Nearly every business today is under pressure to do more with less: faster operations, lower costs, and better customer service. That’s where Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is stepping in. Companies like Deloitte report that 53% of organizations have already started their RPA journey, with early adopters experiencing up to 92% improved process efficiency and significant cost reductions.
The robotic process automation market is projected to grow from $22.58 billion in 2025 to $72.64 billion by 2032, yet many businesses still struggle with a fundamental question: which platform actually delivers results? Some well-known brands like Coca-Cola and Deutsche Bank have saved millions by using the right RPA tools, but others have struggled when they picked a solution that didn’t scale or align with their processes.
This is why having a clear RPA tools selection guide matters, not just to save money, but to ensure long-term success and avoid costly mistakes.
Partner with Kanerika to Modernize Your Enterprise Operations with High-Impact Data & AI Solutions
Key Takeaways
- RPA market will triple to $72.64 billion by 2032 with proven 92% efficiency gains.
- Enterprise Success depends on evaluating scalability, integration capabilities, security features, and total ownership costs.
- Different tools excel in specific areas: UiPath for ease, Blue Prism for security.
- Benefits include cost savings, improved accuracy, compliance, and quick ROI within months.
- Start with simple processes, build business case, test thoroughly, and optimize continuously.
Implement RPA to Propel Your Business Forward!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert RPA implementation Services
What Are RPA Tools?
RPA Tools, or Robotic Process Automation Tools, are software applications designed to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks typically performed by humans in various business processes. These tools create and manage software robots, or “bots,” that can interact with digital systems and software in the same way a human user would.
They mimic human actions to perform a variety of tasks, such as data entry, transaction processing, and responding to emails. By leveraging these tools, businesses can achieve significant efficiency gains, reduce errors, and free up human employees for more complex and value-added activities.
10 Key Functionalities of RPA Tools
1. Task Automation
Automating repetitive and routine tasks that follow a specific set of rules.
RPA tools can execute tasks such as data entry, form filling, and report generation without human intervention. This automation ensures consistency, accuracy, and speed in task completion.
Example: A bank uses RPA to process loan applications automatically, reducing the processing time from days to minutes.
2. Process Recording
Capturing user actions to create automation scripts.
RPA tools often include recording features that track user interactions with applications. These recorded actions are then used to build automation workflows, simplifying the setup process.
Example: Recording the steps to log into a system, retrieve data, and enter it into another application, creating a repeatable automation sequence.
Also Read- RPA in Finance: Ways to Unlock Hidden Profits Through Automation
3. Integration with Multiple Systems
Connecting and interacting with various software systems and applications.
RPA tools can integrate with ERP systems, CRM platforms, databases, and other enterprise applications, allowing them to perform tasks across different systems seamlessly.
Example: An RPA tool fetching customer data from a CRM system and updating it in an ERP system without manual intervention.
4. Data Extraction and Processing
Extracting data from documents, emails, and other sources, and processing it according to predefined rules.
Advanced RPA tools utilize optical character recognition (OCR) and artificial intelligence (AI) to extract and process unstructured data from various sources.
Example: Extracting invoice details from PDF files and entering them into an accounting system automatically.
5. Workflow Management
Designing and managing end-to-end business processes.
RPA tools provide workflow design capabilities, allowing users to create complex automation sequences involving multiple steps and decision points.
Example: Creating a workflow that starts with receiving an email request, validating the information, updating a database, and sending a confirmation email.
6. Error Handling and Exception Management
Managing errors and exceptions that occur during automation.
RPA tools include features to handle errors and exceptions gracefully, ensuring that processes can continue running smoothly or be paused for human intervention if necessary.
Example: An RPA tool detecting an invalid input and either correcting it automatically or notifying a human operator to resolve the issue.
7. Scalability
Ability to scale operations up or down based on demand.
RPA tools can scale to handle increased workloads by deploying additional bots or reducing the number of bots during lower demand periods.
Example: A retail company scaling up its RPA bots during the holiday season to manage the increased volume of orders and customer queries.
8. Security and Compliance
Ensuring data security and regulatory compliance.
RPA tools come with robust security features, including encryption, access controls, and audit logs, to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Example: A healthcare provider using RPA to handle patient records while ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations.
9. Analytics and Reporting
Providing insights into process performance and efficiency.
RPA tools offer analytics and reporting features to monitor and analyze the performance of automated processes, helping organizations identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Example: Generating reports on the time saved and error rates reduced through automation, providing valuable insights for decision-making.
10. User-friendly Interface
Easy-to-use interface for designing and managing automation.
