Automation is everywhere in today’s digital-first enterprises, but not all automation is true AI. Many organizations struggle to distinguish between automated intelligence vs artificial intelligence, leading to missed opportunities for innovation and efficiency. Automated intelligence focuses on predefined rules and predictable workflows, while AI adapts, learns, and makes decisions in complex, data-driven environments.
According to Gartner, “By 2026, 70% of enterprises will blend automated intelligence with AI to optimize workflows and enhance decision-making” (source). This convergence is reshaping industries — from finance and healthcare to manufacturing and retail — by moving beyond static process automation to intelligent, self-optimizing systems.
This blog will clarify the key differences between automated intelligence and artificial intelligence, explore their business impact, and highlight practical use cases where each excels. You’ll also learn how blending the two — often referred to as intelligent automation — can unlock scalable, adaptive workflows and future-proof your digital transformation strategy.
Key Takeaways
- Automated Intelligence is rule-based and predictable, ideal for repetitive, structured tasks like data entry and compliance reporting.
- Artificial Intelligence is adaptive and self-learning, capable of handling dynamic, unstructured data and making autonomous decisions.
- Automation drives efficiency and cost savings, while AI enables innovation, advanced analytics, and complex problem-solving.
- Combining automation and AI creates scalable, intelligent workflows that reduce manual effort and enhance decision-making.
- The future trend is Intelligent Automation, where autonomous AI agents blend automation speed with AI reasoning for end-to-end business processes.
What is Automated Intelligence?
Automated intelligence refers to technology systems designed to perform repetitive, predictable tasks by following clearly defined rules and logic. Unlike artificial intelligence (AI), which can learn and adapt over time, automated intelligence is strictly rule-based. It excels at streamlining structured, routine processes that do not require complex reasoning or decision-making.
These systems work by using structured workflows, “if-then” logic, and simple algorithms to carry out tasks with speed and consistency. For example, if a purchase order meets certain criteria, an automated system can approve it instantly without human intervention. Because the process is predefined, outcomes are highly predictable, and the risk of errors is minimal when the rules are well-defined.
Common examples include Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools like UiPath and Automation Anywhere, which can automate invoice processing, claims filing, or employee onboarding tasks. Other everyday uses include email filtering, data entry, report generation, and basic chatbots that handle FAQs.
Key characteristics of automated intelligence include:
- Rule-based execution — follows explicit instructions without deviation.
- Predictability — produces the same outcome every time.
- No self-learning — does not improve or adapt beyond programmed rules.
Automated intelligence is ideal for back-office operations, compliance reporting, and data processing, where reliability and efficiency are crucial. By eliminating repetitive manual work, it saves time, reduces costs, and frees employees to focus on higher-value strategic tasks.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems that mimic human intelligence by perceiving their environment, learning from data, reasoning, and making decisions with minimal human intervention. Unlike automated intelligence, which strictly follows predefined rules, AI is adaptive and self-improving, capable of handling dynamic, complex scenarios.
At its core, AI leverages several advanced technologies:
- Machine Learning (ML): Systems learn patterns from data and improve predictions or actions over time.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables AI to understand and communicate in human language.
- Computer Vision: Allows machines to analyze and interpret visual data from the world.
- Generative Models: Create new content, such as text, images, music, and code, based on learned patterns.
Key characteristics of AI include:
- Adaptability: Learns and evolves beyond its initial programming.
- Decision-making: Handles complex, unstructured problems that lack predefined rules.
- Personalization: Creates tailored experiences by analyzing user behavior and preferences.
AI is ideal for complex problem-solving and dynamic decision-making in industries like healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and customer experience. By enabling systems to think, learn, and act intelligently, AI transforms innovation and competitiveness at scale.
