A data migration checklist is more than a planning document; it is a practical control framework that helps enterprises move data safely, accurately, and with minimal disruption. But ask yourself: Why do so many data migrations still run over budget, miss deadlines, or fail outright? The answer is often simple; there is no structured checklist guiding the process from start to finish.
Without a clear checklist, migration teams overlook critical steps such as data quality validation, dependency analysis, and compliance controls. As a result, organizations face common risks including data loss, extended downtime, regulatory gaps, and expensive rework. According to IBM, poor data quality alone costs organizations an average of $12.9 million per year, a risk that increases significantly during migrations if checks are missing.
Therefore, a structured data migration checklist becomes essential. It brings repeatability, governance, and accountability to complex migration programs. The purpose of this blog is to provide a practical, end-to-end data migration checklist that enterprises can actually follow from planning and execution to validation and post-migration success.
Key Learnings
- A structured data migration checklist is essential to reduce risks such as data loss, downtime, compliance gaps, and costly rework.
- Most migration failures occur due to skipped planning steps, poor data quality checks, and missing governance controls.
- A checklist brings repeatability, accountability, and clarity across all migration phases from assessment to post-migration validation.
- Data migration success depends not only on tools but also on strong validation, security, and compliance processes.
- CIOs, data leaders, and migration teams can use a standardized checklist to deliver faster, safer, and business-ready migrations.
Accelerate Your Data Transformation by Migrating to Power BI!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Modernization Services
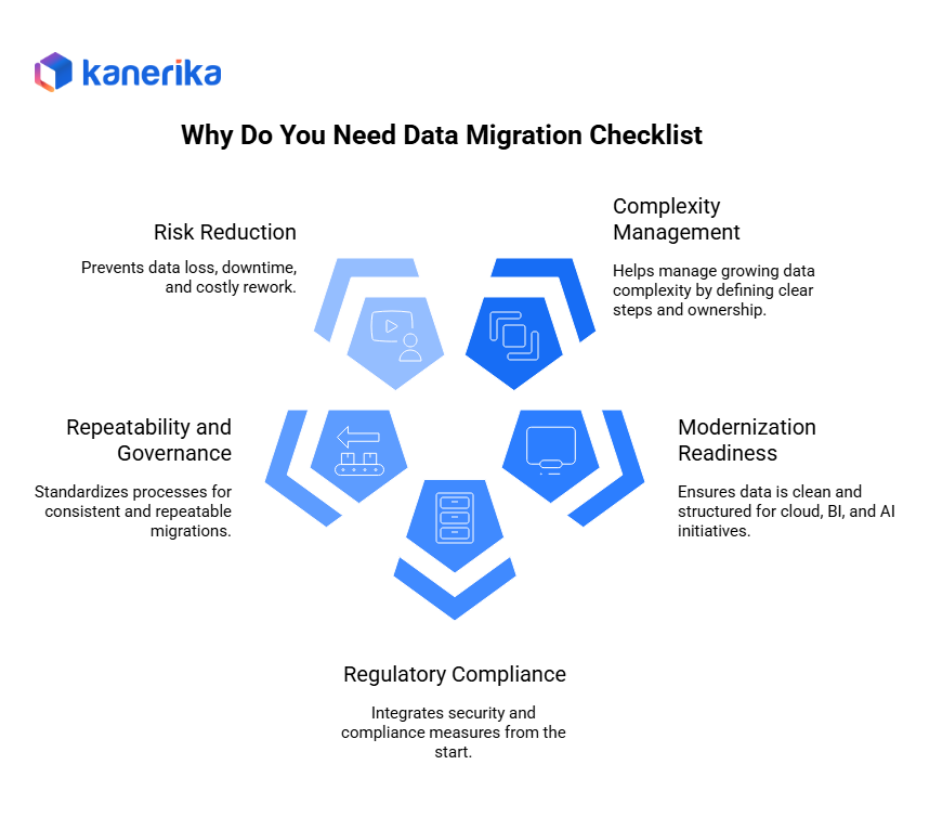
Why You Need a Data Migration Checklist?