Most RPA tools feature intuitive, drag-and-drop interfaces that make it easy for non-technical users to design and deploy automation workflows.
Example: Business analysts creating automation processes without needing extensive programming knowledge.
Partner with Kanerika to Modernize Your Enterprise Operations with High-Impact Data & AI Solutions
A Quick Comparison of the Top 10 RPA Tools
| RPA Tool | Key Features | Best Use Cases |
| UiPath | Drag-and-drop interface, 250K+ community, AI capabilities | Invoice processing, customer service, data entry |
| Automation Anywhere | IQ Bots, web-based control room, mobile management | HR processes, financial reporting, supply chain |
| Blue Prism | 24/7 digital workforce, enterprise security, no-code | Back-office processes, compliance, customer onboarding |
| Microsoft Power Automate | Microsoft ecosystem integration, AI Builder, templates | Email automation, data collection, workflow approvals |
| Appian | Low-code platform, FedRAMP-compliant, AI recommendations | Case management, compliance tracking, customer service |
| Kofax Kapow | Advanced analytics, data integration, ML capabilities | Document processing, web extraction, financial operations |
| NICE | Real-time AI decisions, contact center focus, cloud/on-premise | Contact center operations, fraud detection, employee management |
| Datamatics | Universal recorder, intelligent document processing, low-code | Insurance claims, healthcare data, banking operations |
| WorkFusion | AI-driven pre-trained bots, cloud-scalable, security focus | Regulatory compliance, customer onboarding, finance processes |
| Pega | Unified RPA/BPM platform, real-time analytics, ML integration | Customer service workflows, case management, IT operations |
RPA for Data Migration: Best Practices and Considerations
Explore best practices and key considerations for leveraging RPA in data migration to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and smooth transitions.
Top 10 RPA Tools That Can Elevate Your Enterprise Productivity
1. UiPath
UiPath’s platform fosters a strong community with over 250,000 users contributing to its rapid development and innovation. Its ease of use and extensive integration options make it a favorite among businesses seeking to enhance automation without deep technical expertise.
Features
- User-friendly drag-and-drop interface
- Advanced AI capabilities
- Extensive library of pre-built automation components
- Integration with multiple platforms and applications
Use Cases: Automating invoice processing, customer service interactions, and data entry tasks.
2. Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere emphasizes a secure and resilient automation environment, suitable for large enterprises needing scalable solutions. Its community edition allows users to explore features freely, promoting a hands-on learning approach.
Features
- Intelligent automation with IQ Bots
- Web-based centralized control room
- Mobile application for managing bots on the go
- Natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) integration
Use Cases: Automating HR processes, financial reporting, and supply chain management.
3. Blue Prism
Blue Prism’s virtual workforce is designed to operate 24/7, providing consistent and reliable task automation. It’s highly regarded for its robust security measures, making it suitable for industries with stringent compliance requirements.
Features
- Digital workforce for automating enterprise operations
- Integration with various automation tools
- Secure and scalable architecture
- No coding required for basic tasks
Use Cases: Automating back-office processes, regulatory compliance, and customer onboarding.
4. Microsoft Power Automate
Microsoft Power Automate is part of the larger Microsoft ecosystem, allowing seamless integration with other Microsoft products. Its intuitive design makes it accessible to users with minimal technical background, facilitating quick adoption across departments.
Features
- Hundreds of pre-built connectors
- AI Builder for integrating AI models
- User-friendly interface with templates
- Supports both attended and unattended RPA
Use Cases: Automating email notifications, data collection, and workflow approvals.
5. Appian
Appian stands out with its low-code platform, enabling rapid development and deployment of automation workflows. Its FedRAMP-compliant cloud deployment ensures high security standards, catering to government and regulated industries.
Features
- Low-code development platform
- AI-driven automation recommendations
- Integration with existing enterprise systems
- FedRAMP-compliant cloud deployment
Use Cases: Automating case management, compliance tracking, and customer service processes.
Also Read- RPA in Manufacturing: Enhancing Quality Control and Compliance
6. Kofax Kapow
Kofax Kapow offers strong analytics capabilities, providing valuable insights into automated processes. Its advanced data integration features make it a powerful tool for extracting and processing large volumes of information from various sources.
Features
- Advanced data integration capabilities
- Intelligent automation with AI and ML
- Scalable and flexible deployment options
- Strong analytics and reporting tools
Use Cases: Automating document processing, web data extraction, and financial operations.
