Manufacturing firms need quick analysis of precise information to operate production, supply chains, inventories, and quality assurance. With the increase in data between machines, ERP systems, and shop-floor tools, older BI platforms cannot always keep pace. For this reason, the migration of BI in manufacturing organizations has been a priority. The shift to a new BI system helps teams work with more current data, minimize manual reporting, and make decisions across plants and operations.
According to Deloitte’s 2025 Smart Manufacturing Survey, more than 60% of manufacturing leaders intend to upgrade or replace their analytics systems, as older systems fail to process real-time data from sensors and connected machines. Their problems include slow dashboards, low automation, and expensive maintenance, as well as many others. As a result, a modern BI setup solves these problems by enabling faster data pipelines, advanced analytics, and seamless integration with systems such as MES, ERP, and IoT platforms.
This blog explains why BI migration is important to manufacturing, the advantages it offers, and how businesses can undergo the transition without disrupting their day-to-day activities.
Key Takeaways
- Manufacturing companies migrate BI to handle real-time data, reduce manual reporting, and improve visibility.
- Modern BI platforms unify ERP, MES, SCM, QA, and IoT data for faster, more accurate insights.
- Typical migration takes 3 to 6 months, depending on data size, integrations, and dashboard complexity.
- Main challenges include data quality issues, complex integrations, poor documentation, and low user readiness.
- Manufacturers see benefits such as faster reporting, better forecasting, real-time production monitoring, and improved supply chain control.
- A successful migration follows a structured flow of assessment, cleansing, platform selection, migration, testing, and rollout.
- Real-world examples demonstrate cost savings, faster refresh rates, better governance, and scalable analytics.
- Kanerika accelerates BI and data migration with automation, secure processes, and AI-ready architectures using its FLIP platform.
Elevate Your Enterprise Reporting by Migrating to Power BI!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Migration Services
Why Do Manufacturing Companies Need BI Migration
Manufacturing companies operate in a fast-moving environment where every decision requires accurate, timely information. However, older BI dashboards cannot address this issue due to their slowness, isolation, and inability to handle modern manufacturing loads. As plants adopt IoT tools, integrate ERP and MES systems, and expand digital operations, the old BI tools stand out as a bottleneck. Actually, they procrastinate reporting, augment manual labor, and restrict visibility of operations.
Conversely, the current BI systems address these issues by transforming them into a single, cloud-based analytics platform. They take data from production lines, inventory tools, supply chain tools, and quality control tools, all in a single location. This makes real-time dashboards, automatic data update, AI-based forecasting, and better decision-making based on operations, financial, and top management possible. Thus, BI migration will be a breakthrough in manufacturers’ quest to roll out, automate, and enhance plant efficiency by eliminating data silos and outdated workflows.
Key improvements manufacturers gain with modern BI include:
- Faster reporting and real-time insights
- Unified data across ERP, MES, SCM, and QA systems
- Support for IoT and machine-level analytics
- More accurate forecasting and production planning
- Better visibility into quality, downtime, and bottlenecks
Overall, this upgrade strengthens both strategic and day-to-day decision-making, making BI migration an essential step for modern manufacturing operations.
How Long Does BI Migration Take and What Factors Influence the Timeline
An average BI migration of manufacturing companies takes 3-6 months. Nevertheless, the time depends on the size of the data, the number of systems that it connects to, the complexity of the dashboard, and the quality of available data. In addition, manufacturers with numerous plants, extensive datasets, or side-by-side ERP systems often take longer to ensure accuracy and consistency across systems.
The migration timeline may proceed more slowly if the data is not clean, integrations are non-standard, or business requirements are not well-defined. Conversely, obsolete hardware, discontinuity in historical records, or unrecorded reports may slow down the process. To set realistic expectations, manufacturers are encouraged to view BI migration as a structured process with defined stages. It typically begins with an elaborate assessment, data cleansing, platform setup, dashboard redesign, testing, and user onboarding.
