In recent years, the finance sector has witnessed a dramatic shift towards automation, with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leading the charge. According to a Gartner report, finance departments can save up to 25,000 hours of avoidable rework caused by human errors by deploying RPA, potentially saving $878,000 for an average-sized finance department.
The impact of RPA in finance is not just theoretical. A Deloitte Global RPA Survey revealed that 78% of those who have implemented RPA expect to significantly increase investment in RPA over the next three years. Furthermore, 61% of organizations that have implemented RPA reported exceeding their cost reduction expectations.
From automating routine transactions to streamlining complex financial processes, RPA is transforming the financial landscape, unlocking hidden profits that were once trapped in inefficient workflows. But how exactly does RPA in finance work, and more importantly, how can it maximize your business’s ROI? Let’s find out.
Implement RPA to Propel Your Business Forward!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert RPA implementation Services
What Are the Advantages of Integrating RPA in Financial Operations?
As financial operations become increasingly complex and the volume of data continues to grow, automation is no longer optional. It’s a fundamental requirement for finance departments to remain efficient, accurate, and competitive in the modern business landscape. RPA represents the cutting edge of this automation trend, offering unprecedented opportunities for financial operations to transform from cost centers into strategic drivers of business value.
This transformative technology goes beyond simple cost-cutting. It’s about unleashing the full potential of your finance team, eliminating errors, enhancing compliance, and uncovering insights that drive strategic decision-making. From accounts payable to financial close processes, RPA is revolutionizing how financial operations are conducted.
Whether you’re a CFO looking to optimize your department’s performance, a finance professional aiming to stay ahead of the curve, or a business owner seeking to boost profitability, RPA can offer unprecedented financial gains. Some keys ways in which Implementing RPA in finance can elevate your business:
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
- Automation eliminates time-consuming manual tasks
- Enables finance teams to process higher volumes of transactions
- Allows for 24/7 operation without human intervention
2. Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
- Minimizes human errors in data entry and calculations
- Ensures consistency in financial processes
- Reduces the risk of financial misstatements
3. Improved Compliance and Risk Management
- Automates regulatory reporting processes
- Provides audit trails for all transactions
- Helps in detecting and preventing fraud
4. Cost Reduction
- Lowers operational costs by reducing manual labor
- Minimizes overtime and temporary staffing needs
- Reduces costs associated with errors and rework
5. Faster Financial Close and Reporting
- Accelerates month-end, quarter-end, and year-end closing processes
- Enables real-time financial reporting
- Provides quicker insights for decision-making
6. Enhanced Data Analysis and Insights
- Frees up time for financial analysts to focus on strategic tasks
- Enables more comprehensive and frequent data analysis
- Facilitates predictive analytics and forecasting
7. Improved Customer and Vendor Relations
- Speeds up processes like invoice processing and payments
- Enhances accuracy in customer billing and statements
- Provides faster response times to inquiries
8. Scalability and Adaptability
- Allows finance departments to handle growth without proportional increases in headcount
- Easily adapts to changes in regulations or business processes
- Enables quick implementation of new financial strategies
9. Competitive Advantage
- Allows organizations to operate more efficiently than competitors
- Enables faster response to market changes
- Frees up resources for innovation and strategic initiatives
RPA Tools: What to Look for and How to Choose the Best One
Discover key features to consider when selecting the right RPA tool for your business.
Top 8 Use Cases of RPA in Finance
1. Accounts Payable and Receivable
Invoice Processing: RPA can automate the entire invoice processing cycle, from receipt to payment. Bots can extract data from invoices in various formats (PDF, email, scanned images), validate information against purchase orders and receipts, route for approvals, and initiate payments. Modern Ramp corporate credit cards further enhance this automation by providing real-time transaction data and automatic expense categorization, reducing manual data entry and improving AP efficiency.
For example, an RPA bot could process thousands of supplier invoices overnight, flagging discrepancies and preparing a summary report for the AP team to review in the morning.