1. Data Environments Are Getting More Complex
Most companies now have data scattered across on-prem systems, cloud platforms, SaaS tools, data warehouses, and lakehouse setups. The average enterprise uses over 400 different SaaS applications, and each one generates data that needs managing. More data keeps piling up, and more sources keep getting added. Controlling all of this during a migration gets complicated fast.
A checklist helps by laying out what needs to happen, who does it, and what depends on what. Companies that use structured checklists report 40% fewer migration failures compared to those that don’t.
2. Modern Initiatives Depend on Clean Data
Cloud adoption, BI modernization, and AI-driven analytics all need data that’s clean, reliable, and structured correctly. Without a checklist, critical tasks get skipped. Schema alignment gets forgotten, data quality checks get missed, and pipeline prep falls through the cracks.
One financial services company learned this the hard way when its BI modernization project stalled for six months because it discovered data quality issues only after migration. The cost of fixing bad data post-migration can be 10 times higher than addressing it upfront.
3. Compliance Pressure Keeps Increasing
Companies face growing pressure from regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and SOX. GDPR violations alone can cost up to 4% of annual global revenue. A checklist builds security controls, access rules, encryption, and audit trails into the process from the start. This beats scrambling to patch things together later when regulators come knocking.
4. Repeatable Processes Save Time and Money
Checklists create standards that make future migrations easier. When you migrate data more than once (and most companies do this every 2-3 years), having a repeatable process saves significant time and effort. Teams can complete subsequent migrations up to 60% faster when they follow a proven checklist.
5. Prevention Costs Less Than Fixes
Data loss, downtime, and expensive fixes happen when migrations go wrong. IBM estimates that the average cost of data loss is $3.86 million per incident. A good checklist keeps you on track through planning, testing, validation, and monitoring. You get better accuracy, faster execution, and results you can actually use.
Pre Data Migration Checklist: Planning & Readiness
A strong data migration starts long before any data is moved. Therefore, a well-defined pre-migration checklist helps enterprises reduce risk, control costs, and ensure successful outcomes. This phase focuses on strategy, assessment, data quality, and governance areas that directly impact migration success.
1. Business & Strategy Readiness
First, clearly define why migration is happening. Common objectives include cloud migration, BI modernization, regulatory compliance, cost optimization, and AI/ML readiness. At this stage, enterprises should define measurable success metrics such as reduced reporting latency, improved data accuracy, lower infrastructure costs, or faster analytics delivery.
Next, align migration goals with business SLAs, timelines, and operational priorities. This ensures that critical systems are not disrupted during peak business periods. In addition, identify executive sponsors, data owners, IT leads, and security stakeholders. Clear ownership and accountability improve decision-making and prevent delays during execution.
2. Current-State Assessment
Once objectives are clear, perform a detailed current-state assessment. Begin by creating a complete inventory of source systems, including databases, data warehouses, files, ETL pipelines, BI reports, and downstream consumers. This visibility helps uncover hidden complexity early.
After that, identify legacy dependencies and integrations, such as upstream applications, batch jobs, APIs, and third-party tools. Many migration risks come from undocumented dependencies. At the same time, assess data volumes, historical data retention needs, and future growth patterns. This step is critical for sizing cloud storage, compute resources, and migration timelines accurately.
3. Data Quality & Profiling
Data quality is one of the most common migration challenges. Therefore, before migration begins, profile source data for completeness, accuracy, duplicates, and inconsistencies. This step helps avoid moving bad data into modern platforms.
In addition, identify schema drift, mismatched data types, and inconsistent naming conventions across systems. Early detection allows teams to standardize schemas and reduce transformation complexity later. Finally, flag sensitive and regulated data such as PII, PHI, and financial records, as these require special handling during migration.
4. Governance & Compliance Readiness
Finally, ensure governance and compliance are built into the migration plan from day one. Identify all applicable regulations, including GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and SOX, based on industry and geography.
