Data lineage is the process of understanding, recording, and visualizing the complete data flow from start to finish. It involves tracking the origin of data, the transformations it undergoes, and the final destination. Moreover, it allows companies to track errors, implement process changes, and confidently perform system migrations. It is crucial in ensuring data accuracy and consistency, helping users validate the data’s source, transformation, and location.

Why is Data Lineage Important?
Data lineage is of utmost importance in the realm of data management. This process provides businesses with a clear and comprehensive view of how data flows across their entire tech stack. Organizations can ensure data accuracy, reliability, and consistency by understanding the complete journey of data from its origin to its final destination.
It plays a crucial role in maintaining data quality and reliability. It allows businesses to proactively identify and resolve issues in the data pipeline, ensuring that the data undergoes the necessary transformations accurately. With data lineage, organizations can have confidence in the integrity of their data and make informed decisions based on accurate information. Moreover, data lineage is essential for data security and compliance.
By tracking the movement and transformations of data, businesses can ensure that sensitive information is handled securely and by privacy regulations. Data lineage provides transparency into how data is accessed, used, and transferred, enabling organizations to comply with regulatory standards.

Data Lineage and Data Classification
They are two interconnected processes that play a crucial role in data management and governance. Let’s explore how these concepts work together to ensure data integrity, security, and compliance.
Data Lineage and Metadata
Data lineage involves tracking the complete life cycle of data, from its origin to its final destination. It provides visibility into how data moves and transforms across systems and processes.
On the other hand, metadata refers to the information about the data, such as its structure, format, and characteristics. Metadata plays a vital role in this by providing additional context and details about the data’s attributes, which helps businesses understand its lineage better. Metadata management tools enable businesses to capture and document metadata, allowing for comprehensive analysis.
Types of Data Lineage
- Forward Lineage: Tracks the path of data from its source to its target, displaying the transformations it undergoes.
- Backward Lineage: Traces the origin of data, providing insights into its creation and initial sources.
- Horizontal Lineage: Maps the data flow within a specific process or system, highlighting interactions and dependencies between different data elements.
- Vertical Lineage: Shows the end-to-end data flow across multiple systems or processes, providing a holistic view of how data moves and transforms across an entire data infrastructure.

Data Classification
Data classification involves categorizing data based on specific attributes, such as sensitivity, access permissions, and compliance requirements. By classifying data, organizations can better manage and protect sensitive information, implement proper access controls, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Data lineage and data classification go hand in hand. The former provides visibility into the movement and transformations of classified data, allowing organizations to track their journey, identify any potential vulnerabilities or risks, and ensure their integrity and confidentiality.
By leveraging lineage and classification together, businesses can establish effective data management strategies, optimize governance practices, and enhance overall quality, security, and compliance.

How to Perform Data Lineage Strategically
Performing data lineage strategically involves using the right tools, implementing effective management practices, and following best practices. By adopting these strategies, businesses can ensure accurate data lineage analysis and optimize their data management processes.
Tools
It is essential to leverage tools to perform data lineage effectively. These tools help automate tracking data flow, transformations, and destinations. They provide visualizations, insights, and analysis of the complete data lineage, making it easier to understand and manage. Read our guide to tools here.
Management
Effective data lineage management involves establishing clear processes, guidelines, and governance structures. Defining roles and responsibilities for data lineage management is essential, ensuring that the right individuals are accountable for maintaining data lineage accuracy and consistency.
Regular audits and reviews of data lineage processes should be conducted to identify and address any issues or gaps. Establishing data lineage documentation standards is also important, ensuring that all relevant information is captured and updated regularly.