Also, during the transition to a new BI, most companies continue to operate the old and new systems in parallel to minimize disruptions to production schedules, the purchase cycle, sales reporting, or shop-floor processes. Finally, an effective migration will enhance reporting speed, improve forecasting, and provide leadership with a single source of truth. With proper planning and the right technology partner, manufacturers can modernize their analytics environment without downtime.
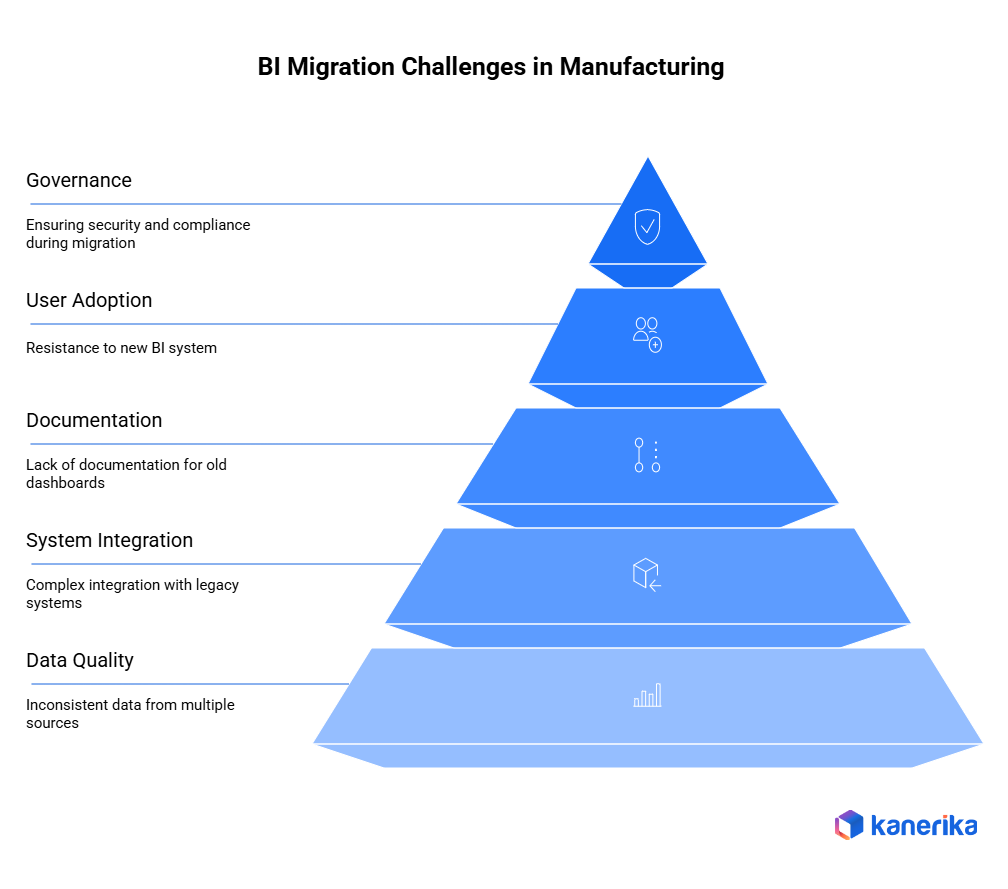
What Challenges Do Manufacturers Commonly Face During BI Migration
The benefits of BI migration are significant, and manufacturers are likely to encounter numerous obstacles driven by the complexity of systems, the variety of data sources, and the need for critical operational reporting. In that regard, it is better to know these obstacles beforehand to make the planning and implementation of the action smoother.
1. Data Quality and Inconsistencies
Data used in manufacturing may originate from a variety of different sources, including ERP, MES, SCADA, production logs, quality systems, and machine sensors. This data can contain gaps, duplicates, or format inconsistencies over the years. Consequently, data quality is low, which prevents migration, as cleansing, standardization, and validation require additional work. Furthermore, wrong data can lead to poor dashboards in the new BI environment.