Define role-based access control, data classification standards, and approval workflows. Plan encryption for data at rest and in transit, masking or tokenization for sensitive fields, and audit logging for traceability. When governance is addressed early, enterprises avoid rework, security gaps, and compliance risks after migration.
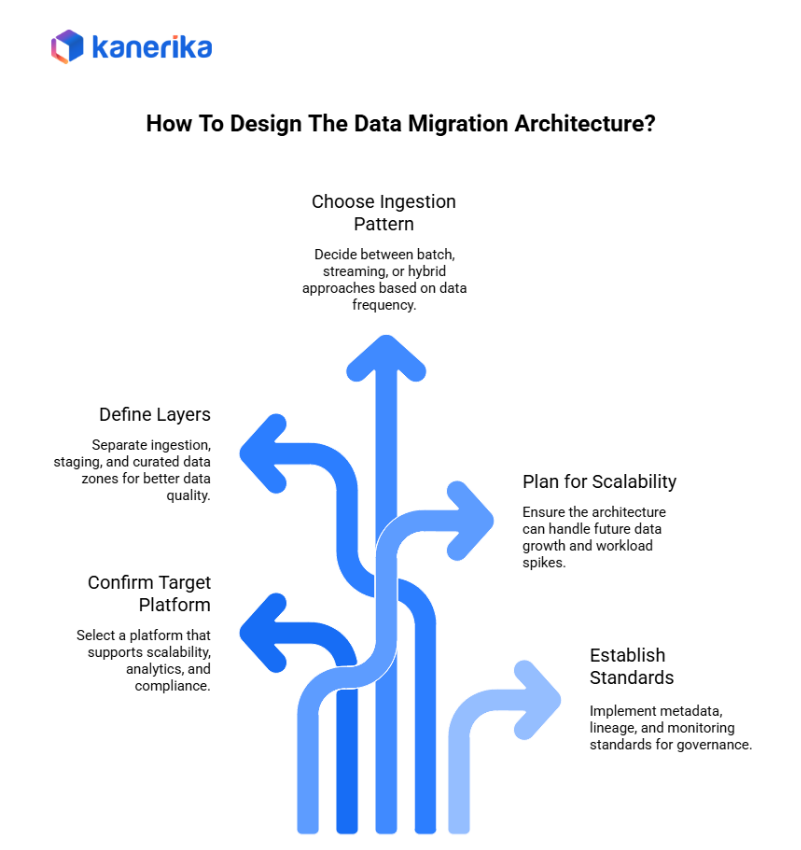
Data Migration Checklist: Architecture & Design
A well-defined architecture is critical to executing a reliable and scalable data migration. Therefore, before implementation begins, enterprises should validate architectural decisions using a clear checklist. This step ensures performance, governance, and long-term flexibility.
1. Choose the Right Target Platform
Decide where the data is actually going based on your business and technical requirements. Options include cloud-native data lakes for raw data storage, modern data warehouses for structured analytics, or lakehouse platforms like Databricks, Snowflake, or Microsoft Fabric that combine both approaches.
Whatever you choose needs to handle scale effectively. A media company processing 50TB of daily log data needs different infrastructure than a retail chain analyzing point-of-sale transactions. The platform should work well for your specific analytics and AI workloads while meeting compliance requirements. Make sure it aligns with where you want your data strategy to go long term, not just what solves today’s problem.
2. Set Up Proper Data Layers
Don’t just dump everything in one place. Separate your ingestion zone from staging and from your clean, curated data. This layered approach (often called bronze, silver, gold) makes quality management easier, simplifies transformations, and gives you better access control.
A good layered setup also helps when something breaks because you can troubleshoot without messing up downstream systems. A financial institution saved two weeks of debugging time by having clear layer separation when a data quality issue appeared. They could isolate the problem to the ingestion layer without impacting their production reports.
3. Choose Your Ingestion Pattern
Decide how you’re moving data into the system. Batch processing works fine for historical data and information that doesn’t change frequently, like monthly sales summaries or quarterly financial reports. Streaming handles real-time needs and operational reporting, such as website clickstreams or IoT sensor data.