7. NICE
NICE integrates AI to enhance real-time decision-making processes, improving operational efficiency. Its solutions are particularly effective in customer service environments, helping organizations manage large volumes of interactions smoothly
Features
- Real-time decision-making with AI
- Comprehensive automation analytics
- User-friendly interface with drag-and-drop functionality
- Cloud and on-premises deployment options
Use Cases: Automating contact center operations, fraud detection, and employee management.
8. Datamatics
Datamatics leverages AI and ML to provide intelligent automation solutions, offering a competitive edge in processing unstructured data. Its comprehensive platform supports diverse industries, including banking and healthcare.
Features
- Universal recorder for process automation
- Integrated intelligent document processing (IDP)
- Low-code design and development
- Dynamic bot station selection
Use Cases: Automating insurance claims processing, healthcare data management, and banking operations.
9. WorkFusion
WorkFusion focuses on combining RPA with AI to create intelligent automation solutions, enabling businesses to automate complex tasks. Its strong emphasis on security and compliance makes it a trusted partner for regulated industries.
Features
- AI-driven automation with pre-trained bots
- Cloud-based and scalable architecture
- Advanced analytics and reporting
- Strong security features with role-based access control
Use Cases: Automating regulatory compliance, customer onboarding, and finance and accounting processes.
10. Pega
Pega’s unified platform for RPA and BPM offers a holistic approach to business process management and automation. Its AI-driven features enable real-time analytics and decision-making, improving overall operational efficiency.
Features
- Unified platform for RPA and BPM (Business Process Management)
- AI and ML integration for intelligent automation
- Real-time analytics and decision-making
- Extensive integration capabilities
Use Cases: Automating customer service workflows, case management, and IT operations.
7 Ways Enterprise Automation Can Boost Your ROI
Understand how enterprise automation can drive significant ROI by optimizing processes, reducing costs, and enhancing productivity across your organization.
Top 10 Benefits of Using RPA Tools for Businesses
1. Increased Efficiency
Robotic process automation accelerates business operations by executing repetitive tasks at speeds far exceeding human capability. Software robots work 24/7 without breaks, completing processes in minutes that would take hours manually, enabling faster cycle times and improved operational throughput.
- Process acceleration reduces task completion times by 50-90% for activities like invoice processing, data entry, and report generation
- Continuous operation with bots working around the clock eliminates downtime and enables overnight batch processing without overtime costs
- Resource optimization frees employees from mundane tasks to focus on strategic initiatives requiring human judgment and creativity
2. Cost Savings
RPA implementation delivers substantial cost reduction across labor expenses, error remediation, and infrastructure investments. Organizations typically achieve 25-50% operational cost savings within the first year through reduced headcount requirements, minimized rework, and improved resource utilization.
- Labor cost reduction by automating routine tasks equivalent to multiple FTEs without salaries, benefits, or training expenses
- Error cost elimination prevents costly mistakes in data entry, invoice processing, and compliance reporting that require expensive corrections
- Infrastructure savings through efficient resource usage and reduced need for additional staffing during peak periods
3. Improved Accuracy and Consistency
RPA bots execute tasks with near-perfect precision, eliminating human errors caused by fatigue, distraction, or inconsistent processes. This reliability ensures standardized outputs, reduces quality issues, and improves data integrity across business operations.
- Error-free processing achieves 99%+ accuracy rates in data entry, calculations, and transaction processing compared to 5-10% human error rates
- Standardized execution ensures every process instance follows identical rules and procedures, eliminating variations in output quality
- Data quality improvement through consistent validation, formatting, and verification reduces downstream issues and system integration problems
4. Enhanced Compliance
Automated processes ensure strict adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies while maintaining comprehensive audit trails. RPA tools automatically document every action, creating detailed compliance records for industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
- Regulatory adherence with built-in compliance rules for GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and industry-specific regulations embedded in automated workflows
- Complete audit trails capture timestamps, user actions, data changes, and system interactions for regulatory reporting and internal audits
- Risk mitigation through consistent policy enforcement and elimination of compliance gaps caused by manual oversights or procedure deviations
5. Scalability
RPA solutions easily scale to meet fluctuating business demands without significant infrastructure investments or lengthy hiring processes. Organizations can rapidly deploy additional bots during peak periods and scale down during slower times, maintaining operational flexibility.
- Elastic capacity allows quick deployment of virtual workers to handle seasonal spikes, product launches, or unexpected demand surges
- Cost-effective scaling adds processing capacity without recruiting, onboarding, or training expenses associated with human workforce expansion
- Flexible resource allocation enables redistribution of bots across departments and processes based on changing business priorities
6. Better Customer Experience
Automation enables faster response times, consistent service quality, and 24/7 availability for customer interactions. By eliminating wait times and processing delays, businesses deliver superior customer service that drives satisfaction scores and brand loyalty.
