You’ve successfully implemented RPA, unlocking unprecedented efficiency and productivity gains for your organization. You have seen the transformative power of automation—efficiency is up, costs are down, and productivity is soaring. The initial euphoria of watching bots streamline complex processes is undeniable, yet there’s a critical component that may have slipped through the cracks: security. The rapid deployment and operational benefits of RPA sometimes overshadow the equally vital need to implement RPA security best practices. Neglecting the security, RPA risks and the data they manage is a risk no organization can afford to take.
So, how do you enhance your bots’ defense mechanisms and ensure that your automation journey is successful and secure? Let’s dive in.
Understanding RPA Security
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances business efficiency by automating routine tasks. However, it introduces specific security considerations that you need to address.
Threat Landscape
RPA operates in a dynamic environment where threat actors constantly evolve their methodologies. Your RPA system could face challenges such as:
- Unauthorized access to RPA tools and scripts
- Data exfiltration through RPA processes
- Manipulation of automated workflows
Being aware of these potential threats is the first step toward safeguarding your RPA infrastructure.
RPA vs. Traditional Security
RPA security best practices differ from traditional IT security in several ways:
- Scope of Access: RPA bots often have elevated privileges compared to average users
- Speed of Operations: Bots work faster, making it harder to monitor their actions manually
- Automation Complexity: RPA scripts can be complex, making the detection of malicious changes challenging
Understanding these differences helps you tailor your security measures for RPA systems
Core Components
To secure your RPA deployment, consider the following key components:
- User Access Control: Implement role-based access to restrict bot and user capabilities
- Audit Trails: Maintain comprehensive logs to track all RPA activities
- Network Security: Use encryption and secure channels for bot communication
- Data Protection: Ensure sensitive data handled by bots is encrypted and stored securely
Establishing a Governance Framework
When implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA), establishing a strong governance framework is crucial to ensure security and compliance. This includes developing clear policies, controlling access based on roles, and implementing thorough compliance and auditing procedures.
Security Policy Development
- Define Clear Security Policies: You need to create comprehensive security policies that dictate the governance of your RPA initiative. This should include data protection guidelines, incident response plans, and rules for bot development and deployment.

Role-Based Access Control
Ensure that access to RPA systems is governed by a role-based access control (RBAC) model. This model assigns permissions to roles rather than individuals, reducing complexity and enhancing security.
Steps for RBAC implementation:
- Identify different roles within your RPA operations
- Assign the least privilege necessary for each role
- Regularly review and update access rights
Compliance and Auditing Procedures
- Establish Compliance Measures: You must align your RPA process with relevant industry regulations and standards. Develop and maintain an up-to-date auditing trail for compliance purposes.
- Compliance Checklist:
- Regulatory Alignment: Ensure your RPA bots comply with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, etc
- Documentation: Keep thorough records of bot operations and changes
- Compliance Checklist:
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to verify adherence to security policies and regulatory compliance, promptly addressing any deviations or weaknesses discovered.
- Audit Frequency: At minimum, perform audits annually or after significant changes to the RPA system
Secure Deployment Practices
In ensuring the security of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) deployments, prioritize configurations, manage credentials effectively, and routinely scan for vulnerabilities.
Secure Configuration
You must establish a robust configuration policy to minimize the attack surface. Ensure that all RPA tools and associated components are deployed in a secure manner by following these guidelines:
- Least Privilege: Apply the principle of least privilege to all RPA processes. Each bot should have only the permissions necessary to perform its tasks
- Network Segmentation: Use network segmentation to isolate RPA tasks from critical network segments. This limits potential damage in case of a security breach
Credential Management
Credential management is critical for safeguarding the automation environment. Adhere to these practices:
- Centralized Credential Store: Utilize a secure, centralized credential store like CyberArk or HashiCorp Vault to manage bot credentials
- Rotation and Complexity: Regularly rotate credentials and enforce complexity requirements to prevent unauthorized access
Code Review and Vulnerability Scanning
Maintaining RPA security best practice in your automation codes is essential to avoid exploitable flaws.
- Regular Code Reviews: Conduct regular code reviews to identify and rectify insecure coding practices before deployment
- Automated Scanning Tools: Integrate automated vulnerability scanning tools in your CI/CD pipeline to detect security issues early. Tools such as Veracode or Fortify can be instrumental in your security toolkit
Operational Security
Ensuring robust operational security in your RPA environment involves continuous monitoring, a solid response plan for incidents, and diligent patch management.
