Tesla’s autonomous driving technology, powered by sophisticated AI agents, has logged over 3 billion miles using Autopilot, with over 1 billion of those miles driven using the advanced Navigate on Autopilot feature. The various types of AI agents working in harmony within Tesla’s vehicles – from perception systems that process sensor data to decision-making agents that control steering and acceleration – showcase how modern AI technology can revolutionize entire industries.
Even companies like Spotify have transformed user experiences by using AI agents. Their recommendation engine, which analyzes user behavior to suggest music. AI agents, ranging from chatbots to autonomous systems, play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, optimizing processes, and improving customer engagement. These intelligent agents can process vast amounts of data, make decisions, and even learn from their environment.
As AI technology continues to advance, understanding the different types of AI agents becomes essential for businesses seeking to leverage these solutions to solve complex challenges and drive growth. This guide dives into the various AI agents, showcasing their functionalities, applications, and benefits, while offering a closer look at their impact on industries from retail to healthcare.
What Are the Different Types of AI Agents?
1. Simple Reflex Agents
Simple Reflex Agents are the most basic type of AI agents that operate based solely on the current input, without considering any past information. They make decisions based on predefined rules for specific situations.
Characteristics
- Operates based on current perceptions without memory.
- Responds to stimuli with predetermined actions.
- Does not store past experiences or states.
Examples
- Automatic door sensors.
- Traffic lights responding to vehicle presence.
Applications
- Environments with clear, unchanging conditions.
- Situations requiring quick, reactive actions with no need for past context.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-Based Reflex Agents improve upon simple reflex agents by maintaining an internal model of the world, allowing them to adapt to partially observable environments and make more informed decisions.
Characteristics
- Maintains an internal model of the environment.
- Can make decisions based on both current perceptions and past information.
- Capable of handling partially observable scenarios.
Examples
- Self-driving cars using internal maps.
- Robotic arms in manufacturing with a model of the workspace.
Applications
- Dynamic environments requiring real-time decision-making.
- Complex systems where past information influences future actions.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-Based Agents focus on achieving specific objectives. These agents evaluate different actions based on the end goal and select the one that best serves the goal, allowing for more strategic decision-making.
Characteristics
- Operates with specific goals to guide actions.
- Takes actions based on expected outcomes that help achieve a goal.
- Plans actions based on objective priorities.
Examples
- Robotic vacuum cleaners aiming to clean an entire room.
- Navigation systems guiding users to a destination.
Applications
- Tasks requiring planning, goal-setting, and strategy.
- Situations where long-term objectives must be achieved step-by-step.
Harness The Power Of AI Agents To Transform Your Workflow!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-Based Agents choose actions that maximize a utility function, allowing them to balance and optimize multiple objectives. These agents can make trade-offs to achieve the best possible outcome in complex environments.
Characteristics
- Chooses actions to maximize utility.
- Balances multiple competing goals.
- Capable of making trade-offs between different objectives.
Examples
- AI in video games optimizing for both score and player experience.
- Resource management in cloud computing systems.
Applications
- Complex scenarios with competing objectives.
- Systems that require trade-offs between different factors (e.g., performance vs. cost).
5. Learning Agents
Learning Agents are designed to improve their performance over time by learning from experiences and adapting to new conditions. These agents continuously enhance their capabilities based on new data and interactions.
Characteristics
- Improves performance through learning from experiences.
- Adapts over time based on feedback.
- Learns patterns from past interactions to make better future decisions.
- Recommendation systems adapting to user preferences.
- Email spam filters learning from past behavior.
Applications
- Environments where conditions change and continuous improvement is needed.
- Systems requiring adaptive learning to optimize results over time.
Types of AI Agents: Modern Classifications
1. Task-Specific Agents
Task-Specific Agents are single-agent systems designed to perform specialized tasks within a defined scope. These agents excel in handling specific challenges but lack adaptability for broader use.
Characteristics
- Focused on executing predefined tasks efficiently.
- Limited scope and functionality beyond their designated task.
- Optimized for accuracy and speed in their domain.
Examples
- Weather forecasting systems.
- Fraud detection in banking.
Applications
- Industries requiring precision for repetitive tasks, like financial analysis.
- Specialized use cases such as medical diagnostics or supply chain optimization.
