AI adoption is accelerating at an extraordinary pace, and enterprises are rapidly moving from simple chatbots to fully autonomous systems. In this fast-changing environment, many leaders exploring Enterprise Workflow Automation Solutions are asking an important question: What is the real difference between an AI agent and an LLM? This confusion is common because both technologies use advanced AI, yet they serve very different roles in automation.
According to McKinsey, Automation delivers $2.6–$4.4 trillion in annual economic value across industries. To unlock this value, organizations must clearly understand how LLMs and AI agents contribute to automation, decision-making, and ROI.
At a high level, LLMs excel at understanding and generating language, while AI agents use LLMs along with memory, tools, and actions to complete multi-step tasks autonomously. Knowing this difference is critical for shaping an efficient AI roadmap and choosing the right automation strategy.
In this blog, we will break down AI Agent vs LLM, explore their architectures, strengths, real-world use cases, and explain when to use each, especially when building enterprise-grade automation solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Enterprise workflow automation reduces manual work, improves accuracy, and speeds up operations across all departments.
- Modern automation relies on core components such as orchestration engines, integrations, rules engines, AI/ML, RPA, and strong data layers.
- AI and LLM-driven automation enable intelligent decision-making, document processing, and multi-step task execution.
- Workflow automation improves compliance through audit trails, standardized processes, and automated reporting.
- Successful automation depends on governance, scalability, security, and continuous improvement.
What Are Enterprise Workflow Automation Solutions?
Enterprise workflow automation solutions help organizations replace slow, manual processes with automated, rule-based, and AI-powered workflows. Instead of relying on people to move tasks from one step to another, these systems automatically execute actions, apply business rules, and route work to the right teams. This reduces delays, eliminates human error, and improves overall efficiency.
However, enterprise-grade workflow automation goes far beyond basic task automation. It is designed to be scalable, secure, governed, and fully integrated with core systems such as ERP, CRM, HRMS, finance platforms, and data warehouses. These solutions can handle high volumes of work, maintain strict security controls, and provide full visibility across processes.
Enterprise workflow automation also includes key capabilities such as:
- Orchestration of multi-step processes
- Automated approvals and routing
- Event triggers that activate workflows
- Connectors for system integrations
- AI/ML-powered decisioning for intelligent actions
- Auditability with complete tracking and logs
It is important to distinguish between simple task automation and enterprise workflow automation. Task automation handles small, isolated actions, like auto-filling a form or sending a reminder. In contrast, enterprise workflow automation manages end-to-end business processes, connecting multiple teams, systems, and data sources.
Why Enterprises Need Workflow Automation Today
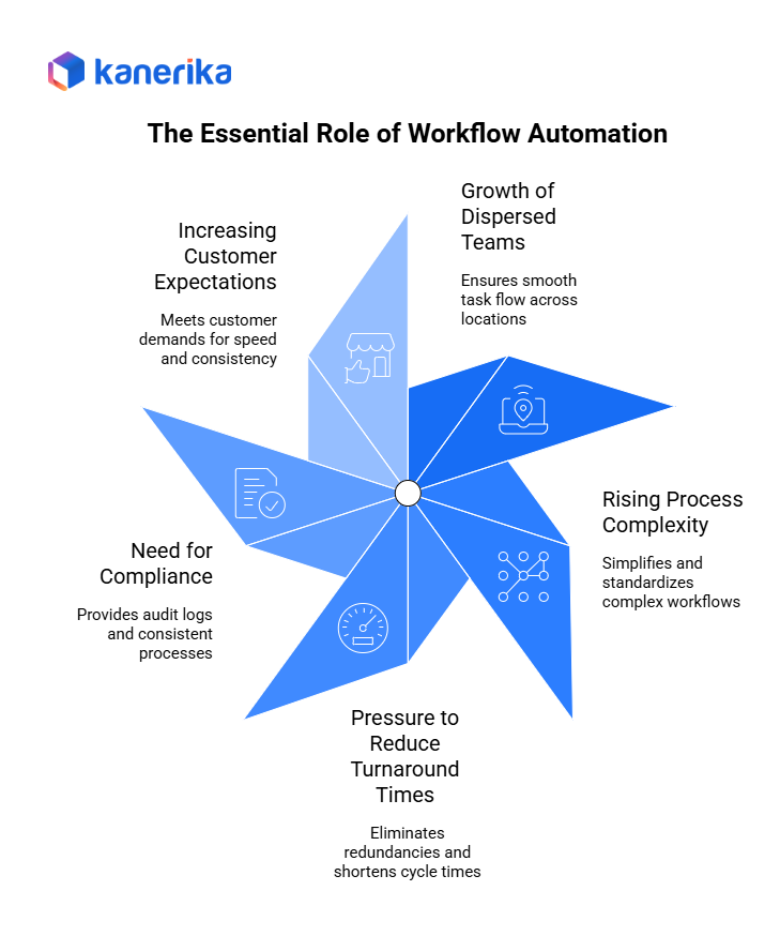
Modern organizations face increasing pressure to operate faster, more efficiently, and with greater accuracy. Because of these demands, workflow automation has become essential. Below are the key reasons enterprises need workflow automation today:
1. Growth of dispersed teams and remote collaboration
With teams spread across locations and time zones, manual processes slow down work. Workflow automation ensures tasks move smoothly, regardless of where employees are.