- Instant query resolution through automated customer service processes provides immediate responses to routine inquiries and service requests
- Reduced processing times for account updates, order tracking, and refund processing improves customer satisfaction and Net Promoter Scores
- Consistent service quality ensures every customer interaction meets the same high standards regardless of time, day, or volume
7. Increased Employee Productivity
RPA liberates workers from repetitive, low-value tasks, enabling them to focus on complex problem-solving, customer relationships, and innovation. This shift improves job satisfaction, reduces burnout, and maximizes human talent utilization.
- Task elimination removes soul-crushing manual work like data copying, form filling, and spreadsheet updates from employee workloads
- Skill utilization allows professionals to apply expertise to judgment-based activities, strategic planning, and customer-facing interactions
- Employee satisfaction increases through meaningful work assignments, reducing turnover costs and improving workplace morale
8. Data-Driven Insights
RPA platforms generate valuable analytics from automated processes, providing visibility into operational performance, bottlenecks, and improvement opportunities. This business intelligence enables data-driven decision-making and continuous process optimization.
- Performance metrics track processing times, transaction volumes, exception rates, and ROI to quantify automation value
- Process mining reveals inefficiencies, redundancies, and optimization opportunities through detailed workflow analysis and pattern recognition
- Predictive analytics identify trends, forecast demand, and enable proactive resource planning based on historical automation data
9. Improved Workflow Management
End-to-end process automation eliminates handoffs, reduces bottlenecks, and ensures smooth operations across departments. RPA orchestrates complex workflows involving multiple systems, creating seamless integration and efficient process execution.
- Bottleneck elimination through automated task routing and queue management prevents delays caused by manual handoffs and approval chains
- Cross-system integration connects disparate applications and legacy systems, enabling straight-through processing without manual intervention
- Process standardization establishes consistent workflows across teams and locations, eliminating variations that cause delays and errors
10. Quick ROI
RPA implementations typically deliver measurable returns within 6-12 months through immediate efficiency gains and cost savings. The combination of reduced labor costs, error prevention, and productivity improvements creates compelling business value rapidly.
- Fast payback periods with many automation projects achieving positive ROI within the first year of deployment
- Immediate impact on processing times, accuracy rates, and operational costs visible within weeks of bot deployment
- Measurable business value through quantifiable metrics like hours saved, errors prevented, and transactions processed per bot
Lead Your Industry with Cutting-edge Automation Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert RPA implementation Services
Factors to Consider in Selecting the Right RPA Tool
1. Ease of Use
An intuitive RPA platform with a user-friendly interface significantly reduces the learning curve and accelerates deployment timelines. Modern automation tools featuring drag-and-drop functionality and visual workflow designers enable citizen developers to build bots without extensive programming knowledge, democratizing automation across your organization.
- Low-code/no-code development environments allow business users to create automation workflows using visual process builders and pre-built templates, minimizing dependence on IT resources
- Intuitive bot design interfaces with guided wizards and process recorders help teams quickly map out automation logic, reducing development time from weeks to days
- Comprehensive training resources including tutorials, documentation, and certification programs ensure smooth user adoption and maximize the RPA software’s value across departments
2. Scalability
Your chosen robotic process automation solution must accommodate future growth without requiring complete infrastructure overhauls or experiencing performance bottlenecks. Enterprise-grade scalability ensures your automation strategy can expand from pilot projects to organization-wide digital transformation initiatives seamlessly.
- Elastic bot orchestration capabilities allow you to spin up additional software robots during peak processing periods and scale down during off-hours, optimizing resource utilization
- Multi-tenant architecture supports departmental segregation while maintaining centralized governance, enabling different business units to manage their automation pipelines independently
- Cloud-native scalability with containerized bot deployment ensures your RPA infrastructure can handle thousands of concurrent processes across distributed environments without degradation
3. Integration Capabilities
Seamless connectivity across your technology stack is critical for end-to-end process automation and maximizing ROI. The right RPA vendor should offer extensive API support, pre-built connectors, and integration frameworks that work with both legacy applications and modern cloud platforms.
- Pre-configured connectors for popular enterprise systems like SAP, Oracle, Salesforce, and Microsoft Dynamics eliminate custom integration development and accelerate implementation
- API-first architecture enables smooth data exchange between your RPA bots and external applications, databases, web services, and third-party platforms
- Legacy system compatibility through screen scraping, OCR technology, and mainframe integration ensures older applications without APIs can still participate in automated workflows
4. Security Features
Enterprise RPA solutions must implement multi-layered security protocols to protect sensitive business data and maintain regulatory compliance throughout automated processes. Credential management, data encryption, and access controls are non-negotiable requirements for any automation platform handling confidential information.
- Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures only authorized personnel can create, modify, or execute specific bots, with granular permissions aligned to organizational hierarchies
- Encrypted credential vaults store login information and API keys securely, preventing unauthorized access while enabling bots to authenticate across multiple systems without exposing passwords
- Comprehensive audit trails automatically log all bot activities, user actions, and data modifications, creating detailed compliance reports for regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX
5. Cognitive Capabilities
Intelligent automation combining RPA with artificial intelligence extends beyond rule-based tasks to handle unstructured data and complex decision-making scenarios. AI-powered bots can process documents, understand context, and make judgment calls that traditional automation couldn’t manage.
- Natural language processing (NLP) enables bots to extract meaning from emails, contracts, and customer communications, automatically categorizing and routing information appropriately
- Machine learning algorithms allow bots to improve accuracy over time by learning from patterns, exceptions, and human corrections in invoice processing, data validation, and predictive analytics
- Computer vision and OCR capabilities extract data from scanned documents, images, and PDFs with high accuracy, eliminating manual data entry for document-heavy processes
6. Analytics and Reporting
Robust analytics dashboards and performance metrics are essential for measuring automation success, optimizing bot efficiency, and demonstrating business value. Real-time monitoring and historical reporting help identify bottlenecks, calculate ROI, and prioritize future automation opportunities.
- Real-time bot performance monitoring tracks execution times, error rates, and throughput metrics across your automation environment, enabling proactive issue resolution
- ROI calculators and business intelligence dashboards quantify cost savings, time reductions, and productivity gains, providing executive-level insights into automation program value
- Process mining analytics identify inefficiencies, exception patterns, and optimization opportunities by analyzing how bots handle various scenarios and edge cases
7. Vendor Support and Community
The level of ongoing support, training resources, and ecosystem strength significantly impacts long-term automation success. A responsive vendor with comprehensive documentation, active user forums, and regular product updates ensures you maximize your RPA investment.
- Dedicated customer success teams provide implementation guidance, best practice recommendations, and troubleshooting assistance throughout your automation journey
- Active developer communities offer peer-to-peer knowledge sharing, reusable bot components, and crowdsourced solutions to common automation challenges through forums and user groups
- Regular product updates and feature releases demonstrate the vendor’s commitment to innovation, security patches, and staying current with evolving automation technologies
8. Total Cost of Ownership
Understanding the complete financial picture beyond initial licensing fees is crucial for budgeting and ROI calculations. Hidden costs in infrastructure, training, maintenance, and scaling can significantly impact the true cost of your RPA implementation.
- Licensing models vary from per-bot pricing to concurrent user licenses and consumption-based pricing—evaluate which structure aligns best with your automation roadmap and budget
- Implementation and consulting costs including process assessment, bot development, testing, and change management can equal or exceed software licensing expenses
- Ongoing maintenance expenses cover bot updates, infrastructure hosting, support renewals, and staff training—factor these recurring costs into multi-year financial projections
9. Deployment Options
Your organization’s IT infrastructure, security policies, and data residency requirements dictate whether cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid RPA deployment makes sense. Modern RPA platforms offer flexible hosting models to accommodate various enterprise needs.
- Cloud-based RPA (SaaS) offers rapid deployment, automatic updates, and eliminates infrastructure management overhead, ideal for organizations prioritizing speed and minimal IT burden
- On-premises deployment maintains complete control over data, security, and customization for highly regulated industries with strict compliance requirements and legacy system dependencies
- Hybrid architectures combine cloud control rooms with on-premises bot execution, balancing centralized management benefits with data sovereignty and security requirements
10. Process Discovery and Mining
Advanced RPA platforms incorporating process intelligence capabilities help identify and prioritize automation opportunities based on actual user behavior and system interactions. These tools eliminate guesswork by providing data-driven insights into which processes deliver maximum automation value.
- Automated process discovery uses desktop activity monitoring and task mining to map how employees currently perform work, revealing automation candidates you might overlook
- Process mining algorithms analyze system logs and event data to visualize end-to-end workflows, identify bottlenecks, and quantify potential time savings from automation
- AI-powered opportunity assessment scores potential automation candidates based on complexity, frequency, ROI potential, and standardization level, helping prioritize your automation pipeline
11. Exception Handling
Robust error management capabilities ensure your automated processes can gracefully handle unexpected scenarios, data anomalies, and system failures without requiring constant human intervention. Well-designed exception handling maintains business continuity and prevents automation breakdowns.