Payment Reconciliation: RPA can automatically match payments received against outstanding invoices, updating accounts receivable records in real-time. Bots can handle complex matching scenarios, flag discrepancies, and generate exception reports for human review.
For instance, a bot could reconcile daily bank statements with the company’s AR system, automatically applying payments to the correct customer accounts and highlighting any unmatched transactions.
2. Financial Close and Reporting
Data Gathering and Consolidation: RPA can streamline the financial close process by automatically collecting data from various sources (ERP systems, subsidiary ledgers, bank statements) and consolidating it into a standardized format. This reduces manual effort and minimizes errors.
For example, a bot could gather month-end data from multiple regional offices, convert currencies, and compile it into a single report for the corporate finance team.
Report Generation: Once data is consolidated, RPA can automate the creation of financial reports, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. Bots can apply pre-defined templates, perform calculations, and generate reports in various formats (Excel, PDF, PowerPoint).
An RPA solution could, for instance, automatically generate a complete set of monthly financial reports, including variance analysis and key performance indicators, ready for management review.
Read More – 10 Ways AI and RPA Are Shaping The Future of Automation
3. Compliance and Risk Management
KYC (Know Your Customer) Processes: RPA can automate many aspects of KYC processes, including data collection, verification, and ongoing monitoring. Bots can gather information from multiple sources, cross-reference data, flag discrepancies, and update customer profiles.
For example, a bot could continuously monitor customer transactions, automatically triggering enhanced due diligence processes when certain risk thresholds are exceeded.
Regulatory Reporting: RPA can streamline the preparation and submission of regulatory reports by automatically collecting required data, performing necessary calculations, and populating reporting templates. This ensures accuracy and timeliness in compliance.
A bot could, for instance, automate the preparation of daily liquidity reports for a bank, ensuring all required data is collected, calculated, and submitted to regulators within the mandated timeframe.
4. Audit and Fraud Detection
Continuous Auditing: RPA enables continuous monitoring of financial transactions and controls. Bots can perform regular checks on various processes, flagging exceptions and unusual patterns for human review.
For example, an RPA solution could continuously monitor journal entries, automatically identifying and flagging any entries that violate predefined rules or thresholds.
Anomaly Detection: RPA, often combined with machine learning, can analyze large volumes of financial data to identify potential fraudulent activities or errors. Bots can apply complex algorithms to detect unusual patterns or transactions that deviate from the norm.
For instance, a bot could analyze employee expense reports, flagging any unusual spending patterns or policy violations for further investigation.
Read More – RPA Risks For Enterprises And How to Mitigate Them
5. Tax Preparation and Filing
RPA can significantly streamline tax preparation processes by automatically gathering relevant financial data, applying tax rules, performing calculations, and populating tax forms. Bots can handle complex tax scenarios across multiple jurisdictions, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
For example, an RPA solution could automate the preparation of sales tax returns across multiple states, calculating tax due, preparing returns, and even submitting them electronically to tax authorities.
6. Expense Management
RPA can automate various aspects of expense management, from receipt processing to reimbursement. Bots can extract data from receipts (using OCR technology), match expenses to corporate policies, route for approvals, and initiate reimbursements.
An RPA system could, for instance, process employee expense reports, automatically categorizing expenses, flagging policy violations, and preparing a summary for manager approval.
Read More – RPA Use Cases That Will Transform Your Supply Chain Management
7. Bank Reconciliation
RPA can automate the tedious process of bank reconciliation by matching transactions in the company’s financial records with those in bank statements. Bots can handle high volumes of transactions, identify discrepancies, and prepare exception reports for human review.
For example, a bot could perform daily bank reconciliations, automatically matching cleared checks and deposits, and flagging any unreconciled items for the treasury team to investigate.
8. Financial Planning and Analysis
RPA can enhance FP&A processes by automating data collection, performing complex calculations, and generating forecasts and budgets. Bots can update financial models with the latest data, run scenario analyses, and prepare variance reports.
For instance, an RPA solution could automatically update rolling forecasts each week, incorporating the latest sales data, expense information, and market trends, providing finance teams with up-to-date projections for decision-making.
