark notebooks.
5. Performance and Scale
Tableau scales effectively for interactive visualization across many data sources, but large-scale analytics workloads often rely on enterprise data platforms beneath Tableau for processing power.
Fabric architecture is designed for scale with capacity-based compute and lakehouse storage, reducing data movement and accelerating large-query workloads. Recent updates add caching and query optimizations aimed at repetitive performance patterns common in enterprise reporting.
6. Data Source Coverage and Connectors
Tableau supports over 75 native connectors across databases, cloud warehouses, and SaaS applications. The January 2026 release added AWS Private Link support for secure connections to AWS-hosted databases without public internet exposure.
Fabric leverages Azure connectivity and supports common cloud sources, favoring scenarios where data already resides on Azure or where organizations want to centralize on Microsoft services. OneLake shortcuts enable connecting to AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, and ADLS Gen2 without copying data.
Partner with Kanerika for help.
Move Your Azure Workloads to Microsoft Fabric for a Unified Setup.
Pricing: Microsoft Fabric vs Tableau Cost Analysis
Pricing model and total cost of ownership often decide platform selection. The two platforms use materially different cost approaches, so direct comparisons need careful context.
How Each Vendor Structures Cost
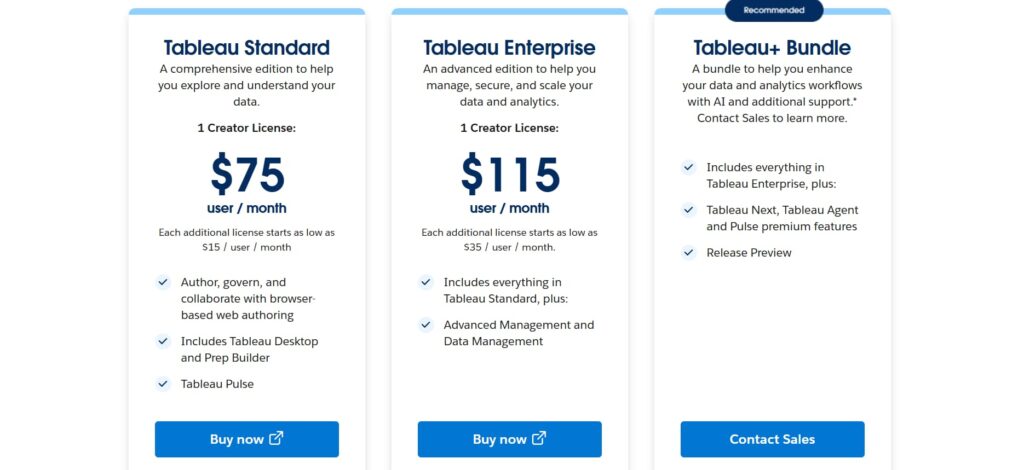
Tableau Pricing is per-user and role-based with Creator, Explorer, and Viewer tiers. This approach is straightforward for licensing but requires consideration of user mix and adoption patterns.
- Creator licenses: $75 per user per month when billed annually ($900 per year), including Tableau Desktop, Prep Builder, and publishing rights
- Explorer licenses: $42 per user per month ($504 per year) for interacting with published data and creating custom views
- Viewer licenses: $15 per user per month ($180 per year) for consuming dashboards with filtering and exporting capabilities
Microsoft Fabric Pricing uses capacity and meter-based pricing for compute, measured in Capacity Units (CUs) that bundle CPU, memory, and I/O.
- SKUs range from F2 at $262.80 monthly to F2048 at $269,107.20 monthly
- Reserved capacity offers approximately 40 percent savings versus pay-as-you-go pricing
- OneLake storage costs $0.023 per GB monthly (about $23 per TB)
- Below F64 capacity, users need Power BI Pro licenses at $10 per month
- F64 and above eliminate viewer license requirements, making it cost-effective for organizations with large viewing audiences
Key Cost Drivers to Evaluate
- User Licensing Versus Capacity: Tableau is user-centric, with costs scaling linearly by headcount. Fabric is consumption and capacity-centric. If you have many passive viewers, Tableau per-user costs may rise significantly. If you run heavy, repeated compute jobs, Fabric consumption can dominate costs.
- Data Storage and Egress: In Fabric, OneLake storage, and associated Azure storage costs must be factored into the total cost. Tableau deployments paired with cloud storage will have separate storage costs depending on your chosen data platform.
- ETL and Pipeline Costs: Fabric bundles data engineering tools whose runtime costs are meter-based and included in capacity pricing. With Tableau, ETL costs come from separate tools such as Tableau Prep or cloud data pipelines.
