As per WHO, each year, 17 million people die from Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) before age 70; 86% of these premature deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries. This staggering figure establishes that implementing automation in healthcare is becoming increasingly crucial as the demand for efficient, high-quality care continues to rise globally.
Automation in healthcare is key to adopting more sustainable and effective approaches to patient management and care delivery. Moreover, technologies like artificial intelligence and robotics are at the forefront of this transformation, influencing a wide range of healthcare functions. Additionally, automation promises to enhance service quality, enabling you to focus on patient-specific needs by reducing the time spent on routine processes.
Technology like AI, RPA, and analytics can strengthen health systems. Their potential can transform healthcare delivery through improved data management, decision support systems, and patient engagement tools. Furthermore, by automating routine administrative tasks, healthcare providers can allocate more time and resources to patient care, thus enhancing the effectiveness of healthcare services.
Understanding Automation in Healthcare
What is Automation in Healthcare?
Healthcare automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks that were traditionally done manually, improving efficiency, accuracy, and patient care. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from administrative processes like scheduling and billing to more complex tasks such as diagnostics and clinical decision-making. Automation in healthcare includes the use of software to streamline workflows, reduce human error, and ensure consistent and timely care for patients.
Some key examples of automated tasks in healthcare include:
- Administrative Tasks: Automating appointment scheduling, medical billing, insurance claims, and patient data entry.
- Clinical Workflows: Automating clinical processes such as patient monitoring, drug administration, and lab results management.
- Patient Care: AI-powered chatbots for patient support, robotic systems for surgery, and remote patient monitoring to track vital signs in real-time.
Scope of Automation
The scope of healthcare automation extends from administrative tasks to complex clinical operations. Automation optimizes back-office processes, ensures consistent patient monitoring, and improves overall efficiency in healthcare delivery. Additionally, it is instrumental in modernizing diagnostic tools and enhancing decision-making by integrating AI and data analytics.

Technological Foundations
Integrating automation technologies in healthcare represents a transformative shift aimed at enhancing operational efficiency, patient care, and decision-making processes. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are two pivotal technologies at the forefront of this revolution. These technologies, moreover, are instrumental in redefining the landscape of healthcare services, offering innovative solutions to longstanding challenges.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI in healthcare leverages algorithms and software to approximate human cognition in the analysis, interpretation, and comprehension of complex medical and healthcare data. The primary aim of AI applications in healthcare is to analyze relationships between prevention or treatment techniques and patient outcomes. AI programs have been developed to assist in diagnostic processes, treatment protocol development, drug development, personalized medicine, and patient monitoring and care. Applications include:
- Diagnostics: AI algorithms can support radiologists in spotting subtle changes in imaging data that might be overlooked by the human eye, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze vast datasets to predict disease outbreaks, patient admissions, and other important health trends
- Personalized Medicine: By analyzing data from patient records, AI can help tailor treatment plans to individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and risk factors
- Virtual Health Assistants: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 support to patients, offering advice, monitoring health status, and even alerting professionals in case of a health emergency.
- AI-Powered Knowledge Base: Use tools like Document360 to centralize medical documentation, protocols, and device docs offering quick, accurate access for staff and patients.
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA uses software robots or ‘bots’ to automate highly repetitive and routine tasks traditionally performed by human workers. In healthcare, RPA can significantly reduce the administrative burden, streamline processes, and improve the accuracy of data handling. Applications include:
- Patient Scheduling: Automating appointment bookings, cancellations, and rescheduling, improving efficiency and patient satisfaction
- Claims Management: RPA can automate the processing of healthcare claims, reducing processing time and errors, and ensuring compliance with regulations
- Data Management: Automating data entry and migration tasks helps maintain accurate and up-to-date patient records and reduces the risk of data breaches
- Supply Chain Management: RPA can streamline the ordering and management of medical supplies, ensuring that healthcare providers always have the necessary materials on hand
Drive Business Growth and Efficiency with Agentic Automation!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Technologies Enabling Automation in Healthcare
1. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices can monitor patients’ health in real-time, providing data that can be used to prevent hospital readmissions and improve patient outcomes.