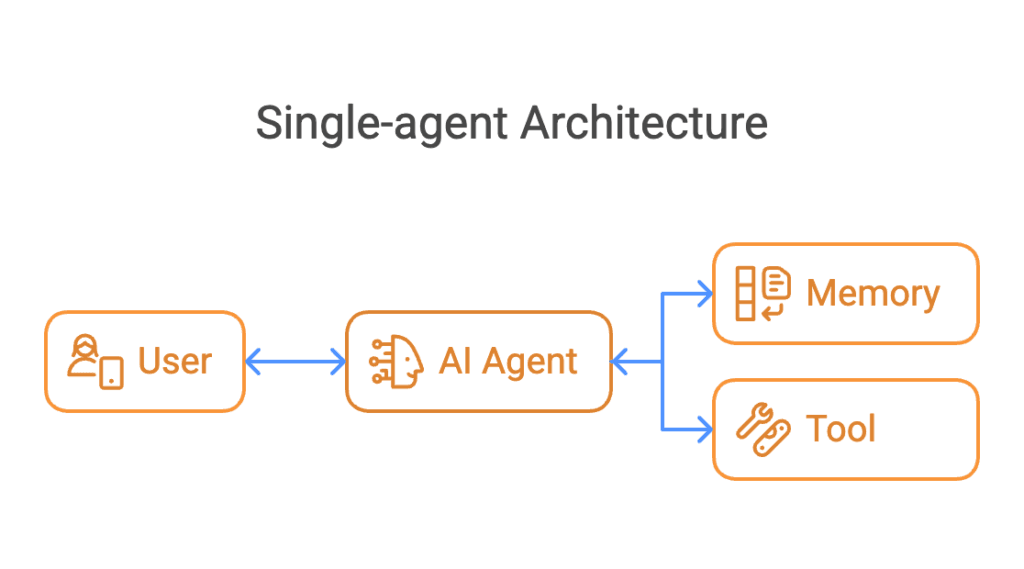
2. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Multi-Agent Systems consist of multiple agents working collaboratively or independently to solve complex problems. They can interact with each other, sharing information and distributing workloads.
Characteristics
- Comprised of multiple interacting agents.
- Collaboration or competition among agents to achieve goals.
- Distributed decision-making.
Examples
- Swarm robotics for warehouse logistics.
- Smart grid energy management systems.
Applications
- Distributed systems requiring scalability, like traffic management.
- Scenarios involving collaborative problem-solving, such as supply chain networks.
3. Autonomous Agents
Autonomous Agents operate independently, making decisions without human intervention. They are capable of perceiving their environment, learning, and adapting to new situations.
Characteristics
- Operate independently with minimal external guidance.
- Continuously learn and adapt to new conditions.
- Self-sufficient in achieving defined goals.
Examples
- Autonomous vehicles navigating roads.
- AI-powered drones for delivery services.
Applications
- Systems requiring minimal supervision, like space exploration.
- Real-time applications, such as disaster response or remote monitoring.
AI Agents Vs AI Assistants: Which AI Technology Is Best for Your Business?
Compare AI Agents and AI Assistants to determine which technology best suits your business needs and drives optimal results.
Applications of Various AI Agents Across Industries
1. Healthcare
AI agents assist in diagnosing diseases, personalizing treatment plans, and managing patient records. For instance, predictive analytics powered by AI improves early detection of illnesses like cancer, while chatbots enhance patient engagement by providing instant responses to queries. Autonomous agents streamline hospital workflows, boosting efficiency and reducing administrative burdens.
2. Finance
AI agents optimize trading, detect fraud, and personalize financial services. For example, machine learning algorithms analyze market trends for better investment strategies. Chatbots provide real-time customer support, while fraud detection systems identify anomalies in transactions, ensuring secure and efficient financial operations.
3. Manufacturing
AI agents enhance production efficiency through predictive maintenance, quality control, and inventory management. Autonomous robots in assembly lines minimize errors, while AI-powered systems optimize supply chains by forecasting demand and streamlining logistics.
4. Transportation
Autonomous vehicles, powered by AI agents, improve safety and efficiency by analyzing traffic patterns and making real-time decisions. AI also aids in route optimization for logistics and public transportation, reducing fuel consumption and delivery times.
5. Customer Service
Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI agents handle customer queries 24/7, ensuring faster response times and improved satisfaction. These agents analyze user behavior to provide personalized recommendations and solutions, enhancing the overall customer experience.
6. Research and Development
AI agents accelerate R&D by analyzing vast datasets, identifying patterns, and generating insights. In pharmaceuticals, they assist in drug discovery, while in technology, they enhance innovation by simulating prototypes and testing models efficiently.
Kanerika’s AI Agents: Redefining Workflows with AI-powered Automation

Alan – AI Legal Document Summarizer
Alan simplifies legal workflows by transforming lengthy documents into clear, concise summaries.
What Alan Can Do
- Analyze extensive contracts and legal documents.
- Generate tailored summaries based on user-defined rules.
- Provide unlimited summary generation for consistent efficiency.
Key Features and Benefits
- Customizable summarization using natural language rules.
- Saves hours spent on legal reviews and contract analysis.
- Enhances decision-making by focusing on key legal points.
How It works
- Upload your legal document.
- Define custom summarization rules.
- Receive a concise, actionable summary to your email
Susan – AI PII Redactor
Susan ensures your documents meet data privacy regulations by redacting sensitive information securely.
What Susan Can Do
- Identify and redact Personally Identifiable Information (PII), such as names, numbers, and more.
