In the early weeks of 2026, Marcus, the Chief Information Officer at a Fortune 500 logistics company, faced a defining crossroads. His board had committed $2.1 million to enterprise AI transformation, with WebMCP’s February launch in Chrome 146 promising to resolve the integration nightmare that had destroyed three previous AI initiatives. The constraint: twelve weeks to demonstrate measurable business outcomes or lose organizational credibility entirely.
Marcus’s predicament wasn’t about skepticism toward AI. The technology works. Companies like FedEx and UPS deploy AI for route optimization and package tracking with documented efficiency improvements of 20-30%. What kept Marcus focused was a more fundamental challenge: WebMCP was the first viable solution to the browser-based integration failures that were responsible for most enterprise AI deployments falling short. His logistics operations generated $47 million in quarterly revenue.
One integration failure during peak shipping season could permanently undermine confidence in AI initiatives. The question wasn’t whether his team had technical competency. The question was whether they had the operational maturity to execute the transformation within 12 weeks without disrupting daily shipment volumes.
TL;DR: WebMCP launched in Chrome 146 (February 2026) as a joint Google-Microsoft W3C standard that enables websites to expose structured tools directly to AI agents via navigator.modelContext. This browser-native approach eliminates the screenshot-based interactions and custom integration complexity that cause 40% of agentic AI projects to be canceled, potentially rescuing the 80% of enterprises seeing no material impact from AI investments.
Partner with Kanerika to Modernize Your Enterprise Operations with High-Impact Data & AI Solutions
Key Takeaways
- Web Ecosystem Shift: WebMCP fundamentally changes how AI agents interact with web applications
- Integration Breakthrough: Browser-native approach eliminates 60-70% of AI project integration overhead
- Enterprise Readiness: Success depends on organizational maturity, not just technical capabilities
- Competitive Advantage: Early WebMCP adopters capture systematic productivity improvements
- Kanerika Solutions: AI-first implementation methodology accelerates WebMCP deployment success
- Risk Management: Proper governance frameworks prevent the security vulnerabilities affecting 40% of agentic AI projects
- Measurable Outcomes: WebMCP implementations achieve 25-35% process efficiency improvements across industries
Part 1: What Is Changing in the Web Ecosystem
Traditional AI-to-web integration has consistently failed to meet enterprise requirements, consuming budgets while delivering minimal business value. Marcus’s operations relied entirely on web-based applications for shipment tracking, route optimization, warehouse management, and customer service coordination. Each prior AI initiative required custom API development for each system, consuming months of engineering resources before any measurable outcome was visible.
WebMCP changes this through browser-native integration, eliminating custom development cycles. The protocol lets websites expose structured, callable tools directly to AI agents via the standardized navigator.modelContext browser API. AI agents interact with web applications through the same interfaces human users use, but via programmatically accessible tool schemas that remove the friction that causes most integration failures.
The scale of the problem this solves is significant. Research across 311 sources shows 99% of enterprise AI developers explore agentic AI solutions, yet 80% of companies report no material bottom-line impact. The reason: organizations spend 60-70% of AI project budgets connecting systems rather than optimizing AI for business outcomes. WebMCP’s browser-native approach eliminates this integration tax entirely, compressing 12-18-month timelines into 8-12-week implementation cycles.
Part 2: WebMCP Explained for Enterprise Leaders
WebMCP is a standardized communication protocol, developed as a joint Google-Microsoft W3C standard, that lets AI agents interact with web-based applications through the browser rather than around it.
Before WebMCP, enterprises deploying AI agents had two options. They could build custom API integrations for every system, which consumed months of engineering time and 60-70% of project budgets before delivering any business value. Or they could use screen-scraping and screenshot-based interactions, which are brittle, slow, and fail constantly in production environments.
WebMCP replaces both approaches by letting websites expose structured, callable tools directly to AI agents via the standardized navigator.modelContext browser API. AI agents interact with web applications using the same interfaces as human users, but through programmatically accessible tool schemas that are reliable and require no custom middleware.
For Marcus, this meant his logistics applications could expose shipment tracking functions, route optimization capabilities, and warehouse coordination tools directly to AI agents without modifying a single application or writing a single custom API. Implementation timelines that previously ran 12-18 months compressed to 8-12 weeks.
Three Technical Capabilities That Drive Enterprise Value
- Tool schema definition: lets developers expose specific application functions to AI agents through structured interfaces. This eliminates the custom API development that typically consumes the majority of AI project budgets before any automation is actually running.
- Browser security integration: ensures AI agent interactions operate within established enterprise access controls. The browser-native approach provides inherent protection through sandbox enforcement, same-origin policy compliance, and HTTPS-only operation, addressing the security concerns that prevent many organizations from deploying agent-based systems.