Most companies end up using both approaches. A hybrid model gives you the performance you need without driving up costs unnecessarily. An e-commerce company uses batch loading for historical orders but streams current shopping cart data for real-time inventory management.
4. Plan for Growth
Your data volume is going to grow, so plan for it now. Industry data shows enterprise data grows at 40-60% annually on average. Consider your partitioning strategy (date-based partitioning reduces query costs by 70% in many cases), compute sizing, autoscaling capabilities, and query optimization.
Getting these right means your platform keeps performing well as you add more data. A SaaS company properly architected its data platform to handle 10x growth over three years without a major redesign. Planning properly also keeps your cloud costs under control as you scale.
5. Establish Metadata and Monitoring Standards
Set clear standards for metadata management, lineage tracking, and monitoring. A central catalog shows what data you have and where it lives. Lineage tracking reveals where data comes from and where it goes, which is critical when something goes wrong or when regulators ask questions.
Pipeline monitoring keeps tabs on job performance and alerts you to problems. Companies with comprehensive monitoring detect and resolve data issues 5x faster than those relying on user reports. These capabilities improve governance and make audits much easier. You get real visibility into what’s happening across your entire data setup.
Data Migration Execution Checklist
Planning is done and architecture is set. Now comes the actual migration phase. Research shows that 83% of data migration projects exceed their original timeline, usually because of issues discovered during execution.
1. Validate Mappings and Transformations
Check all your source-to-target mappings before you start moving data. Every column, data type, and relationship needs to line up correctly with the target schema. An insurance company once mapped date fields incorrectly, converting all policy start dates to UTC without accounting for time zones. The fix took three months and cost $1.2 million.
Standardize naming and formatting across systems. Review business rules and transformation logic carefully, especially calculations, aggregations, and currency conversions. These directly affect your reports and analytics.
2. Select the Right Migration Strategy
Big bang migration works for smaller systems where everything moves at once. For complex environments, phased migration is safer. A manufacturing company successfully migrated 15 years of production data by moving one plant at a time over six months.
For critical systems, run old and new platforms in parallel first. A bank caught 47 data transformation issues during a 90-day parallel run that would have disrupted customer accounts.
Need zero downtime? Use Change Data Capture (CDC) to replicate changes continuously. Plan cutover windows carefully and have rollback plans ready.
3. Automate for Reliability
Automate your pipelines for repeatable execution. Use orchestration tools like Apache Airflow, Azure Data Factory, or AWS Step Functions to handle dependencies between jobs.
Set up error handling, automatic retries, and alerts. One company reduced migration failures by 65% simply by implementing proper retry logic. Track metrics like records processed per minute, error rates, and data quality scores in real time. Companies using real-time monitoring complete migrations 40% faster on average.
4. Test Continuously
Validate row counts and checksums between source and target systems as you migrate. A pharmaceutical company caught a critical issue during incremental testing, where 15% of clinical trial data wasn’t transferring due to character encoding problems.
Confirm that reports match, dashboards show correct numbers, and downstream applications work properly. Business validation has prevented countless issues from reaching production.
5. Maintain Security Throughout
Keep role-based access in place, maintain encryption for data in transit (TLS 1.2 or higher), and continue masking sensitive information. Audit logs should capture who accessed what data and when. A healthcare provider avoided a $500,000 fine by maintaining proper audit trails during their migration.
6. Testing Everything Properly
Testing confirms the data transferred correctly and everything still works. Companies that conduct thorough testing catch 95% of issues before go-live, while those that skip testing face an average of 23 critical issues in the first month.
Check row counts and checksums between old and new systems. A retail chain discovered 50,000 missing customer records during testing, avoiding a customer service disaster.
Data Migration Checklist: Testing & Validation
Testing and validation are critical to ensuring data accuracy, trust, and business continuity after migration. Therefore, a structured testing checklist helps enterprises reduce migration risks, avoid data loss, and ensure reliable analytics outcomes.