Data Lineage Best Practices
Some key best practices include:
- Start with a clear understanding of your data sources, data flows, and transformations
- Define data lineage objectives and requirements based on business needs
- Regularly validate data lineage accuracy and completeness
- Document data lineage processes and workflows
- Implement data lineage governance to ensure data lineage quality and consistency

Data Lineage vs. Data Provenance vs. Data Governance
Data lineage, provenance, and governance are related concepts essential for effective data management. While they share similarities, each approach has a distinct focus and purpose.
Data lineage focuses on tracking the flow and transformations of data to provide clarity and understanding. It encompasses the entire journey of data, from its origin to its destination, and helps organizations visualize how data moves across the tech stack. Data lineage allows businesses to identify potential errors, troubleshoot issues, and ensure accuracy and consistency.
On the other hand, data provenance emphasizes the origin and history of data elements. It provides a detailed record of where the data comes from, who created it, and how it has been modified throughout its lifecycle. Data provenance ensures data integrity and accuracy by verifying the authenticity and reliability of data sources. It is particularly important for industries requiring strict compliance and auditing, such as finance, healthcare, and government.
Data governance encompasses the policies, processes, and controls to manage data quality, privacy, and compliance. It ensures that data is managed according to organizational standards and regulatory requirements. Data governance defines roles and responsibilities, establishes data quality metrics, and enforces data privacy and security measures. It provides a framework for organizations to manage and govern their data assets effectively.
Also Read- AI in Action: 5 Ways Actionable AI is Transforming Businesses
Table: Data Lineage vs. Data Provenance vs. Data Governance
Lineage | Provenance | Governance |
| Tracks the flow and transformations of data | Focuses on the origin and history of data elements | Encompasses policies and processes for managing data quality, privacy, and compliance |
| Ensures data accuracy and consistency | Verifies the authenticity and reliability of data sources | Establishes standards and controls for data management |
| Helps troubleshoot data errors and identify issues | Provides a detailed record of data modifications | Defines roles, responsibilities, and data governance measures |
Data Lineage Benefits
Data lineage offers several benefits to businesses. It enables impact analysis, helping troubleshoot data errors and identify the root cause of issues. Tracing the data flow, you can quickly pinpoint where problems occur in your data pipeline and take necessary corrective actions. This streamlined debugging process reduces downtime and ensures the accuracy and reliability of your data.
It is crucial to build trust and transparency in your data practices. You can validate your data’s source, transformation, and location by providing a clear record of data transformations and movements. This transparency fosters trust among stakeholders and helps maintain data integrity, which is vital for making informed decisions and complying with regulatory requirements.