2. Blockchain
Offers a secure and transparent way to store and share medical records, enhancing data security and patient privacy.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Powers tools that can understand and process human language, enabling the analysis of unstructured data from medical literature, patient records, and other sources to support clinical decision-making.
4. Robotics
Robotics has a significant role in both surgical procedures and patient care. Surgical robots allow for precision in complex operations, reducing patient recovery times. Robotic aids also support nurses and staff by handling repetitive tasks, which frees up more time for patient care.
5. Electronic Health Records
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) serve as the digital backbone for healthcare data management. Through EHR systems, healthcare providers gain instant access to patient histories, which improves coordination and eliminates redundant testing. The push towards workflow automation within EHRs seeks to streamline administrative tasks, thus increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Applications of Automation in Healthcare
Healthcare automation has transformed medical delivery across multiple domains, creating significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and patient outcomes.
1. Clinical Applications
Robotic surgical systems enable surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision and control. These systems translate a surgeon’s hand movements into smaller, more precise actions while providing magnified 3D visualization of the surgical site. In medication management, automated dispensing cabinets and robot pharmacists accurately prepare and track medications, reducing dispensing errors and improving patient safety.
2. Diagnostic Automation
Computer-aided detection systems analyze medical images to identify potential abnormalities that human radiologists might miss, particularly beneficial for early cancer detection. Automated laboratory equipment processes thousands of samples daily with minimal human intervention, delivering faster results with greater consistency than manual methods.
3. Administrative Automation
Electronic health record systems with automated documentation capabilities convert dictation to structured clinical notes, reducing documentation time while improving record completeness. Automated appointment scheduling systems optimize provider calendars based on urgency, provider availability, and patient preferences, reducing wait times and improving resource utilization.
4. Patient Monitoring
Remote monitoring devices automatically collect and transmit vital signs from patients at home, allowing for early intervention when parameters fall outside normal ranges. Within hospitals, automated early warning systems continuously analyze patient data to identify deteriorating conditions before they become critical emergencies.
5. Operational Automation
Supply chain management systems automatically track inventory levels and initiate reordering when supplies reach predetermined thresholds, preventing shortages of critical items. Automated patient flow systems coordinate admissions, transfers, and discharges to optimize bed utilization and reduce bottlenecks in emergency departments.
6. Public Health Applications
Disease surveillance systems automatically aggregate and analyze data from multiple sources to detect potential outbreaks early. Automated contact tracing tools help quickly identify individuals who may have been exposed to infectious diseases, enabling faster containment responses.
Hyperautomation Trends Guide 2024: Everything you need to know
Elevate enterprise performance through intelligent, comprehensive automation technologies and strategic digital transformation.
