Microsoft Fabric is rapidly becoming a go-to platform for enterprise analytics as organizations seek unified, AI-powered data solutions. In 2025, Fabric received the highest possible ranking in the Forrester Wave: Data Platforms Q4 2025 report, with more than 25,000 customers adopting it for end-to-end analytics. The platform leads in real-time analytics, integration, governance, and unified data workflows that help teams move from raw data to insight faster than before.
The demand for modern analytics continues to grow. The global data analytics market is valued at about $64.75 billion in 2025 with a projected compound annual growth rate of nearly 29.4%, reflecting how critical analytics is to business success. With OneLake providing a single place for all organizational data and built-in AI assistance through Copilot and agent features, Microsoft Fabric helps teams reduce data silos, accelerate time to insight, and support real-time decision-making.
Continue reading this blog to explore how Microsoft Fabric for Data Analytics works in practice, key capabilities that set it apart, and real-world use cases where it is delivering faster, more scalable insights for modern enterprises.
Key takeaways
- Microsoft Fabric brings data engineering, analytics, real-time intelligence, and BI into one unified data analytics platform.
- Data analytics workflows become faster because engineers, analysts, and business users work on the same data without extra movement or sync.
- Built-in governance, security, and compliance help organizations manage analytics data at scale with less operational effort.
- Native Power BI and Direct Lake enable near real-time dashboards and reporting without complex refresh cycles.
- Fabric supports both historical analysis and real-time analytics, making it suitable for modern, AI-driven decision-making.
- Kanerika, through its FLIP platform, helps enterprises automate and scale Microsoft Fabric workflows for reliable, production-ready analytics.
Transform Data Operations with Microsoft Fabric!
Work with Kanerika to Simplify Your Adoption Journey
What is Microsoft Fabric for Data Analytics?
Microsoft Fabric is a unified analytics platform combining data engineering, data science, real-time analytics, data warehousing, and business intelligence in a single Software as a Service environment. Launched in November 2023 and generally available since May 2024, Fabric addresses the challenge of managing multiple disconnected tools across the analytics lifecycle.
Before Fabric, organizations relied on separate services: Azure Synapse Analytics for warehousing, Azure Data Factory for integration, and Power BI for visualization. This fragmentation led to data duplication, inconsistent governance, and significant integration efforts.
Fabric provides an integrated platform where all analytics activities share the same data foundation. Built on OneLake, which functions as a single enterprise data lake, every piece of data lives in one place. All analytics tools access this shared storage directly without the need for data movement.
The platform uses the Delta Lake format, providing ACID transaction support, time travel capabilities, and automatic format conversion. Security and governance are centralized at the storage layer.
Fabric serves multiple roles:
- Data engineers build and manage pipelines
- Analysts create reports and dashboards
- Data scientists train and deploy ML models
- Business users explore data through self-service
For organizations using Microsoft’s ecosystem (Office 365, Power BI, Dynamics 365), Fabric offers a natural extension with familiar interfaces.
Understanding Microsoft Fabric Architecture
Microsoft Fabric operates as a Software-as-a-Service platform built on a lake-centric architecture that unifies storage, compute, and analytics workloads.
OneLake: The Unified Foundation
At the core sits OneLake, a single, logical data lake automatically provisioned with every Fabric tenant. Built on Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, OneLake stores all data in Delta Parquet format—an open-source standard that combines transactional database capabilities (ACID compliance, versioning, time travel) with analytics-optimized Parquet files. This standardization enables zero-copy data sharing across all Fabric engines (T-SQL, Apache Spark, Analysis Services) without duplication or movement.
Every workspace appears as a container within OneLake, with data items as folders. Organizations can address OneLake as one unified storage account across the enterprise. The OneLake Catalog provides centralized discovery, exploration, and governance of all data assets.
Compute and Capacity Model
Fabric uses capacity-based compute measured in Capacity Units (CUs). Organizations purchase capacity that is pooled across all workloads—data engineering, warehousing, real-time analytics, and business intelligence share the same resource allocation. This architecture separates compute from storage, allowing independent scaling. Workloads can “burst” beyond base capacity temporarily during heavy processing, with lighter workloads contributing unused resources back.
Key Architectural Features
- Lakehouse Design: When creating a lakehouse, two storage areas are provisioned—Tables (for Delta, Parquet, CSV tables) and Files (for any format). This provides data lake flexibility with warehouse performance.
