You’ve invested millions in enterprise data migration to the cloud. Your team celebrated at cutover. But here’s the thing—enterprise data migration best practices aren’t about moving data faster. They’re about modernizing your architecture so it actually feeds your AI and analytics strategy.
Companies that execute enterprise data migration without thinking about modernization from the start? They spend 40-60% more time in post-migration cleanup. And, find data quality issues after cutover. They can’t integrate new analytics tools. Then—surprise—they’re migrating again in 12 months when the strategy shifts.
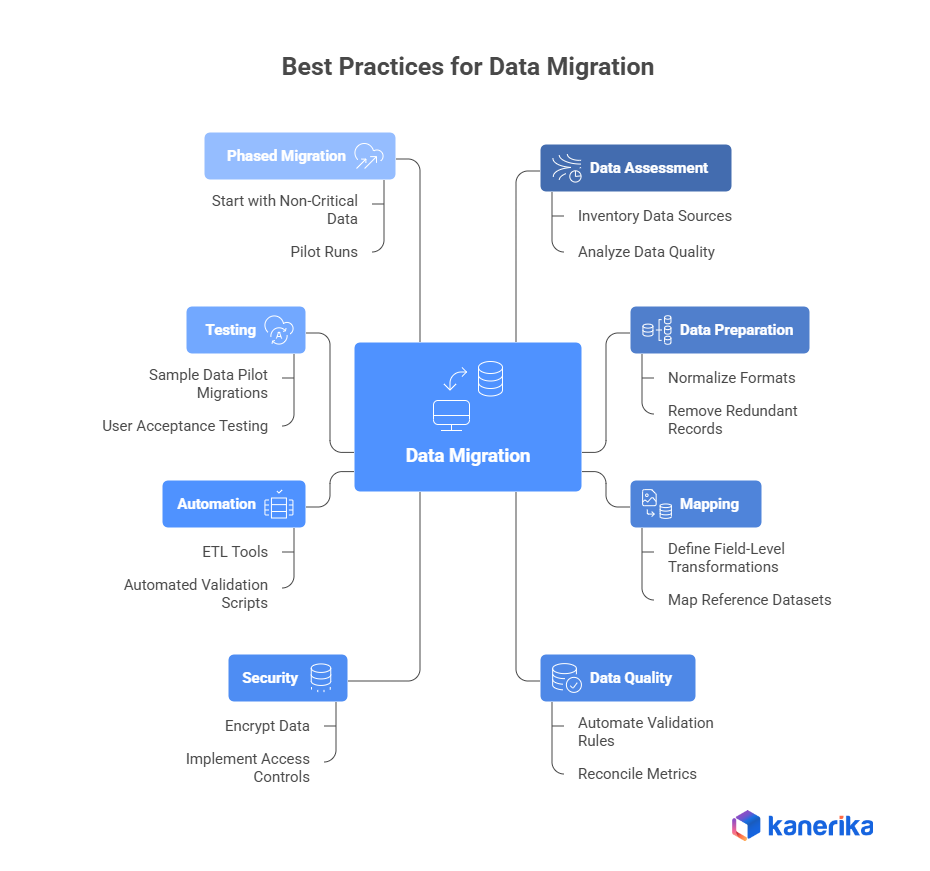
If you’re managing a large enterprise migration of Informatica, SSIS, SSRS, or Tableau (hundreds or thousands of ETL objects), there’s a smarter path. It’s not manual migration. It’s not risky. And it costs 65% less than traditional approaches.
This guide covers enterprise data migration best practices for 2026—not the foundational checklist (we have that), but the strategic playbook that separates successful enterprise migrations from costly, prolonged ones.
Key Takeaways
The Problem: Companies that migrate without thinking about AI and analytics from the start spend 40-60% more time fixing data quality issues after cutover.
The Solution:
- Separate move from modernize. Lift-and-shift your cold data. Refactor the pipelines that feed AI and analytics. Both happen in parallel.
- Use automation for legacy ETL conversion. Converting 450 Informatica workflows manually takes 26 weeks and costs 65% more. Automation does it in 12 weeks with less technical debt.
- Design for analytics from day one. Don’t build your data migration architecture around the old system. Build it around where your data needs to go (Fabric, Databricks, Snowflake)—and what your ML and BI teams actually need.
- Do phased cutover, not big-bang. Run old and new systems in parallel for 2-4 weeks. Catch issues while you have a fallback. Support for 90 days post-migration, not 30.
The Real Win: Enterprises that do this right move smarter, not faster. They avoid $2-3M in post-migration rework. They actually achieve their AI and analytics goals instead of repeating migration in 12 months.
