Intelligent automation vs. hyperautomation is a critical choice for enterprises modernizing their operations. Walgreens, global pharmacy-led, health and wellbeing enterprise used intelligent automation in its HR processes, automating tasks like leave requests and workers’ compensation data entry. The result was a 73% increase in efficiency, freeing staff to focus on more strategic, people-centric work.
This example shows the power of intelligent automation to solve targeted challenges. Hyperautomation goes beyond isolated tasks. By combining RPA with AI, analytics, and process mining, it creates a connected system that continuously improves end-to-end workflows.
We’ll explore how intelligent automation differs from hyperautomation, the unique benefits each brings, and how businesses can decide which automation approach best aligns with their digital transformation strategy.
What is Intelligent Automation (IA)?
Intelligent automation integrates artificial intelligence technologies with automation tools such as robotic process automation to handle complex business processes that require cognitive capabilities. Unlike traditional rule-based automation that simply replicates repetitive keystrokes and clicks, intelligent automation incorporates machine learning for pattern recognition, natural language processing for understanding unstructured text, and computer vision for interpreting images and documents.
This combination enables systems to analyze data from multiple sources, recognize patterns across large datasets, make informed decisions based on learned behaviors, and adapt to changing conditions without requiring manual reprogramming. The result is smarter, more adaptive workflow automation that handles multi-step tasks while continuously improving through experience.
Key statistics on intelligent automation adoption:
- Basic automation reduces operational costs by 20-30%, while intelligent automation delivers 50-70% cost reductions (BigSur.ai research)
- The global intelligent process automation market reached $16.81 billion in 2024, with projections indicating growth to $61.23 billion by 2034
- 87% of organizations have implemented or are actively scaling intelligent automation initiatives
- 76% of enterprises consider intelligent automation essential for their digital transformation strategies
- Fortune 500 adoption has reached 65%, with finance and accounting departments accounting for 44% of deployments
What is Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation represents a broader and more strategic automation approach. It aims to automate as many business and IT processes as possible across an entire organization by using a wide range of technologies, including IA, process mining, analytics, no-code/low-code platforms, and workflow orchestration tools.
Hyperautomation is designed for scalability and continuous process improvement, enabling businesses to adapt swiftly to changing market demands and operational complexities.
Key statistics on hyperautomation growth:
- The hyperautomation market stood at $15.62 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach $38.43 billion by 2030, representing a 19.73% compound annual growth rate (Mordor Intelligence)
- Gartner predicts organizations will reduce operational costs by 30% by combining hyperautomation technologies with redesigned operational processes
- 90% of large enterprises now consider hyperautomation a staple discipline for operational excellence
- North America leads adoption with approximately 37% market share, driven by deep enterprise technology budgets and mature digital infrastructure
Key Differences Between Intelligent Automation and Hyperautomation
| Aspect | Intelligent Automation | Hyperautomation |
| Scope | Focus on automating tasks and workflows | Automates entire processes across enterprise |
| Technology Stack | AI, ML, cognitive tech, enhanced RPA | Broader toolset including process mining, orchestration, IDP, low-code apps |
| Approach | Process-first automation | People-first and process-first holistic approach |
| Implementation Complexity | Medium, suitable for specific workflows | High, requires mature digital infrastructure and cross-system orchestration |
| ROI | High ROI with targeted implementations | Highest ROI over long term with broad automation impact |
| Decision-making | AI-powered intelligent decisions within tasks | AI and ML for end-to-end intelligent process decisions |
| Goal | Make complex workflows efficient and adaptive | Streamline & optimize all automatable processes enterprise-wide |
| Governance | Focus on process automation governance | Emphasizes security, governance, and alignment of business & IT |
1. Scope
Intelligent Automation (IA): IA focuses on narrowly defined, process-level automation. It handles specific business functions or repetitive workflows, often within a department (automating invoice approvals in finance or resume screening in HR). The scope is usually limited to solving well-defined operational inefficiencies.
Hyperautomation: Hyperautomation takes a company-wide, enterprise-scale approach. Instead of isolated process-level fixes, it creates a cohesive automation ecosystem where multiple technologies integrate to transform end-to-end value chains. It looks beyond efficiency to deliver scalable, adaptive, and strategic automation across the entire business.
2. Technology Stack
Intelligent Automation (IA): IA typically combines Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities, such as Machine Learning (ML) for predictive insights and Natural Language Processing (NLP) for handling unstructured data (emails, documents, chat). The focus is on augmenting task automation with intelligence to go beyond rule-based bots.