Benefits of Automation in Healthcare
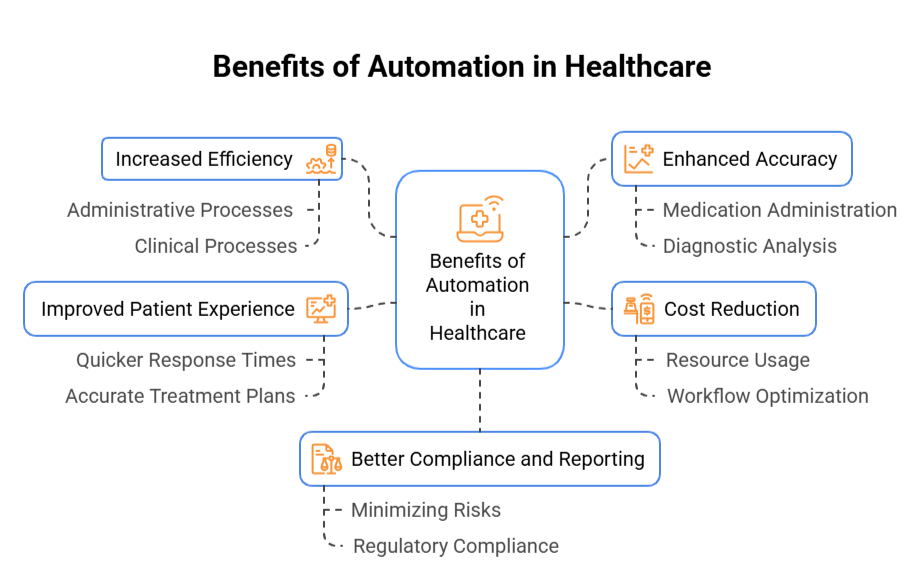
Automation in healthcare brings numerous benefits, from improving operational efficiency to enhancing patient care and safety. Here are some of the primary advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation helps streamline various administrative and clinical processes, reducing manual effort and increasing operational efficiency. Tasks like appointment scheduling, patient data entry, and insurance claims processing are handled faster and with fewer errors, freeing up healthcare staff to focus on more critical patient care activities.
- Enhanced Accuracy: By automating processes such as medication administration, patient monitoring, and diagnostic analysis, the likelihood of human error is reduced. This ensures higher accuracy in patient care and decision-making.
- Cost Reduction: Automation helps healthcare organizations reduce operational costs by minimizing manual intervention, optimizing resource usage, and improving the workflow. Tasks that traditionally required large teams can now be handled by fewer staff, lowering overhead expenses.
- Improved Patient Experience: Automation facilitates quicker response times, faster appointments, and more accurate treatment plans. This results in higher patient satisfaction and improves their overall healthcare experience.
- Better Compliance and Reporting: Automated systems ensure that healthcare providers stay compliant with regulations like HIPAA and that proper records and reports are generated without delay. This also aids in minimizing risks related to legal and regulatory compliance.
Challenges of Automation in Healthcare
While automation in healthcare offers a host of benefits, there are also challenges that organizations must consider before implementing such systems:
1. Reliability and System Failures: While automation can reduce human error, the systems themselves are not infallible. System crashes, data corruption, and technical glitches can disrupt operations, leading to potential delays in patient care or billing processes. Ensuring these systems are well-maintained and reliable is critical to preventing such issues.
2. Integration with Legacy Systems: Many healthcare providers still use older, legacy systems that may not easily integrate with modern automation technologies. This can lead to compatibility issues and hinder the seamless implementation of new automated solutions.
3. Data Security and Privacy: With the increased use of automation comes the need to safeguard sensitive patient data. Automated systems that handle patient information need to comply with stringent data security regulations like HIPAA. Ensuring that these systems are secure and capable of handling data privacy concerns is crucial.
4. Cost of Implementation: The upfront costs of integrating automation systems into healthcare organizations can be substantial. This includes expenses for software, hardware, staff training, and potential integration with existing systems. For many organizations, these initial investments can pose a challenge, especially in the face of limited budgets.
5. Resistance to Change: Healthcare professionals, including administrative and clinical staff, may be resistant to adopting automated systems due to fears of job displacement or discomfort with new technology. Overcoming this resistance through proper training and communication is essential to ensure successful implementation.
Regulatory and Ethical Aspects of Automation in Healthcare
When exploring the integration of automation in healthcare, you must navigate through complex regulatory frameworks and address the ethical implications of artificial intelligence (AI). The importance of aligning with legal standards and maintaining ethical integrity cannot be overstated.
Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
Healthcare regulations set forth strict guidelines that ensure patient safety, data security, and quality of care. Automated systems, like any other medical technology, must adhere to these regulations. For instance, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) mandates the protection of patient privacy when handling medical records. When AI is used for diagnostic or treatment purposes, it must also satisfy the requirements of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In practice, this means AI software used in healthcare settings should undergo rigorous testing for accuracy and reliability before it’s implemented.