Automated Intelligence vs Artificial Intelligence — Core Differences
The terms automated intelligence and artificial intelligence are often confused, but their capabilities and impact on business are fundamentally different. While both aim to improve efficiency and reduce manual effort, their approach, adaptability, and outcomes diverge significantly.
| Aspect | Automated Intelligence | Artificial Intelligence |
| Definition | Rule-based task automation | Adaptive, self-learning intelligence |
| Learning | None — follows fixed workflows | Learns from data & experience |
| Decision-making | Predefined rules | Dynamic, predictive & generative |
| Data Handling | Structured data only | Structured & unstructured data |
| Adaptability | Low | High — adjusts to new patterns |
| Examples | RPA, macros, basic chatbots | GPT models, predictive analytics, self-driving cars |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower initial investment | Higher upfront cost but greater long-term ROI |
| Scalability | Linear — more rules = more effort | Exponential with more data & training |
1. Automation vs Adaptation
Automated intelligence focuses on doing tasks faster and with fewer human errors by strictly following predefined rules. For example, a Robotic Process Automation (RPA) bot may process invoices by reading structured fields and entering them into an ERP system. It doesn’t learn from mistakes or adapt if the invoice format changes.
Artificial intelligence, on the other hand, adapts and evolves. AI-powered systems like predictive analytics tools or GPT-based assistants analyze patterns in vast, diverse datasets. If an invoice format changes, an AI system can learn the new structure over time, making it far more resilient to business changes.
2. Static Rules vs Dynamic Learning
Automated intelligence is static. It’s ideal for repetitive, rule-based tasks such as:
- Auto-approving expense claims under a set limit.
- Extracting data from fixed-format forms.
- Moving files or triggering workflows when certain conditions are met.
AI thrives on dynamic learning. It uses machine learning algorithms to understand unstructured data (emails, images, text) and make predictions or generate outputs. Examples include:
- Fraud detection systems learning from evolving attack patterns.
- Virtual assistants understanding natural language and adapting to user preferences.
- Generative AI creating new content based on historical data.
3. Integration Depth
Automated intelligence usually connects to structured, predictable data sources such as databases, spreadsheets, and ERP systems. Its strength lies in consistency and compliance but it struggles with unstructured content like videos, free-text reports, or images.
Artificial intelligence integrates across a wider data ecosystem — structured and unstructured. AI can analyze text documents, images, audio files, and real-time IoT sensor data simultaneously. For instance, AI can combine patient health records with medical imaging and wearable device data to improve healthcare outcomes — something pure automation cannot handle.
4. Business Impact
Automated Intelligence → Efficiency & Cost Savings
It eliminates human intervention in redictable tasks, reduces errors, and accelerates back-office processes. Ideal for compliance reporting, payroll, invoice processing, and system updates.
Artificial Intelligence → Innovation & New Revenue
AI drives strategic decision-making and creates entirely new possibilities. It powers product recommendations, risk prediction in finance, personalized marketing, and self-driving vehicles — creating new business models beyond simple cost-cutting.
Automated Intelligence vs Artificial Intelligence: Business Use Cases
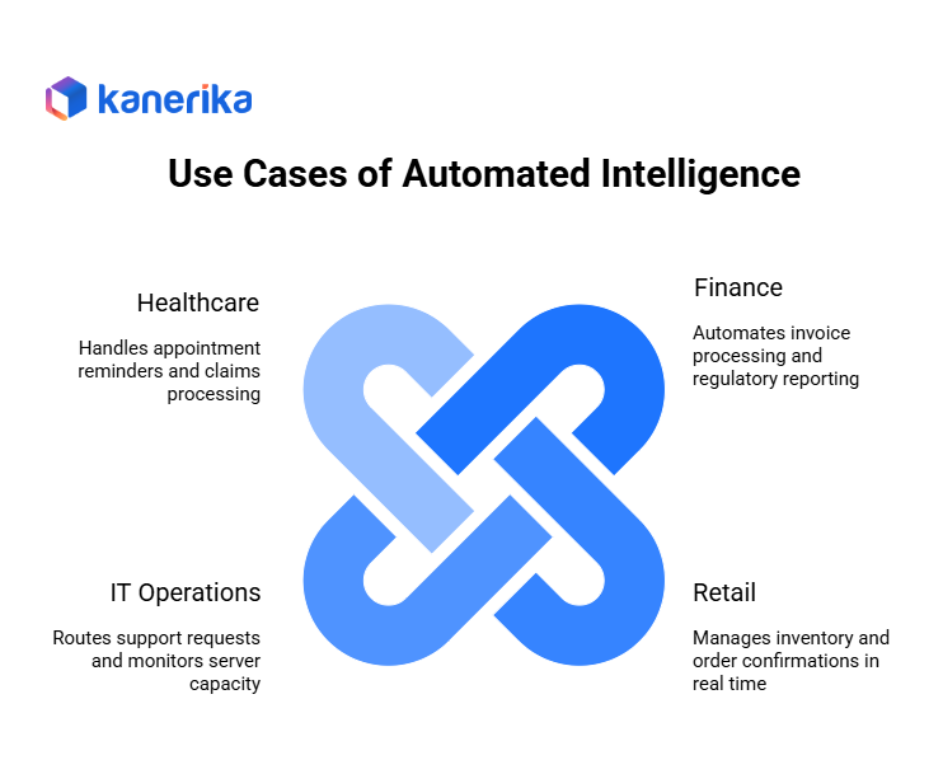
Automated Intelligence in Action
Automation handles repetitive, rule-based tasks without human intervention. These systems follow set instructions to process data, route information, and complete transactions.
