Businesses have more data than ever, but the real challenge is turning it into decisions that matter. That’s where machine learning comes in. It’s no longer just a buzzword—nearly half of companies worldwide are already using it, and around 80% say it’s directly helping them grow revenue. In fact, some platforms report that every dollar invested in machine learning and advanced analytics can return nearly seven dollars in value.
The reason is simple: machine learning goes beyond describing the past. It predicts demand shifts, flags potential fraud before it occurs, personalizes customer interactions, and identifies operational efficiencies. For leaders trying to compete in fast-moving markets, this is no longer a nice-to-have tool. It’s becoming one of the main drivers of smarter, faster, and more reliable business decisions.
Drive Business Excellence with Machine Learning in Business Analytics.
Partner with Kanerika for smarter strategies and results.
What Is Machine Learning in Business Analytics?
Machine learning (ML) is transforming the way organizations make decisions, optimize operations, and engage with customers. At its core, machine learning enables systems to learn from data without explicit programming, improving accuracy and adaptability over time.
Traditional business analytics relied heavily on historical reports and static models built on predefined rules. For example, a company might set simple conditions, such as “if sales drop below X, cut marketing spend.” While this works for straightforward cases, it doesn’t scale well in today’s complex business environments where variables constantly change.
Machine learning addresses this limitation. It can process massive amounts of structured and unstructured data—such as customer transactions, website clicks, social media interactions, and IoT sensor feeds—and detect patterns invisible to humans. Unlike fixed models, ML algorithms continuously update and refine themselves as new data arrives, making insights more accurate and forward-looking.
For businesses, this means the ability to:
- Predict future outcomes such as demand spikes, fraud attempts, or customer churn.
- Adapt quickly to changes in customer preferences, competitor moves, or supply chain disruptions.
- Automate decision-making in areas like pricing, credit scoring, and inventory planning.
In short, ML moves analytics from being a rearview mirror tool (looking only at past performance) to a real-time GPS and compass that helps navigate the future.
Core Techniques of Machine Learning
Machine learning is not a single technique—it encompasses a range of approaches, each designed for specific types of problems. In business analytics, four main categories are most widely used:
1. Supervised Learning
- Works with labeled data, where inputs and outputs are known.
- The algorithm learns to map input variables (e.g., income, spending behavior) to an outcome (e.g., default or repay loan).
Examples:
- Credit scoring in banking.
- Email spam detection.
2. Unsupervised Learning
- Works with unlabeled data to find hidden structures or groupings.
- Often used for segmentation, clustering, or pattern recognition.
Examples:
- Grouping customers based on shopping behavior.
- Identifying unusual patterns in expenses.
- Market basket analysis in retail.
3. Reinforcement Learning
- The system learns through trial and error, receiving rewards or penalties for actions.
- Best suited for dynamic decision-making in conditions that change constantly.
Examples:
- Dynamic pricing strategies in e-commerce.
- Optimizing supply chain routes.
- Robotics in warehouses.
4. Popular Models in Business Analytics
- Decision Trees – Transparent, easy-to-interpret models for classification and regression.
- Regression Models – Useful for making continuous predictions, such as revenue forecasting.
- Neural Networks – Handle complex data types such as images, speech, or customer sentiment.
- Ensemble Methods (e.g., Random Forest, XGBoost) – Combine multiple models for higher accuracy.
Together, these techniques form the toolbox businesses use to turn raw data into actionable insights.
The Ultimate Guide to Machine Learning Consulting
Discover how Kanerika’s machine learning consulting helps businesses innovate and scale with AI.
Traditional Analytics vs Machine Learning Analytics
Traditional analytics relies on fixed rules, historical data, and manual interpretation. It helps generate reports and track performance, but it struggles with scale, speed, and complexity. These systems often require human input to define what to measure and how to interpret results.