Success Stories: Kanerika’s RPA Expertise
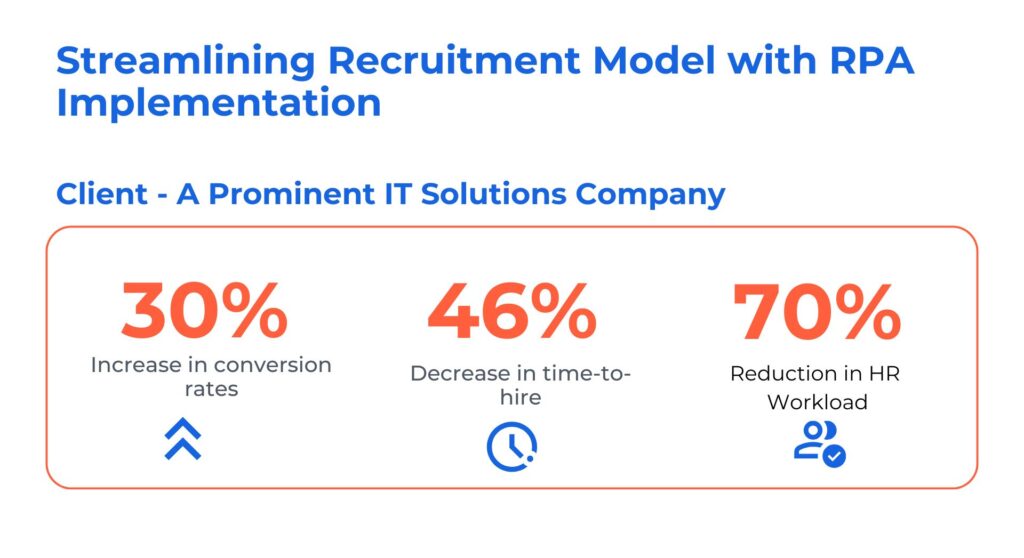
Case Study 1. Transforming Recruitment with Process Automation by RPA in HR
The client is a distinguished service provider renowned for their unwavering commitment to timely delivery. They faced HR challenges due to the manual hiring process which had become burdensome, causing delays and inefficiencies and placing an excessive workload on the HR team.
Kanerika addressed these challenges by providing the following solutions:
- Implemented end-to-end process automation using UiPath, streamlining candidate screening and enhancing efficiency
- Deployed HR Bot to receive, filter, and consolidate resumes from various portals, improving candidate management
- Ensured accurate candidate evaluation, correct routing, and efficient candidate handling, enhancing the quality of hires with RPA services
Case Study 2: Revolutionizing Fraud Detection in Insurance with AI/ML-Powered RPA
A leading insurance provider, specializing in healthcare, travel, and accident coverage wanted to automate their insurance claim process solution with AI/ML to spot unusual patterns that are unnoticeable by humans. The overall goal was to use deep anomaly detection to anticipate fraud detection in insurance claims quickly, reduce the loss ratios, and fasten the claim processing.
Kanerika tackled these challenges by:
- Implementing AI RPA for fraud detection in the insurance claim process, reducing fraud-related financial losses.
- Leveraging predictive analytics, AI, NLP, and image recognition to monitor customer behavior, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Delivering AI/ML-driven RPA solutions for fraud assessment and operational excellence, resulting in cost savings.

What Are the Best Practices for Implementing RPA in Finance?
1. Start with a Pilot Project
Begin your RPA journey with a small-scale pilot project. Choose a process that’s repetitive, rule-based, and has a clear ROI potential. This allows you to demonstrate the value of RPA while minimizing risks. A successful pilot builds confidence, generates buy-in from stakeholders, and provides valuable lessons for larger-scale implementation. For example, you might start by automating a simple reconciliation process or basic data entry task.
2. Involve Stakeholders from IT and Finance
RPA implementation requires collaboration between finance and IT departments. Finance teams understand the processes and business requirements, while IT ensures technical feasibility, security, and integration with existing systems. Regular meetings and clear communication channels between these departments are crucial. This collaboration helps in selecting the right processes for automation, addressing technical challenges, and ensuring smooth implementation.