2. Rising process complexity across business functions
Departments such as finance, HR, supply chain, legal, and IT service management now handle more data and more steps than ever. Automation helps simplify, standardize, and streamline these complex workflows.
3. Pressure to reduce turnaround times and remove redundancies
Enterprises are expected to deliver results quickly. Automated workflows eliminate repetitive steps, reduce handoffs, and shorten cycle times dramatically.
4. Need for compliance, audit trails, and standardized processes
Industries must follow strict rules and retain records. Automation provides built-in audit logs, controlled approvals, consistent steps, and full process visibility, making compliance easier.
5. Increasing customer expectations for speed and consistency
Customers expect instant updates, quick service, and error-free responses. Automated workflows allow organizations to meet these expectations every time.
6. Clear business value
Workflow automation leads to:
- Faster execution with fewer delays
- Lower error rates due to reduced manual work
- Higher productivity across teams
- Lower operational costs through efficiency
Core Components of Enterprise Workflow Automation Solutions
Enterprise workflow automation relies on several connected components that work together to streamline processes, improve accuracy, and increase efficiency. Each layer plays a specific role, and together they create a complete automation ecosystem. Below are the essential components of a modern enterprise workflow automation solution.
1. Workflow Orchestration Engine
This is the core engine that manages end-to-end workflows. It controls the sequence of steps, applies business logic, and ensures tasks move smoothly from one stage to the next.
2. Integration Layer
Because enterprises depend on many systems, the integration layer is critical. It connects ERP, CRM, HRMS, databases, and SaaS tools through APIs or connectors, enabling seamless data exchange across platforms.
3. Rules & Policy Engine
This component applies conditional logic, validation rules, and approval paths. It ensures processes follow business policies and remain consistent across teams.
4. AI & ML Layer
AI adds intelligence to workflows by supporting smart decision-making, predictions, NLP-based document processing, and classification tasks. This layer helps automate decisions that previously required human judgment.
5. RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA bots handle repetitive, rule-based tasks, such as data entry, screen navigation, and interactions with legacy systems that cannot be integrated through APIs.
6. Data Layer
This layer stores workflow metadata, logs, audit trails, and analytics information. It improves visibility, compliance, and reporting.
7. User Interface Layer
Finally, the UI layer provides forms, dashboards, drag-and-drop builders, alerts, and notifications. It enables users to monitor workflows, submit requests, and manage exceptions.
Transform Your Business with AI-Powered Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Types of Enterprise Workflow Automation Solutions
Organizations choose from various automation technologies depending on their specific needs, existing infrastructure, and workflow complexity. Understanding these different solution types helps businesses select the right approach for their automation initiatives.
1. Business Process Management (BPM) Tools
BPM platforms provide comprehensive workflow management for complex, structured business processes. These tools allow organizations to design, execute, and monitor end-to-end processes involving multiple departments and systems. Camunda offers open-source flexibility with strong developer support for building custom workflows.
Appian combines low-code development with AI capabilities, enabling business users to create workflows without extensive programming. Pega focuses on customer engagement workflows with built-in decisioning and case management capabilities.
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Platforms
RPA platforms automate repetitive, rules-based tasks by mimicking human interactions with applications. These software robots log into systems, copy data between applications, fill forms, and perform calculations without changing underlying infrastructure.
UiPath provides an intuitive visual designer making automation accessible to business users alongside powerful enterprise features. Automation Anywhere offers cloud-native architecture with integrated AI for handling unstructured data. Blue Prism emphasizes security and governance, making it popular in financial services and healthcare.