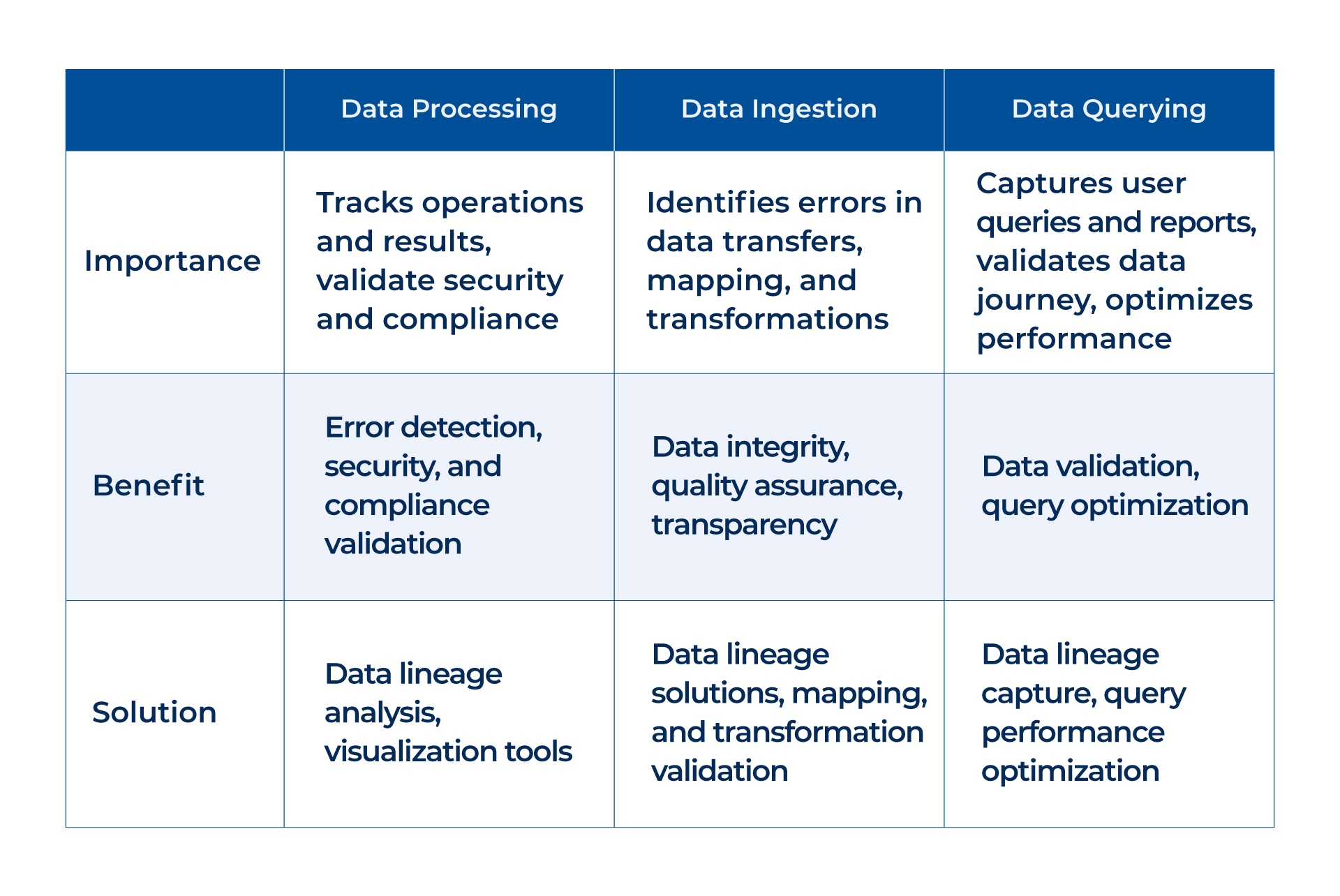
Data Lineage for Data Processing, Ingestion, and Querying
Data lineage is crucial for tracking and analyzing various stages of data processing, ingestion, and querying. With lineage analysis, businesses can gain insights into the movement and transformations of data, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and compliance.
Lineage helps identify errors in data transfers, mapping, and transformations for data ingestion, ensuring the integrity and quality of ingested data. It allows businesses to visualize the entire data journey from source to the destination, providing transparency and validation.
Regarding data processing, lineage tracks specific operations performed on the data and their results. This enables businesses to detect errors, validate security and compliance measures, and troubleshoot data issues efficiently. These solutions provide comprehensive analysis and visualization of data lineage, enabling businesses to optimize their data processing pipelines.
Similarly, lineage captures user queries and reports for data querying, allowing businesses to validate the journey of the data used in the queries. It helps optimize query performance by providing insights into the data sources and transformations. Businesses can ensure data accuracy, enhance decision-making, and improve overall data management processes by leveraging data lineage solutions.
Data Lineage for Data Processing, Ingestion, and Querying
Conclusion
In summary, data lineage is crucial for businesses to understand and track the complete data flow. By visualizing the origin, transformations, and destination of data, companies can ensure data accuracy and compliance and make informed decisions. It works hand in hand with data classification, data provenance, and data governance to provide comprehensive insights into data movements, integrity, and governance practices.