2. Complex ERP, MES, and SCADA Integrations
The adoption of the current BI systems with the manufacturing systems is not necessarily smooth. Most factories use old machines, older software versions, or even depend on their own plant application. In other instances, systems lack APIs or standard connectors, so integrations must be developed manually. This is time-consuming, and only good technical expertise is needed in order to make all the data flows work effectively.
3. Limited Documentation of Legacy Dashboards
Older BI systems can have hundreds of personalized dashboards, equations, KPIs, and filters that have been created over many years. In the absence of documentation, it is hard to determine which dashboards are important, how they are computed, and how some reports are being used. This, in turn, causes delays in the migration process and the demand for user interviews and human verification.
4. Training and Adoption Barriers
Even when the new BI system is faster and more capable, users may hesitate to adopt it. Operators, supervisors, and managers are often used to their old dashboards and reporting formats. Therefore, moving them to a new environment requires training workshops, clear communication, and ongoing support to build confidence and reduce resistance.
5. Governance, Security, and Compliance Requirements
The manufacturing data contains personal information on production volumes, suppliers, quality, and plant performance. As this information is transferred to a cloud-based or hybrid-BI system, there should be stringent governance by the teams. During the migration, they ensure role-based access, security measures, audit records, and adherence to internal policy. Lack of this can lead to security threats or operational hitches.
Will BI Migration Disrupt Ongoing Operations?
A common concern among manufacturing leaders is whether BI migration will disrupt production schedules or reporting cycles. With the right strategy, the transition can be executed without interrupting daily operations. In essence, the goal is to modernize analytics while keeping the plant running smoothly.
1. Parallel Run Approach
The safest way to prevent disruptions is to run both the old and new BI systems in parallel. Teams continue using their existing dashboards while the new system is tested in the background. Then, once the data is validated and performance is stable, departments gradually shift to the new platform. This reduces risk and allows for side-by-side comparison of KPIs.
2. Minimizing Downtime
BI migration is completed in phases to avoid large-scale interruptions. First, critical reports like production efficiency, downtime analysis, order status, and quality metrics are migrated. Less often-used dashboards are moved later. This phased approach ensures that key operations never lose access to data, even during system updates or backend changes.
3. Ensuring Continuity in Production and Reporting
Continuous testing, data validation, and user feedback keep reporting reliably throughout the migration. Meanwhile, IT teams monitor performance, adjust data pipelines, and fix issues before the final switch. As a result, production teams, planners, and leadership consistently receive accurate insights, ensuring decision-making remains unaffected.
BI Modernization: How to Migrate from Legacy BI Tools in 2025
Explore BI modernization strategies to improve analytics and decision-making.
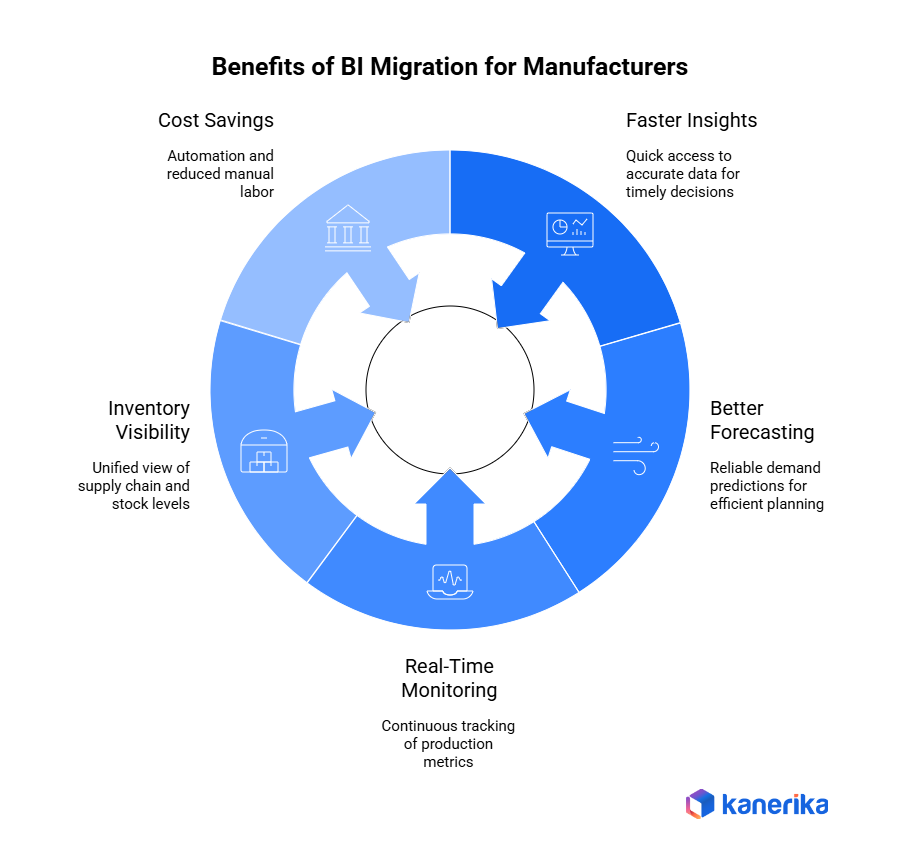
What Business Benefits Can Manufacturers Expect After BI Migration?