HypHyperautomation: Incorporates all intelligent automation technologies plus additional capabilities that enable discovery, orchestration, and continuous optimization:
- Process mining and task mining tools that analyze system logs and user behavior to identify automation candidates
- Advanced analytics platforms for data-driven decision making and performance monitoring
- Low-code and no-code development environments that accelerate solution delivery and enable business users to create applications
- Orchestration platforms that coordinate workflows across multiple systems, departments, and technologies
- Intelligent document processing solutions that extract structured data from unstructured sources at scale
According to Gartner, by 2024, 65% of organizations that deployed automation technologies had introduced artificial intelligence, machine learning, natural language processing, process mining, task mining, and intelligent document processing capabilities.
3. Goal
Intelligent Automation (IA): IA’s primary goal is operational optimization at a micro level. It ensures processes run faster, with fewer human errors, and more consistency across repetitive tasks. By embedding AI-driven intelligence, IA also improves decision-making, creating smarter workflows that align with departmental goals.
Hyperautomation: The overarching goal of hyperautomation is full-scale digital transformation. Rather than improving individual workflows, it seeks to align technology and automation with business strategies. The final objectives include greater organizational agility, enterprise scalability, and the ability to adapt rapidly to market or customer demands.
4. Deployment
Intelligent Automation (IA): Deployed at department or function level.
- HR: resume parsing, employee onboarding automation
- Finance: invoice matching, reconciliations, automated reporting
- Customer Service: ticket routing, response automation
These deployments are localized and designed for fast adoption with immediate returns.
Hyperautomation: Covers enterprise-wide deployments involving cross-functional collaboration.
- Integrates end-to-end processes such as order-to-cash or procure-to-pay
- Requires alignment between IT, operations, compliance, and business units
- Orchestrates workflows across different teams and technologies for maximum impact
Drive Business Growth and Efficiency with Intelligent Automation!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
5. Complexity
Intelligent Automation (IA): Because IA targets specific processes, it is relatively simpler to implement. Deployment is usually handled within a single business unit and requires less governance or change management. With ready AI models or pre-configured bots, implementations can be fast and straightforward, producing measurable gains quickly.
Hyperautomation: Hyperautomation projects are inherently complex as they demand enterprise-wide alignment. The process often involves rethinking workflows, harmonizing data across systems, ensuring governance, and managing organizational change. This complexity also means hyperautomation requires executive sponsorship, long-term vision, and a governance framework to ensure lasting benefits.
6. Outcome
Intelligent Automation (IA): The immediate outcomes of IA include faster process execution, reduced manual workload, and improvement in accuracy across repetitive activities. IA helps achieve cost savings, compliance consistency, and better resource allocation. However, these results are important for operational efficiency but are generally confined to localized processes.
Hyperautomation: The outcomes of hyperautomation are strategic in nature, as it fundamentally changes how organizations operate. Businesses achieve resilience, adaptability, and scalability, making them better prepared for disruption. Hyperautomation also enhances experiences for both customers and employees by enabling end-to-end, seamless, and personalized interactions across the enterprise.
7. Adoption Path
Intelligent Automation (IA): IA often represents the first phase in an organization’s automation journey. Companies begin with simple RPA deployments to demonstrate efficiency, then gradually introduce AI/ML and NLP models. This progression helps build confidence, showcase ROI, and establish the foundation for more advanced automation initiatives.
Hyperautomation: Hyperautomation is the maturity stage that follows IA. Once organizations gain experience with targeted automation, they shift toward scaling automation enterprise-wide. At this stage, automation is combined with intelligence, process mining, and orchestration tools, ensuring digital transformation is embedded into the company’s long-term strategy.
Data Automation: A Complete Guide to Streamlining Your Businesses
How-to Automate Your Data Workflows for Optimal Performance?
Business Benefits of Intelligent Automation and Hyperautomation
Benefits of Intelligent Automation
1. Cost Savings Intelligent automation reduces dependency on manual labor by handling repetitive tasks like data entry, form processing, and report generation. This leads to lower operational costs while freeing employees to focus on higher-value work.
2. Faster Process Execution By automating rule-based and routine workflows, tasks that once took hours can now be completed in minutes. This speed not only accelerates delivery but also improves turnaround time for customers and internal teams.
3. Improved Accuracy Manual processes are prone to errors, especially when performed at scale. Intelligent automation ensures consistency, reduces rework, and provides reliable outputs that help maintain compliance and quality standards.