Machine learning analytics works differently. It learns from data patterns and improves over time. Instead of relying on static models, ML systems adapt to new inputs, uncover hidden trends, and make predictions without manual intervention. This makes analytics more dynamic, scalable, and forward-looking.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Traditional Analytics | Machine Learning Analytics |
| Approach | Rule-based, manual | Data-driven, automated |
| Model Type | Static | Adaptive |
| Use Case | Reporting, tracking | Prediction, optimization |
| Scalability | Limited | High |
| Human Involvement | High | Low to moderate |
| Speed & Flexibility | Slower, predefined | Faster, responsive to new data |
| Insight Type | What happened | What will happen and what to do next |
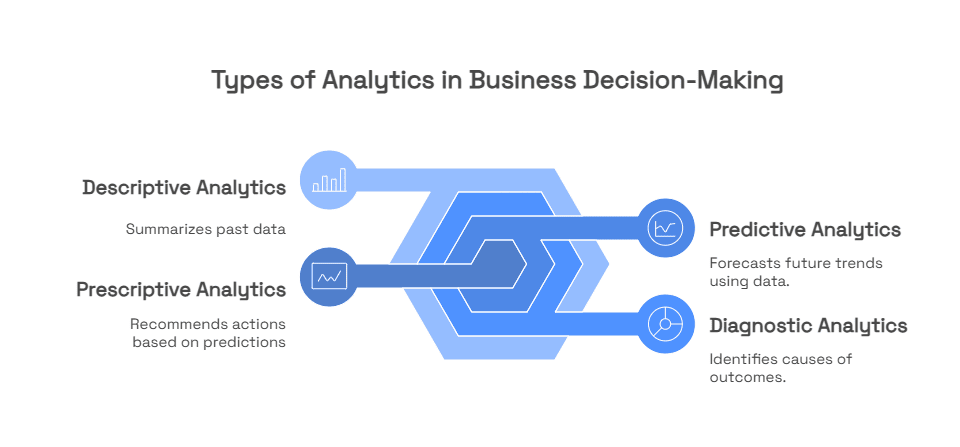
The Four Types of Analytics in Business Decision-Making
Analytics can be broken down into four types. Each one answers a different question and supports a different type of decision.
1. Descriptive Analytics – What happened?
This level summarizes past data. It’s used for reports, dashboards, and performance tracking.
Example: Last quarter’s sales report showed a 12% drop in revenue.
2. Diagnostic Analytics – Why did it happen?
This level explains the reasons behind outcomes. It helps identify patterns and root causes.
Example: Sales dropped due to supply chain delays and low inventory.
3. Predictive Analytics – What is likely to happen?
This level forecasts future outcomes using historical data and trends.
Example: The forecast indicates a continued decline in sales next quarter if inventory issues persist.
4. Prescriptive Analytics – What action should we take?
This level recommends actions based on predictions. It supports decision-making and strategy.
Example: Increase production, adjust pricing, and prioritize restocking high-demand items.
Key Applications and Real-World Examples of Machine Learning in Business Analytics
Machine learning is now part of everyday business operations. It helps teams make faster decisions, reduce manual work, and improve accuracy across departments. Here’s how it’s being used—and where it’s making a real impact.
1. Marketing & Customer Experience
ML helps marketers personalize campaigns, predict customer behavior, and improve retention. It powers recommendation engines, churn models, and customer value predictions.
Example
Sephora uses machine learning to analyze browsing behavior and purchase history. Its recommendation engine has led to a 20% increase in conversion rates and stronger repeat engagement.
2. Finance & Risk Management
ML models detect fraud, assess credit risk, and flag anomalies in financial data. They process millions of transactions in real time, improving accuracy and reducing losses.
Example
American Express uses ML to monitor transaction patterns and detect fraud early. This system has helped prevent losses and saved the company over $2 billion annually.
3. Operations & Supply Chain
ML improves demand forecasting, inventory planning, and logistics. It helps companies respond to market shifts, optimize delivery routes, and reduce waste.
Example
UPS uses machine learning in its ORION system to optimize delivery routes. Hence, it has saved 10 million gallons of fuel annually and significantly reduced delivery times.
4. Sales & Revenue Optimization
Sales teams use ML to score leads, forecast revenue, and adjust pricing dynamically. It helps prioritize efforts and increase deal conversion.
Example
Airbnb applies ML-powered dynamic pricing to adjust rates based on demand and local events. Hosts using smart pricing see up to 40% higher booking rates.
5. Human Resources & Workforce Planning
HR teams use ML to predict attrition, automate resume screening, and optimize staffing. It helps reduce hiring time and improve workforce planning.
Example
Unilever uses ML to screen resumes and assess candidates through video interviews. This has cut hiring time by 75% and improved diversity in recruitment.
Benefits of Machine Learning in Business Analytics
Machine learning in business analytics brings speed, accuracy, and scale to decision-making. It helps businesses move from reactive reporting to proactive strategy.