3. Enterprise Integration Platforms (iPaaS)
Integration platforms connect disparate systems, enabling data flow and process orchestration across cloud and on-premises applications. MuleSoft provides API-led connectivity with strong support for enterprise architecture patterns and microservices.
Boomi offers a cloud-native integration platform with pre-built connectors for hundreds of applications and a visual interface for designing integrations. Workato combines integration with workflow automation, using AI to suggest connections and automate data mapping.
4. AI-Powered Automation Platforms
Modern automation platforms incorporate artificial intelligence to handle more sophisticated workflows requiring judgment and adaptation. Microsoft Power Automate integrates deeply with Microsoft 365 and Azure services, using AI Builder for document processing, sentiment analysis, and predictive models. It enables citizen developers to automate tasks through intuitive design tools.
Zapier Enterprise extends its popular consumer product with security, governance, and support for business needs, connecting thousands of applications through simple trigger-action workflows. ServiceNow provides comprehensive workflow automation across IT, HR, customer service, and business operations with AI-driven recommendations and intelligent routing.
5. Custom Automation Using AI Agents
The newest frontier involves building custom automation using AI agents powered by large language models. These agents understand natural language instructions, reason through complex scenarios, and execute multi-step workflows autonomously. Unlike traditional automation requiring explicit programming of every step, AI agents receive high-level goals and determine appropriate actions independently.
LLM-driven automation handles processes with significant variability where predefined rules prove insufficient. They adapt to changing circumstances without reprogramming. Autonomous workflow execution allows agents to operate continuously, monitoring for triggers, gathering necessary information, and completing tasks without human intervention for routine cases.
Choosing the Right Solution
- Consider BPM tools when processes are well-defined, involve multiple stakeholders, require strong audit trails, and need process mining capabilities.
- Select RPA platforms when automating legacy systems, handling high-volume repetitive tasks, and making quick tactical improvements without changing existing systems.
- Choose iPaaS solutions when integrating multiple cloud applications, building event-driven architectures, and creating reusable integration patterns.
- Opt for AI-powered platforms when seeking rapid deployment, empowering business users, and handling semi-structured processes with some variability.
- Build custom AI agents when facing highly variable workflows, requiring natural language understanding, and needing adaptive decision-making without constant human oversight.
Many organizations ultimately deploy combinations of these technologies, using each where it fits best. A comprehensive automation strategy leverages multiple solution types working together rather than forcing one approach for all scenarios.
Architecture Overview
A modern enterprise workflow automation architecture brings together multiple layers that operate in a coordinated and reliable way. To make this clearer, below is a structured view of how the architecture works and why each part matters.
High-Level Workflow Sequence
Every automated process typically follows this sequence:
- Event-Based Triggers – Workflows start when an event occurs such as, a form submission, new ticket creation, database update, API call, or scheduled timer.
- Workflow Logic Execution – The orchestration engine applies business rules, routing paths, validation steps, and conditional logic.
- System Integrations – APIs, connectors, or RPA bots communicate with ERP, CRM, HRMS, finance systems, or databases.
- Human Approval (when needed) – Tasks requiring judgement or compliance checks are sent to managers or teams with clear audit trails.
- Final Action Completion – The workflow updates records, sends notifications, generates documents, or triggers downstream workflows.
Key Architectural Principles
- Microservices Architecture – Breaks the automation platform into small, independent services that improve flexibility, scale, and maintenance.
- Cloud-Native Infrastructure – Enables elastic scaling, high availability, and lower operational overhead.
- API-First Design – Ensures smooth integration with enterprise systems and external applications.
Operational Requirements
- Scalability: Able to support thousands of concurrent workflows without slowing down.
- Resilience & Failover: Automatic recovery during system failures, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
- Monitoring & Observability: Real-time dashboards track workflow performance, errors, and bottlenecks.
- Compliance & Auditability: Built-in logging, access control, and audit trails support regulatory needs.
This architecture ensures that workflow automation is robust, scalable, secure, and ready for enterprise-wide adoption.
Data Automation: A Complete Guide to Streamlining Your Businesses
Explore how automating data processes enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and drives growth.