Finance: Software processes invoices automatically, matching purchase orders to receipts and flagging discrepancies. Compliance systems generate regulatory reports on schedule without manual input.
Retail: Inventory systems update stock levels in real time as items sell. Order confirmations send automatically when customers complete purchases.
IT Operations: Ticketing systems route support requests based on keywords and priority levels. Automated monitoring sends alerts when servers reach capacity thresholds.
Healthcare: Scheduling systems send appointment reminders via text or email. Claims processing software validates insurance eligibility and submits standard claims electronically.
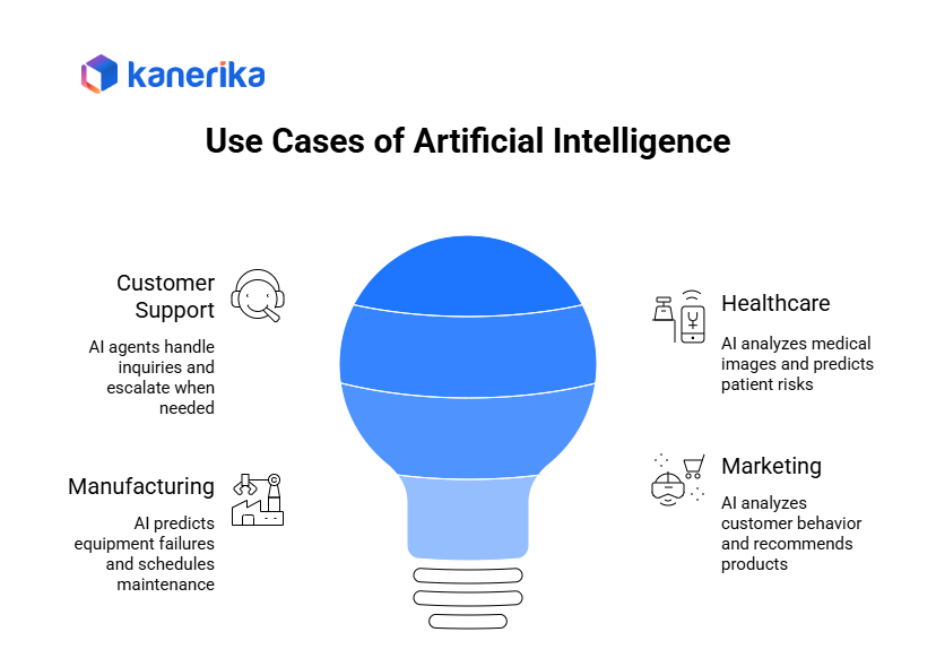
Artificial Intelligence in Action
AI goes beyond automation by learning patterns, making predictions, and adapting to new information. These systems improve accuracy over time.
Customer Support: Conversational AI agents understand natural language and provide context-aware responses. They handle complex inquiries and escalate when needed.
Healthcare: AI analyzes medical images to detect anomalies. Predictive models identify patients at risk for readmission based on multiple health factors.
Manufacturing: Machine learning predicts equipment failures before they happen. Sensors track vibration patterns and temperature changes to schedule maintenance proactively.
