Artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving beyond simple chatbots and rule-based automation, ushering in a new era of autonomous agents—AI systems that can perceive, reason, and act independently. Unlike static tools that only respond to predefined inputs, autonomous agents learn, adapt, and make decisions in real time, transforming how enterprises operate.
According to Gartner, “By 2026, 40% of enterprise applications will include autonomous agents, up from less than 5% today.” This shift signals more than just an upgrade in automation—it marks a fundamental change in how businesses approach efficiency, decision-making, and innovation. From finance to healthcare and supply chain management, autonomous agents are becoming mission-critical partners.
This blog will explore what autonomous agents are, their real-world applications, business benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping their adoption.
Key Takeaways
- Autonomous agents go beyond chatbots – they don’t just converse but can perceive, reason, and act independently to complete multi-step workflows.
- Core capabilities include goal-setting, planning, integration with enterprise tools, continuous learning, and proactive decision-making.
- Industries leading adoption: finance (fraud detection, compliance), healthcare (triage, diagnostics), retail (dynamic pricing, supply chain), and logistics.
- Business benefits: higher efficiency, cost savings, scalability, enhanced decision-making, and improved customer experiences.
- Challenges remain—data privacy, integration with legacy systems, explainability, governance, and high implementation costs.
- Future outlook: By 2030, enterprises may run on fully autonomous multi-agent ecosystems, combining edge + cloud deployments and plug-and-play agents from AI marketplaces.
- Getting started: Enterprises should begin with high-ROI pilot projects, enforce governance, train teams for human-AI collaboration, and partner with AI solution providers.
Take Your Business to the Next Level with Powerful AI Agents!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
What Are Autonomous Agents?
Autonomous agents are advanced AI systems designed to perceive their environment, reason through data, and take independent actions to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional automation, which operates on fixed rules, or chatbots that mainly respond to text-based queries, autonomous agents go several steps further—they plan, decide, and act with minimal human intervention.
The core difference lies in intelligence and adaptability. Traditional automation is rigid: it follows predefined workflows and fails when unexpected scenarios arise. Chatbots, even those powered by NLP, remain reactive—answering questions or performing simple, scripted tasks. Autonomous agents, on the other hand, are proactive. They can monitor processes continuously, anticipate issues, and execute multi-step workflows across systems.
Key capabilities of autonomous agents include:
- Goal-setting and planning: Breaking complex objectives into smaller, manageable tasks.
- Tool usage and integration: Connecting with APIs, CRMs, databases, or enterprise systems to complete tasks.
- Continuous learning and adaptation: Improving performance over time by learning from feedback and new data.
In practice, these systems are already being deployed. LangChain agents orchestrate reasoning with tool usage for multi-step tasks. AutoGen enables collaborative interactions between multiple agents to solve complex problems collectively. CrewAI allows specialized AI “roles” to work together across business workflows like finance, compliance, and operations.
Core Features of Autonomous Agents
| Core Feature | Technical Capability | Business Impact |
| Autonomy & Decision-Making | Execute tasks without human intervention | 70-90% reduction in manual work |
| Context Awareness | Persistent memory across interactions | 40-60% improvement in accuracy |
| Multi-Step Workflows | Handle complex processes end-to-end | 50-80% faster process completion |
| Tool Usage & APIs | Connect with enterprise systems | 30-50% increase in productivity |
| Collaboration | Multi-agent coordination | 2-10x scaling capability |
| Explainability & Governance | Transparent decision tracking | 90%+ compliance achievement |
1. Autonomy & Decision-Making
Autonomous agents operate independently without requiring constant human supervision. They analyze situations, evaluate options, and execute appropriate actions based on predefined goals and learned patterns. Unlike traditional automation that follows rigid rules, these agents adapt their approach based on context and changing conditions.
This independence enables agents to handle routine tasks continuously, making decisions about prioritization, resource allocation, and problem resolution. For example, a customer service agent can determine the urgency of support tickets, escalate complex issues to humans, and resolve standard inquiries automatically.
2. Context Awareness
Modern autonomous agents maintain persistent memory across interactions, learning from sprevious experiences and building comprehensive understanding over time. They can reference past conversations, track project history, and understand evolving customer relationships without losing important context.