Benefits of Enterprise Workflow Automation Solutions
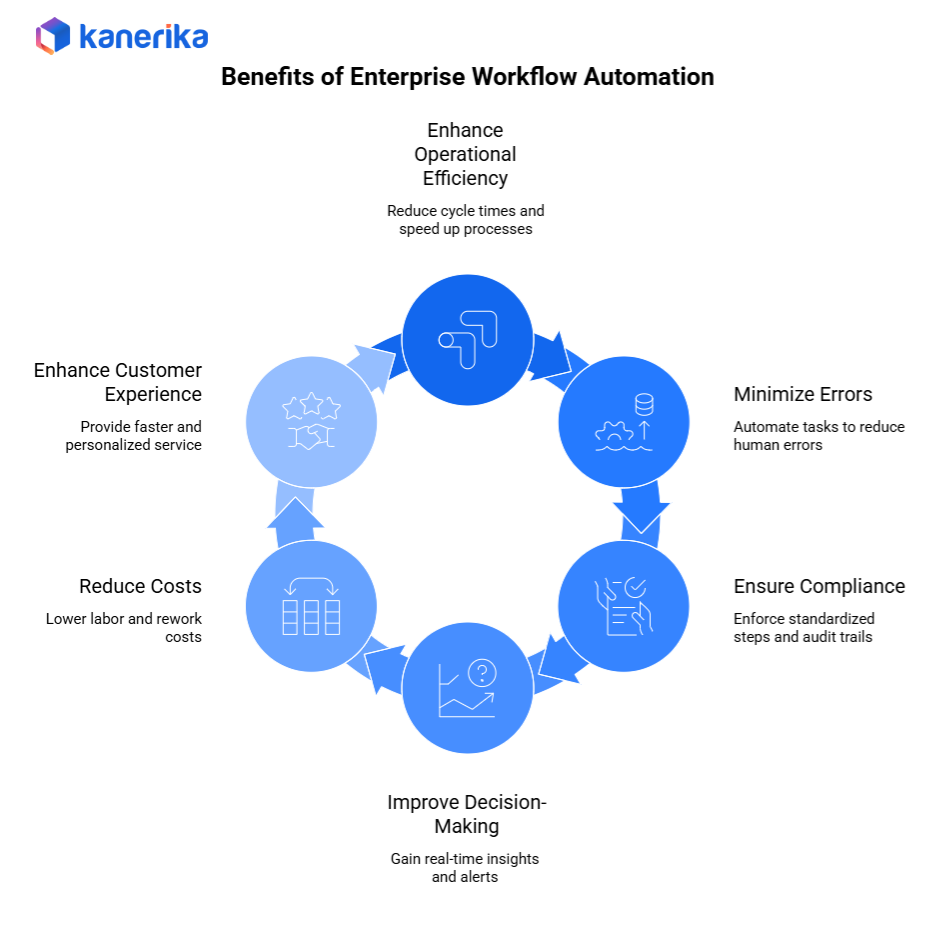
Enterprise workflow automation delivers a wide range of benefits that directly improve business performance. Below are the key advantages explained in simple and clear points.
1. Operational Efficiency
Automated workflows significantly reduce cycle times by removing delays caused by manual handoffs. Approvals move faster because tasks are routed instantly, helping teams complete processes with greater speed.
2. Reduced Errors & Improved Accuracy
By automating repetitive tasks, organizations minimize human intervention, which reduces mistakes caused by manual entry or oversight. Processes become more consistent and predictable, improving overall quality.
3. Better Compliance & Visibility
Automation enforces standardized steps, ensuring that every workflow follows approved business rules and policies. Built-in audit trails, logs, and automated reporting make compliance checks easier and more reliable.
4. Faster Decision-Making
With AI-powered recommendations, organizations gain real-time insights that support quick and informed decisions. Automated alerts and dashboards help teams act sooner on risks or opportunities.
5. Cost Savings
Workflow automation reduces the need for manual labor in routine processes. It also lowers rework costs, since errors decrease and processes require fewer corrections.
6. Improved Customer Experience
Customers benefit from faster responses, shorter waiting times, and accurate updates. Personalized communication and prompt service increase satisfaction and trust.
Real-World Use Cases for Enterprise Workflow Automation
Enterprise workflow automation is transforming how organizations operate across departments. By replacing manual work with automated, rule-based processes, businesses achieve higher accuracy, faster execution, and better visibility. Below are the most impactful real-world use cases, explained clearly and simply.
1. Finance & Accounting
Finance teams deal with high-volume and time-sensitive tasks, making automation extremely valuable.
- Invoice Processing: Automates data capture, validation, and posting into ERP systems.
- AP/AR Workflows: Streamlines approvals, reminders, and payment scheduling.