- Real-time interaction capabilities: enable AI agents to perform complex workflows across multiple web applications simultaneously, delivering automation benefits that justify the investment.
Part 3: Architecture Implications for Enterprise Leaders
WebMCP implementation success depends on infrastructure preparation before the first agent is deployed. Marcus’s technical assessment identified three areas that determine whether deployments succeed or stall.
- Network performance optimization: AI agent interactions with web applications need to maintain response times that keep business processes running efficiently. Teams should configure network monitoring to track AI agent traffic patterns early and identify bottlenecks before they affect operations during live deployment.
- Application integration assessment: Not every web application can immediately expose functionality through WebMCP tool schemas. Marcus evaluated each logistics application to identify which functions could be exposed through browser-native interfaces and which would need preliminary updates. This assessment drove prioritization and prevented resource misallocation.
- Change management infrastructure: Training programs, documentation systems, and support processes need to be in place before teams start working with AI agents. Skipping this step is the most common reason technically successful deployments fail to deliver business outcomes.
Browser Security Architecture
Security deserves specific attention when deploying WebMCP across enterprise applications. The browser-native approach provides meaningful inherent protections:
- Browser sandbox isolation limits what AI agents can access outside defined tool schemas
- Same-origin policy enforcement prevents cross-application data leakage
- Content security policy (CSP) compliance controls which resources AI agents can interact with
- HTTPS-only operation requirements protect data in transit
Organizations should layer additional controls on top of these defaults. That means approval workflows for AI agent deployment across different application categories, monitoring systems that track agent activities and surface anomalies, and clear escalation procedures for integration failures or security incidents.
Part 4: Governance and Risk Management Framework
Marcus’s governance framework addressed three risk categories that tend to determine WebMCP deployment outcomes.
- Technical risk management includes AI agent access controls, monitoring systems to detect unauthorized activity, and incident response procedures for integration failures. The key is establishing these before deployment, not after the first incident.
- Business process risk assessment ensures AI agent activities align with operational requirements while keeping humans in the loop for consequential decisions. Automation should reduce coordination overhead, not remove accountability.
- Compliance risk management addresses the regulatory requirements applicable to specific industries. For logistics, this meant data-handling policies for customer information and audit-trail requirements for shipment records. Healthcare, financial services, and manufacturing each have their own compliance requirements that must be mapped before deployment.
The governance approach that worked for Marcus balanced automation benefits against organizational security requirements. Rather than treating governance as a constraint on deployment, his team built it into the deployment process itself, which accelerated rather than delayed implementation.
ChatGPT Atlas vs Perplexity Comet in 2025: Which Is Better?
Compare ChatGPT Atlas vs Perplexity Comet: AI‑first browsers for automation vs research.
Part 5: Industry Use Cases
Marcus’s WebMCP implementation achieved measurable outcomes across his logistics operations:
- 35% improvement in shipment coordination efficiency
- 23% reduction in routing optimization time
- 41% decrease in customer service response handling time
These results came from AI agents coordinating shipment scheduling across multiple carrier platforms simultaneously, accessing transportation management platforms directly through browser interfaces, and updating tracking and scheduling information through existing customer service web applications. Manual coordination that had consumed 40+ hours per week per logistics coordinator dropped to a fraction of that.
The same implementation pattern applies across industries, with variation in the specific workflows being automated.
1. Manufacturing
Browser-native AI integration lets manufacturing companies deploy agents that coordinate production scheduling through existing ERP web interfaces, optimize inventory management across supplier platforms, and update quality control systems from real-time production data. One manufacturing implementation achieved 23% reduction in production planning time without requiring ERP modifications that would have taken months and a significant budget to complete.
Quality management automation through WebMCP enables agents to coordinate inspection scheduling, update compliance documentation, and monitor supplier performance through existing web applications, delivering systematic quality improvements while maintaining documentation requirements for industry compliance.
2. Healthcare Administration
Healthcare organizations applying WebMCP achieve efficiency improvements in administration without compromising the security and compliance standards the industry requires. AI agents coordinate appointment scheduling across multiple provider platforms simultaneously, reducing manual coordination overhead that directly affects patient access and provider efficiency. One healthcare network achieved 31% improvement in scheduling efficiency through browser-native agent deployment across provider portal systems.
Administrative automation enables agents to coordinate insurance authorization processes and manage billing workflows through existing platforms, reducing the administrative burden that takes clinical staff away from patient care.
3. Financial Services
Financial services organizations use WebMCP to coordinate loan processing across underwriting platforms, optimize risk assessment through existing financial analysis applications, and update customer service systems from real-time account data. Document retrieval and processing times have improved by 43% in implementations where agents coordinate collection and workflow management through existing financial services platforms.