Make Your Migration Hassle-Free with Trusted Experts!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Modernization Services
Why Enterprise Data Migration Projects Fail (And How to Avoid Cost Overruns)
Most enterprise migration strategies fail the same way. Truth is technology limitations are rarely the challenge. Main issue is with architectural decisions made at the start.
Someone does a lift-and-shift—taking an Informatica pipeline and moving it to the cloud as-is, without rethinking whether it belongs in the new architecture at all. Six months later, teams are debugging performance issues that wouldn’t exist if the legacy ETL migration had included a redesign. Post-migration maintenance explodes. Timelines slip.
The enterprise migrations that actually work do this: they separate the problem.
Move what’s stable. Modernize what matters.
Think of it this way: imagine trying to navigate a modern Formula 1 race using a road atlas from the 1980s. Sure, the roads are still there. But you’re missing all the real-time traffic updates.
That’s legacy system modernization without a plan. You’ve moved to the cloud, but you haven’t designed for it.
Enterprise-scale migration best practices separate rehosting (lift-and-shift) from refactoring. Keep your cold data, compliance archives, and low-change systems where they are. Refactor the data pipeline modernization for systems that feed AI, analytics, and real-time operations. Both happen in parallel. One’s fast. One’s strategic. You need both.
And bring everyone into the room early—not after the enterprise data architecture is locked. If your analytics team isn’t in on scoping, they’ll spend months complaining about latency after go-live. If security isn’t there, you’ll hit compliance walls mid-project. Gartner found that projects with strong stakeholder alignment finish 25% faster.
One more thing: don’t do big-bang data cutover strategy. Ever. Pilot with something non-critical first (a reporting warehouse, a test system). Validate quality and performance for 2-4 weeks. Then expand in waves. Slower? Maybe. Safer? Absolutely. You catch integration issues while you still have a fallback. Teams trust the new system because they watched it work.
How to Migrate from SSRS to Power BI: Enterprise Migration Roadmap
Discover a structured approach to migrating from SSRS to Power BI, enhancing reporting, interactivity, and cloud scalability for enterprise analytics.
The Real Opportunity: Automating Legacy ETL Migration and Conversion
This is where enterprise migrations either become a story you tell, or a disaster you endure.
Here’s the problem: Informatica PowerCenter, SSIS, SSRS, Tableau—these tools have been the backbone of enterprise data integration for 10+ years. They work. But they weren’t built for cloud. And they’re nightmares to maintain. Converting 300+ workflows manually? You’re looking at 5-6 months and a team of 8-10 people doing copy-paste work. Mistakes guaranteed.
Cloud ETL automation and legacy ETL conversion frameworks change that math completely.
Kanerika’s FLIP and FIRE automate Informatica migration and SSIS migration by converting Informatica workflows and SSIS packages into native Azure Data Factory, Talend, or Databricks Jobs automatically. Then they validate outputs against the original. No hand-coding. No guessing.
Best Data Reconciliation Tools for Enterprises: A Complete Guide
Explore what data reconciliation tools are, how they work within the migration lifecycle, common challenges they address, and best practices for choosing the right solution in enterprise environments.
Real example of enterprise ETL migration:
A mid-market manufacturing company had 450 Informatica workflows running daily. Manual Informatica PowerCenter migration would’ve taken 26 weeks. Using FLIP automation:
- 380 workflows (84%) converted automatically with full code and metadata
- The remaining 16% (complex multi-source joins) got flagged for manual review—took one week instead of a month
- Testing ran parallel, caught issues early
- Total time: 12 weeks. Cost: 65% lower than manual legacy data migration.
Why does cloud ETL automation matter beyond just speed? Because automated ETL conversion means less technical debt. The code gets generated clean, follows cloud-native patterns from day one. Not some Frankensteined lift-and-shift.
When does ETL migration automation work best?
To answer simply, when you’ve got 100+ ETL objects, you’re targeting Azure Data Factory or Talend, and you’ve got 8-12 weeks to do it phased. Additionally, you may ask, when does it need human judgment? When there is proprietary logic, custom code, undocumented lineage, business logic buried in SQL that needs rethinking. But even then—automation handles 60-70%. You focus your people on the 30-40% that actually matters.
Design for Analytics and AI From Day One (Or Pay for Redesign Later)
Here’s the uncomfortable truth: most large enterprise data migrations architecture for the system you had, not the one you need.
Result? Your enterprise data modernization stalls because your ML team can’t build unified models. Customer data lives in Fabric and transactions are in Snowflake. Your BI team runs queries across three platforms. You’ve swapped one complexity for another.
