Microsoft Fabric now powers data operations for 70% of the Fortune 500. At FabCon 2025, Microsoft announced major upgrades: Copilot is now available across all tiers, CosmosDB is integrated into Fabric, and agentic AI features enable data agents to act on insights in real-time. These changes make Microsoft Fabric adoption stronger for enterprise-scale automation, analytics, and AI-driven decision-making.
Microsoft Fabric is a unified data platform built to simplify how organizations manage, analyze, and share data. It combines tools for data engineering, data science, real-time analytics, and business intelligence into one ecosystem. With built-in governance, AI capabilities, and integration across Microsoft 365 and Azure, Fabric helps teams work from a single source of truth.
Instead of juggling multiple platforms, Fabric lets you centralize data in OneLake, Microsoft’s cloud-based data lake. It supports structured and unstructured data, connects with over 180 data sources, and offers real-time insights through Power BI and other services.
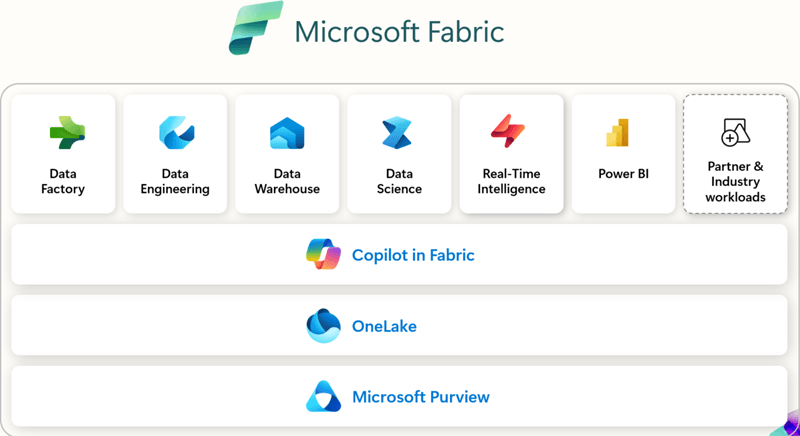
Core Components of Microsoft Fabric Architecture
1. OneLake – Unified Data Lake
If you have worked with data platforms before, you know the pain of having data scattered across five different systems that do not talk to each other. OneLake is Microsoft’s answer to that. It is one central data lake where everything lives, built on the Delta Lake format. Every tool inside Fabric reads from and writes to the same place. That alone eliminates a huge chunk of the governance headaches most teams deal with.
2. Experiences – Role-Specific Workloads
Microsoft Fabric offers tailored experiences for different data roles, each providing specialized tools and functionalities:
- Data Engineering: Utilizes Spark-based services for data ingestion, transformation, and pipeline orchestration.
- Data Factory: Provides a unified data integration service for building and managing complex data workflows.
- Data science: Supports the development and deployment of end-to-end data science workflows at scale.
- Data Warehouse: Offers lake-centric warehousing that scales compute and storage independently.
- Real-Time Intelligence: Enables cloud-based analysis of data from applications, websites, and devices.
- Power BI: Microsoft’s flagship business intelligence service for interactive dashboards and analytics.
- Data Activator: No-code monitoring that watches your data and triggers actions when something changes.
3. Workspaces – Collaborative Environments
Workspaces in Microsoft Fabric provide collaborative environments where teams can create and manage data assets such as reports, notebooks, and lakehouses. These workspaces facilitate role-based access control, ensuring that users have the appropriate permissions to interact with data and resources.
4. Semantic Models – Unified Data Representation
Here is a problem most companies run into at some point: two teams pull the same metric and get two different numbers. Semantic models fix that. Semantic models in Microsoft Fabric enable the creation of a unified data representation layer. These models standardize data definitions and metrics, ensuring consistency across various reports and analyses. They play a crucial role in bridging the gap between raw data and actionable insights.
5. Governance and Security – Ensuring Data Integrity
Microsoft Fabric incorporates robust governance and security features to protect data assets:
- Purview Integration: Provides comprehensive data governance capabilities, including data lineage tracking and classification.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Ensures that users have the appropriate permissions to access and modify data resources.
- Data Sensitivity Labels: Helps identify and protect sensitive information within the data ecosystem.