Marketing: AI analyzes customer behavior to recommend products. Systems predict when customers might switch to competitors and trigger retention campaigns.
Mini Case Study: Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola uses automation for routine supply chain operations like order processing and inventory tracking. For AI, the company signed a $1.1 billion deal with Microsoft to use Azure OpenAI Service for demand forecasting. AI-driven forecasting improved accuracy from 70% to 90%, helping the company optimize production and reduce waste.
AI-powered vending machines analyze transaction patterns at each location. By stocking the right products based on local preferences, Coca-Cola saw a 15% increase in vending machine transactions and reduced restocking visits by 18%.
The company handles routine tasks with automation while using AI for complex predictions that require learning from data patterns.
Benefits of Automated Intelligence vs Artificial Intelligence
Benefits of Automated Intelligence
Efficiency: Automation handles repetitive tasks without human involvement. Invoice processing that took hours now takes minutes. Data entry errors drop when software follows consistent rules.
Cost-Effective: Lower upfront costs make automation accessible. Most businesses can start automating basic processes without major capital investment. You pay for software licenses or subscriptions, not expensive AI infrastructure.
Reliability: Automated systems execute the same steps every time. This consistency matters in regulated industries like healthcare and finance. Compliance reporting happens on schedule with no missed deadlines.
Fast Implementation: Most automation tools deploy in weeks, not months. Teams learn straightforward workflows quickly. Scaling up means adding more processes to existing systems.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
Smarter Decision-Making: AI analyzes patterns humans miss. It processes thousands of variables to predict outcomes. Financial institutions spot fraud faster. Manufacturers prevent equipment breakdowns before they happen.
Personalization: AI tailors experiences to individual preferences. Netflix recommends shows based on viewing history. Online retailers suggest products customers actually want. Healthcare providers identify treatments most likely to work for specific patients.
Innovation: AI enables entirely new services. Self-driving cars learn from millions of road scenarios. Voice assistants understand natural conversation. Medical imaging AI detects diseases earlier than traditional methods.
Long-Term ROI: AI improves over time as it learns from more data. Early investments pay off as systems become more accurate. Companies gain competitive advantages that compound year after year.
Benefits Comparison
| Automated Intelligence | Artificial Intelligence |
| Efficiency – Eliminates manual work | Adaptability – Learns and improves continuously |
| Cost Savings – Lower initial investment | Innovation – Creates new capabilities |
| Reliability – Consistent execution | Personalization – Tailors to individual needs |
| Speed – Quick to implement | Intelligence – Makes complex predictions |
| Compliance – Follows exact rules | ROI – Delivers compounding value over time |
The right choice depends on your needs. Use automation for predictable, rule-based work. Choose AI when you need systems that learn, adapt, and handle complexity.
Challenges & Considerations Before Adopting AI or Automation
Adopting AI or automated intelligence can transform business operations, but it also introduces important challenges that leaders must anticipate and address. Understanding these issues early helps ensure a smoother transition and higher ROI.
1. Data Quality & Availability
AI systems thrive on high-quality, diverse, and unbiased data. Poor data can lead to inaccurate predictions, unfair outcomes, or even reputational damage. For example, Amazon’s hiring AI tool was discontinued after it showed bias against women — a direct result of training on historical, male-dominated hiring data. Organizations must invest in data cleansing, enrichment, and governance before deploying AI.
2. Implementation Costs
While automation tools (e.g., RPA) have relatively lower setup costs, AI adoption often demands higher upfront investment. Training or fine-tuning AI models requires compute resources (GPUs), cloud infrastructure, and specialized tools. Businesses should conduct a clear cost-benefit analysis to avoid budget overruns and plan for both initial setup and ongoing maintenance.
3. Skills Gap
Automation can often be handled by IT and process specialists, but AI requires data scientists, machine learning engineers, and domain experts. Many organizations face a talent shortage, making it necessary to upskill existing teams or partner with external vendors to fill the gap.
4. Security & Compliance
AI models often access sensitive or regulated data. Without strong security measures — such as encryption, role-based access control (RBAC), and audit trails — organizations risk data breaches or non-compliance with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Building a governance-first approach is essential.