- Configurable retry logic automatically reattempts failed transactions with customizable delays and retry counts, resolving transient issues caused by network glitches or temporary system unavailability
- Human-in-the-loop escalation routes complex exceptions to designated personnel for review and resolution, creating a seamless handoff between automated and manual processing
- Comprehensive error logging captures detailed failure information including screenshots, data states, and system responses, enabling rapid root cause analysis and continuous improvement
12. Speed and Performance
Bot execution efficiency and resource optimization directly impact how many processes you can automate and the value delivered. High-performance RPA tools minimize processing time while efficiently utilizing CPU, memory, and network resources across your infrastructure.
- Parallel processing capabilities allow multiple bots to execute simultaneously, dramatically increasing throughput for high-volume transactional processes like invoice processing or data migration
- Optimized resource consumption ensures bots operate efficiently without overwhelming server capacity, enabling more automation workload on existing infrastructure investments
- Queue management and load balancing automatically distribute work items across available bots, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring consistent processing speeds during peak demand periods
13. Compliance and Governance
Enterprise-grade RPA platforms must include governance frameworks and compliance tools that satisfy regulatory requirements while maintaining operational control. Centralized policy management, audit capabilities, and certification support protect your organization from compliance risks.
- Compliance reporting automation generates required documentation, audit trails, and certification evidence automatically, reducing manual effort for regulatory submissions and internal audits
- Regulatory compliance features built specifically for industries like healthcare (HIPAA), finance (SOX, PCI-DSS), and data privacy (GDPR) ensure automated processes meet sector-specific requirements
- Centralized bot governance with version control, change management approval workflows, and production promotion gates maintains quality standards and prevents unauthorized automation deployments
Automation in Insurance: Everything You Need to Know
Uncover how automation is transforming the insurance industry by streamlining operations, improving customer experiences, and driving cost efficiencies.
How to Implement RPA in Your Business
Implementing RPA in your business involves several key steps. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the process:
1. Assess and Identify Opportunities
Begin your automation journey by conducting comprehensive process discovery to identify high-value automation candidates across your organization. Analyze workflows to find repetitive, rule-based tasks consuming significant time and resources, focusing on processes with high transaction volumes, minimal exceptions, and clear business rules.
- Process mining workshops with department stakeholders reveal bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and manual tasks suitable for robotic process automation
- Automation feasibility assessment evaluates processes based on complexity, ROI potential, standardization level, and strategic business impact
- Quick win identification targets low-hanging fruit like data entry, invoice processing, and report generation for initial automation success
2. Build a Business Case
Develop a compelling ROI analysis demonstrating the financial and operational benefits of RPA implementation to secure executive buy-in and budget approval. Quantify expected cost savings, efficiency gains, error reduction, and productivity improvements to justify your automation investment.
- Financial modeling calculates labor cost savings, error remediation reduction, and productivity gains against implementation and licensing expenses
- Strategic alignment connects automation initiatives to broader digital transformation goals, competitive positioning, and customer experience objectives
- Risk assessment identifies implementation challenges, change management requirements, and mitigation strategies for stakeholder concerns
3. Select the Right RPA Tool
Evaluate enterprise automation platforms based on your specific technical requirements, budget constraints, and long-term scalability needs. Compare vendors on ease of use, integration capabilities, cognitive features, security, and total cost of ownership through proof-of-concept testing.
- Vendor evaluation examines licensing models, deployment options (cloud vs. on-premises), AI capabilities, and pre-built connectors for your tech stack
- Pilot testing validates tool performance with real business processes before committing to enterprise-wide deployment
- Technical compatibility ensures seamless integration with legacy systems, databases, ERP platforms, and cloud applications
4. Form a Center of Excellence (CoE)
Establish a dedicated RPA governance team combining IT expertise, business process knowledge, and change management skills to drive successful automation adoption. This centralized hub sets standards, manages bot development, and scales automation across departments.
- Cross-functional team includes developers, business analysts, process owners, and IT infrastructure specialists for comprehensive program oversight
- Governance framework defines bot development standards, security protocols, change management procedures, and compliance requirements
- Knowledge sharing creates best practice documentation, reusable components, and training resources for organization-wide automation literacy
5. Prioritize Processes for Automation
Create a strategic automation roadmap ranking processes by business value, implementation complexity, and resource requirements. Balance quick wins that build momentum with transformative projects delivering significant long-term impact.