This contextual intelligence enables more sophisticated reasoning and personalized interactions. An agent helping with project management remembers team preferences, deadline patterns, and resource constraints from previous projects, applying these insights to new situations.
3. Multi-Step Workflows
Autonomous agents excel at managing complex, multi-step processes that span different systems and timeframes. They can orchestrate sequences of actions, handle dependencies between tasks, and adapt workflows based on intermediate results or changing requirements.
Rather than executing single commands, these agents manage entire business processes from initiation to completion. They coordinate approvals, gather required information, update multiple systems, and ensure all stakeholders receive appropriate notifications throughout the workflow.
4. Tool Usage & APIs
Enterprise autonomous agents integrate seamlessly with existing business systems through APIs and tool interfaces. They can access databases, update CRM records, generate reports, send emails, and interact with specialized software applications as needed.
This integration capability transforms agents from isolated tools into central orchestrators of business operations. They bridge gaps between different systems, automate data transfers, and ensure consistency across the entire technology stack.
5. Collaboration
Advanced autonomous agents work together in coordinated teams, sharing information and dividing complex tasks among specialized agents. Each agent brings specific expertise while contributing to larger organizational objectives through intelligent collaboration.
Multi-agent systems enable sophisticated problem-solving that exceeds what individual agents can accomplish. Sales agents collaborate with finance agents for contract approvals, while customer service agents coordinate with inventory agents to resolve shipping issues.
6. Explainability & Governance
Enterprise-grade autonomous agents provide transparent decision-making processes through detailed audit trails and explainability dashboards. Human supervisors can understand why agents made specific choices, review decision criteria, and adjust parameters when needed.
This transparency builds trust and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. Governance features include approval workflows for high-value decisions, performance monitoring, and the ability to intervene when agents encounter unusual situations or operate outside defined parameters.
These core features work together to create intelligent systems that augment human capabilities while maintaining the oversight and control necessary for enterprise environments.
Autonomous Agents vs Traditional Automation & Chatbots
| Feature | Traditional Chatbots | Traditional Automation | Autonomous Agents |
| Intelligence Level | Rule-based responses | Pre-programmed workflows | AI-driven reasoning |
| Adaptability | Static conversation flows | Fixed process rules | Dynamic adaptation |
| Scope of Action | Text conversations only | Single system tasks | Cross-system coordination |
| Decision Making | Limited to predefined options | Rule-based triggers | Context-aware choices |
| Learning Capability | No learning | No learning | Continuous improvement |
| Proactivity | Reactive to user input | Event-triggered only | Self-initiated actions |
| Complexity Handling | Simple Q&A | Linear workflows | Multi-step reasoning |
| Integration | Basic API connections | Single-purpose tools | Enterprise-wide systems |
| Personalization | Template responses | Standard processes | Adaptive experiences |
| Error Handling | Escalate to humans | Stop on exceptions | Problem-solving attempts |
1. Traditional Automation: The Foundation
Traditional automation follows predetermined rules and workflows without deviation. These systems excel at repetitive, predictable tasks like data entry, file transfers, and scheduled reports. When a specific trigger occurs, the automation executes a predefined sequence of actions exactly as programmed.
However, traditional automation breaks down when encountering unexpected situations or requiring judgment calls. It cannot adapt to new scenarios or learn from experience, making it suitable only for highly structured processes.
2. Chatbots: Conversational but Limited
Chatbots handle text-based interactions through scripted conversation flows or simple pattern matching. They answer frequently asked questions, guide users through basic processes, and collect information through predefined forms.
While modern chatbots use natural language processing to understand user intent, they remain fundamentally reactive tools. They wait for user input and respond with information or actions from their knowledge base, but cannot initiate conversations or take independent action.
3. Autonomous Agents: Intelligent Decision-Makers
Autonomous agents represent a fundamental leap beyond traditional automation and chatbots. They combine artificial intelligence with decision-making capabilities to handle complex, dynamic situations that require reasoning and adaptation.
Unlike their predecessors, autonomous agents can analyze context, learn from experience, and make decisions without explicit programming for every scenario. They proactively monitor situations, identify opportunities or problems, and take appropriate action independently.