5. Change Management
Employees may resist AI-driven workflow changes, fearing job displacement or complexity. Leaders should focus on transparent communication, training programs, and positioning AI as an assistant — not a replacement — to drive adoption and trust.
6. Vendor Lock-In
Both AI and RPA tools can lead to dependency on a single platform. This can limit flexibility, increase costs, and create challenges if the vendor changes pricing or support. Choosing tools with open standards, APIs, and multi-cloud compatibility reduces this risk.

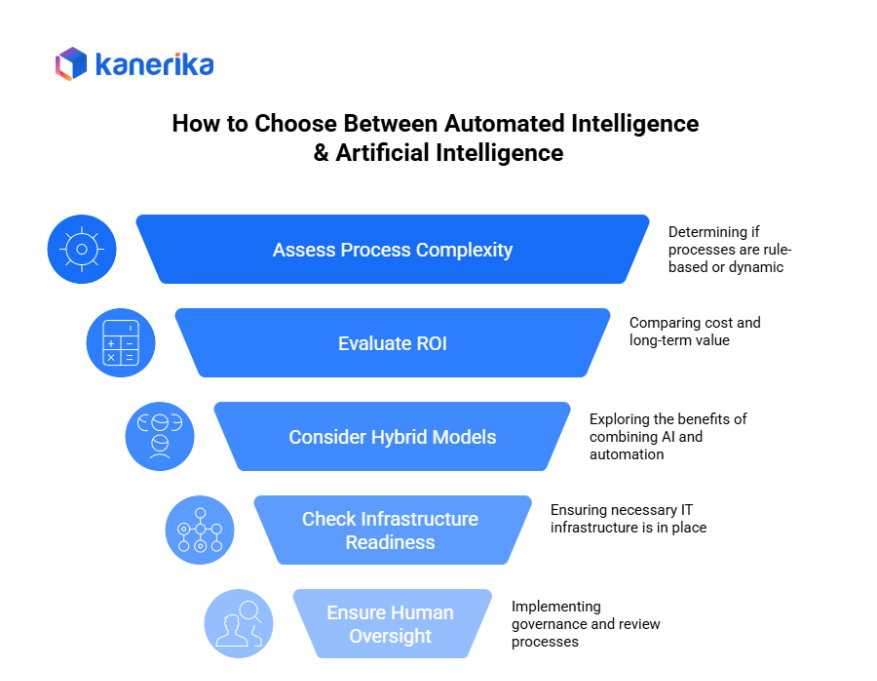
How to Choose Between Automated Intelligence & Artificial Intelligence
Selecting the right technology — automated intelligence or artificial intelligence (AI) — depends on your business needs, process complexity, and growth strategy. The wrong choice can lead to wasted investment or limited impact, so it’s critical to assess carefully.
1. Assess Process Complexity
If a workflow is predictable and rule-based (e.g., invoice processing, email filtering, or report generation), automation such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is often sufficient. But if processes involve dynamic, data-driven decisions — like fraud detection, personalized recommendations, or predictive maintenance — AI is the better fit.
2. Evaluate ROI
Automation delivers quick wins and cost savings with lower upfront investment, making it ideal for fast operational improvements. AI, while costlier initially, offers long-term value creation through smarter decisions, new revenue opportunities, and innovation. Consider the payback period and scalability before committing.
3. Start with Hybrid Models
Many organizations succeed by combining both approaches. Automation handles repetitive, rules-based tasks, while AI powers decision-heavy and analytical processes. This hybrid model reduces complexity and accelerates digital transformation while managing risk.
4. Check Infrastructure Readiness
AI often requires data lakes, APIs, cloud platforms, and robust integration to function effectively. Automation tools, on the other hand, work with simpler IT setups and can be implemented faster with fewer changes.
5. Ensure Human Oversight
AI systems should have governance, explainability, and human-in-the-loop review to maintain trust and compliance, especially in regulated industries.
Future Outlook — Convergence of Automation Intelligence vs Artificial Intelligence
The future of business technology lies in the seamless convergence of automation and artificial intelligence (AI). What began as simple rule-based workflows is evolving into intelligent, self-optimizing systems capable of adapting, learning, and driving strategic decisions.