- Management, Governance, and Admin Overhead: A consolidated platform like Fabric can reduce integration and governance overhead. A mixed stack with Tableau plus external data engineering can increase operational costs unless integrated tightly.
Practical Pricing Scenarios
Small Business (10 Users) A company with 2 creators and 8 viewers pays approximately $3,240 annually for Tableau. The same company using Fabric F4 capacity plus Pro licenses and storage pays around $7,783 annually. Tableau is cheaper for small, purely visualization needs.
Mid-Size Organization (100 Users) With 10 creators, 30 explorers, and 60 viewers, Tableau costs approximately $34,920 annually. Fabric F64 capacity with Pro licenses only for creators totals around $104,875 annually. Fabric includes unlimited viewers and complete data platform capabilities that justify the premium for comprehensive analytics needs.
Practical Pricing Guidance
- Create a usage profile – Estimate the number of creators, explorers, and viewers for Tableau. For Fabric, estimate compute hours for transformation jobs, warehousing queries, and expected storage volumes.
- Model multi-year total cost of ownership – Include license fees, cloud compute, storage, ETL tooling, integration work, and governance overhead. Platform consolidation may have higher near-term migration costs but lower ongoing operational costs.
- Use vendor calculators and run proof of value projects – Both Tableau and Microsoft provide cost calculators and trial options. For Fabric, capacity choices and reserved pricing can materially change the cost profile, so test on expected workloads.
Ease of Use: Learning Curve and User Experience
User experience often decides adoption faster than raw features. Tableau is built around fast visual exploration and drag-and-drop authoring that many analysts find intuitive from day one. Power BI experiences inside Microsoft Fabric favor integration with Microsoft ecosystems, familiar Office-like interactions, and a model-driven approach that feels more structured to analysts accustomed to governed metrics.
1. What to Expect for Different User Groups
Business Analysts and Data Storytellers
- Tableau enables quick prototyping, visual tweaking, and iteration without heavy IT support. This gives Tableau an edge for ad hoc exploration and presentation-ready dashboards. Most users create basic charts within their first day using Tableau.
- Fabric (Power BI) is fast for teams already using Excel and Power Platform. The semantic model and shared datasets make scaling reports easier, but authors may need to learn modeling best practices. Business analysts familiar with Microsoft tools typically achieve basic reporting in 1-2 weeks.
Data Engineers and Platform Teams
- Fabric includes built-in pipelines, OneLake, and Data Factory tooling that reduce handoffs between engineering and analytics. This makes operational tasks and automation simpler to run and maintain. Understanding lakehouses, pipelines, and distributed computing is necessary for effective use.
- Tableau often relies on separate ETL or data engineering platforms. This gives flexibility but requires more orchestration and integration work across tools.
2. Learning Curve and Adoption Patterns
- Expect Tableau to offer faster initial adoption for pure visualization teams. The 2026 Tableau Public Help Agent provides instant answers and personalized education, accelerating learning for beginners and experts.
- Expect Fabric to require more upfront learning on platform modeling, pipelines, and governance, but then deliver consistent, reusable assets. Microsoft provides DP-600 (Fabric Analytics Engineer) and DP-700 (Fabric Data Engineer) certifications with free Learn modules.
3. Practical Tips for Easing Adoption
- Start with a small pilot focused on real user needs, not proof-of-concept vanity dashboards. Build use cases that deliver immediate business value.
- Pair experienced modelers with visual authors to share best practices and accelerate skill transfer.
- Build a short internal training track covering core modeling concepts, governance basics, and common visualization patterns.
- Monitor adoption metrics and gather user feedback regularly to identify friction points and training gaps.
Integration and Compatibility: Ecosystem Advantages
Integration is not only about how many connectors a tool provides. It concerns how seamlessly the platform fits into your existing data estate, how it supports data pipelines, and how governance and security flow from source to insight.
Key Integration Strengths
Tableau provides very broad connector coverage across databases, cloud data warehouses, and SaaS applications. This makes Tableau flexible in multi-cloud and multi-vendor environments. The platform works effectively with specialized data preparation or integration tools when complex transformations are required. January 2026 added AWS Private Link support and programmatic SAML configuration through REST APIs.
Microsoft Fabric uses OneLake as a central data layer, reducing data movement when working with Azure services like Synapse, Data Factory, and Copilot for analytics. This lowers integration friction for Azure-first organizations. Fabric includes native runtime for pipelines, transformations, and governance, reducing the need for external orchestration. The January 2026 update added GitHub Enterprise Cloud integration with data residency support for professional development workflows.