Key Differentiators:
- Adaptive Intelligence: Autonomous agents adjust their behavior based on new information and changing circumstances, while traditional systems follow rigid patterns.
- Proactive Behavior: Instead of waiting for triggers or user input, autonomous agents actively monitor environments and initiate actions when beneficial.
- Complex Reasoning: They handle multi-step processes that require evaluating multiple factors, understanding dependencies, and making judgment calls.
- Enterprise Integration: Autonomous agents coordinate across multiple systems and departments, orchestrating complex business processes that traditional automation cannot manage.
The evolution from simple automation to intelligent agents represents a shift from replacing manual tasks to augmenting human decision-making and strategic thinking.
Generative AI Examples: How This Technology is Reshaping Creativity and Innovation
Redefining creativity and innovation, generative AI produces unique content, designs, and solutions across industries.
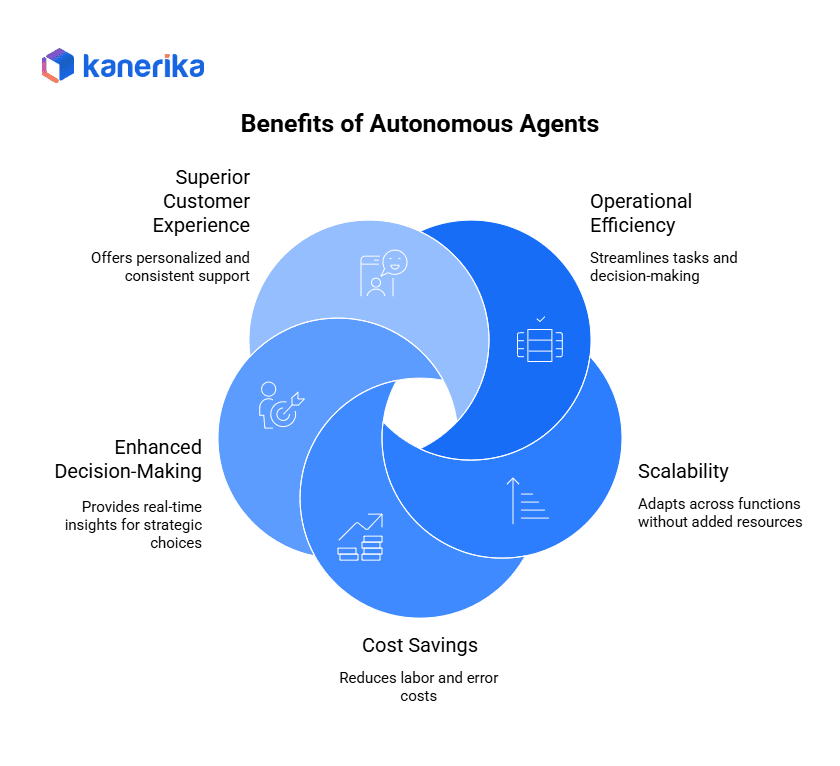
Benefits of Autonomous Agents
1. Operational Efficiency: Beyond Simple Automation
Autonomous agents transform business operations by handling both repetitive tasks and complex decision-making processes. Unlike traditional automation that requires detailed programming for every scenario, these agents adapt to new situations while maintaining consistent performance standards.
They excel at processing documents, analyzing data patterns, managing workflows, and making routine business decisions without human intervention. This capability frees employees from mundane tasks while ensuring critical processes continue running smoothly around the clock.
2. Scalability Across Business Functions
Autonomous agents scale effortlessly across different departments and business functions without requiring proportional increases in human resources. A single agent framework can handle customer service inquiries, process financial transactions, manage inventory levels, and coordinate supply chain activities simultaneously.
This cross-functional adaptability means organizations can expand operations, enter new markets, or handle seasonal demand spikes without hiring additional staff or restructuring existing processes. The same intelligent system that manages customer onboarding can be adapted to handle employee HR requests or vendor management tasks.
3. Significant Cost Savings
Organizations achieve substantial cost reductions through decreased labor requirements and improved accuracy. Autonomous agents work continuously without breaks, benefits, or training costs while maintaining consistent quality standards that reduce expensive errors and rework.