4. Smarter Decision Making When paired with AI and machine learning, intelligent automation can analyze data in real time and provide actionable insights. This allows businesses to make faster, smarter, and more informed decisions without relying solely on human judgment.
5. Quick Implementation Wins Intelligent automation can be implemented in individual departments with minimal disruption. These quick wins deliver measurable ROI early, building confidence and creating momentum for larger automation initiatives.
Benefits of Hyperautomation
1. Enterprise-Wide Scale Hyperautomation goes beyond isolated processes and integrates automation across multiple business units. This creates a connected ecosystem where different teams and systems work seamlessly together.
2. Business Agility and Flexibility With a combination of process mining, low-code platforms, and orchestration tools, hyperautomation allows businesses to adapt quickly. Whether it is scaling up operations or introducing new services, organizations can remain agile in changing markets.
3. Digital Resilience Hyperautomation embeds monitoring, governance, and compliance into automation strategies. This makes enterprises more resilient to disruptions, ensuring continuity and stability even when market or operational conditions shift unexpectedly.
4. Enhanced Customer and Employee Experiences By eliminating silos and streamlining workflows, hyperautomation creates smoother experiences for customers and employees. Customers enjoy faster service with fewer errors, while employees gain tools that reduce repetitive work and improve satisfaction.
5. Long-Term Digital Transformation Unlike point solutions, hyperautomation is a long-term approach aligned with digital transformation goals. It fosters continuous improvement, future-readiness, and scalable value creation across the organization.
Intelligent Automation: Transforming Business Operations in 2025
Explore how Intelligent Automation enhances productivity and decision-making through AI-driven workflows for modern enterprises.
How Intelligent Automation and Hyperautomation Work Together
1. Foundation vs. Strategy
First, intelligent automation is the foundation that combines RPA, AI, and NLP to automate tasks. Meanwhile, hyperautomation is the broader strategy that scales these capabilities across the enterprise with orchestration, discovery, and governance.
2. Discovery to Continuous Improvement Cycle
The collaboration between intelligent automation and hyperautomation creates a continuous optimization loop:
- Insights feed back into the discovery phase, creating ongoing cycles of optimization
- Process mining and analytics tools identify automation opportunities by analyzing how work actually flows through the organization
- Intelligent automation executes the automations, handling routine tasks while surfacing exceptions for human review
- Performance monitoring tracks results and identifies areas for improvement
3. Orchestration Across Processes
Typically, intelligent automation handles specific workflows such as invoice approvals or customer queries. However, hyperautomation connects these workflows, creating smooth end-to-end processes across departments.
4. Scaling Data and Insights
First, intelligent automation generates valuable data like logs, outcomes, and exceptions. Then, hyperautomation aggregates this data, uses it for analytics, retrains AI models, and identifies the next automation opportunities.
5. Humans and Automation in Balance
While intelligent automation manages repetitive and rule-based tasks, humans step in for exceptions. Meanwhile, hyperautomation provides dashboards, audit trails, and SLAs to ensure human intervention is structured and consistent.
6. Governance and Risk Management
Initially, intelligent automation needs controls to protect data and reduce errors. Subsequently, hyperautomation enforces enterprise-level governance with policies, monitoring, and compliance frameworks.
7. Reusability and Scale
First, intelligent automation creates reusable components such as bots, connectors, and AI models. Then, hyperautomation enables these assets to be cataloged and shared, making automation scalable across multiple teams and functions.
Intelligent Automation: Real-World Examples
Intelligent Automation: Real-World Examples
Customer Service Automation in Telecommunications
A Southeast Asian telecommunications provider deployed IBM Watson Assistant to automate customer service interactions across billing inquiries, plan changes, and service status requests. The implementation integrated with backend systems for instant account verification and enabled proactive notifications for service disruptions.
Results: The telecom provider automated over 60% of customer service interactions, improved Net Promoter Score by 25% through faster resolution times, and reduced the burden on human agents who could then focus on complex customer issues requiring empathy and judgment.
According to SuperAGI research, AI-powered tools like Watson Assistant can handle up to 95% of customer interactions by 2025, resulting in a 37% reduction in first response times and a 52% decrease in resolution times.
Document Processing in Financial Services
JPMorgan Chase developed the Contract Intelligence (COiN) platform to automate legal document analysis across its commercial lending operations. The platform uses machine learning to analyze commercial credit agreements, extracting critical data points, identifying key contract clauses, and flagging compliance issues.
Results: COiN can analyze 12,000 commercial credit agreements in seconds, saving over 360,000 work hours annually. The platform identifies critical contract clauses including default terms, renewal conditions, and regulatory requirements with greater consistency than manual review. JPMorgan estimates its artificial intelligence use cases have the potential to generate up to $1.5 billion in value.