Contemporary BI migration delivers tangible, quantifiable enhancements to manufacturing operations, planning, and profitability. With a transition to a new BI environment, manufacturers will gain real-time insight into their data, enabling more accurate predictions and faster, more confident decisions across the entire value chain. The following are the most effective outcomes organizations typically achieve after migrating to a contemporary BI system.
1. Faster and More Accurate Insights
Migrated BI systems offer high-speed reporting, automated data refreshes, and unified dashboards. Decision-makers no longer wait hours for reports or depend on manual Excel updates. Instead, teams can access accurate, up-to-date insights to respond quickly to production issues, supplier delays, or quality changes.
2. Better Demand Forecasting and Capacity Planning
With centralized data and advanced analytics, manufacturers can forecast demand more reliably. As a result, this improves production scheduling, reduces stockouts, and helps teams plan capacity with confidence. Additionally, predictive models also highlight seasonal patterns and customer trends earlier.
3. Real-Time Production Monitoring
The current BI systems are integrated with shop-floor systems such as MES, SCADA, IoT devices, and machine sensors. This will allow a real-time view of machine performance, unproductive time, throughput, and equipment effectiveness. Quick visibility helps teams detect problems early, minimize unplanned downtime, reduce waste, and generally enhance line efficiency.
4. Improved Inventory and Supply Chain Visibility
BI migration places inventory, procurement, logistics, and supplier data in one trusted view. Manufacturers can monitor the movement of raw materials, supplier lead times, and the optimal stock level across multiple locations. This enhanced visibility helps to cut down on excess inventory, avoid shortages, enhance coordination among suppliers, and develop a more resilient supply chain.
5. Cost Savings Through Automation and Reduced Manual Work
Automated reporting saves time and operational expenses as well, since manufacturers do not have to manually manage their data. Teams require less time to collect and clean as well as to reconcile data, and more time on insights. Less manual interaction also minimizes the chances of errors that may result in wrong decisions, rework, or loss of finances.
What Does a Successful BI Migration Process Look Like?
An effective BI migration is based on a well-defined, organized approach that reduces risk and enables the new system to deliver value as quickly as possible. In manufacturing organizations, the process is usually designed with six major stages: assessment, cleansing, platform selection, migration, testing, and rollout.
1. Assessment: Understanding Current Systems and Needs
It will start with an in-depth evaluation of available data sources, reports, dashboards, and integrations. Manufacturers assess what is performing and what is dragging teams back, as well as points of data deficiency. Business stakeholders are engaged to establish specific objectives for the new BI system, such as faster reporting, real-time production visibility, improved forecasting, or better cost control.
2. Cleansing: Preparing and Standardizing Data
Data must be cleaned and standardized before migration to ensure accuracy in the new BI environment. This step involves eliminating duplicate records, correcting inconsistencies, adhering to naming conventions, and appropriately mapping tables across systems. Formatted, clean data is also a good guarantee of reliable reporting and the eradication of legacy errors that tend to permeate new platforms.