Studies show companies implementing autonomous agents achieve maximum reductions in operational costs for targeted processes, while error rates drop by 80% compared to manual operations. These savings compound over time as agents learn and improve their performance.
4. Enhanced Decision-Making Through Real-Time Insights
Autonomous agents process vast amounts of data continuously, providing leaders with timely insights and recommendations based on current market conditions, customer behavior, and operational metrics. They identify trends, predict potential issues, and suggest corrective actions before problems become critical.
This real-time intelligence enables faster strategic responses and more informed decision-making compared to traditional reporting cycles that rely on historical data analysis.
5. Superior Customer Experience
Customers receive intelligent, context-aware support that understands their history, preferences, and current needs. Autonomous agents provide personalized recommendations, resolve complex issues, and maintain consistent service quality across all interaction channels.
They remember previous conversations, anticipate customer needs, and coordinate with backend systems to provide comprehensive support without requiring customers to repeat information or wait for human agents.
Success Story: Banking Compliance Revolution
According to McKinsey research, banks commonly assign 10-15% of their workforce to KYC/AML compliance tasks while detecting only 2% of global financial crime flows. Leading financial institutions are now deploying autonomous agents with Retrieval-Augmented Generation to transform these processes.
These autonomous agents automatically access verified regulatory databases, process compliance queries, and maintain complete audit trails for every interaction. Banks implementing agentic AI report that each human supervisor can now oversee 20+ AI agents, achieving productivity gains of 200-2,000% while maintaining strict regulatory standards.
This transformation demonstrates how autonomous agents don’t just improve efficiency—they fundamentally reimagine how complex, regulated industries can operate at scale while exceeding compliance requirements.
Source: McKinsey – How agentic AI can change the way banks fight financial crime
Real-World Applications of Autonomous Agents
1. Finance: Intelligent Risk and Compliance Management
Financial institutions deploy autonomous agents for comprehensive fraud detection that analyzes transaction patterns, user behavior, and risk indicators in real-time. These agents adapt to new fraud techniques automatically, reducing false positives while catching sophisticated schemes that rule-based systems miss.
Compliance automation agents continuously monitor regulatory changes, update internal policies, and ensure adherence to complex financial regulations across multiple jurisdictions. Risk analysis agents process market data, credit information, and economic indicators to provide dynamic risk assessments for lending and investment decisions.
2. Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care and Research
Hospital autonomous agents perform patient triage by analyzing symptoms, medical history, and vital signs to prioritize care urgency. UC San Diego Health’s COMPOSER system monitors 150 live data points per patient, achieving a 17% reduction in sepsis deaths by flagging risks hours before symptoms become obvious.
Diagnostic support agents analyze medical imaging, lab results, and patient data to assist physicians with accurate diagnoses and treatment recommendations. Research automation agents process clinical trial data, identify suitable candidates, and accelerate drug discovery by analyzing vast datasets that would take researchers months to review manually.
3. Retail & E-commerce: Personalized Shopping Experiences
E-commerce platforms use autonomous agents for dynamic pricing that adjusts product costs based on demand, competitor analysis, inventory levels, and customer purchasing patterns. These agents optimize revenue while maintaining competitive positioning across millions of products simultaneously.
Personalized recommendation agents analyze customer behavior, purchase history, and preferences to suggest relevant products and create customized shopping experiences. Inventory optimization agents predict demand patterns, manage stock levels across multiple locations, and automatically trigger reorders to prevent stockouts while minimizing carrying costs.
4. Insurance: Streamlined Claims Processing
Insurance companies deploy autonomous agents that automatically process claims from submission to settlement. These agents parse documents, assess damage from photos, cross-reference policy terms, and approve routine settlements without human intervention.
Document parsing agents extract relevant information from accident reports, medical records, and repair estimates, while validation agents verify claims against historical data and fraud patterns to ensure accuracy and prevent abuse.
5. Logistics & Supply Chain: Optimized Operations
Logistics autonomous agents continuously optimize delivery routes based on traffic conditions, weather patterns, priority levels, and vehicle capacity. Warehouse robotics agents coordinate picking, packing, and shipping operations while managing inventory levels and space utilization.
Supply chain forecasting agents predict demand fluctuations, identify potential disruptions, and recommend proactive measures to maintain smooth operations across complex global networks.