Must-Know Features of The Best Accounts Payable Automation Tools
Discover the key functionalities of top-tier accounts payable automation tools to streamline your financial processes and boost organizational efficiency.
Hyperautomation: Real-World Examples
Financial Services Loan Process Automation: JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase uses hyperautomation technologies that integrate RPA, AI, and machine learning to automate loan origination and processing. The process includes automatic data extraction from loan applications, fraud detection, credit risk analysis, and compliance checks, all managed in an orchestrated workflow.
This end-to-end automation compresses approval times from days to hours, leading to faster customer onboarding and significant operational cost savings.
Manufacturing Supply Chain and Quality Control: Siemens’ Digital Factory
Siemens implemented hyperautomation in its digital factories by integrating IoT sensors, AI analytics, and RPA-driven workflows. Real-time monitoring of supply chain logistics allows automatic adjustments to inventory and production schedules based on demand forecasts.
Quality control uses AI-powered image recognition to detect defects during production, with instant feedback loops through automated workflows for corrective actions. This end-to-end automation optimizes manufacturing efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves product quality.
Intelligent automation vs. Hyperautomation : Implementation Considerations & Challenges
1. Technology Integration Complexity
Both automation approaches require integration with existing enterprise systems. Intelligent automation implementations typically connect with two to five core applications, while hyperautomation may involve dozens of systems across the technology landscape. Organizations should assess their integration capabilities, application programming interface availability, and middleware requirements before selecting an approach.
2. Change Management Requirements
Automation initiatives succeed when employees understand their evolving roles and receive appropriate support during transitions. Intelligent automation projects require departmental change management focused on specific workflow changes. Hyperautomation demands organization-wide programs that address role evolution, skill development, and cultural adaptation to working alongside digital coworkers.
About 75% of knowledge workers already use artificial intelligence tools in some form, even when their companies have not formally deployed them, suggesting that change management must address both formal and informal adoption patterns.
3. Data Quality and Governance
Automation performance depends directly on data quality. Inconsistent data formats, duplicate records, and missing information create exceptions that reduce automation effectiveness and require human intervention. Gartner research indicates poor data quality costs organizations $12.9 million annually on average. Establishing data governance practices, cleansing existing datasets, and implementing validation rules improves outcomes for any automation initiative.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Defining clear metrics before implementation enables accurate return on investment measurement and ongoing optimization. Intelligent automation metrics typically focus on task completion rates, processing time reduction, and error elimination. Hyperautomation measurement includes enterprise-wide metrics like total automation coverage, time-to-market for new automations, and business agility indicators.
According to Optezo research, recommended hyperautomation metrics include automation coverage index (percentage of addressable processes automated), time saved versus time reinvested in higher-value work, first-contact resolution rates for AI-enhanced interactions, and revenue per digital worker.
Choosing the Right Approach: Intelligent Automation vs. Hyperautomation
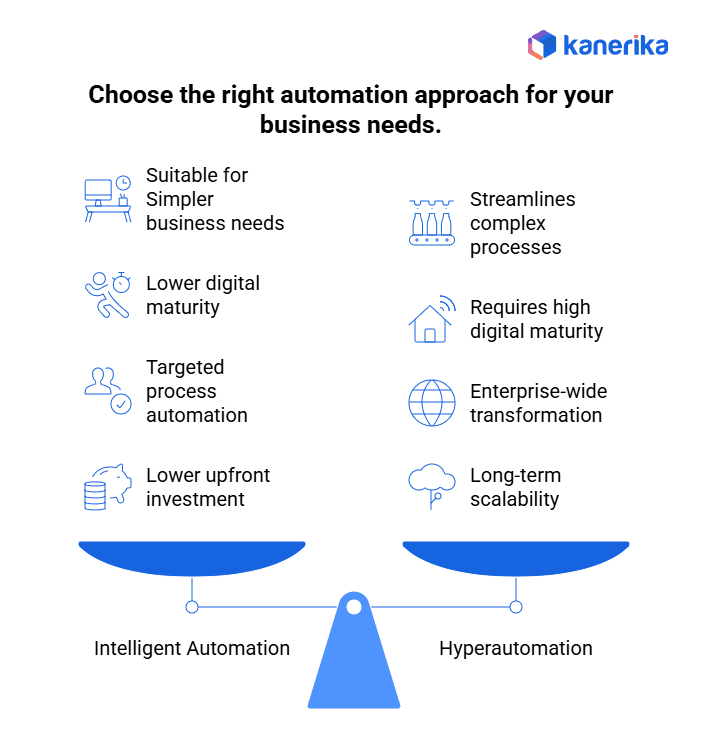
1. Business Complexity and Scale
For organizations with limited operations or a need to automate only a few repetitive workflows, intelligent automation is often sufficient. Larger enterprises with complex, interconnected processes benefit more from hyperautomation, as it integrates multiple tools to streamline operations at scale.