- Shortcuts: Reference external data in AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, ADLS Gen2, or on-premises without copying. Data appears local while remaining in its original location.
- Direct Lake Mode: Power BI queries OneLake data directly without import, eliminating refresh cycles and enabling near real-time reporting.
- Governance: Microsoft Purview provides built-in governance. Security policies and access controls apply at the OneLake level and automatically inherit across all workloads, making sure consistent security without separate tool configurations.
Core Microsoft Fabric Components
Microsoft Fabric includes eight integrated workloads built on a shared data foundation powered by OneLake. Each workload serves a specific analytics role, but all operate on the same data without duplication. This unified design allows teams to move from ingestion to analytics, real-time insights, and BI within a single platform.
1. Data Engineering
Fabric Data Engineering supports large-scale processing using Apache Spark through notebooks and pipelines. It supports Python, Scala, R, and SQL, with automatically managed Spark clusters that reduce infrastructure overhead. A visual designer with pre-built activities helps simplify pipeline creation.
2. Data Factory
Data Factory enables ETL and ELT workflows with over 90 built-in connectors. It includes Power Query-based transformations accessible to both engineers and analysts. Dataflows Gen2 write directly to lakehouses, warehouses, and KQL databases, making data available across Fabric workloads.
3. Data Science
The Data Science workload supports machine learning development with Jupyter notebooks, MLflow tracking, and model versioning. AutoML accelerates prototyping, while optional GPU support enables advanced workloads such as deep learning.
4. Data Warehouse
Fabric Data Warehouse provides T-SQL–based analytics with distributed, columnar storage. It scales automatically and offers familiar SQL interfaces, while data remains in OneLake for seamless access across workloads.
5. Real-Time Intelligence
Real-Time Intelligence handles streaming data using no-code Eventstreams for ingestion. KQL databases are optimized for time-series data, logs, and IoT telemetry, supporting near real-time analytics and operational monitoring.
6. Power BI
Power BI is natively integrated into Fabric for reporting and dashboards. Direct Lake mode queries OneLake directly without importing data, removing refresh delays. Semantic models can be reused across reports for consistency.
7. Fabric Activator
Fabric Activator enables automated responses to data conditions without code. Users define rules to trigger alerts, notifications, or workflows based on data patterns, supporting operational use cases.
8. IQ (Preview)
IQ, currently in preview, focuses on unifying business semantics across data and systems. It introduces an ontology-based semantic layer that connects to OneLake and existing models, helping create consistent, AI-ready definitions and reusable metrics.
Microsoft Fabric vs Traditional Analytics Platforms
| Aspect | Traditional Analytics Stack | Microsoft Fabric |
| Platform model | Separate tools for ingestion, storage, analytics, and BI | Single SaaS platform covering the full analytics lifecycle |
| Data storage | Multiple data lakes, warehouses, and marts | OneLake as a shared data layer for all workloads |
| Data movement | Regular ETL and data duplication between systems | Data accessed in place with minimal movement |
| Integration | Custom connectors and ongoing maintenance | Built-in integration across Fabric workloads |
| Governance | Policies managed separately per tool | Centralized governance using Microsoft Purview |
| Cost and billing | Multiple subscriptions and invoices | Single capacity based pricing model |
| User experience | Different interfaces for each tool | Consistent workspace for all analytics roles |
Microsoft Fabric Benefits for Data Analytics Teams