3. Focus on Process Standardization
Before implementing RPA, standardize your financial processes. Inconsistent or poorly defined processes are difficult to automate effectively. Document each step of the process, identify variations, and create a standardized workflow. This might involve creating detailed process maps, establishing clear business rules, and eliminating unnecessary steps. Standardization not only facilitates RPA implementation but also improves overall efficiency.
Read More – Navigating The Future Of Healthcare With RPA Consulting
4. Invest in Training and Change Management
RPA implementation often requires significant changes in how finance teams work. Invest in comprehensive training programs to help staff understand RPA technology, its benefits, and how to work alongside bots. Address concerns about job security and emphasize how RPA can enhance their roles. Develop a change management strategy to guide the transition, including regular communication, feedback mechanisms, and support systems for employees adapting to new ways of working.
5. Establish Governance and Control Mechanisms
Implement robust data governance structures to oversee RPA implementation and operation. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, establishing approval processes for new automations, and setting up monitoring and auditing procedures. Create clear policies for bot access, data handling, and error resolution. Regular audits ensure that RPA operations comply with internal controls and regulatory requirements. This governance framework helps maintain control, manage risks, and ensure the long-term success of your RPA initiative.
6. Continuously Monitor and Optimize RPA Performance
RPA implementation is not a one-time event but an ongoing process of refinement and optimization. Regularly monitor bot performance, tracking metrics like processing time, error rates, and cost savings. Gather feedback from users and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. Stay updated on new RPA technologies and best practices. Continuously look for opportunities to expand automation to new processes or enhance existing ones. This ongoing optimization ensures that your RPA implementation continues to deliver value and stays aligned with evolving business needs.
RPA for Data Migration: Best Practices and Considerations
Explore best practices and key considerations for leveraging RPA in data migration to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and smooth transitions.
Real-life Examples: Companies That Have Successfully Implemented RPA in Finance
1. Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola implemented RPA to automate their order-to-cash process. They deployed bots to handle tasks such as order processing, invoicing, and payment reconciliation. This implementation resulted in a 60% reduction in order processing time and improved accuracy in financial reporting. The company also achieved significant cost savings by reducing manual labor in their finance department.
2. Deutsche Bank
Deutsche Bank utilized RPA to automate various processes in their finance and risk departments. One significant application was in regulatory reporting. The bank implemented bots to gather data from multiple systems, perform calculations, and generate reports for regulatory compliance. This automation reduced the reporting time from several days to just a few hours, improved accuracy, and allowed staff to focus on more value-added tasks.
3. Walmart
Walmart implemented RPA in their finance department to automate invoice processing and reconciliation. The retail giant deployed bots to extract data from invoices, match them with purchase orders and receipts, and process payments. This implementation resulted in a 50% reduction in invoice processing time and significantly improved accuracy. Walmart also reported substantial cost savings and improved vendor relationships due to faster payment processing.
4. Siemens
Siemens implemented RPA across various finance functions, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, and financial reporting. One notable use case was in their order management process. Bots were deployed to validate and process customer orders, update inventory systems, and generate invoices. This automation resulted in a 65% reduction in processing time and a significant decrease in errors. Siemens also reported improved cash flow due to faster order processing and invoicing.
5. American Express Global Business Travel
American Express Global Business Travel implemented RPA to automate their travel expense management process. They deployed bots to extract data from receipts, validate expenses against company policies, and process reimbursements. This implementation resulted in a 75% reduction in processing time for expense reports and improved accuracy in expense tracking. The company also reported increased employee satisfaction due to faster reimbursements.
RPA in Manufacturing: Enhancing Quality Control and Compliance
Explore how RPA transforms quality control and compliance in manufacturing.
Measuring ROI and Success of RPA in Finance
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for RPA
When measuring the success of RPA implementation in finance, it’s crucial to track specific KPIs:
1. Processing Time: Measure the reduction in time taken to complete tasks. Example: Time to process an invoice reduced from 15 minutes to 2 minutes.