Successful enterprise data migration strategy starts here: What datasets are actually strategic (customer, product, financial, operational)? Those live in one primary cloud platform, architected for both transactional access and analytics. Everything else—logs, archives, reference data—lives elsewhere with clear integration points. One golden source of truth. Dependent systems pull from it.
For most enterprises, that’s Microsoft Fabric, Databricks, or Snowflake. One well-designed lakehouse or warehouse. Not three.
Second, build your analytics-ready data architecture for ML, not just BI. Analytical schemas for humans (star schemas, cubed dimensions) are not the same as data structures for ML. ML needs dense feature sets, no missing values in key columns, history of values (not just current state).
During your data migration planning, document this upfront. Work with your ML and analytics teams to define what “good data” looks like—precision, completeness, consistency standards. Build data quality validation checks that test for those, not just row counts.
Third, if your enterprise data modernization roadmap includes real-time analytics or AI (predictive inventory, dynamic pricing, streaming dashboards), your migration architecture has to support it now. Legacy ETL runs nightly batches. Cloud tools ingest and serve in seconds. Set up streaming capability from day one, even if you’re not using it yet. It’s cheap to add now. It’s expensive to re-architect later.
This is analytics modernization at scale—building infrastructure that grows with your AI needs.
How Do You Ensure Business Continuity Post-Migration?
Business continuity after data migration is about stabilizing systems, validating operations, and minimizing disruption to users. Even upon successful data transfer, there are operational risks in case systems are not closely monitored.
Key steps to ensure continuity are:
- Monitoring application performance, data access, and system availability in real-time
- Validating critical business processes like reporting, transactions, and integrations
- Maintaining rolling back plans and backups during the stabilization period
- Providing support and training to business users to deal confidently with the changes
- Responding rapidly to post-migration problems using well-defined incident management processes
A well-organized post-migration support phase helps organizations keep business running while users transition to the new data environment.
The Specific Enterprise Data Migration Paths We See in 2026
Informatica to Azure Data Factory + Talend Migration
Informatica’s powerful. It’s also expensive (licensing scales with CPU). Talend and Azure Data Factory cost less, integrate with modern cloud stacks, scale better.
Informatica to Azure Data Factory migration using FLIP converts 85-90% automatically. Validate outputs. Decommission Informatica. Enterprises typically see 18-month ROI from licensing savings alone.
SSIS to Microsoft Fabric Migration
SSIS is tied to SQL Server. When you move to Fabric, SSIS becomes obsolete. SSIS to Fabric conversion via FIRE transforms packages to Spark jobs and ADF pipelines. Benefit? SSIS is batch. Fabric is streaming. Post-migration, you add real-time data migration without rebuilding. One healthcare organization completed their SSIS to Fabric migration in 10 weeks, then added live patient data streaming that would’ve required a whole new platform under SSIS.
SSRS is desktop. Power BI is cloud, mobile, modern. Don’t convert 1:1. Reimagine. Map to Power BI datasets, rebuild reports to use interactive features. More work upfront. Orders of magnitude better user experience.
This business intelligence migration is more of a data modernization project than a lift-and-shift.
Case Study 1: Transforming Enterprise Data with Automated Migration from Informatica to Talend
Client Challenge
The client used a large Informatica setup that became costly and slow to manage. Licensing fees kept rising. Workflows were complex, and updates needed heavy manual work. Modernization stalled because migrations took too long.
Kanerika’s Solution
Kanerika used FLIP to automate the conversion of Informatica mappings and logic into Talend. FIRE extracted repository metadata so the team could generate Talend jobs with minimal manual rework. Outputs were validated through controlled test runs and prepared for a cloud-ready environment.
Impact Delivered
• 70% reduction in manual migration effort
• 60% faster time to delivery
• 45% lower migration cost
• Better stability through accurate logic preservation and smooth cutover
How Kanerika Helps Companies Move to Modern Data Platforms Without Business Disruption
Here’s the reality: most enterprise data migration projects fail because they’re treated as IT infrastructure upgrades instead of business strategy projects. You need a partner who understands that moving data isn’t just about technical conversion—it’s about ensuring your business keeps running while you build for the future.
That’s where Kanerika comes in.
We’ve spent years working with enterprises migrating from legacy platforms (Informatica, SSIS, Tableau, SSRS) to modern cloud stacks (Talend, Microsoft Fabric, Power BI, Databricks). Our FLIP migration accelerators automate the heavy lifting—converting hundreds of ETL workflows and pipelines while maintaining data accuracy and security.
But automation is only part of it. We also design your enterprise data architecture so information flows cleanly across your entire organization. Real-time data sync, API-based automation, cloud-ready patterns—the infrastructure that makes analytics-ready data actually work. When your teams have a single version of truth instead of pulling from three different systems, everything gets faster. Reporting works. Analysis is accurate. Operations don’t grind to a halt mid-migration.