6. AI and Automation – Enhancing Productivity
Microsoft Fabric integrates AI-driven tools to automate tasks and enhance productivity:
- Copilot Features: Assist users in data preparation, transformation, and analysis by providing intelligent suggestions and automating repetitive tasks.
- Data Activator: Monitors data changes and triggers actions based on predefined conditions, facilitating real-time data operations.
Benefits for Data Teams and Business Users
Microsoft Fabric supports both technical and non-technical users. Moreover, data engineers gain scalable tools to build and manage pipelines, while analysts and business users benefit from simplified reporting and actionable insights.
For data teams:
- Simpler integration across multiple data sources
- Faster development thanks to low-code and no-code options
- One place to handle governance and monitoring
For business users:
- Self-service analytics with Power BI
- Real-time dashboards for decision-making
- Access to trusted data without needing deep technical skills
Fabric also helps reduce costs by consolidating tools and licenses into one platform.
Microsoft Fabric Raises the Bar Again: The Undisputed #1 Analytics Platform
Learn why Microsoft Fabric is the #1 analytics platform with AI-powered insights and unified data.
Understanding the Microsoft Fabric Adoption Roadmap
The Microsoft Fabric adoption roadmap serves as a guide for organizations to transition from initial setup to full-scale usage. It outlines 12 key steps, organized to ensure alignment between culture, governance, user enablement, and system oversight.
1. Data Culture
Building a strong data-driven culture is the first step. Organizations need to instill a mindset where data is treated as a strategic asset and decisions are guided by insights rather than intuition.
2. Executive Sponsor
Securing an executive sponsor ensures leadership backing for the Fabric adoption initiative. This sponsor advocates for resources, sets priorities, and supports organization-wide adoption.
3. Business Alignment
Aligning the adoption strategy with business goals guarantees that the implementation addresses real business needs and drives tangible outcomes.
4. Content Ownership and Management
Define ownership of data assets and content. Clear roles and responsibilities ensure accountability and improve the quality, accuracy, and reliability of data across the organization.
5. Content Delivery Scope
Determine the scope of content delivery, which includes identifying the datasets, reports, dashboards, and insights that will be made available to teams. This helps prioritize efforts and manage expectations.
6. Center of Excellence (CoE)
Establish a Center of Excellence to oversee the adoption of fabric. The CoE provides best practices, develops templates, and supports teams in implementing and scaling solutions efficiently.
7. Governance
Implement strong governance frameworks to manage data quality, compliance, and security. Governance ensures that Fabric is used responsibly and consistently across the organization.
8. Mentoring and User Enablement
Enable users with training, mentoring, and workshops. Educated users can better leverage Fabric tools, enhancing productivity and adoption success.
9. Community of Practice
Build a community of practice where users can share knowledge, best practices, and tips. This collaborative approach accelerates learning and fosters innovation.
10. User Support
Provide ongoing user support to address challenges, answer queries, and maintain smooth operations. A support mechanism increases confidence and adoption rates.
11. System Oversight
Ensure system oversight through monitoring, performance tracking, and reporting. Oversight guarantees that the platform operates reliably and meets organizational needs.
12. Change Management
Finally, implement a robust change management strategy. Continuous communication, feedback loops, and iterative improvements help integrate Fabric into the organizational workflow effectively.
Types of Adoption and Maturity Levels in Microsoft Fabric
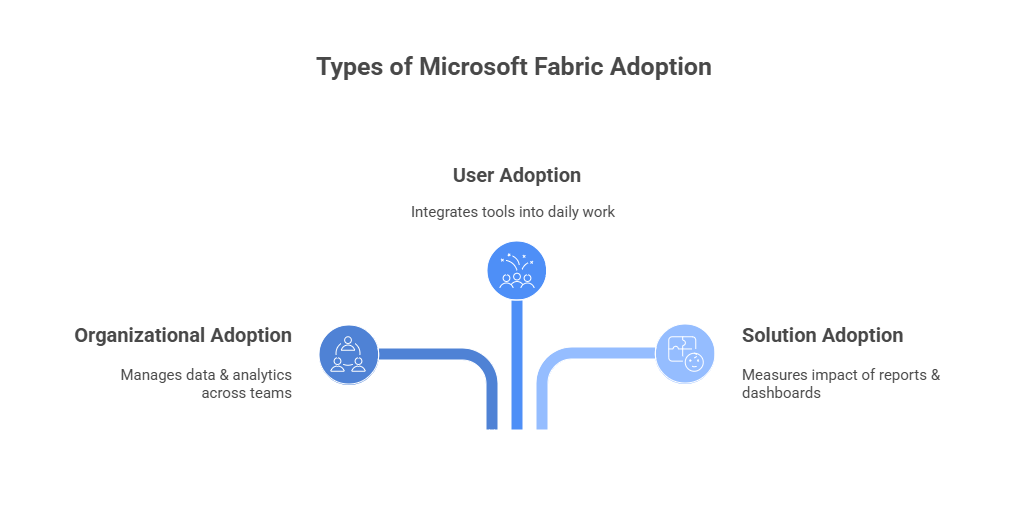
1. Organizational Adoption
Organizational adoption focuses on how effectively an organization manages analytics governance, data management practices, and processes to support business intelligence (BI) across departments.