6. Creative Industries: AI-Powered Content Creation
Marketing agencies use autonomous agents for campaign generation that creates personalized content across multiple channels while maintaining brand consistency. Video editing agents automate routine editing tasks, apply style transfers, and generate multiple versions for different audiences.
Content personalization agents adapt messaging, imagery, and offers based on individual user preferences and behavioral data, enabling mass customization at unprecedented scale.
Why Causal AI is the Next Big Leap in AI Development
Revolutionizing decision-making, Causal AI identifies cause-and-effect relationships to deliver deeper insights and accurate predictions.
Mini Case Studies
1. Aviva: Revolutionary Claims Automation
Aviva deployed more than 80 AI models across their claims domain, cutting liability assessment time for complex cases by 23 days and improving claim routing accuracy by 30%. Customer complaints dropped by 65%, while the transformation saved over £60 million in 2024 alone.
Source: McKinsey – The future of AI in the insurance industry
2. Netflix: Intelligent Content Orchestration
Traditional recommendation systems act like sophisticated chatbots, responding to user behavior with suggested content. Netflix’s AI agents go further by analyzing viewing patterns, predicting optimal release timing for new content, and even influencing production decisions based on audience preferences. This proactive approach drives higher engagement and reduces churn compared to reactive recommendation systems.
Note: Based on industry analysis of Netflix’s evolution from recommendation systems to intelligent content strategy agents
3. Amazon: Supply Chain Intelligence
Amazon announced investments in AI applications including Wellspring (generative AI mapping technology), AI-powered demand forecasting models, and new robotics capabilities using agentic AI systems for their global supply chain. These systems work behind the scenes to provide more accurate delivery locations, faster shipping options, and improved product availability.
Source: Fortune – How Walmart, Amazon, and other retail giants are using AI to reinvent the supply chain
Challenges & Limitations of Autonomous Agents
While autonomous agents promise efficiency, scalability, and adaptability, their adoption comes with significant challenges that organizations must address thoughtfully.
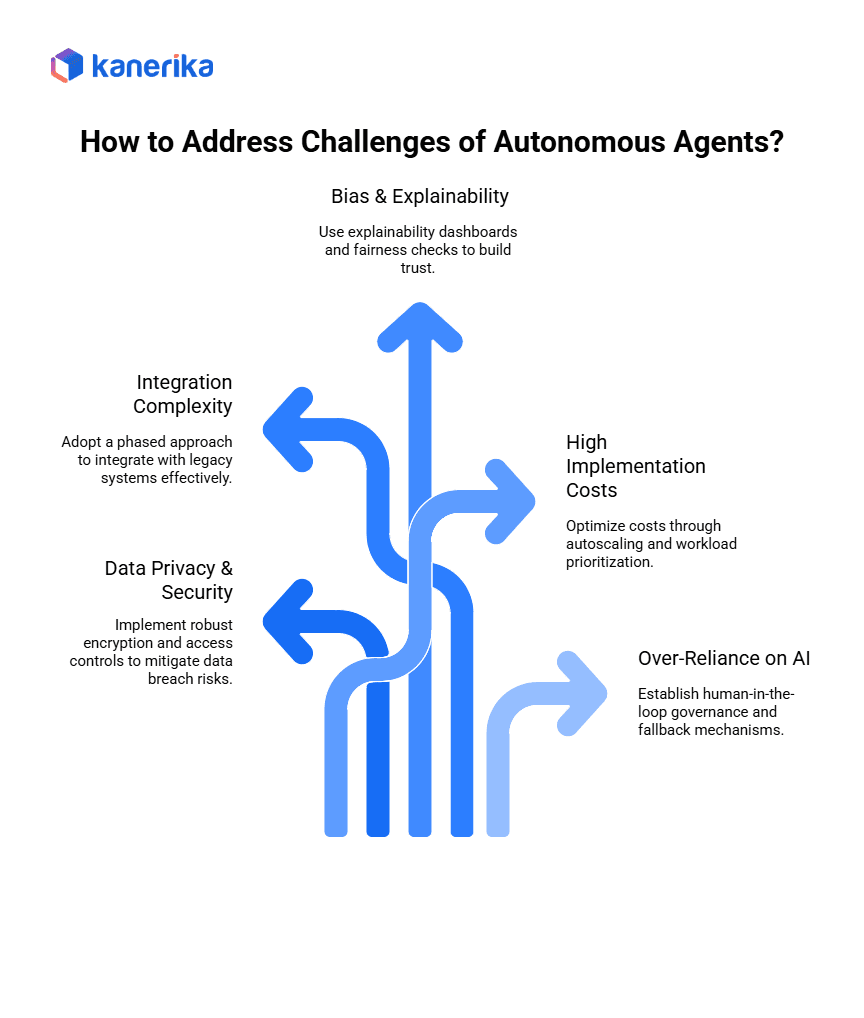
1. Data Privacy & Security Risks
Autonomous agents often handle sensitive business and customer data, such as financial transactions, medical records, or compliance reports. This raises risks of data breaches, unauthorized access, or non-compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Enterprises must implement robust encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring to mitigate these risks.