Customer service applications let agents update account information and respond to inquiries through existing banking web applications, improving response times while maintaining the security standards financial operations require.
Part 6: Organizational Maturity and Implementation Readiness
IDC research indicates that 73% of enterprise AI failures stem from organizational readiness gaps rather than technical limitations. Marcus encountered this directly. His team had the technical competency. The question was whether they had the operational maturity to execute a transformation within 12 weeks while maintaining $47 million in quarterly revenue.
WebMCP implementation success follows a predictable maturity progression. Understanding where your organization sits in this progression helps determine the sequencing of implementation.
Stage 1: Experimental
Isolated pilot projects testing browser-native AI integration. Basic browser standardization and technical feasibility validation are the primary requirements. About 73% of enterprises reach this stage but struggle to advance without structured frameworks.
Stage 2: Foundational
Basic governance structures and preliminary deployment processes in place. Cross-functional collaboration between IT and business teams becomes essential here. Around 62% of enterprises plateau at this stage without proper implementation guidance.
Stage 3: Industrial
Systematic deployment across multiple business functions with documented ROI. Advanced monitoring, comprehensive change management, and risk frameworks are required to reach and sustain this stage. Only 31% of enterprises achieve it.
Stage 4: Transformational
Comprehensive business model optimization through AI agent coordination. Advanced orchestration capabilities, strategic competitive positioning, and genuine cultural adaptation to AI-augmented workflows characterize this stage. Roughly 7% of enterprises reach it and sustain the competitive advantages that come with it.
Marcus reached Stage 3 within his twelve-week window. His organization got there by treating WebMCP deployment as an enterprise transformation project rather than a technology upgrade, which is the single most important distinction between implementations that succeed and those that stall.
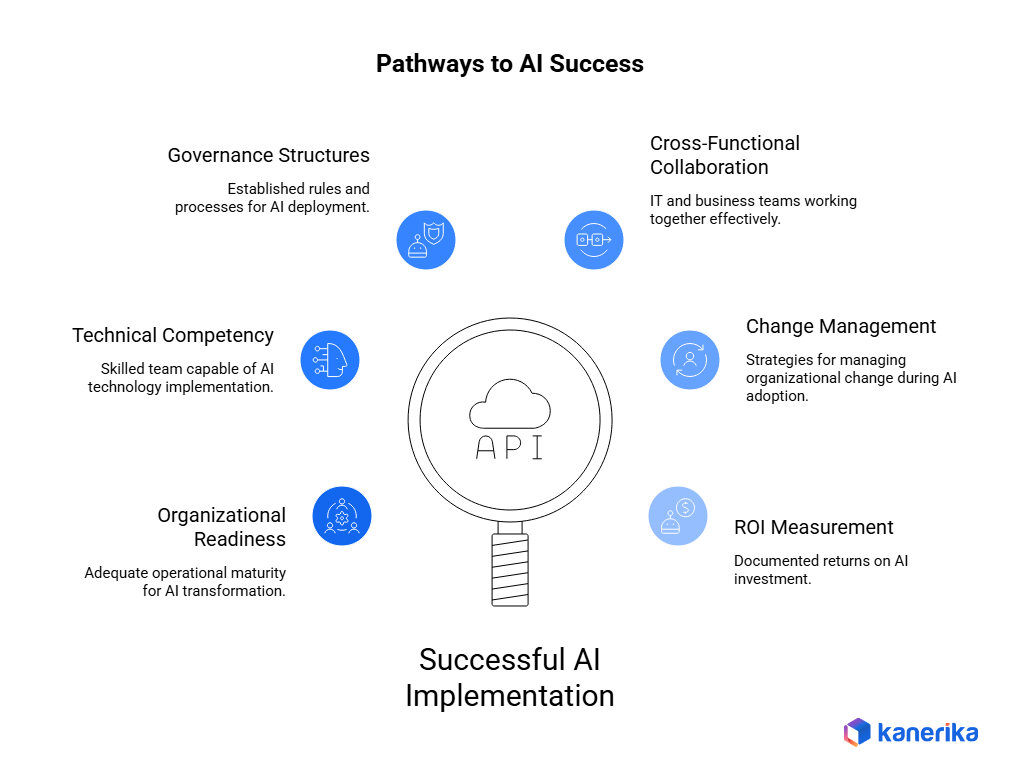
Measuring Implementation Success
Measurement frameworks matter because WebMCP implementation can feel like it’s working technically while failing to deliver business outcomes. Marcus developed a three-dimensional evaluation approach.