Monitoring and Reporting
- Continuous Monitoring: You should implement continuous monitoring of RPA activities. This includes tracking user activities, login attempts, and changes to workflows or scripts
- Reporting Systems: Establish reporting mechanisms to alert you to suspicious activities. Automate audit trail generation and review for any anomalies
Incident Response Planning
- Incident Response Team: Create a dedicated incident response team with clear roles and responsibilities
- Response Procedures: Develop and document incident response procedures to swiftly manage potential security events. This should include steps for containment, eradication, and recovery
| Incident Response Planning Overview | ||||
| Phase | Responsibilities | Actions | Communication | Tools/Resources |
| Preparation | IT Security Team | Develop and update incident response plan; Conduct training and simulations | Establish communication protocols; Create contact lists for key personnel | Incident response plan; Training materials |
| Identification | Security Analysts | Detect and determine the scope of the incident; Prioritize the incident based on impact | Notify incident response team and management | SIEM tools; Intrusion detection systems |
| Containment | Incident Response Team | Isolate affected systems to prevent spread; Implement temporary fixes | Update stakeholders on containment efforts | Forensic tools; Network segmentation tools |
| Eradication | IT and Security Teams | Remove malware or threats; Secure vulnerabilities that were exploited | Communicate eradication measures and status | Anti-malware tools; Patch management systems |
| Recovery | IT Department | Restore systems and data from backups; Monitor for anomalies | Inform stakeholders of recovery status and any impacts | Backup and recovery solutions; Monitoring tools |
| Lessons Learned | Entire Incident Response Team | Review and analyze the incident response; Update policies and procedures based on findings | Share lessons learned with the organization | Incident review reports; Updated incident response plan |
Patch Management
- Routine Updates: Regularly apply software updates and patches to your RPA system. Schedule these to minimize disruption to operations
- Patch Testing: Before deploying, test patches in a non-production environment to ensure they don’t interfere with existing processes or introduce new vulnerabilities
Securing RPA Tools and Platforms
When implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA), securing your tools and platforms is essential to protect sensitive data and maintain business continuity.
Choosing Secure RPA Software
Selecting an RPA solution: Ensure the software you choose has a strong security framework. Key elements to look for include role-based access control (RBAC), data encryption both at rest and in transit, and audit logs. These features help safeguard your automated processes against unauthorized access and potential breaches.
- Role-Based Access Control: Limits system access to users based on their role within the organization
- Data Encryption: Look for AES 256-bit encryption as a standard
- Audit Logs: Essential for tracking user activities and identifying potential security incidents
Vendor Risk Management