2. Integration Complexity
Many organizations still rely on legacy ERP, CRM, or supply chain systems. Integrating autonomous agents into these environments requires significant effort, APIs, and infrastructure upgrades. Without careful planning, integration challenges can delay ROI. A phased approach—starting with high-value workflows and expanding gradually—can ease this transition.
3. Bias & Explainability
Like other AI systems, autonomous agents can suffer from algorithmic bias if trained on incomplete or skewed datasets. Their “black box” decision-making also raises explainability concerns, especially in regulated sectors such as healthcare and finance. Businesses need explainability dashboards, audit logs, and fairness checks to build trust and comply with governance standards.
4. High Implementation Costs
Deploying autonomous agents requires powerful GPUs, cloud infrastructure, and specialized expertise. For smaller organizations, upfront costs may be a barrier. While cloud-based AI services reduce hardware expenses, ongoing costs for compute and maintenance can still be significant. Careful cost optimization strategies, like autoscaling and workload prioritization, are essential.
5. Over-Reliance on AI
As enterprises automate critical workflows, there’s a risk of over-dependence. System failures, downtime, or incorrect decisions could disrupt operations. Human-in-the-loop governance, fallback mechanisms, and redundancy planning are crucial safeguards.
Future of Autonomous Agents
The next decade will mark a turning point for autonomous agents as they move from experimental pilots to becoming core drivers of enterprise transformation.
1. Rise of Multi-Agent Ecosystems
By 2025 and beyond, we’ll see multi-agent systems where specialized agents—finance, compliance, operations, HR—work collaboratively. Instead of siloed automation, these agents will negotiate, delegate, and coordinate, creating digital ecosystems that run complex workflows seamlessly across departments.
2. Convergence with RAG for Real-Time Knowledge
One of the most promising advances will be the integration of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). Agents will not only reason with large language models but also pull real-time, verified knowledge from enterprise databases, regulatory portals, or customer records. This ensures decisions are accurate, compliant, and grounded in current information.
3. Edge + Cloud Hybrid Deployments
As latency-sensitive use cases expand (e.g., healthcare monitoring, autonomous vehicles), agents will increasingly run in hybrid models—combining the scale of cloud with the responsiveness of edge computing. This dual architecture will allow enterprises to balance speed, cost, and security.
4. AI Marketplaces & Plug-and-Play Agents
The “app store” for agents is already emerging. Platforms like Hugging Face Agents and Microsoft Copilot Studio are paving the way for plug-and-play autonomous agents that can be customized quickly. This democratizes access, making enterprise-grade AI more affordable and accessible.
5. Long-Term Vision: Fully Autonomous Enterprises
Looking ahead to 2030, the vision is clear: fully autonomous enterprises where multi-agent systems handle procurement, compliance, customer service, and logistics with minimal human intervention. Gartner predicts that by 2030, over 60% of enterprise applications will embed AI agents as core features, while McKinsey projects trillions in annual productivity gains from widespread adoption.
Boost Productivity and Efficiency with Next-Gen AI Agents!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
How Businesses Can Get Started with Autonomous Agents
Adopting autonomous agents can feel overwhelming, but a structured approach helps businesses unlock value quickly while minimizing risks.