3. Platform Choice: Selecting the Right BI Environment
After the database preparation is complete, manufacturers choose a BI platform that fits both their technical and business requirements. Such aspects as the ability to integrate with ERP, MES, and SCADA systems, the possibility to scale to meet the requirements of a new business, the presence of in-built analytics and visualization tools, and high-level security and compliance are important.
4. Migration: Moving Data and Rebuilding BI Assets
In this stage, the existing data is moved to the new platform, and the available reports, dashboards, and data models will be rebuilt or optimized. The majority of manufacturers use a phased migration strategy, starting with high-priority reports and operational dashboards. This minimizes the risk, maintains business continuity, and prevents the business, production, and planning activities from being disrupted.
5. Testing: Validating Accuracy, Speed, and Usability
After migration, every dashboard, dataset, and workflow is tested. Teams verify data accuracy, check load times, validate KPIs, and ensure that operational reporting meets daily manufacturing needs. Any mismatches or delays are fixed before full release.
6. Rollout: Training Teams and Enabling Adoption
The last phase is the implementation of the new BI system to the users in the operations, planning teams, supply chain, and the top leadership. High adoption is achieved with the help of training sessions, documentation, and role-based dashboards. As soon as teams learn to trust the information and have confidence in it, the BI platform turns into a daily decision-making tool and not a reporting system.
Crystal Reports to Power BI Migration 2025: Key Considerations
Learn how to migrate from Crystal Reports to Power BI for modern, interactive analytics.
Real-World Examples
1. High-Tech Manufacturing / Semiconductor Company (KPI Partners)
This company migrated 1,897 Tableau reports to Microsoft Power BI as part of a SAP S/4HANA modernization.
Results:
- 70% cost reduction compared to a fully manual migration process.
- 73% faster migration timeline using KPI’s BI modernization tools.
- Data quality was maintained throughout via continuous validation, ensuring accurate metrics in the new Power BI dashboards.
2. Tullis Russell (Specialist Paper & Film Coatings Manufacturer)
Tullis Russell replaced its legacy BI systems with a Power BI + Azure solution.
Results:
- Data refresh frequency improved significantly; their finance data now updates every 15 minutes, giving almost real-time visibility.
- Substantial cost savings, because they moved to serverless Azure architecture (pay only for what they use) and removed maintenance overhead.
- Greater agility: decision-making became faster and more data-driven thanks to updated, timely dashboards.
3. Major US Global Manufacturer (phData)
A large manufacturer with 40,000+ employees used phData to standardize and modernize its BI using Power BI.
Results:
- They built a Power BI Center of Excellence, creating governance policies, templates, and standardized workspaces.
- Achieved repeatable, governed analytics: teams across departments now use a common, central repository and BI standards.
- The project was delivered in 12 weeks for high-priority dashboards, but the partnership has continued for over 18 months, showing long-term value and maturity.
4. Chemical Manufacturer (CelebalTech)
A leading chemical manufacturing firm, spread across 18 global facilities, migrated its data to Azure Data Lake and Power BI with CelebalTech.
Results:
- Faster data processing through automated data pipelines (Azure Data Factory) and centralized storage.
- Real-time or near real-time insights for plant operations, enabling decision-makers to react quickly.
- Scalable solution: the cloud setup ensures the BI system can grow with their data needs, preparing them for future expansion.
5. Leading Manufacturer (WeShape + Power BI Migration)
This manufacturer migrated its analytics platform to Microsoft Power BI to improve data visibility and internal processes.
Results:
- Automated data integration across fragmented systems, reducing manual data entry.
- Improved data quality and efficiency through architectural and automation redesign.
- Enabled scalable BI usage across business units with Power Platform and Power BI.