2. Error Rates: Track the decrease in errors in financial processes. Example: Reduction in data entry errors from 5% to 0.1%.
3. Volume Handling: Monitor the increase in transaction volume processed. Example: Number of daily reconciliations increased from 1,000 to 5,000.
4. Compliance Adherence: Measure improvements in regulatory compliance. Example: Reduction in compliance-related incidents by 95%.
5. Employee Productivity: Track the increase in value-added tasks performed by staff. Example: 30% increase in time spent on analysis and strategic planning.
Calculating Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains
1. Labor Cost Savings
Calculate the reduction in labor hours for automated tasks
Multiply by the average hourly rate of employees Example: 1,000 hours saved per month * $50/hour = $50,000 monthly savings
2. Error Reduction Savings
Estimate the cost of errors (rework, penalties, etc.) before RPA
Calculate the reduction in these costs post-implementation Example: Reduction in error-related costs from $100,000 to $5,000 per year
3. Capacity Increase
Measure the increase in processing capacity without additional hiring
Calculate the cost avoidance of not hiring additional staff Example: Ability to handle 50% more transactions without new hires, saving $200,000 in annual salaries
4. Speed to Market
Assess the financial impact of faster processing times
This could include earlier revenue recognition or improved cash flow Example: 5-day reduction in month-end close, allowing earlier strategic decisions
Workflow Automation: The Ultimate Guide to Boosting Productivity
Master workflow automation with this ultimate guide to enhancing productivity, streamlining processes, and achieving operational efficiency.
Qualitative Benefits Assessment
1. Customer Satisfaction
Track improvements in customer-facing financial processes
Monitor customer feedback and satisfaction scores Example: 40% reduction in customer queries related to invoicing or payments
2. Data Quality and Integrity
Assess improvements in data accuracy and consistency
Monitor the reduction in data-related issues or disputes Example: 90% reduction in data reconciliation efforts across systems
3. Risk Mitigation
Evaluate the reduction in financial risks due to improved accuracy and compliance
Assess the impact on audit processes and outcomes Example: 50% reduction in audit preparation time and improved audit results
4. Strategic Focus
Measure the increase in time spent on strategic financial activities
Assess the quality of financial insights and decision-making Example: Finance team now spends 40% more time on predictive analysis and strategic planning.
RPA Security Best Practices: Enhancing Bot Defense Mechanism
Explore how to safeguard your automation with robust RPA security measures.
Make Your Finance Processes Future-Ready with Kanerika’s Expert RPA Implementation
Kanerika offers unparalleled expertise in Robotic Process Automation (RPA) implementation for finance operations. With a track record of success across diverse industries, we helped numerous businesses transform their financial processes. From manufacturing giants streamlining their accounts payable to healthcare providers optimizing revenue cycle management, our tailored RPA solutions have consistently delivered remarkable results.
At Kanerika, we understand that every business is unique. Our team of seasoned RPA experts works closely with you to identify your specific pain points and opportunities for automation. We don’t just implement technology; we craft bespoke solutions that align perfectly with your business objectives and existing systems.
Our clients have reported significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and cost savings. Many have seen a significant decrease in processing times, error rates reduced to near zero, and staff freed to focus on strategic initiatives.
By choosing Kanerika, you’re not just implementing RPA – you’re gaining a competitive edge. Our solutions empower your finance team to work smarter, faster, and more strategically, positioning your business for sustained growth and success in an increasingly digital world.
Let us be your partner in revolutionizing your finance processes. Together, we’ll unlock the full potential of your financial operations and set new industry standards.
Maximize Resources and Achieve Operational Excellence Through RPA!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert RPA implementation Services
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RPA in financial analysis?
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, in financial analysis automates repetitive, rule-based tasks. Think data entry, report generation, or reconciliation – freeing up analysts for higher-level, strategic work. It improves accuracy and efficiency, leading to faster insights and better decision-making. Ultimately, RPA enhances the productivity and analytical capabilities of financial teams.