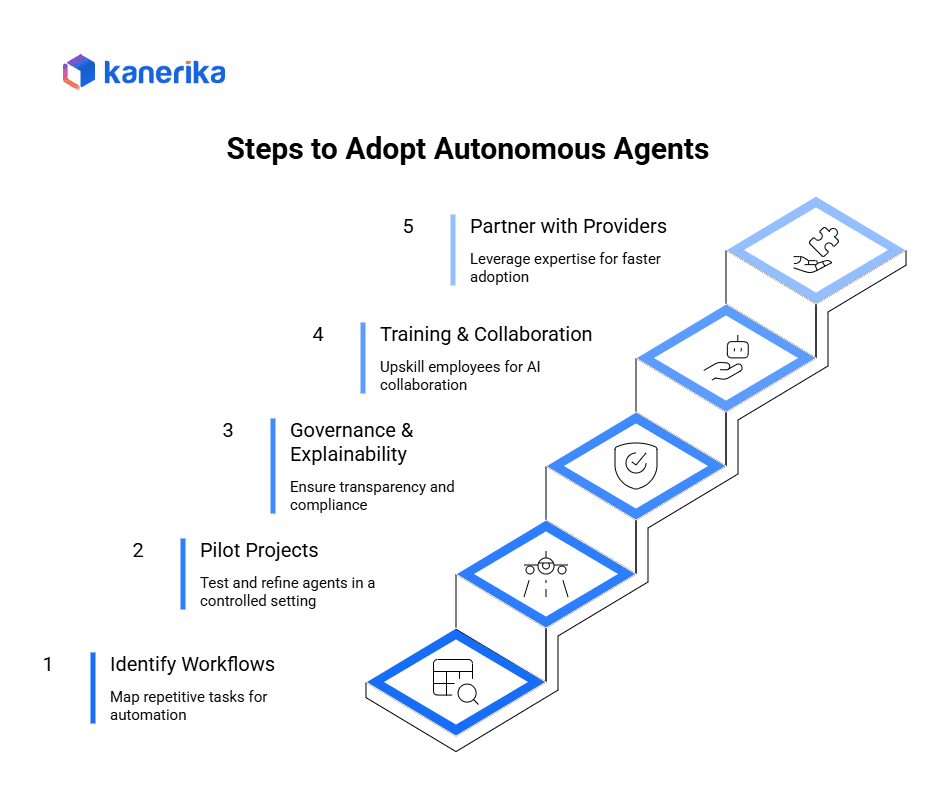
1. Identify High-ROI Workflows
Start by mapping repetitive, data-heavy, or decision-driven tasks that drain resources—such as compliance checks, claims processing, or inventory planning. These offer the fastest return on investment when automated with agents.
2. Begin with Pilot Projects
Rather than going all-in, launch small pilot projects in a controlled environment. This allows you to test performance, measure outcomes, and fine-tune models before scaling across the enterprise.
3. Ensure Governance & Explainability
Build trust by implementing explainability dashboards and human-in-the-loop controls. Clear audit trails and transparent decision-making are essential for regulatory compliance and stakeholder confidence.
4. Invest in Training & Human-AI Collaboration
Agents work best when they complement people. Upskill employees to collaborate with AI systems, shifting their focus from manual tasks to higher-value strategic work.
5. Partner with AI Solution Providers
Collaborating with experienced AI solution providers accelerates adoption. They bring technical expertise, industry-specific models, and integration capabilities that help enterprises avoid costly trial-and-error.