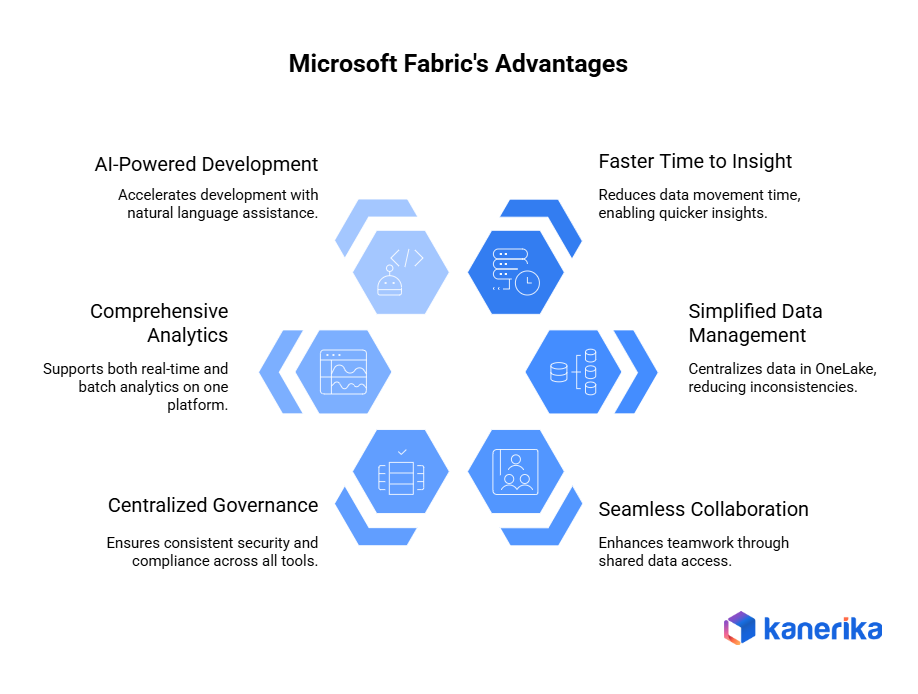
1. Faster Time to Insight
Microsoft Fabric reduces the time spent moving data between systems. Data engineers can ingest and prepare data directly in OneLake, and analysts can start building reports in Power BI as soon as the data is ready. Because there is no need to export or replicate data across tools, analytics workflows move faster and insights reach decision-makers sooner.
2. Simplified Data Management
With OneLake acting as a single, unified data lake, teams no longer maintain multiple copies of the same data. Everyone works from the same trusted source, which reduces inconsistencies and rework. This also lowers storage costs and simplifies data lifecycle management, including retention, updates, and archival.
3. Seamless Collaboration Across Teams
Shared access to OneLake allows data engineers, analysts, and data scientists to collaborate more effectively. Changes made by one team are immediately available to others, removing delays caused by handoffs or data synchronization. This shared environment improves alignment and speeds up end-to-end analytics delivery.
4. Centralized Governance and Compliance
Microsoft Fabric applies security, access control, and governance policies consistently across all workloads. Teams do not need to configure governance separately for each tool. Integration with Microsoft Purview enables data lineage tracking, sensitivity labeling, and cataloging, helping organizations maintain compliance and trust in their data.
5. Comprehensive Analytics Capabilities
Fabric supports both streaming and batch analytics within the same platform. Teams can analyze real-time operational data for immediate insights while also exploring historical datasets for trends and forecasting. This eliminates the need for separate systems for real-time and traditional analytics.
6. AI-Powered Development with Copilot
Microsoft Fabric includes Copilot capabilities that assist teams through natural language interactions. Copilot can generate code, suggest optimizations, and help identify patterns in data. This accelerates development for experienced users while making advanced analytics more accessible to teams with varying skill levels.
Microsoft Fabric Use Cases Across Industries
Organisations across different sectors are adopting Microsoft Fabric to unify data, accelerate analytics, and drive measurable business value. Here are real, documented examples from the official Microsoft customer stories collection:
1. Manufacturing & Consumer Goods – Migros Industrie
Migros Industrie, a major Swiss food manufacturer, faced performance limits with its legacy analytics systems. Before adopting Fabric, data updates could take up to 30 minutes, slowing down decision-making. After implementing Fabric’s unified analytics and data storage, data updates are now complete in seconds, enabling real-time analytics across the production environment. Around 3,000 employees actively use Fabric for reporting and operational decisions across the company.
This change helped Migros Industrie move from fragmented, slow systems to a scalable, future-ready data foundation that supports real-time production monitoring, predictive maintenance, and ongoing operational improvements.
2. Consumer Packaged Goods – Gay Lea Foods
Gay Lea Foods, a Canadian dairy cooperative, used Microsoft Fabric to unify data across financial, supply chain, and operational systems. Before Fabric, monthly reporting took 24 days to complete. After migration, reporting time dropped dramatically to one day, and data refreshes that previously took hours now complete in about 3 minutes. This improvement enabled daily decision-making with fresh data instead of slow, delayed reporting.
This transformation also helped the company move away from scattered Excel-based reporting and inconsistent numbers, giving teams a single source of truth and supporting more strategic planning and analytics.