- Deliver a redacted version of the document quickly and securely.
Key Features and Benefits
- Compliant with stringent data privacy standards.
- Customizable fields for precise redaction.
- Minimizes risk of data breaches and ensures regulatory compliance.
How It Works
- Upload your document.
- Specify the fields for redaction.
- Receive a secure, redacted file in your inbox.
Mike – AI Quantitative Proofreader
Mike enhances document accuracy by validating numerical data and ensuring consistency.
What Mike Can Do
- Verify arithmetic accuracy across quantitative data.
- Cross-check data consistency across multiple documents.
- Flag errors and discrepancies for review.
Key Features and Benefits
- Reduces manual proofreading efforts and errors.
- Provides detailed discrepancy reports.
- Ensures reliable, error-free documentation for critical business needs.
How It Works
- Upload your document(s).
- Allow Mike to analyze and cross-validate numerical data.
- Receive an error report and suggestions for corrections.
12 Unique AI Applications To Transforming Industries
Explore groundbreaking AI applications driving innovation, efficiency, and growth across diverse industries.
Future Trends and Developments in AI Agents
1. Emerging Agent Types
The future of AI agents will see the rise of hyper-personalized agents designed to provide highly tailored user experiences, particularly in retail and healthcare. Explainable AI (XAI) agents are another emerging trend, focusing on providing transparent decision-making processes to enhance trust in critical applications like finance and law.
Additionally, collaborative agents that work seamlessly with human teams are expected to grow, especially in fields like education and professional services.
2. Technological Advancements
The integration of Generative AI is set to transform AI agents by enabling them to create new content, such as text, images, or designs, on demand. Advancements in edge computing will allow agents to operate with minimal latency, making them more effective in IoT environments, such as smart cities and autonomous vehicles.
Reinforcement learning will also make AI agents more capable of adapting to dynamic environments, while advancements in quantum computing promise to exponentially increase their problem-solving abilities.
3. Industry Predictions
By 2030, AI agents are predicted to play a pivotal role in automating repetitive tasks across industries. In healthcare, AI agents will become central to remote monitoring and telemedicine, improving patient outcomes. The finance sector is expected to rely more on AI agents for fraud detection and risk assessment.
Moreover, as sustainability becomes a priority, AI agents in energy management will optimize resource use and reduce waste. Collaborative AI systems are expected to dominate sectors like manufacturing, improving efficiency through human-agent teamwork.
SLMs vs LLMs: Which Model Offers the Best ROI?
Explore the cost-effectiveness, scalability, and use-case suitability of Small Language Models versus Large Language Models for maximizing your business returns.
Kanerika: Leading Enterprise Transformation with Powerful AI Agents
Kanerika is redefining how businesses operate by harnessing the potential of AI agents. As a top-rated AI solutions company, we specialize in building intelligent systems and deploying custom AI models that deliver measurable results. With a proven track record across industries, our solutions optimize operations, enhance decision-making, and unlock new opportunities. Whether it’s automating workflows, improving efficiency, or tackling complex challenges, our AI expertise ensures exceptional outcomes tailored to your needs. Trust Kanerika to lead your enterprise transformation journey with innovative AI solutions that deliver results.
Transform Business Challenges Into Opportunities With AI Agents!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 types of agents in AI?
The five fundamental types of AI agents are: Simple Reflex Agents (condition-based responses), Model-Based Agents (internal state tracking), Goal-Based Agents (decision-making toward objectives), Utility-Based Agents (optimization for best outcomes), and Learning Agents (adapt through experience).
What is an example of an AI agent?
A robotic vacuum cleaner is a classic example of an AI agent. It perceives its environment through sensors (detecting obstacles, dirt, battery level), makes decisions based on this input, and takes actions (moving, cleaning, returning to charge) to achieve its designated tasks autonomously.
What is the difference between AI assistants and AI agents?
AI assistants (like Siri) primarily respond to direct user commands and queries, while AI agents operate more autonomously, making decisions and taking actions independently to achieve goals. Agents have more autonomy in their environment and can initiate actions without direct user input.
Why use AI agents?
AI agents automate complex tasks, operate continuously without human intervention, adapt to changing conditions, and can handle multiple objectives simultaneously. They’re especially valuable for tasks requiring constant monitoring, rapid decision-making, or operation in environments where human intervention is impractical.
Is ChatGPT an AI agent?
ChatGPT is more accurately classified as an AI language model/assistant rather than a true agent. While it processes inputs and generates responses, it lacks the ability to take independent actions, maintain long-term state, or interact with its environment beyond text processing.
How are AI agents developed?
AI agents are developed through a combination of machine learning, rule-based programming, and environment modeling. Development involves defining sensors (inputs), actuators (outputs), decision-making algorithms, learning mechanisms, and extensive testing in simulated and real environments.