Evaluating RPA vendors: Your RPA tool’s security is as strong as the vendor’s commitment to security. Perform due diligence with each vendor to assess their security policies and incident response capabilities.
- Security Policies Evaluation: Review the vendor’s policies for consistency with industry standards
- Incident Response: Ensure they have a robust incident response plan to address potential vulnerabilities quickly
Update and Maintenance Schedules
Keeping software up to date: Regularly scheduled updates and maintenance are crucial for addressing security vulnerabilities. You should adhere to a strict schedule of updates provided by the RPA vendor to mitigate risks.
- Scheduled Updates: Implement a consistent schedule for updates as recommended by the vendor
- Security Patches: Apply security patches immediately to close any exposed vulnerabilities
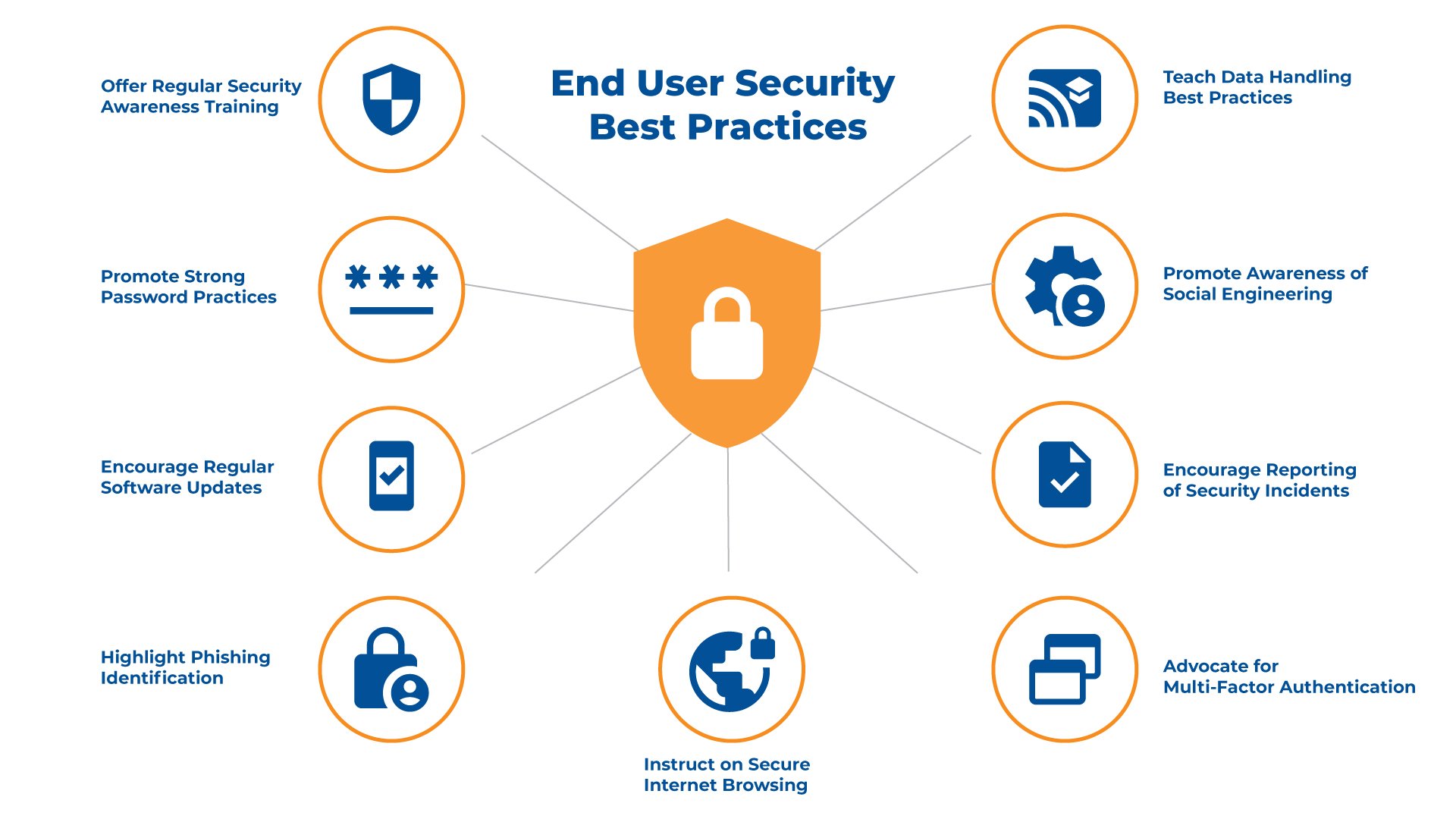
End-User Security Training
Training end-users in security measures is critical to a robust RPA framework. Your vigilance and understanding of potential threats are the first defense against security breaches.
Awareness Programs
You should participate in regular awareness programs that inform you of the latest cybersecurity threats and the role of RPA in your organization.
Key Components:
- Frequency: Engage in training sessions at least quarterly
- Content: The programs should cover the evolving nature of cyber threats and how they can affect RPA systems
RPA Security Best Practices
Adopting and adhering to security best practices is fundamental to protecting RPA systems from unauthorized access.
Essential Practices:
- Password Management: Use complex passwords and update them regularly
- Principle of Least Privilege: Access rights should be limited to only what is necessary for your role
Phishing and Social Engineering Defense
Phishing and social engineering attacks specifically target you to gain access to sensitive information. It’s crucial to recognize and respond appropriately to these threats.
Defensive Strategies:
- Recognition Training: Learn to identify suspicious emails or messages
- Verification Protocols: Always verify requests for sensitive information, especially if unusual or unexpected
Connect with Us to Get Started on Your RPA Journey
At Kanerika, our commitment to delivering top-notch RPA secure services for our clients remains steadfast. We believe RPA is a crucial foundation for transforming businesses by streamlining operations, enabling scalability, and reducing costs.
Why Choose Kanerika for RPA Implementation?
- Experience: Chosen by CIO Insider magazine as one of the Top 10 Most Recommended RPA Start-Ups in 2022, demonstrating a proven track record in helping businesses achieve their RPA goals
- Expertise: Certified partners with leading RPA vendors like Automation Anywhere, UiPath, and Blue Prism, ensuring expertise in implementing RPA solutions across platforms
- Scalability: Offers scalable RPA solutions that allow easy addition or removal of bots to meet changing business needs, providing cost-effectiveness for any business size
- Security: Delivers secure RPA solutions with robust measures like encryption, access control, and auditing to safeguard data
- Support: Provides ongoing support for RPA solutions, ensuring assistance is always available when needed
Onboard a seamless automation journey. Book a consultation with us today!