Maturity Levels:
- Maturity level 100 – Initial: Pockets of success and experimentation exist in some areas.
- Maturity level 200 – Managed: Basic governance structures are in place; processes partially defined.
- Maturity level 300 – Defined: Standardized and documented processes; aligned with business objectives.
- Maturity level 400 – Quantitatively Managed: Metrics and insights are used to monitor and improve governance.
- Maturity level 500 – Efficient: Analytics solutions are widely accepted; continuous improvement is embedded.
2. User Adoption
User adoption measures the effectiveness with which individuals (creators and consumers) utilize analytics tools, integrating them into their daily workflows and leveraging their capabilities.
Maturity Levels:
- Stage 1 – Awareness: Users are aware of analytics tools and benefits.
- Stage 2 – Exploration: Users experiment with features and understand capabilities.
- Stage 3 – Adoption: Tools are integrated into daily workflows.
- Stage 4 – Proficiency: Users optimize usage and leverage advanced features.
- Stage 5 – Advocacy: Users share best practices and encourage others to adopt tools.
3. Solution Adoption
Solution adoption evaluates the impact and business value of analytical solutions, such as reports, dashboards, Power BI apps, or Fabric lakehouses.
Maturity Levels:
- Phase 1 – Initiation: Solutions are experimental with limited scope and impact.
- Phase 2 – Expansion: Solutions are deployed to a broader audience, gathering feedback.
- Phase 3 – Integration: Solutions are embedded in core business processes.
- Phase 4 – Optimization: Solutions are continuously improved based on metrics and feedback.
- Phase 5 – Transformation: Solutions drive significant business transformation and efficiencies.
Microsoft Fabric Implementation Framework
Implementing Microsoft Fabric requires a structured approach to ensure data, analytics, and insights drive real business value. This framework provides a clear, step-by-step guide to streamline adoption and maximize impact across the organization.
Phase 1: Discover
Objective: Understand business needs, data landscape, and stakeholder expectations.
Steps:
- Stakeholder Discovery Sessions – Engage business leaders and IT teams to gather requirements and expectations.
- Current State Assessment – Evaluate existing data systems, analytics processes, and gaps.
- Goal Alignment – Define business objectives, pain points, and target outcomes.
- Document Findings – Create a discovery report to align all stakeholders.
Outcome: Clear understanding of business priorities, data challenges, and readiness for Fabric adoption.
Phase 2: Architect
Objective: Design a scalable, secure, and efficient Microsoft Fabric environment.
Steps:
- Roadmap Creation – Develop a long-term data platform strategy with milestones.
- Data Source Identification – Map all relevant internal and external data sources.
- Architecture Design – Build detailed architecture diagrams covering OneLake, Lakehouse/Warehouse layers, and data flow.
- Security & Governance Planning – Define policies for access, compliance, and data protection.
- Custom Implementation Plan – Tailor the plan for organizational requirements and timelines.
Outcome: Blueprint of the Microsoft Fabric environment with clear governance, security, and integration strategy.