Our Expertize
We work closely with your teams to understand how your business actually runs, what you’re trying to achieve, and where your data challenges come from. That means we design cloud migration strategies that match your reality, not a template.
Our experience spans banking, retail, logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing—each with different security, compliance, and operational needs. We’ve cut migration costs by 60%+, reduced risk through phased cutover, and strengthened security posture during data platform transitions.
But the real win? You gain a long-term partner for enterprise data modernization, not just a project vendor. A clear path to modern analytics and AI readiness. Confidence that the move won’t disrupt your business. And infrastructure built for the next three years, not just today.
If you’ve got Informatica, SSIS, or Tableau at scale—let’s talk about your specific landscape.
FAQs
How long does enterprise data migration take?
For 300-500 ETL objects, expect 12-26 weeks depending on your approach. Manual migration of Informatica or SSIS workflows takes 24-26 weeks with 8-10 people doing hand-coded conversions. Automated migration using FLIP cuts this to 12-16 weeks—the accelerators handle 80-90% of conversion, and your team focuses on validation and complex logic. Add 2-4 weeks for phased cutover. Kanerika has completed 450-workflow migrations in 12 weeks instead of 26, cutting duration in half while reducing costs by 65%.
What does it cost to migrate from Informatica?
Informatica migration costs typically run $200K-$800K for implementation, plus $50K-$150K for cloud infrastructure and licensing over 12 months. The hidden costs are the real killers: post-migration rework ($300K-$500K if architecture isn’t right), extended support ($100K-$200K), or re-migration in 18 months ($500K+). Most enterprises see 18-month ROI just from Informatica licensing savings (cloud ETL is 50-70% cheaper annually). Kanerika structures migrations with fixed-price FLIP automation plus flexible validation work, which typically costs 30-40% less than manual migration quotes.
How Do You Prevent Data Loss and Downtime During Migration?
Three strategies eliminate risk: phased cutover (run old and new systems in parallel for 2-4 weeks to validate outputs match), real-time data validation (hourly automated checks instead of end-of-month), and staged migration by data source (pilot non-critical systems first, then expand in waves). Never do big-bang cutover. Kanerika recommends 90-day post-migration support, not 30. On-call engineers catch issues in week 2 that would become disasters in production week 6, preventing surprise failures.
Can You Automate the Conversion of Legacy ETL (Informatica, SSIS)?
Yes—automation converts 80-90% automatically (mappings, transformations, data types, scheduling, metadata). The remaining 10-20% requires manual review (custom code, complex business logic, undocumented transformations). Manual migration of 450 workflows takes 26 weeks and costs $600K+. FLIP automation does it in 12 weeks for $200K-$300K—same outcome, 50% faster, 65% cheaper. Code gets generated clean with cloud-native patterns, not hand-written with technical debt.
Which cloud platform should we migrate to—Azure Data Factory, Talend, or Databricks?
Choose based on your existing stack. Microsoft-aligned (Azure, Office 365, Dynamics)? Azure Data Factory is fastest, especially for SSIS migrations. Large ETL environment needing vendor flexibility? Talend has better abstraction layers. Data science and ML focused? Databricks supports real-time streaming better. Kanerika assesses your landscape first and recommends accordingly—but FLIP automation works across all three platforms, so platform choice doesn’t change the migration speed or cost model.
How Do You Ensure Data Quality After Migration?
Three layers: pre-migration assessment (profile source data for issues before cutover), parallel validation during migration (automated comparisons between source and target in real-time), and continuous monitoring post-migration (hourly checks on record counts, data distributions, completeness, freshness). Kanerika builds validation into FLIP—automated checks compare outputs line-by-line. After cutover, we monitor continuously for 90 days; most issues surface week 1-2 when we’re still there to fix them, not discovered months later.
What's the Real ROI of Enterprise Data Migration?
Yes, if done right. Most enterprises see 18-month payback from Informatica licensing savings alone ($200K-$400K annually). Add operational efficiency gains ($50K-$150K year 1, growing to $150K-$300K by year 3) and new analytics/BI capabilities ($100K-$500K by year 3). Total year-3 benefit: $400K-$1.25M against a $600K investment. Strategic ROI includes AI-readiness, faster insights, compliance improvements, and talent retention. Poor ROI comes from skipping architecture redesign, not involving analytics teams, or rushing big-bang cutover instead of phasing. Kanerika’s conservative estimate: 14-16 month positive ROI from licensing savings plus efficiency gains.