1. Testing and Validation
Testing confirms the data transferred correctly. Companies that test thoroughly catch 95% of issues before go-live, while those that skip testing face an average of 23 critical problems in the first month.
2. Check Row Counts and Checksums
Compare row counts and checksums between source and target systems. This spots missing records, duplicates, or partial loads early. A retail chain discovered 50,000 missing customer records during testing, avoiding a customer service disaster.
3. Validate Schemas and Data Types
Check that column names, data types, constraints, and relationships match your target design. When they don’t, things break downstream. One tech company spent $300,000 fixing schema mismatches that reached production because they skipped this step.
4. Test Business Rules
Reconcile key metrics and calculations between old and new systems. Financial totals need to match exactly. A financial services firm caught a calculation error during testing that would have misreported $50 million in quarterly earnings.
5. Run Performance Tests
Test query speeds, refresh times, and pipeline execution against your SLAs. A logistics company found that their new system was 5x slower than expected during testing, giving them time to optimize before launch.
6. Conduct User Acceptance Testing
Get business users involved in UAT. Real users catch things technical teams miss. During UAT at a healthcare provider, analysts discovered that patient demographics weren’t displayed correctly across 12 reports.
7. Define Sign-Off Criteria
Set clear criteria before go-live. Examples include 99.9% data accuracy, less than 5% performance degradation, zero critical security findings, and written approval from key stakeholders.
How to Migrate from SSRS to Power BI: Enterprise Migration Roadmap
Discover a structured approach to migrating from SSRS to Power BI, enhancing reporting, interactivity, and cloud scalability for enterprise analytics.
Post Data Migration Checklist
Going live isn’t the finish line. Post-migration work ensures everything stays reliable and performs well over time. Data shows that 60% of migration issues surface within the first 30 days post-launch, making this phase critical.
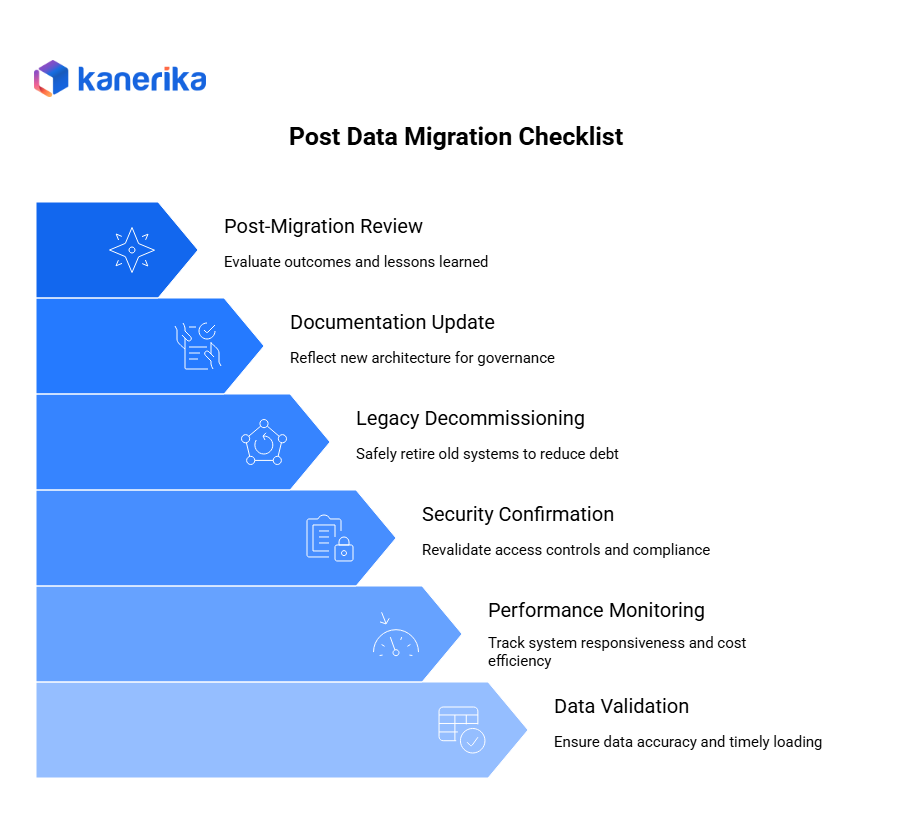
1. Validate Data Freshness and Accuracy
Keep validating that data is loading on schedule and stays accurate across all systems. Compare refresh times, timestamps, and key metrics against your agreed SLAs. Business users need to trust what they see right away because any delays or accuracy problems will make people stop using the new system.