FAQs
What do you mean by data lineage?
Data lineage traces a data element’s journey through your systems. It shows where the data originated, how it was processed, and where it ended up, like a digital breadcrumb trail. This helps you understand data quality, track down errors, and ensure compliance. Essentially, it’s the complete history of your data’s life cycle.
What is an example of a data lineage?
Data lineage traces a data element’s journey. Think of it like a breadcrumb trail showing where your data originated, how it was processed, and where it ended up. This ensures data quality and accountability by highlighting transformations and potential issues along the way. Essentially, it’s a complete audit trail for your data.
What are the two types of data lineage?
Data lineage tracks a dataset’s journey. We broadly categorize it as *technical lineage*, focusing on the technical transformations a dataset undergoes (e.g., ETL steps), and *business lineage*, which traces the dataset’s meaning and purpose within the organization’s context, linking it to business decisions and processes. Understanding both is crucial for data governance and trust.
What is the difference between data lineage and data mapping?
Data lineage tracks a data element’s journey throughout its lifecycle – from origin to its final use. Data mapping, conversely, focuses on the *structure* and *relationships* between datasets, showing how data fields correspond across different systems. Think of lineage as a data element’s biography, and mapping as a comparison of their family trees. Essentially, lineage is about *what happened*, mapping is about *how things relate*.
How to create a data lineage?
Data lineage traces a dataset’s journey from origin to final use. It involves documenting data transformations, sources, and dependencies at each stage. This is crucial for data governance, debugging, and understanding impact from changes. Tools and techniques range from manual documentation to automated lineage tracking software.
What do you mean by data dictionary?
A data dictionary is like a comprehensive instruction manual for your data. It details what each piece of information means, its format (numbers, text, dates), and how it relates to other data. Essentially, it’s a central repository defining all the elements within a database or dataset. This ensures everyone understands and uses the data consistently.
What is the difference between data lineage and data model?
Data lineage tracks a dataset’s journey: where it originated, how it was processed, and where it ended up. A data model, conversely, describes the structure and organization of data *within* a specific dataset—think of it as a blueprint. Essentially, lineage is about the data’s *history*, while the model is about its *current form*. They’re complementary; a good data model relies on understanding its lineage.
What is data lineage in EDC?
In Informatica EDC (Enterprise Data Catalog), data lineage traces a data asset’s journey. It shows you where the data originated, how it was transformed, and where it ultimately ends up. Think of it as a detailed family tree for your data, crucial for understanding data quality, impact analysis, and compliance. This helps you manage and govern your data effectively.
What is the meaning of data lineage?
Data lineage is like a roadmap for your data. It shows you exactly where the data came from, all the changes it went through, and where it ended up. This helps you understand its history, check its quality, and trust the information you’re using.
Who needs data lineage?
Anyone who relies on data to make decisions, understand its origins, or ensure its quality benefits from data lineage. This includes business leaders, data analysts, and IT teams needing to trust their information. It’s also vital for meeting compliance and regulatory demands.
What are the 5 stages of data lifecycle?
The 5 stages of the data lifecycle are: 1. Creation & Storage: Gathering new data and keeping it securely. 2. Processing & Analysis: Organizing and making sense of the information. 3. Usage & Sharing: Applying the data for decisions or allowing others to access it. 4. Archiving & Deletion: Safely keeping data for future use or securely removing it when no longer needed.
What are the 4 pillars of data governance?
The 4 pillars of data governance are: People: Defining who is responsible for data and what their roles are. Processes: Establishing clear procedures for managing data from start to finish. Technology: Implementing tools to help manage, secure, and access data effectively. Policies & Standards: Setting the rules for how data should be used, protected, and stored.
What are the benefits of data lineage?
Data lineage shows you exactly where your data comes from and how it has changed. This builds trust in your information, making it easier to meet compliance rules and audit requirements. It also helps you quickly pinpoint problems and understand the impact of any data changes.
What are the 7 steps of data analysis?
The 7 steps of data analysis typically involve defining your question, collecting relevant data, and cleaning it for accuracy. Next, you analyze the data to find patterns, interpret the results to understand their meaning, and visualize your findings clearly. Finally, you communicate these insights and recommendations.
What is the future of data lineage?
The future of data lineage is highly automated, using AI to track data flow and changes in real-time. This will make it much easier to understand data origins, quality, and impact. It will be crucial for building trust, improving decision-making, and ensuring compliance across all data uses.
What are the three types of data in GIS?
GIS primarily uses three types of data: 1. Vector data: Represents distinct features as points (like trees), lines (like roads), or polygons (like lakes). 2. Raster data: Uses a grid of cells for continuous data, such as satellite images, aerial photos, or elevation maps. 3. Attribute data: This is the descriptive information (text or numbers) linked to your vector or raster features, like a road’s name or a tree’s species.
How to define data lineage?
Data lineage is like a roadmap for your data. It shows you where data comes from, how it’s changed or processed along the way, and where it’s used now. This helps you understand its history, track its movement, and ensure its reliability.