Compatibility Considerations
- If your organization is cloud-agnostic and uses multiple data warehouses across different vendors, Tableau may offer faster connector coverage and lower upfront integration work.
- If your organization is standardizing on Azure or already uses Microsoft services at scale, Fabric reduces handoffs, simplifies governance, and can lower operational complexity significantly.
Integration Comparison Table
| Integration Factor | Microsoft Fabric | Tableau |
| Native Cloud Platform | Strong for Azure; OneLake centralizes storage | Platform neutral; depends on chosen data lake/warehouse |
| Connector Breadth | Good for Azure and common cloud sources; growing third-party support | Very broad native connectors to databases, warehouses, and SaaS |
| Data Engineering Support | Built-in pipelines and transformation runtimes (Data Factory, lakehouse) | Typically relies on external ETL/ELT tools or cloud pipelines |
| Governance and Lineage | Integrated cataloging and governance via OneLake and Fabric services | Strong governance features but often requires tied-in data platform |
| Best Fit | Azure-first enterprises seeking end-to-end analytics stack | Organizations needing broad connectivity and best-in-class visualization |
Microsoft Fabric vs Tableau: Which Should You Choose?
Choosing between Fabric and Tableau is less about which product is technically superior and more about which approach matches your architecture, governance needs, and user base.
Choose Microsoft Fabric If
- Your data estate is heavily invested in Azure, or you plan to standardize on Microsoft cloud services. Fabric reduces integration work and centralizes governance via OneLake.
- You want a single vendor stack handling ingestion, transformation, governance, analytics, and operationalization in one place. Fabric favors platform consolidation and asset reuse.
- You need to operationalize machine learning and AI workflows close to data. Fabric’s notebooks, Azure ML integration, and Copilot features streamline this workflow path.
- Large viewing audiences can benefit from cost savings, as F64 capacity and above eliminate per-user viewer licenses, while Tableau charges for every viewer.
- Real-time analytics and streaming data processing are business requirements. Fabric’s Real-Time Intelligence with Eventhouse and Direct Lake mode provides native streaming capabilities.
Choose Tableau If
- Visual quality, rapid exploration, and a wide connector ecosystem are top priorities. Tableau gives analysts the freedom to explore many data sources without waiting for centralized engineering.
- Your environment is multi-cloud or includes many third-party data sources, where a neutral BI layer is preferable. Tableau’s connector library is an advantage in heterogeneous environments.
- You expect to onboard a broad, non-technical user base quickly and want a strong design-first visualization experience.
- Salesforce CRM integration is essential for sales and customer analytics. Tableau’s native Salesforce connectivity and pre-built analytics accelerate deployment.
- Small teams need quick visualization capabilities without implementing complex platform infrastructure.
Decision Checklist for Practical Selection
- Model a practical proof of value measuring the full cost of ownership, including compute, storage, ETL, and governance overhead. Vendor calculators and small pilots are useful for realistic cost projections.
- Assess your primary cloud and data platform – If Azure-based, Fabric is a natural fit. If heterogeneous across multiple clouds, Tableau may integrate more simply.
- Determine if you are optimizing for visualization speed or platform consolidation – Pick Tableau for speed and flexibility, Fabric for consolidation and governance.
- Evaluate whether you need to operationalize AI and ML next to where data lives. Fabric’s native integrations provide advantages for machine learning workflows.
- Consider implementation timelines – Tableau deployments for visualization-only needs typically complete in 2-4 weeks for small teams. Fabric implementations for complete platform capabilities typically require 3-6 months for initial deployment, including data engineering setup.
Final Recommendation
Both Microsoft Fabric and Tableau represent mature, capable platforms backed by major technology companies. Your organization can succeed with either choice when implementation, training, and adoption receive appropriate investment and attention. The decision should align with your existing infrastructure, technical capabilities, user base size, and whether you need comprehensive data engineering or focused business intelligence capabilities.
Choosing the Right Analytics Platform with Kanerika
Kanerika is a certified Microsoft Data & AI Solutions Partner that helps enterprises adopt Microsoft Fabric to modernize their analytics platforms. Our team of certified experts and Microsoft MVPs builds scalable, secure, and business-focused data ecosystems that simplify complex environments, support real-time analytics, and strengthen governance using Fabric’s unified architecture.
We support organizations in upgrading legacy data platforms through structured migration and automation-first approaches. Since manual migrations are time-consuming and prone to errors, Kanerika uses automation tools, including FLIP, to enable smooth transitions from SSRS to Power BI, SSIS and SSAS to Microsoft Fabric, and Tableau to Power BI. This improves data access, increases reporting accuracy, and reduces long-term maintenance effort.