Set up automated data quality monitoring that runs daily. Track metrics like completeness (percentage of required fields populated), accuracy (comparison against known good sources), and timeliness (data freshness). A media company prevented a major revenue reporting error by catching a data feed delay within hours of it starting.
2. Monitor Performance and Costs
Monitor query performance, pipeline execution times, and overall system responsiveness closely. Track your cloud usage and spending at the same time because you’ll likely find inefficiencies. Cloud costs can increase by 30-50% in the first three months if not monitored properly.
Fix performance and cost issues early before they spiral out of control. Optimize compute resources, storage allocation, and job scheduling based on what you’re actually seeing in production. One company reduced its monthly cloud bill from $85,000 to $52,000 by identifying and fixing inefficient queries and over-provisioned resources in the first 60 days.
3. Confirm Security and Access Controls
Revalidate security configurations after migration. Make sure role-based access control works correctly, encryption is active, masking is functioning, and audit logging is running properly. Run penetration tests if your security policies require them.
This step is especially critical for compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and SOX. Security gaps that appear after migration create a real risk. A financial institution discovered post-migration that audit logging wasn’t capturing database queries, which would have been a SOX violation. They caught and fixed it during their security review.
4. Decommission Legacy Systems Safely
Once you’ve confirmed stability in the new system (typically after 30-90 days of smooth operation), plan how to decommission legacy systems in a controlled way. Retire old databases, ETL jobs, and reports in phases rather than all at once.
Don’t rush this process because that’s when accidental data loss happens. Keep read-only access to legacy systems for 6-12 months for comparison purposes and regulatory requirements. Proper decommissioning reduces technical debt and cuts ongoing infrastructure costs. Companies typically save 40-60% on infrastructure costs after properly retiring legacy systems.
5. Update Documentation and Lineage
Update technical documentation, data dictionaries, and lineage records to reflect the new architecture accurately. Document key decisions, workarounds implemented, and lessons learned. Good documentation improves governance, supports audits, and makes future enhancements or migrations much simpler.
Include runbooks for common operational tasks, troubleshooting guides for known issues, and contact information for subject matter experts. Teams with comprehensive documentation resolve issues 70% faster than those with poor documentation.
6. Conduct a Post-Migration Review
Conduct a formal post-migration review with IT, data, security, and business stakeholders within 60 days of go-live. Talk about what worked well and what didn’t. Identify gaps and areas for improvement.
Capture these lessons learned in a structured format because they’ll make your next migration better and help with the continuous improvement of your data platform. One enterprise created a lessons learned database from five migrations that reduced their average migration time from 9 months to 5 months by avoiding repeated mistakes.
Common Checklist Gaps to Avoid
Even with a data migration checklist, certain gaps can significantly increase migration risk if overlooked. Therefore, understanding and avoiding these common mistakes is critical for a successful migration.
- First, skipping data quality checks often leads to inaccurate reports, broken analytics, and low trust in the migrated data. Data profiling and validation should always happen before and during migration, not after issues appear.
- Next, underestimating system dependencies creates hidden failures. Many enterprises overlook upstream applications, downstream reports, APIs, and scheduled jobs. As a result, migrations may break critical workflows once systems go live.
- Ignoring compliance requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or SOX exposes organizations to regulatory and security risks. Governance and security controls must be embedded into the checklist from the start.