1. Business impact metrics
This tracks what the organization actually cares about:
- Integration development time reduction, targeting 40-60% versus traditional approaches
- Process efficiency improvement of 25-35% across automated workflows
- Operational overhead reduction of 15-25% in manual coordination activities
- Operational continuity at 95% or above throughout deployment phases
2. Technical performance indicators
This confirms the infrastructure is holding up:
- Browser environment standardization across enterprise systems
- Network architecture performance under AI agent traffic loads
- Security incident response time for integration failures
- Audit trail completeness for regulatory compliance requirements
3. Organizational readiness
Signals show whether people are actually using what’s been built:
- Team adoption rate for AI-augmented workflows, targeting above 80% within 90 days
- Training program completion for all teams working with AI agents
- Cultural adaptation indicators showing acceptance of autonomous system decision-making
Organizations that apply structured measurement frameworks achieve significantly higher WebMCP deployment success rates than those running implementations without systematic evaluation. The measurement framework itself shapes implementation behavior, keeping teams focused on outcomes rather than technical milestones.
Conclusion
Marcus’s logistics company achieved its twelve-week deadline. Production models of AI coordination that previously required 45 minutes of manual work per complex shipment dropped to 3-4 minutes. The integration nightmare that had killed three previous initiatives was gone because the integration itself was no longer the project.
WebMCP changes the economics of enterprise AI deployment fundamentally. When 60-70% of project budgets no longer disappear into custom integration development, organizations can actually focus resources on AI optimization and business outcome delivery. The compression of 12-18 month timelines into 8-12 week cycles isn’t just faster, it’s a different category of investment with different risk characteristics.
The constraint isn’t the technology. It’s organizational readiness. Companies that prepare systematically, establish governance before deployment, invest in change management, and measure outcomes against business metrics will capture the advantages that browser-native AI integration makes available. Those that treat WebMCP as a technical upgrade rather than an organizational transformation will join the 40% of agentic AI projects facing cancellation.
The browser is now an integration layer. How organizations use that layer will determine which side of that statistic they land on.
Kanerika Enabling Intelligent, Scalable AI for Modern Enterprises
Kanerika delivers scalable AI solutions that transform raw business data into meaningful, actionable insights. By leveraging Microsoft technologies such as Power BI, Azure ML, and Microsoft Fabric, we develop dynamic dashboards, predictive models, and automated reporting systems that empower faster, data-driven decision-making across healthcare, finance, retail, and logistics.
Our expertise spans AI strategy, predictive analytics, intelligent automation, marketing workflows, cloud migration, hybrid environments, and strong data governance, with ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 certifications ensuring security and privacy at every step.
Our AI agents—DokGPT, Jennifer, Alan, Susan, Karl, and Mike Jarvis—support document intelligence, risk analysis, customer insights, and voice data processing, seamlessly integrating into existing workflows. Combined with our data engineering and low-code automation capabilities, Kanerika’s modular solutions help businesses modernize systems, reduce manual effort, and scale AI initiatives with confidence.
Transform Your Business with AI-Powered Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
What is WebMCP and how does it differ from traditional API integration approaches?
WebMCP (Web Model Context Protocol) is a W3C standard that enables websites to expose structured tools directly to AI agents through the navigator.modelContext browser API. Unlike traditional approaches that require custom API development for each integration, WebMCP uses browser-native interfaces, eliminating development overhead while maintaining security through existing browser protections.
Which browsers currently support WebMCP implementation?
WebMCP is currently available in Chrome 146 Canary builds with experimental flags enabled. Microsoft co-authored the W3C specification, indicating likely Edge support. The specification is transitioning from community incubation to formal W3C standard status, with broader browser support expected by mid-to-late 2026.
What are the primary security considerations for enterprise WebMCP deployment?
WebMCP operates within browser security frameworks including same-origin policy enforcement, content security policy compliance, and HTTPS-only requirements. Enterprise deployments should implement additional governance controls, including AI agent access policies, activity monitoring systems, and incident response procedures for integration failures.
What industries benefit most from WebMCP implementation?
WebMCP delivers value across industries with web-based business applications, including logistics (35% coordination efficiency improvement), manufacturing (23% production planning reduction), healthcare (31% scheduling efficiency gains), and financial services (43% document processing acceleration). Success depends on systematic implementation rather than industry-specific factors.
How does Kanerika's approach to WebMCP implementation differ from other providers?
Kanerika’s AI-first methodology uses the proven FLIP platform to accelerate WebMCP deployment while ensuring organizational readiness through systematic change management. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner with 10+ years experience and 98% client retention rate, Kanerika delivers co-creation implementations that transfer complete knowledge ownership rather than creating vendor dependencies.