3. Hospitality & Customer Experience – Valamar Riviera
Valamar Riviera, a leading hospitality group, deployed Microsoft Fabric to centralize data from properties across Europe. With Fabric’s real-time analytics and dashboards, the company gained ongoing visibility into operations and guest services. One early outcome reported was a €20 million increase in call center sales, driven by insights from unified data.
Fabric’s integration with Power BI and AI tools also allowed Valamar teams to answer complex business questions faster and improve responsiveness to operational issues across properties.
4. Mobility & Data Integration – Verne
Verne, a company innovating in urban autonomous mobility, brought more than 10 different data sources together using Microsoft Fabric and plans to integrate over 30 data sources total. This consolidation enabled the automation of operational reporting and extended access to Power BI dashboards across departments.
By centralizing datasets and automating reporting, Verne reduced manual data preparation and expanded visibility into operations, making insights more accessible across teams.
Partner with Kanerika to Modernize Your Enterprise Operations with High-Impact Data & AI Solutions
Is Microsoft Fabric Right for Your Organization?
Microsoft Fabric is well-suited for organizations that need unified analytics with shared data access, centralized governance, and support for multiple workloads. It delivers the most value for teams working across data engineering, analytics, and reporting that want to reduce fragmentation and shorten time to insight.
Fabric is a strong fit for organizations already using Microsoft technologies such as Power BI, Azure, or Dynamics 365. Familiar interfaces reduce the learning curve and make it easier to consolidate analytics without rebuilding the entire data stack from scratch.
Fabric is worth considering when organizations are:
- Managing 5 or more analytics tools across ingestion, storage, analytics, and BI
- Facing governance and security gaps across platforms
- Carrying a high operational overhead from maintaining multiple systems
- Needing better collaboration across data engineers, analysts, and business users
- Prioritizing faster time to insight for decision-making
Organizations with strict multi-cloud mandates, heavy open-source investments, or limited Azure adoption may find traditional approaches more suitable. Smaller teams should also evaluate whether Fabric’s capacity-based pricing aligns with their needs. In these cases, a phased adoption starting with focused use cases like financial reporting or operational monitoring often works best.
FLIP by Kanerika: Automating Data Workflows for Smarter Outcomes
Kanerika is a certified Microsoft Data & AI Solutions Partner, specializing in Microsoft Fabric adoption for enterprises looking to modernize their analytics platforms. Our team of certified professionals and Microsoft MVPs designs scalable, secure, and business-aligned data ecosystems that simplify complex data environments, enable real-time analytics, and establish strong governance using Fabric’s unified architecture.
We help organizations modernize legacy data platforms through structured migration and automation-led approaches. Manual migrations are often slow and error-prone, so Kanerika leverages automation tools, including FLIP, to ensure smooth transitions across SSRS to Power BI, SSIS and SSAS to Microsoft Fabric, and Tableau to Power BI. This approach improves data accessibility, enhances reporting accuracy, and significantly reduces ongoing maintenance costs.
As one of the early global adopters of Microsoft Fabric, Kanerika follows a proven deployment framework that covers architecture design, semantic modeling, governance setup, and user training. Combined with FLIP’s automated DataOps capabilities, our approach helps organizations roll out Fabric faster, keep data secure, and realize its value quickly with minimal effort and clear business results.
Drive Business Growth with Microsoft Fabric Analytics!
Partner with Kanerika for Smooth and Scalable Fabric Adoption
FAQs
What is Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric is an all-in-one analytics platform unifying data integration, warehousing, real-time analytics, and visualization. It simplifies the entire data lifecycle, eliminating the need for stitching together disparate tools. Think of it as a single, integrated workspace for all your data needs, streamlining everything from ingestion to insights. This reduces complexity and accelerates your data journey.
Is Microsoft Fabric similar to Databricks?
Microsoft Fabric and Databricks are both cloud-based data platforms, but they differ significantly in approach. Fabric is a more integrated, end-to-end solution encompassing data warehousing, analytics, and AI, while Databricks focuses primarily on data engineering and analytics using Apache Spark. Essentially, Fabric aims for simpler, unified workflows whereas Databricks offers more granular control and open-source flexibility. Think of Fabric as an all-in-one kitchen and Databricks as a high-powered chef’s workstation.