- Relying on manual validation only is another major gap. Manual checks are slow and error-prone. Automated reconciliation, checksums, and rule-based validation improve accuracy and scalability.
- Finally, not having a rollback or contingency plan leaves teams unprepared for failures. A well-defined rollback strategy ensures business continuity and reduces downtime during unexpected issues.
Simplifying Data Platform Migrations with Kanerika’s FLIP Migration Accelerators
Kanerika’s data migration strategy centers on FLIP, an AI-powered, low-code/no-code DataOps platform that automates discovery, schema mapping, transformation, validation, lineage extraction, and cutover. FLIP’s migration accelerators can automate 70-80% of repetitive migration work, cutting timelines and reducing human error while keeping business logic and data relationships intact.
FLIP supports multiple migration pathways designed for modern cloud migration and data modernization:
- Cognos / Crystal Reports / SSRS / Tableau → Microsoft Power BI Streamlines the migration of reports, dashboards, calculations, and filters into Power BI while maintaining reporting intent and usability.
- Informatica → Alteryx / Databricks / Microsoft Fabric / Talend Automates the conversion of Informatica workflows and transformations into modern data engineering and analytics platforms.
- Microsoft Azure → Microsoft Fabric Aligns existing Azure data pipelines and workloads with Fabric’s unified analytics architecture for simpler governance and scale.
- SQL Services → Microsoft Fabric Modernizes legacy SQL Server workloads into scalable, secure, and governed Fabric-based solutions.
- UiPath → Microsoft Transitions automation workflows into Microsoft-native environments for tighter integration across the data and analytics stack.
These accelerators help organizations modernize faster, reduce dependence on manual rebuilds, and move confidently toward cloud-ready, analytics-driven platforms.
FAQs
1. What is an enterprise data migration checklist, and why is it critical in 2026?
An enterprise data migration checklist is a structured guide that helps organizations plan, execute, and validate data migration initiatives. In 2026, enterprises deal with higher data volumes, hybrid cloud environments, and stricter compliance requirements. A checklist reduces risk, prevents data loss, and ensures business continuity. It also aligns technical execution with business objectives and regulatory needs.
2. What systems should be included in an enterprise data migration plan?
Enterprises must include ERP, CRM, data warehouses, data lakes, BI tools, and operational systems in their migration scope. Additionally, integrations, APIs, and third-party systems should be evaluated early. Ignoring dependent systems often leads to broken workflows and reporting gaps. A complete system inventory ensures smoother migrations and fewer post-go-live issues.
3. How should enterprises assess data readiness before migration?
Data readiness assessment involves profiling data quality, identifying duplicates, and validating data completeness. Enterprises should also review data formats, schema compatibility, and historical data relevance. This step helps determine what data to migrate, archive, or retire. Clean and validated data significantly improves migration success and post-migration performance.
4. What role does security and compliance play in data migration?
Security and compliance are critical at every stage of enterprise data migration. Organizations must enforce encryption, access controls, and audit trails during data movement. Regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and industry-specific standards must be addressed upfront. A secure migration approach reduces legal risk and protects sensitive enterprise data.
5. How can enterprises minimize downtime during data migration?
Enterprises reduce downtime by using phased migration strategies, parallel runs, and incremental data loads. Testing in non-production environments helps identify issues early. Cutover planning and rollback strategies are also essential. These practices ensure critical business operations continue with minimal disruption during migration.
6. What validation steps should be included after data migration?
Post-migration validation includes reconciling record counts, validating business rules, and testing reports and dashboards. Enterprises should involve business users to confirm data accuracy and usability. Performance benchmarking is also important to ensure systems meet expectations. Validation ensures trust in the new platform and avoids costly rework.
7. What trends are shaping enterprise data migration in 2026?
In 2026, data migration is driven by cloud modernization, AI-ready architectures, and real-time analytics needs. Enterprises are adopting automated migration tools and data observability platforms. There is also a stronger focus on governance, data quality, and sustainability. These trends make structured migration checklists more important than ever.