What is RPA in accounts payable?
In accounts payable, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is like having a tireless digital clerk. It automates repetitive tasks like invoice processing, data entry, and payment approvals. This frees up human AP staff to focus on more complex, strategic work, like vendor relationship management and fraud detection. Essentially, RPA streamlines the entire AP process, increasing efficiency and accuracy.
What does RPA stand for?
RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation. It’s essentially software robots that automate repetitive, rule-based tasks typically done by humans on computers. Think of it as digitally automating office work, freeing up human employees for more strategic activities. This boosts efficiency and accuracy.
What is the use of RPA in finance?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in finance streamlines repetitive tasks, freeing up human employees for more strategic work. It significantly reduces errors inherent in manual processes like data entry and reconciliation, improving accuracy and speed. This translates to cost savings and improved compliance by automating tasks across areas like accounting, reconciliation, and fraud detection. Ultimately, RPA boosts efficiency and allows financial institutions to focus on growth initiatives.
What are KPIs for RPA?
KPIs for Robotic Process Automation (RPA) track its success. Key metrics include efficiency gains (like processing time reduction), cost savings (from reduced labor), error rates (showing improved accuracy), and deployment speed (measuring implementation effectiveness). Ultimately, these KPIs demonstrate RPA’s return on investment and overall business impact.
What is RPA in AML?
In Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is like having a tireless, accurate digital employee. It automates repetitive, rule-based tasks like transaction monitoring and suspicious activity reporting, freeing up human analysts for more complex investigations. This significantly boosts efficiency and reduces the risk of human error in AML compliance. Essentially, RPA streamlines the often tedious AML workload.
What is RPA in loan?
RPA in loan processing automates repetitive, rule-based tasks. Think data entry, document verification, or application routing – all done by software “robots” instead of humans. This speeds up loan applications, reduces errors, and frees human employees for more complex work, ultimately improving efficiency and customer experience. It’s like having a tireless, accurate clerk working 24/7.
What is RPA strategy?
An RPA strategy isn’t just about deploying robots; it’s a roadmap for *transforming* your business using automation. It defines which processes to automate first, prioritizing those with the biggest impact and easiest implementation. This involves careful consideration of technology, people, and overall business goals to ensure successful, scalable automation. Ultimately, it’s about maximizing ROI and achieving sustainable operational efficiency.
What is RPA in cost accounting?
In cost accounting, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based tasks. Think data entry, report generation, or invoice processing – freeing up human accountants for more complex analysis. This boosts efficiency and accuracy, ultimately lowering operational costs and improving the timeliness of financial insights. Essentially, RPA acts as a tireless, precise assistant handling mundane aspects of cost accounting.
Who is the leader in RPA?
There isn’t one single “leader” in Robotic Process Automation (RPA). The market is diverse, with UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism often cited as top players. Leadership depends on specific needs; some excel in ease of use, others in scalability or AI integration. Ultimately, the “best” RPA provider is the one best suited to your particular business requirements.
What is RPA in Analytics?
RPA in analytics automates repetitive, rule-based tasks within analytical processes. Think of it as a digital worker handling data cleaning, report generation, or even basic data analysis freeing up human analysts for more strategic work. It’s not about replacing analysts, but augmenting their capabilities by handling the tedious stuff. This boosts efficiency and allows for faster insights.
What is automation in finance function?
Finance automation streamlines traditionally manual processes. Think robotic processing of invoices, automated reconciliation, and AI-driven fraud detection. This boosts efficiency, reduces human error, and frees up financial staff for higher-value tasks like strategic analysis. Ultimately, it means faster, more accurate financial operations.
How is RPA used in banking?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in banking streamlines repetitive tasks, like processing transactions and verifying identities, freeing up human employees for more complex work. It improves accuracy and speed significantly, reducing errors and processing times for things like loan applications or account updates. Essentially, RPA acts as a tireless, accurate digital worker handling the mundane so humans can focus on customer service and strategic initiatives. This leads to cost savings and enhanced customer experience.