- HIPAA: Protects patient privacy and health information.
- FDA Approval: Ensures safety and efficacy of medical devices and software.
Ethical Implications of AI
The deployment of AI in healthcare raises ethical concerns that you must carefully consider. Central to these concerns are principles such as autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, and justice. Healthcare professionals need to ensure that AI tools do not inadvertently compromise patient autonomy or privacy. Ethical AI use must aim to benefit patients, avoid harm, and be fairly accessible to all segments of the population.
Key ethical considerations include:
- Patient Autonomy: AI must support informed consent and respect patient decisions.
- Patient Outcomes: AI should contribute to effective health management and positive patient outcomes without introducing new inequities.
The Future of Automation in Healthcare
The future of automation in healthcare holds immense potential to transform the way services are delivered, improving both operational efficiency and patient outcomes. As technologies continue to advance, automation will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping healthcare systems globally.
This evolving landscape demands innovation from healthcare providers and calls for a deeper academic understanding from future professionals, especially in nursing and allied health fields. As topics like AI-driven diagnostics, robotic surgery, and predictive analytics become integral to clinical practice, students are expected to critically engage with these developments in their studies. For those navigating this complex intersection of technology and care delivery, academic assistance in “write my nursing paper” can provide valuable support. These resources enable students to better articulate their insights and stay ahead in a rapidly changing healthcare environment.
1. Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are set to further revolutionize healthcare automation by enabling predictive analytics, personalized medicine, and intelligent decision-making. AI algorithms will analyze patient data to detect patterns, predict future health risks, and provide actionable insights to clinicians. Machine learning will continue to optimize treatment plans and improve diagnosis accuracy, making healthcare more proactive than ever before.
2. Expansion of Robotic Surgery
The future of surgery will see greater reliance on robotic systems, where automation ensures precision and reduces human error. Robotic surgeries, which are already gaining popularity, will become more advanced, providing enhanced capabilities such as minimally invasive procedures, quicker recovery times, and more efficient use of operating room resources.
3. Streamlined Workflow Automation
In the future, healthcare systems will increasingly leverage robotic process automation (RPA) and AI-driven tools to streamline administrative and clinical workflows. Automating tasks like billing, insurance claims processing, appointment scheduling, and patient records management will allow healthcare providers to reduce operational overhead and improve service delivery.
4. Personalized Healthcare Experiences
Automated systems will enable healthcare to become more personalized, with tailored treatment plans and continuous patient monitoring through wearable devices and IoT-enabled technologies. Patients will experience more direct, customized interactions with healthcare providers, improving satisfaction and overall health outcomes.
5. Remote and Virtual Care
The future will see further integration of telemedicine and virtual care platforms, powered by automation. AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots will handle routine consultations, while automated monitoring systems will track patient health metrics remotely, offering real-time feedback and continuous support.
RPA for Enterprise: Streamlining Business Processes Automation
Discover how RPA simplifies and accelerates business process automation for enterprises.
Shape the Future of Automation in Healthcare with Kanerika
Kanerika specializes in advanced Automation and AI/ML solutions that streamline operations and transform healthcare delivery. Our expertise enables healthcare organizations to drive innovation, increase operational efficiency, and optimize resource utilization — all while reducing costs.
We’ve successfully implemented intelligent automation frameworks and custom AI agents that eliminate manual bottlenecks, accelerate workflows, and improve patient care delivery. From automating clinical processes to enhancing administrative operations, our solutions empower healthcare professionals with real-time insights and faster decision-making.
By partnering with Kanerika, healthcare providers gain a competitive edge through smart process automation, predictive analytics, and enhanced patient engagement. Our automation-led solutions deliver measurable ROI, driving operational excellence while ensuring a superior patient experience.
Enhance Decision-Making and Reduce Costs with Agentic Automation!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
What is automation in healthcare?