As one of the early global adopters of Microsoft Fabric, Kanerika follows a proven delivery framework that spans architecture design, semantic modeling, governance setup, and user training. Combined with FLIP’s automated DataOps capabilities, our approach helps organizations roll out Fabric faster, keep data secure, and realize business value with minimal effort and clear outcomes.
Drive Business Growth with Microsoft Fabric Analytics!
Partner with Kanerika for Smooth and Scalable Fabric Adoption
FAQs
What is the Microsoft equivalent of Tableau?
Microsoft doesn’t have a single, direct equivalent to Tableau. Power BI is its closest counterpart, offering similar data visualization and business intelligence capabilities. However, Tableau often boasts more advanced analytical features and a stronger reputation within certain data science communities. The best choice depends on specific needs and preferences.
What is the difference between Salesforce and Microsoft Fabric?
Salesforce focuses on customer relationship management (CRM), helping businesses manage interactions with customers. Microsoft Fabric is a data integration and analytics platform, focusing on consolidating and analyzing data from various sources for business intelligence. Essentially, Salesforce manages who your customers are, while Fabric helps you understand what your customers are doing based on their data. They serve distinct but potentially complementary business needs.
What is Microsoft Fabric in Azure?
Microsoft Fabric is Azure’s all-in-one analytics platform. It integrates data warehousing, data integration, real-time analytics, and more into a single, unified environment. This simplifies data management and analysis by eliminating the need for stitching together various disparate tools. Think of it as a one-stop shop for all your data needs within Azure.
Why is Tableau so expensive?
Tableau’s high cost reflects its comprehensive suite of powerful data visualization and analytics tools, catering to both individual users and large enterprises with complex needs. It bundles advanced features, robust data connectivity, and strong collaborative capabilities not found in free alternatives. The price also incorporates ongoing support, maintenance, and frequent software updates. Essentially, you’re paying for a complete, sophisticated solution, not just a basic charting program.
Is Tableau owned by Microsoft?
No, Tableau is not owned by Microsoft. While Microsoft offers its own business intelligence tools, Tableau remains an independent entity, now a part of Salesforce. This means they operate separately, offering distinct features and approaches to data visualization. The two companies compete in some areas but also cooperate in others.
Is SQL used in Tableau?
No, SQL isn’t directly used within Tableau’s interface. Instead, Tableau connects to databases (like those using SQL) to retrieve data. Think of it as Tableau using SQL behind the scenes to pull the information it needs for your visualizations. You write SQL queries separately to prepare or refine data before bringing it into Tableau.
Does Tableau require coding?
No, Tableau’s primary interface is drag-and-drop, making coding unnecessary for most users. However, for advanced customization and integration with other systems, knowledge of scripting languages like R or Python can significantly enhance its capabilities. Think of it as: you can build a stunning visualization without coding, but coding unlocks advanced features.
How long does it take to learn Tableau?
Mastering Tableau isn’t about a specific timeframe, it’s a journey. Your learning speed depends on prior data analysis experience and your desired proficiency level. Expect a few weeks for basic competency, but months or even years for advanced techniques and efficient data storytelling. Think of it as learning a new language – fluency takes time and consistent practice.
Is Tableau compatible with Microsoft?
Yes, Tableau integrates well with the Microsoft ecosystem. You can connect Tableau to various Microsoft data sources like SQL Server, Excel, and Azure. However, direct integration with specific Microsoft apps varies; check Tableau’s documentation for the most up-to-date compatibility details. Essentially, while generally compatible, specific features’ integration might require further setup.
What is Tableau CRM called now?
Tableau CRM is no longer. Salesforce integrated its functionality directly into Salesforce, making it a core part of the platform rather than a separate product. Think of it as evolving, not being renamed; its features are now accessible within the Salesforce ecosystem. It’s now simply part of Salesforce’s analytics capabilities.
What is the best data visualization tool?
There’s no single “best” data visualization tool; the ideal choice depends on your specific needs and skills. Consider factors like data size, complexity, desired interactivity, and your budget. Popular options range from versatile tools like Tableau and Power BI to specialized libraries in programming languages like Python (Matplotlib, Seaborn). Ultimately, the best tool is the one that effectively communicates your data insights.
What are the two versions of Tableau?
Tableau offers two main product lines: Tableau Desktop, for individual data analysis and visualization, and Tableau Server/Online, for collaborative data sharing and centralized management. Desktop focuses on individual creation, while Server/Online prioritizes team work and governed data distribution. Think of Desktop as your personal studio and Server/Online as the gallery showcasing your work.