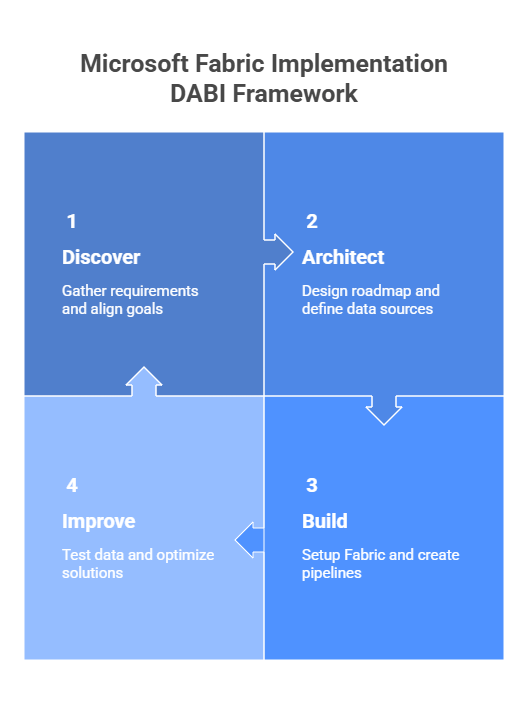
Phase 3: Build
Objective: Implement the designed solution in Microsoft Fabric.
Steps:
- Environment Setup – Configure Fabric workspace, user roles, and permissions.
- Data Integration – Bring data into OneLake and implement Medallion Architecture (Bronze, Silver, Gold).
- Pipeline & Solution Development – Build ETL pipelines, semantic models, and Power BI reports.
- Optimization & Monitoring Setup – Enable performance tracking and automated alerts.
Outcome: Operational Microsoft Fabric environment with integrated data, analytics pipelines, and visualizations.
Phase 4: Improve
Objective: Validate, optimize, and ensure continuous adoption.
Steps:
- Data Validation & Testing – Ensure data accuracy, completeness, and quality.
- User Training & Enablement – Provide workshops, manuals, and support to boost adoption.
- Feedback Loop & Iteration – Collect feedback and optimize solutions based on real usage.
- Documentation of Best Practices – Provide detailed guides for governance, analytics, and user enablement.
Outcome: High adoption, data-driven insights, and continuous improvement of analytics solutions.
Key Benefits of the DABI Framework
- Structured approach reduces risks and accelerates adoption.
- Ensures alignment between business objectives, user adoption, and technical solutions.
- Promotes governance, security, and scalability.
- Provides a repeatable consulting methodology for clients.
Common Challenges and How to Solve Them
Even with a good plan, Microsoft Fabric adoption can hit roadblocks. Here are some common issues and their solutions.
1. Resistance to Change
Some users prefer old tools. Others fear losing control. To overcome this, clearly communicate the benefits. Demonstrate how Fabric streamlines work and enhances results.
Tips:
- Share success stories
- Involve users early
- Offer hands-on demos
When users see real benefits and feel involved, adoption becomes smoother and more impactful.
2. Skill Gaps
Fabric includes advanced tools. Not everyone knows how to use them. Solve this with targeted training and mentoring. Pair new users with experienced ones.
Focus on:
- Power BI for analysts
- Data Factory for engineers
- Synapse for data scientists
Building skills unlocks confidence and ensures long-term success with Microsoft Fabric.
3. Cost Management
Fabric uses a subscription model. Without planning, costs can rise. Monitor usage, scale resources wisely, and automate where possible.
Best practices:
- Use Fabric capacities based on workload
- Set alerts for overuse
- Review licensing regularly
Smart cost governance keeps adoption sustainable and drives measurable ROI.
4. Integration with Existing Systems
Fabric must work with your current tools. Integration can be tricky. Use APIs, connectors, and OneLake shortcuts to connect systems.
Steps:
- Map data flows
- Test ETL pipelines
- Plan staged rollouts
With the right approach and support from partners like Kanerika, organizations can integrate Fabric seamlessly without disrupting existing operations.
Transform Data Operations with Microsoft Fabric!
Work with Kanerika to Simplify Your Adoption Journey
Real-World Use Cases and Success Stories
1. Retail
Iceland Foods, A UK grocery chain with over 960 stores, adopted Microsoft Fabric and Real-Time Intelligence to unify data across stores. They now make real-time decisions on promotions, inventory, and staffing.
Heritage Grocers Group Operating across six US states, they used Microsoft Fabric to unify POS and ERP data across brands like Cardenas Markets and Tony’s Fresh Market. The result: $500,000 in savings and improved customer service.
2. Finance
Bank CenterCredit (Kazakhstan) serves 3 million customers. The bank used Fabric to automate reporting, reduce errors by 40%, and save 800 hours per month. Decision-making speed improved by 50 percent.