1. Faster, data-driven decision-making
ML models process large volumes of data quickly. They surface insights in real-time, helping teams act faster and with greater confidence.
2. More accurate forecasting across business functions
From sales to supply chain, machine learning improves forecast accuracy by learning from historical patterns and adjusting to new data.
3. Personalized customer targeting at scale
ML enables businesses to tailor offers, messages, and experiences to individual customers—automatically and at scale.
4. Reduced operational costs through automation
By automating repetitive tasks such as data entry, fraud detection, or inventory planning, ML helps reduce manual effort and lower costs.
5. Competitive edge by anticipating market trends
ML models can detect shifts in customer behavior or market signals early, giving businesses a head start in adapting their strategies.

Ensemble Learning Techniques for Better ML Accuracy
Discover how ensemble learning combines multiple models to improve accuracy and reliability. Explore key methods such as bagging, boosting, and stacking.
Challenges Businesses Need to Watch
While machine learning in business analytics offers clear advantages, it also presents challenges that require attention.
1. Poor Data Quality
If the input data is incomplete, outdated, or inconsistent, the model’s output will be unreliable. Clean, well-structured data is essential.
2. Model Bias
ML models can reflect and amplify biases present in the training data. This can lead to unfair or inaccurate predictions, particularly in areas such as hiring or lending.
3. Integration Issues
Many businesses struggle to connect ML models with legacy systems. Without proper integration, insights stay siloed and unused.
4. Talent Gap
There’s a shortage of professionals with the right mix of data science, domain knowledge, and engineering skills. This slows down adoption and limits impact.

Essentials of Machine Learning for Business Analytics
Machine learning isn’t just about algorithms. It starts with the right data, the right tools, and a clear plan. Here’s how businesses can take the first steps.
What Kind of Data Do You Need
Machine learning runs on data. If your data is messy or hard to access, your models won’t work well. You need:
- Structured data from systems like CRM or ERP. This includes customer records, transactions, and inventory logs.
- Unstructured data like emails, chat logs, or support tickets. These often hold valuable patterns but need extra work to process.
Before you build anything, make sure your data is clean, consistent, and well-managed. If it’s scattered across systems or incomplete, fix that first.
Tools You Can Use
The tools you choose depend on your team’s skills and the level of control you want.
- Open-source frameworks like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch are ideal for data scientists who want to build custom models from scratch.
- Cloud platforms like AWS SageMaker, Azure ML, and Google Vertex AI offer ready-to-use infrastructure. They help you train, test, and deploy models without worrying about servers or scaling.
- Analytics platforms with built-in ML, like Tableau, Power BI, and ThoughtSpot, let business users apply machine learning without writing code. These are useful for quick insights and simple predictions.
A Simple Way to Get Started
You don’t need to build a complete ML system on day one. Start small and grow from there.
1. Pick a clear business problem
Choose something that matters to your team. It should have enough data and a measurable outcome. For example, predicting customer churn or improving delivery times.
2. Check your data
Ensure the data you need is accurate, complete, and easily accessible. If it’s not, fix that before moving ahead.
3. Build a pilot
Create a small proof of concept. Test the model on a limited dataset. See if it gives valid results.
4. Scale with MLOps
If the pilot works, move to production. Utilize MLOps practices to automate deployment, monitor performance, and maintain model updates.
Unlock the Power of Machine Learning in Predictive Analytics
Discover the role of machine learning in predictive analytics to boost accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making.