1. Rise of Intelligent Automation
Organizations are moving beyond traditional Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) — blending automation’s speed with AI’s adaptability. This shift enables workflows that not only follow rules but also interpret unstructured data, detect anomalies, and make recommendations in real time.
2. AI-Augmented RPA
Future bots won’t just execute tasks; they’ll learn from outcomes, identify process improvements, and adapt over time. For example, AI-enhanced bots can detect fraud patterns in financial transactions or dynamically adjust supply chains based on demand changes.
3. Autonomous Agents
Autonomous agents will combine the efficiency of automation with the reasoning power of AI, enabling end-to-end process execution without human intervention. These agents will manage complex workflows like claims processing, IT troubleshooting, and personalized customer engagement.
4. Generative AI Integration
Generative AI will make automation more dynamic and context-aware. From automatically generating reports and contracts to providing personalized responses in customer support, generative models will elevate traditional automation to new levels of intelligence and adaptability.
Gartner forecasts that “By 2030, 80% of enterprise automation will include AI-driven decision-making” — underscoring how crucial this integration will be for future-ready businesses.
Business Impact: Companies that blend automation and AI will gain unmatched agility, operational efficiency, and innovation speed, outpacing competitors in digital transformation and market responsiveness.
Kanerika: Your AI Consulting Partner for Business Innovation and Growth
Kanerika brings deep expertise in agentic AI and AI/ML, helping businesses across industries transform the way they operate. From manufacturing and retail to finance and healthcare, we build solutions that drive innovation, improve productivity, and lower costs.
We have developed purpose-built AI and generative AI models designed to tackle specific business challenges. These tools help organizations overcome bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and scale with confidence. Our solutions cover a wide spectrum of needs including faster information retrieval, video analysis, real-time data processing, smart surveillance, and inventory optimization.
For finance and operations teams, our AI supports accurate sales forecasting, financial planning, arithmetic data validation, and vendor evaluation. For growth-driven companies, we provide smart product pricing insights and advanced scenario analysis to guide better decisions.
At Kanerika, we focus on building AI systems that deliver measurable results. Partner with us to make your business more agile, efficient, and ready for the future.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Automated Intelligence and Artificial Intelligence?
Automated Intelligence refers to rule-based systems that follow predefined workflows and logic to perform repetitive tasks. They cannot learn or adapt on their own.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), on the other hand, mimics human intelligence by learning from data, adapting to new inputs, and making dynamic, predictive, or even generative decisions. AI evolves over time, while automation stays fixed.
2. How does learning differ between Automation and AI?
Automation does not learn — it runs on static rules and logic that need manual updates if processes change.
AI uses machine learning and other techniques to analyze data, recognize patterns, and improve performance automatically. This makes AI better for complex, changing environments where adaptability is critical.
3. Can businesses use both AI and Automated Intelligence together?
Yes. Many enterprises use Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) — blending automation for repetitive tasks with AI for decision-making and data-driven insights.
For example, a company might use automation to extract invoices from emails while AI analyzes the data to detect fraud or predict cash flow trends.
4. Which is more cost-effective — Automation or AI?
Automation is generally cheaper and faster to implement, making it ideal for well-defined, repetitive workflows.
AI requires a higher upfront investment in data, infrastructure, and talent but can create long-term value through innovation, new revenue opportunities, and smarter decision-making.
5. What are common use cases for Automated Intelligence vs AI?
Automation is best for back-office tasks like payroll processing, invoice approvals, and compliance reporting.
AI excels at dynamic tasks such as customer support chatbots, predictive maintenance, fraud detection, and personalized recommendations.
6. What challenges come with adopting AI compared to automation?
AI adoption faces data quality and governance issues, higher implementation costs, and the need for specialized skills such as data science and ML engineering.
Automation is easier to deploy but can become rigid over time if processes evolve or require adaptability.
7. What is the future of Automated Intelligence and AI in business?
The future lies in intelligent automation, where AI-powered bots not only execute tasks but also learn, adapt, and make decisions.
Gartner predicts that by 2030, most enterprise automation will include AI-driven decision-making, enabling smarter, scalable, and fully autonomous business workflows.