2.Digital Maturity and Infrastructure Readiness
If your business is still building its digital foundation, starting with intelligent automation ensures quick wins without overwhelming infrastructure requirements. Hyperautomation demands a higher level of digital maturity, with cloud readiness, data integration, and analytics capabilities already in place.
3.Specific Process Automation Needs vs. Enterprise-Wide Transformation
When the goal is to reduce manual effort in targeted areas like HR, finance, or customer support, intelligent automation works well. If the objective is enterprise-wide transformation spanning supply chain, operations, and customer experience, hyperautomation becomes the more strategic choice.
4.Available Budget and ROI Expectations
Intelligent automation typically requires lower upfront investment and delivers faster ROI for specific use cases. Hyperautomation, while more resource-intensive, offers long-term returns by continuously optimizing processes, reducing operational costs, and driving scalability across the organization.
Kanerika’s Intelligent Automation and AI Agents Driving Enterprise Growth
Kanerika stands at the forefront of intelligent automation, offering innovative solutions built to address the dynamic needs of modern enterprises. With proven expertise in robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML), Kanerika enables organizations to streamline operations, maximize efficiency, and respond quickly to shifting business demands.
Our automation strategies simplify complex business functions, ranging from finance and HR to supply chain, compliance, and customer support. By eliminating repetitive, error-prone tasks, we help enterprises cut costs and boost accuracy. Complementing these strategies are Kanerika’s AI agents, designed to handle specialized tasks. These intelligent agents act as digital coworkers, accelerating workflows and ensuring higher precision across critical processes.
At the core of our automation suite is FLIP, a low-code/no-code, AI-powered DataOps platform that automates end-to-end data workflows. FLIP ensures real-time data accuracy, automates validation and cleansing, and provides secure, role-based access across teams. With Kanerika, organizations gain the agility to scale, innovate, and secure a lasting competitive edge in an automation-driven world.
Transform Your Business Operations with Seamless Automation
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
What is the difference between automation and intelligent automation?
Automation uses predefined rules or scripts to perform repetitive tasks without human intervention. Intelligent automation, on the other hand, combines automation with technologies like AI and machine learning to handle unstructured data, adapt to changes, and make decisions.
What is the difference between hyperautomation and AI?
AI is a technology that enables machines to mimic human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and decision-making. Hyperautomation is a broader approach that uses AI, intelligent automation, RPA, and other tools together to automate complex, end-to-end business processes at scale.
What are the four types of automation systems?
The four main types are:
- Fixed Automation – best for high-volume, repetitive tasks.
- Programmable Automation – used where products change periodically.
- Flexible Automation – allows quick reconfiguration for varied tasks.
- Integrated Automation – fully digital, connecting systems across the enterprise.
How does intelligent automation work?
Intelligent automation integrates robotic process automation (RPA) with AI, natural language processing (NLP), and analytics. It mimics human actions, learns from data, and improves processes over time, enabling smarter, faster, and more accurate operations.
What is the difference between APC and AI?
APC (Advanced Process Control) focuses on optimizing industrial and engineering processes using mathematical models. AI is broader, enabling machines to learn and make decisions across industries, not just process control. APC is rule-based and domain-specific, while AI adapts to diverse and evolving situations.
What is the difference between the three types of AI?
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): Specialized for one task, like chatbots or image recognition.
- General AI: Capable of performing any intellectual task that a human can do (still theoretical).
- Super AI: A future concept where machines surpass human intelligence and decision-making.
How does hyperautomation differ from intelligent automation?
Intelligent automation combines RPA with AI to make processes smarter. Hyperautomation takes it further by integrating multiple technologies (IA, AI, process mining, analytics, low-code tools) to automate entire business ecosystems, not just isolated tasks.
Which approach is right for my business, intelligent automation or hyperautomation?
If your goal is to improve specific processes with AI-driven automation, intelligent automation may be enough. But if you aim to achieve enterprise-wide digital transformation with scalability and end-to-end automation, hyperautomation is the right choice.