Standard Chartered Bank adopted Microsoft’s data stack, including Dynamics 365 and Azure, to modernize customer relationship management and regulatory reporting. Their Corporate & Investment Banking division unified client data across 67 countries, reduced manual data entry, and improved client engagement using AI-powered insights.
3. Healthcare & Life Sciences
Mount Sinai partnered with Microsoft to centralize electronic health records and research data using Azure and Fabric. Their Clinical Data Science initiative utilizes AI to predict risks such as malnutrition and falls. This led to reduced hospital stays and improved patient outcomes.
ARcare (Nonprofit Healthcare Provider) Operating in rural Arkansas, Kentucky, and Mississippi, ARcare adopted Fabric in two weeks. It eliminated 6–8 hours of manual work daily, improved care plan adherence by a factor of 10, and enabled secure, real-time data sharing.
4. Manufacturing
Siemens uses Microsoft Fabric and Teamcenter to gain complete visibility across the product lifecycle—from design to manufacturing. They analyze sensor data to reduce drag in vehicles, improve efficiency, and accelerate product development. Fabric helps Siemens unify digital and physical systems for better decision-making.
Bridgestone EMEA Faced with scattered data across global factories, Bridgestone used Microsoft Fabric to unify IT/OT data, reduce downtime, and improve predictive maintenance. Workers now use conversational AI to troubleshoot faster.
5. Public Sector
The Metropolitan Police adopted Microsoft Azure and Microsoft 365 to centralize crime data, enhance digital investigations, and improve collaboration across the organization. Officers now access real-time data on patrol, which reduces manual tasks and improves response times. Azure supports secure digital forensics and analytics.
Kanerika: Your #1 Partner for Microsoft Fabric Implementation
Kanerika is a certified Microsoft Data & AI Solutions Partner that helps businesses get more out of Microsoft Fabric. Our team includes certified experts and Microsoft MVPs who build data platforms that are scalable, secure, and actually aligned with how the business works. We simplify messy data environments, set up real-time analytics, and put proper governance in place using Fabric’s unified architecture.
We also help companies move off legacy systems without the headaches that usually come with it. Manual migrations are slow and error-prone, so we built automation tools that handle transitions from SSRS to Power BI, SSIS/SSAS to Fabric, and Tableau to Power BI. The result is cleaner reporting, better data access, and lower maintenance costs.
As one of the first teams globally to implement Microsoft Fabric, we follow a structured approach that covers architecture design, semantic modeling, governance setup, and user training. Every engagement is tailored to the organization, so businesses can move fast, stay secure, and get real value from Fabric without unnecessary disruption.
Drive Business Growth with Microsoft Fabric Adoption!
Partner with Kanerika for Smooth and Scalable Adoption
FAQs
1. Which companies are using Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric is widely adopted, with reports showing usage by over 70% of Fortune 500 firms. Companies like EPAM Systems, Slalom, Harman International, Insight Enterprises, and Microsoft itself rely on it to manage large-scale data, analytics, and AI workloads.
2. How is Microsoft Fabric different from Power BI?
Power BI is primarily a visualization and reporting tool, while Microsoft Fabric is a complete analytics platform. Fabric unifies data ingestion, storage (OneLake), transformation, AI, real-time analytics, and visualization, with Power BI functioning as just one component within it.
3. Who are Microsoft Fabric’s competitors?
Fabric competes with platforms like Databricks, Snowflake, SAS Viya, Dataiku, Informatica, Talend, Tableau (with Tableau Prep), AWS Glue, and Google BigQuery. These solutions offer strong alternatives in data integration, analytics, and AI-driven insights.
4. How does Fabric integrate with other cloud platforms?
Fabric is a SaaS-based end-to-end platform. Unlike AWS, GCP, or OCI, which require combining multiple services for the same experience, Fabric delivers a unified environment built on OneLake, making integration and management simpler.
5. What is the real-world impact of Fabric?
Enterprises using Fabric report faster reporting, improved AI-driven analytics, and reduced complexity in managing data. Its adoption across industries shows that organizations are leveraging it for scalability, real-time insights, and business transformation.
6. What lifecycle and development tools does Fabric provide?
Microsoft Fabric supports lifecycle management with CI/CD pipelines, Git integration, deployment pipelines, and variable libraries. These features help teams collaborate, maintain version control, and deploy updates seamlessly.