- Prioritization matrix scores opportunities based on ROI, processing volume, error rates, and alignment with business objectives
- Phased implementation starts with simple, high-impact processes before tackling complex, multi-system workflows requiring advanced capabilities
- Dependency mapping sequences automation projects to maximize synergies and avoid conflicts between interdependent processes
6. Design and Develop Automation Scripts
Document target processes in detail through process definition documents (PDDs) capturing every step, decision point, and exception scenario. Translate these workflows into efficient bot scripts using your RPA platform’s development environment with robust error handling.
- Process documentation creates detailed workflow maps, business rules, system interactions, and expected outcomes for developer reference
- Bot development follows coding best practices with modular design, reusable components, and proper exception handling for maintainability
- Version control tracks script changes, enables rollback capabilities, and maintains audit trails for compliance requirements
7. Test Thoroughly
Implement comprehensive testing protocols validating bot functionality across normal operations, edge cases, and failure scenarios. Rigorous quality assurance prevents production issues and ensures automated processes deliver expected business outcomes.
- Multi-stage testing includes unit testing for individual components, integration testing across systems, and user acceptance testing with business owners
- Exception scenario validation confirms bots handle errors gracefully through retry logic, human escalation, and proper logging
- Performance testing verifies processing speeds, resource consumption, and concurrent execution capabilities under peak loads
8. Deploy and Monitor
Roll out automation to production environments using controlled deployment strategies with continuous performance monitoring. Track key metrics like processing times, error rates, and cost savings to measure success and identify optimization opportunities.
- Phased rollout begins with pilot groups before full production deployment, minimizing risk and gathering user feedback
- Real-time monitoring dashboards track bot health, transaction volumes, exceptions, and SLA compliance for proactive issue resolution
- Performance analytics quantify time savings, cost reductions, and accuracy improvements demonstrating tangible business value
9. Provide Training and Support
Equip employees with knowledge and resources to work effectively alongside digital workers through comprehensive training programs. Establish support channels addressing technical issues, process questions, and change management concerns.
- User training covers bot capabilities, exception handling procedures, and collaboration workflows between humans and automation
- Support infrastructure provides helpdesk resources, troubleshooting guides, and escalation paths for technical and process issues
- Change management addresses workforce concerns, communicates benefits, and facilitates smooth transition to automated workflows
10. Continuously Improve and Optimize
Establish feedback loops gathering insights from users, stakeholders, and performance data to refine automated processes. Regular optimization ensures your RPA program delivers increasing value and adapts to evolving business requirements.
- Performance reviews analyze bot efficiency, identify bottlenecks, and uncover additional automation opportunities through process mining
- Feedback incorporation integrates user suggestions, addresses pain points, and enhances bot functionality based on real-world experience
- Scaling strategy expands successful automations to additional departments, geographies, and use cases while maintaining quality standards
Workflow Automation: The Ultimate Guide to Boosting Productivity
Master workflow automation with this ultimate guide to enhancing productivity, streamlining processes, and achieving operational efficiency.
Case Studies: Kanerika’s RPA Expertise
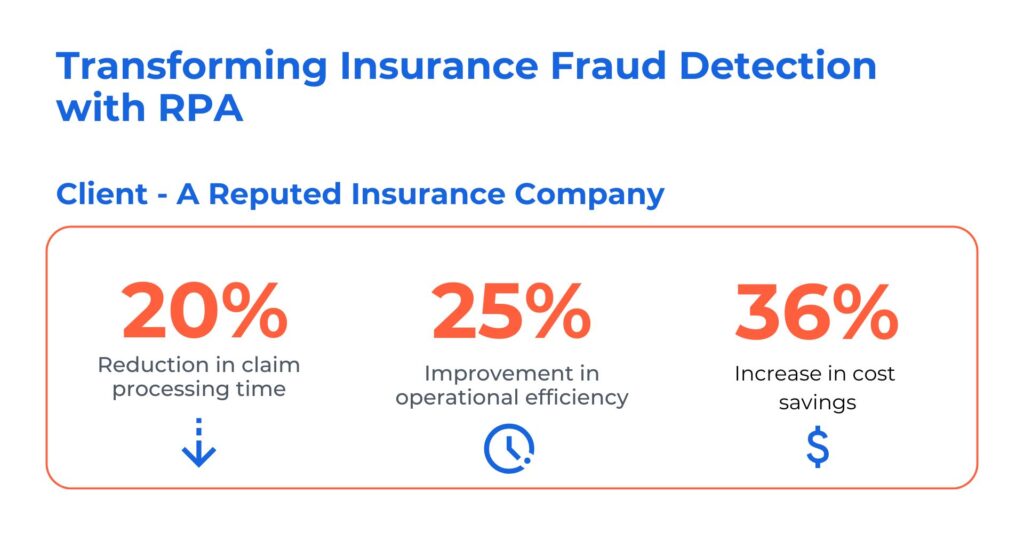
1. Revolutionizing Fraud Detection in Insurance with AI/ML-Powered RPA
The client is a prominent insurance provider, specializing in healthcare, travel, and accident coverage. They wanted to automate their insurance claim process solution with AI/ML to spot unusual patterns that are unnoticeable by the humans. The overall goal was to use deep anomaly detection to anticipate fraud detection in insurance claims quickly, reduce the loss ratios, and fasten the claim processing.