Healthcare automation uses technology to handle tasks typically done by humans, freeing up staff for more complex patient care. This ranges from simple things like appointment scheduling to sophisticated systems analyzing medical images or predicting patient risks. The goal is to improve efficiency, accuracy, and patient outcomes, ultimately leading to better and more affordable healthcare. Think robotic surgery, AI-powered diagnostics, or automated medication dispensing – all examples of automation in action.
What are the 4 types of automation?
Automation isn’t just one thing; it comes in four flavors. There’s robotic process automation (RPA) for repetitive digital tasks, business process automation (BPA) for streamlining entire workflows, machine learning (ML) automation for intelligent, adaptive systems, and finally, integrated automation which blends these approaches for maximum efficiency. Essentially, each type tackles automation at a different level of complexity and intelligence.
What is the newest technology in healthcare?
There isn’t one single “newest” technology; healthcare tech evolves rapidly. Currently, we’re seeing a surge in AI-driven diagnostics and personalized medicine, leveraging massive datasets for improved accuracy and tailored treatments. Further advancements in gene editing and nanotechnology also promise revolutionary changes in disease prevention and treatment. It’s a constantly shifting landscape.
How is RPA used in healthcare?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in healthcare streamlines repetitive tasks, freeing up human staff for more complex patient care. Think automating appointment scheduling, insurance claims processing, or data entry – improving efficiency and reducing errors. This ultimately leads to better resource allocation and potentially improved patient outcomes by freeing up valuable time for clinicians. RPA essentially handles the “behind-the-scenes” busywork.
What is intelligent automation in healthcare?
Intelligent automation in healthcare uses AI and machine learning to streamline complex processes. It goes beyond basic automation by learning from data to improve efficiency and accuracy, unlike rigid, rule-based systems. Think robotic process automation (RPA) combined with AI’s decision-making capabilities for tasks like claims processing or patient scheduling. This boosts productivity and frees up human staff for more complex patient care.
What are the three basic types of automation?
Automation fundamentally boils down to three core approaches: Process automation streamlines repetitive tasks within existing systems. Task automation focuses on individual actions, often using robotic process automation (RPA). Finally, system automation integrates multiple systems for broader, more holistic control and efficiency. These categories aren’t mutually exclusive; they often work together.
What are the advantages of automation?
Automation boosts efficiency by handling repetitive tasks faster and more accurately than humans, freeing up human workers for more creative and strategic roles. It minimizes errors, leading to higher quality output and reduced waste. Ultimately, automation increases productivity and can lower operational costs in the long run, improving a company’s bottom line. This translates to better products or services delivered more effectively.
How are robots being used in healthcare?
Robots are revolutionizing healthcare in several ways. They assist surgeons with precision and minimally invasive procedures, handle repetitive tasks freeing up human staff, and even provide companionship and therapy for patients. This broad application improves efficiency, patient outcomes, and overall care quality. Essentially, they’re augmenting human capabilities to deliver better healthcare.
What are the pros and cons of AI in healthcare?
AI in healthcare offers incredible potential: faster diagnoses, personalized treatments, and streamlined workflows, leading to better patient outcomes and reduced costs. However, concerns exist about data privacy, algorithmic bias potentially exacerbating existing health inequalities, and the need for human oversight to prevent errors and maintain ethical standards. Ultimately, successful AI implementation hinges on responsible development and deployment.
What is automation in pharma?
Pharmaceutical automation streamlines processes, from drug discovery to manufacturing and distribution, using technology. This boosts efficiency, reduces human error (improving safety and quality), and often lowers costs. Essentially, it’s applying robotics, AI, and software to make the drug development and delivery chain faster, more accurate, and more reliable.
What is automation in QA?
Automation in QA uses software to perform testing tasks normally done manually. This boosts efficiency by running tests repeatedly and quickly, uncovering bugs earlier in the development cycle. It’s crucial for scaling testing efforts and ensuring consistent, reliable results across diverse platforms and scenarios. Ultimately, it frees human testers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of quality assurance.