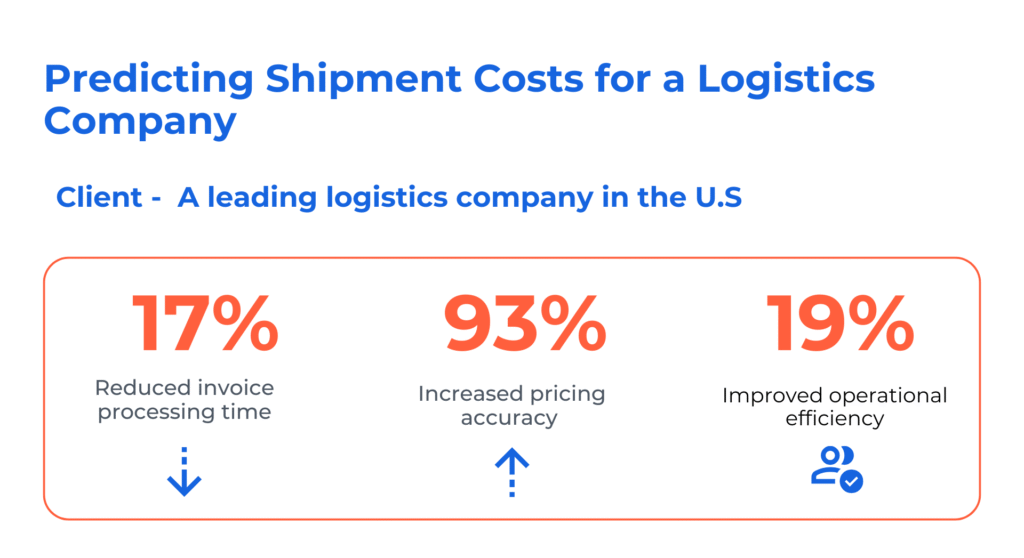
Case Study: Predicting Shipment Costs for a Logistics Company
Client Overview
A leading logistics company in the US was facing frequent budget overruns due to inaccurate shipment cost estimates. Their existing process relied heavily on manual calculations and historical averages, which couldn’t account for real-time variables like fuel prices, weather, and route changes.
Challenge
The company needed a smarter way to estimate costs that could adapt to changing conditions and reduce pricing errors. Their goal was to improve budget planning, resource allocation, and customer transparency.
Kanerika’s Solution
We built a machine learning model that analyzed internal and external data—shipment history, fuel rates, route details, and market trends—to generate accurate cost predictions. The model was integrated into their existing systems, allowing real-time access to estimates during planning and billing.
Results
- Achieved 93% pricing accuracy using ML-based cost predictions
- Reduced invoice processing time by 17%
- Improved operational efficiency by 19% across logistics teams
This case shows how machine learning in business analytics can reduce cost estimation errors, streamline operations, and improve customer satisfaction.
The Kanerika Advantage: Machine Learning in Business Analytics
At Kanerika, we help businesses solve real problems using machine learning in business analytics. Our team combines deep technical expertise with a strong understanding of industry-specific needs. Whether it’s predicting demand, improving customer retention, or automating quality checks, we build solutions that deliver measurable results. We focus on making data useful—turning raw information into clear, actionable insights.
We design our systems to work with what you already use. Our platforms integrate with tools like Power BI, Snowflake, and Microsoft Fabric, so you don’t need to rebuild your infrastructure. We support scalable deployment, real-time performance, and full compliance with standards like GDPR and SOC II. From retail and finance to logistics and healthcare, we tailor every solution to fit your workflows and business goals.
What sets us apart is our focus on outcomes. We don’t just build models—we help you deploy, monitor, and improve them over time. Our approach to machine learning in business analytics is practical, secure, and built for scale. We’re here to help you make faster decisions, reduce costs, and stay ahead of your competition.
Explore Machine Learning’s Role in Optimizing Business Analytics Strategies.
Partner with Kanerika to maximize your business potential.
FAQs
1. What are the 4 types of machine learning?
The four main types of machine learning are supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning uses labeled data to train models, while unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data. Semi-supervised blends both, and reinforcement learning focuses on learning through rewards and penalties.
2. What is the difference between AI and ML?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broader field where machines are designed to mimic human intelligence. Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. In simple terms, AI is the goal, and ML is the method.
3. What is the primary purpose of machine learning in business?
The main purpose of ML in business is to analyze data, identify trends, and support better decision-making. It helps in predicting customer behavior, automating repetitive processes, and optimizing resources. This leads to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and stronger competitive advantage.
4. What is the most popular machine learning algorithm?
One of the most widely used algorithms is the Decision Tree, as it is easy to interpret and apply across industries. Other popular algorithms include Linear Regression for forecasting, Random Forests for accuracy, and Neural Networks for handling complex data patterns like images or speech.
5. What is AutoML, and when should businesses use it?
AutoML (Automated Machine Learning) automates steps like model selection, feature engineering, and parameter tuning. It is especially useful for businesses that lack in-house data science expertise but still want to harness ML. By simplifying the process, AutoML allows companies to build reliable models faster.
6. How is machine learning used in business analytics today?
Machine learning is used in business analytics to automate data analysis, identify hidden patterns, and provide predictive insights. Companies apply ML to optimize marketing campaigns, personalize customer experiences, detect anomalies in operations, and drive strategic decisions with data-driven accuracy.