Kanerika: Accelerating BI Migration for Manufacturing Enterprises
Kanerika assists manufacturing organizations in improving their analytics and data infrastructure by using fast, secure, and intelligent migration plans. Old BI systems tend to be weak in handling high-volume, complex datasets and real-time reporting requirements. Our solution, in turn, will make sure that operations will not be disrupted during the transition to modern platforms.
We provide end-to-end migration services across multiple areas:
- BI Migration: Move from legacy tools like Tableau, Cognos, SSRS, and Crystal Reports to Power BI for interactive dashboards and real-time insights.
- Data Warehouse to Data Lake Migration: Shift from rigid warehouse setups to flexible data lakes or lakehouse platforms for handling structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
- Cloud Migration: Transition workloads to secure, scalable environments such as Azure or AWS for better performance and cost efficiency.
- ETL and Pipeline Migration: Modernize data pipelines to ingest, transform, and orchestrate data faster.
- Migration of RPA Platform: Transfer UiPath to Microsoft Power Automate to get automated workflows.
These migrations are based on our proprietary platform, FLIP, which uses Smart Migration Accelerators. FLIP can automate up to 80% of the migration process, reducing risk, preserving business logic, and enabling organizations to become cloud-native and AI-ready in weeks instead of months. It supports complex migrations, such as Tableau to Power BI, SSIS to Microsoft Fabric, and Informatica to Talend, while ensuring zero data loss and operational continuity.
Therefore, Kanerika complies with international laws such as ISO 27001, ISO 27701, SOC 2, and GDPR during the migration process. With strong expertise in automation, AI, and cloud engineering, we help manufacturers unlock predictive insights, improve production efficiency, and build a future-ready data ecosystem.
Migrate to Power BI for Smarter Analytics and Real-Time Insights!
Partner with Kanerika for Seamless Migration Services.
FAQs
1. What is BI migration in manufacturing, and why is it important?
BI migration in manufacturing involves moving reporting and analytics workloads from legacy BI tools or on-prem systems to modern, scalable platforms. This enables faster insights across production, quality, inventory, and supply chain operations. As manufacturing data volumes grow, legacy BI systems struggle with performance and flexibility. Migration ensures analytics can scale with business growth and operational complexity.
2. How does BI migration improve operational visibility in manufacturing?
BI migration centralizes data from MES, ERP, PLM, and shop-floor systems into a unified analytics layer. This provides real-time visibility into production throughput, downtime, and quality metrics. With faster refresh cycles, plant managers can identify issues earlier. As a result, manufacturers reduce delays and improve operational efficiency.
3. How does BI migration support better production planning and forecasting?
Modern BI platforms process data faster and support advanced analytics. After migration, manufacturers gain timely insights into demand trends, capacity utilization, and inventory levels. This improves production planning accuracy and reduces over- or under-production. Better forecasting directly supports cost control and revenue growth.
4. What role does BI migration play in improving quality and compliance?
BI migration enables consistent tracking of quality KPIs across plants and production lines. It simplifies compliance reporting by automating data collection and validation. Manufacturers can quickly analyze defect rates, root causes, and audit metrics. This improves product quality while reducing compliance risk.
5. How does BI migration help reduce manufacturing costs?
Migrating BI workloads eliminates slow, manual reporting processes and reduces reliance on expensive legacy infrastructure. Faster insights help optimize machine utilization, energy usage, and material consumption. Additionally, improved visibility into inefficiencies reduces waste. These cost savings directly impact profitability.
6. How does BI migration enable data-driven decision-making across teams?
Post-migration BI platforms provide self-service dashboards and role-based insights for operations, finance, and leadership teams. Users access accurate data without waiting on IT. This accelerates decision-making and improves collaboration across departments. Data becomes a shared asset rather than a bottleneck.
7. How does BI migration future-proof manufacturing organizations?
BI migration creates a scalable foundation that supports advanced analytics, AI, and predictive maintenance use cases. It prepares manufacturers for Industry 4.0 initiatives and smart factory adoption. With modern BI platforms, organizations can adapt quickly to market changes. This flexibility drives sustained growth and competitiveness.