Kanerika tackled these challenges by:
- Implementing AI RPA for fraud detection in the insurance claim process, reducing fraud-related financial losses.
- Leveraging predictive analytics, AI, NLP, and image recognition to monitor customer behavior, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Delivering AI/ML-driven RPA solutions for fraud assessment and operational excellence, resulting in cost savings.
2. Transforming Recruitment with Process Automation by RPA in HR
The client is a distinguished service provider renowned for their unwavering commitment to timely delivery. They faced HR challenges due to the manual hiring process which had become burdensome, causing delays and inefficiencies and placing an excessive workload on the HR team.
Kanerika addressed these challenges by providing the following solutions:
- Implemented end-to-end process automation using UiPath, streamlining candidate screening and enhancing efficiency
- Deployed HR Bot to receive, filter, and consolidate resumes from various portals, improving candidate management
- Ensured accurate candidate evaluation, correct routing, and efficient candidate handling, enhancing the quality of hires with RPA services

Kanerika: Where Advanced RPA Solutions Meet Business Transformation
At Kanerika, we excel in harnessing the power of automation to transform business operations. Our expertise in robotic process automation (RPA) allows us to offer solutions precisely tailored to meet the unique challenges of your business. By understanding the specific needs and processes of each client, we develop RPA strategies that are not only efficient but also innovative, ensuring that your business stays ahead of the curve in a competitive landscape.
Our approach to RPA involves a thorough analysis of your existing processes to identify key areas where automation can significantly enhance efficiency and accuracy. This bespoke solution design means that every automation initiative is directly aligned with your strategic objectives, driving productivity and facilitating scalable growth.
Choosing Kanerika means opting for a partner who is committed to your success. Our advanced RPA solutions provide a robust foundation for digital transformation, enabling you to outpace competitors and excel in your industry.
Maximize Resources and Achieve Operational Excellence Through RPA!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert RPA implementation Services
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an RPA tool?
An RPA tool is like a digital assistant for repetitive tasks on your computer. It automates things like data entry, file management, and web browsing, freeing up your time for more creative and strategic work. Think of it as teaching a computer to perform actions you normally do manually, but much faster and more accurately.
What are the three main RPA tools?
There isn’t a definitive “top 3” RPA tools, as the best choice depends on your specific needs. However, three popular and widely-used options are UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism. Each offers a comprehensive suite of features, with strengths in areas like ease of use, scalability, and advanced analytics. Ultimately, the best tool for you will depend on your budget, technical expertise, and the complexity of your automation needs.
Which RPA tool is in most demand?
The RPA tool in highest demand depends on factors like project size, industry, and developer experience. However, tools like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism consistently rank high due to their user-friendly interfaces, robust features, and strong community support. Ultimately, the best RPA tool is the one that best suits your specific needs and workflow.
Is RPA a coding?
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, doesn’t require traditional coding like software development. Instead, you use a visual interface to “teach” the robot how to interact with applications, mimicking human actions like clicking buttons, filling forms, and copying data. Think of it as building a step-by-step instruction manual for the robot, rather than writing complex lines of code.
What are the three types of RPA?
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, has three main types based on their functionality: attended, unattended, and hybrid. Attended RPA requires human interaction to initiate and oversee tasks, while unattended RPA runs autonomously without human intervention. Hybrid RPA combines both approaches, allowing tasks to be automated with human oversight for specific steps.
How to choose RPA tool?
Choosing the right RPA tool depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like the complexity of the tasks you want to automate, the size of your organization, your budget, and the level of technical expertise within your team. Research different tools, compare their features and pricing, and explore free trials or demos to find the best fit for your automation journey.
What are the benefits of RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers significant benefits by streamlining repetitive tasks, reducing human error, increasing operational efficiency, lowering labor costs, improving accuracy, enabling 24/7 processing, and allowing employees to focus on higher-value strategic work that requires creativity and critical thinking.