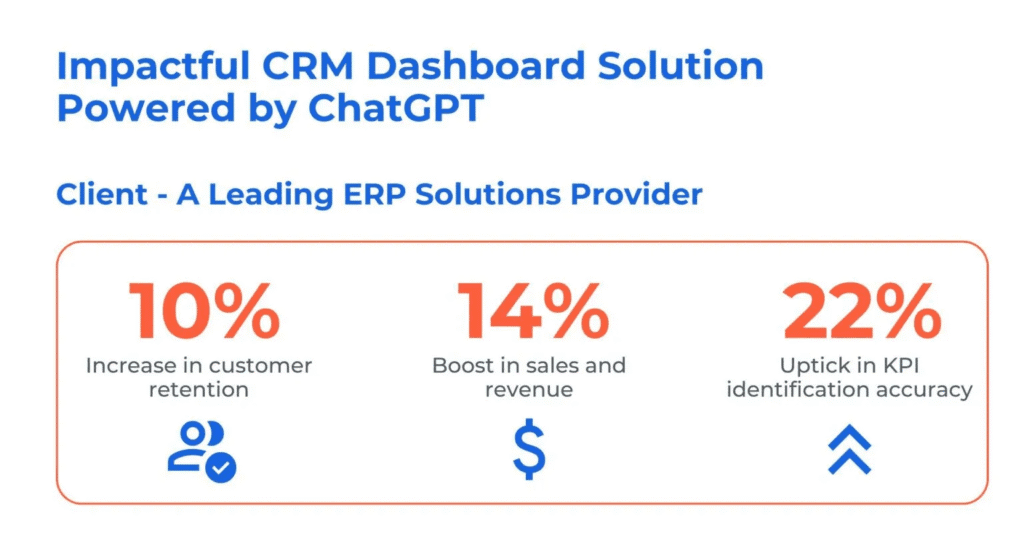
Case Study: Impactful CRM Dashboard Solution Powered by ChatGPT
Business Challenges
A reputed ERP provider that specializes in enterprise-level Customer Relationship Management (CRM) required a user-friendly and intuitive ERP software application and its UX. They also wanted to have an exceptional dashboard to complement their CRM—an effective tool for managing and analyzing sales data.
Kanerika’s Solutions
By leveraging technologies like Open AI’s CHatGPT and Microsoft Azure, Kanerika offered the following solutions:
- Leveraged Generative AI in CRM to create a visually appealing and functional dashboard, ensuring effective data management
- Utilized AI for creating dashboards that provided a holistic view of sales data, allowing businesses to identify KPIs, resulting in improved outcomes
- Enabled an intuitive UI that improved customer satisfaction, noted higher adoption rates, and gave a competitive edge
Become an Industry Leader with Kanerika’s Cutting-edge AI Solutions
Kanerika is a top-rated AI implementation company known for building custom AI models and solutions that align perfectly with each client’s unique business needs. With deep expertise in AI, we empower businesses across industries like banking and finance, retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics to seamlessly integrate AI into their operations. Our tailored AI solutions are designed to elevate operational efficiency, reduce costs, and drive impactful outcomes.
By developing advanced, industry-specific models, we help businesses automate complex processes, make data-driven decisions, and gain competitive advantages. Whether it’s optimizing financial forecasting, enhancing customer experiences in retail, streamlining manufacturing workflows, or advancing patient care, Kanerika’s AI solutions adapt to diverse requirements and challenges. Our commitment to client success has established us as a leader in the AI space, trusted by companies to transform their operations and realize measurable improvements through intelligent automation and analytics.
Streamline, Optimize, and Scale with Autonomous Agents!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
1. What are autonomous agents in AI?
Autonomous agents are AI systems that can perceive their environment, reason, and take actions independently to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional automation, they adapt and learn continuously.
2. How do autonomous agents differ from chatbots?
Chatbots are primarily conversational tools designed to respond to user queries, while autonomous agents go further by making decisions, executing multi-step workflows, and proactively solving problems across systems.
3. What industries benefit most from autonomous agents?
Finance, healthcare, retail, logistics, and manufacturing see the greatest impact. From fraud detection to patient triage and supply chain optimization, autonomous agents streamline complex processes.
4. Are autonomous agents safe and compliant?
Yes—when deployed with governance frameworks. Enterprises must ensure data privacy, regulatory compliance, and explainability features like dashboards and approval layers to maintain accountability.
5. What are examples of autonomous agents in business?
Examples include AI-powered compliance assistants, fraud detection agents in banking, supply chain optimization agents in retail, and patient triage agents in healthcare.
6. What are the risks of adopting autonomous agents?
Key risks include data privacy breaches, bias in decision-making, integration complexity, and over-reliance on autonomous systems. Strong monitoring and human oversight help mitigate these risks.
7. How can enterprises start implementing autonomous agents?
Begin with high-ROI pilot projects, such as compliance monitoring or claims automation. Invest in governance, employee training, and partnerships with AI solution providers for scalable adoption.