Is Microsoft Fabric a competitor to Snowflake?
Microsoft Fabric and Snowflake both offer cloud data warehousing and analytics, but target different needs. Fabric is deeply integrated into the Microsoft ecosystem, aiming for ease of use and streamlined workflows within that environment. Snowflake, conversely, offers broader compatibility and is often preferred for its highly scalable, independent platform catering to larger, more complex data environments. Essentially, they compete for similar customers but with differing approaches and strengths.
What is the difference between Microsoft Fabric and Azure?
Microsoft Fabric is a unified analytics platform *built on top of* Azure. Think of Azure as the foundation – the cloud infrastructure providing the computing power and storage. Fabric is the pre-built house, offering integrated tools for data ingestion, transformation, analysis, and visualization, all within a single workspace. Essentially, Fabric simplifies working with data *on* Azure.
What is the Microsoft tool for data analysis?
Microsoft offers several tools for data analysis, depending on your needs. Power BI excels at interactive visualizations and reporting from diverse data sources. Excel, while familiar, remains a powerful tool for smaller datasets and simpler analyses. For more advanced statistical modeling and machine learning, consider Azure Machine Learning.
Is Microsoft Fabric free?
No, Microsoft Fabric isn’t entirely free. It offers a free tier with limitations on data storage and compute resources, ideal for experimentation and small projects. However, for production workloads and larger datasets, you’ll need a paid subscription, scaling based on your usage. Think of it like a freemium model – a taste of the power, but full access requires a purchase.
Why do I need Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric simplifies your data journey, unifying data integration, engineering, warehousing, analytics, and real-time insights into one cohesive platform. It eliminates the complexity of juggling multiple tools, saving you time and resources. Ultimately, Fabric empowers you to derive actionable intelligence faster and more efficiently from your data. This translates to improved decision-making and a competitive advantage.
Is Microsoft Fabric low code?
Microsoft Fabric isn’t strictly “low-code” in the traditional sense; it’s more of a unified analytics platform. While it offers tools simplifying complex tasks like data integration and report building, it also empowers users with robust coding options for advanced customization. Think of it as having a low-code *foundation* with significant power to go beyond it, depending on your needs and skills.
Is Microsoft Fabric cloud-based?
Yes, Microsoft Fabric is entirely cloud-based. It leverages the Azure cloud infrastructure, meaning you don’t manage any servers or on-premises infrastructure. This offers scalability and accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection. Data is stored and processed within the Azure environment.
What is the difference between Microsoft Fabric and Snowflake?
Microsoft Fabric is a unified analytics platform integrating data warehousing, data engineering, real-time analytics, and more within the Microsoft ecosystem. Snowflake, conversely, is a cloud-based data warehouse focusing primarily on data storage and querying, often requiring integration with other tools for a complete analytics solution. Essentially, Fabric aims for all-in-one convenience, while Snowflake prioritizes powerful, scalable data warehousing. The choice depends on your existing tech stack and desired level of integration.
What is the Microsoft tool for data analytics?
Microsoft’s primary tool for data analytics is Power BI. It’s used to visualize data, create interactive reports, and build dashboards. Power BI helps you transform raw data into clear, actionable insights. This allows you to understand trends and make informed decisions easily.
What is Microsoft Fabric vs Dataverse?
Microsoft Dataverse is where your business applications, like Power Apps, store and manage their day-to-day operational data for transactions. Microsoft Fabric is an all-in-one analytics platform for collecting, processing, and analyzing large amounts of data from many sources. It’s used for data warehousing, engineering, and reporting to generate insights and enable business intelligence.
Is Microsoft Fabric like AWS?
No, not exactly. Microsoft Fabric is a unified platform from Microsoft for *all your data analytics needs*, bringing together tools for data engineering, warehousing, and business intelligence. AWS, on the other hand, is a much broader cloud computing service offering a vast range of products, including its own separate data and analytics tools. Fabric is a focused set of analytics services within Microsoft’s ecosystem, whereas AWS is a whole cloud ecosystem.
Which SQL is used in Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric primarily uses T-SQL (Transact-SQL) for querying data in its Data Warehouse and Lakehouse components. It also widely uses KQL (Kusto Query Language) for real-time analytics and time-series data. For big data processing, Spark SQL is leveraged in the Data Engineering experiences.