- Expense Approvals: Ensures quick validation of employee claims with predefined rules.
- Financial Reconciliation: Matches records automatically across systems, reducing month-end workload.
Through automation, finance achieves faster closing cycles and fewer errors.
2. HR & People Operations
HR processes often involve multiple steps and stakeholders. Automation helps create smooth and consistent employee experiences.
- Onboarding: Generates accounts, assigns tasks, sends documents, and triggers training modules.
- Leave Approvals: Routes requests instantly to managers with automated notifications.
- Payroll Validation: Checks attendance, allowances, and deductions before processing.
- Performance Management: Automates reminders, form submissions, and review cycles.
As a result, HR teams gain more time for strategic work.
3. Sales & Marketing
Automation enables revenue teams to respond faster and manage pipeline activities more efficiently.
- Lead Assignment: Distributes leads based on geography, industry, or scoring models.
- Proposal Workflows: Automates content creation, internal reviews, and approvals.
- Contract Lifecycle Management: Tracks drafts, negotiations, approvals, and renewals.
This ensures quick turnaround and improves customer engagement.
4. IT Service Management (ITSM)
IT teams rely heavily on automation to keep systems running.
- Ticket Triage: Classifies issues, assigns priorities, and routes them to the right teams.
- Access Provisioning: Automatically grants or revokes access based on roles.
- Incident Resolution: Triggers predefined scripts or alerts to resolve issues faster.
This reduces downtime and improves service quality.
5. Supply Chain & Operations
Operational processes become more reliable with automation.
- Purchase Order Processing: Automates creation, approvals, and vendor notifications.
- Inventory Updates: Syncs stock levels across systems in real time.
- Shipment Tracking: Sends automated updates and records movement across hubs.
These improvements help maintain continuity and reduce delays.
6. Legal & Compliance
Legal teams benefit greatly from structured and transparent workflows.
- Policy Reviews: Tracks updates, approvals, and version control.
- Risk Assessments: Automates scoring, review cycles, and reporting.
- Regulatory Reporting: Generates accurate submissions with audit-ready data.
This reduces compliance risk and improves oversight.
AI and LLM-Driven Workflow Automation
AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) are bringing a new level of intelligence to workflow automation. To begin with, LLMs enhance workflows through advanced language capabilities such as natural language processing (NLP), summarization, and data extraction. This allows systems to read emails, understand documents, and extract key information without manual effort.
In addition, AI agents can now perform multi-step tasks autonomously. Instead of automating only simple actions, these agents can plan steps, call APIs, update systems, and complete full processes from start to finish. This makes automation more flexible and capable of handling real-world enterprise tasks.
Common examples include:
- Document Classification: Automatically identifying document types such as invoices, contracts, or tickets.
- Compliance Workflows: Checking documents for missing information, inconsistencies, or policy violations.
- CRM Updates: Reading customer messages and updating lead status or support tickets instantly.
Moreover, LLM-powered automation helps teams make faster decisions by analyzing unstructured content, generating summaries, and highlighting insights that would otherwise take hours.
Looking ahead, the future of workflow automation is moving toward fully autonomous business processes. Predictive workflows will anticipate issues, recommend actions, and even trigger preventive steps automatically. As AI agents mature, organizations will shift from reactive automation to proactive and intelligent operations—transforming how enterprises manage work at scale.
Challenges in Implementing Workflow Automation
Implementing workflow automation offers major benefits, but organizations often face several challenges during adoption. Below are the key issues, explained clearly and simply.
1. Legacy System Compatibility
Many enterprises still use old systems that lack APIs or integration support. This makes it difficult to connect them with modern automation tools.
2. Security and Governance Concerns
Automated workflows must follow strict security rules, maintain audit trails, and protect sensitive data. Ensuring proper access control and governance can be complex.
3. Resistance to Change
Employees may feel uncertain about new tools or worry about how automation impacts their roles. Without training and communication, adoption becomes slow.
4. Unstructured Data Problems
Emails, PDFs, images, and handwritten documents are difficult to automate because they require OCR or AI-based extraction before processing.
5. Inadequate Process Mapping
If a process is unclear or poorly defined, automation will simply repeat inefficiencies. Proper mapping and redesign are essential.
6. Vendor Selection Issues
With many automation platforms available, choosing the right one—based on features, cost, and integration needs—can be challenging.
7. Scalability and Maintenance Costs
Workflows require ongoing monitoring, updates, and optimization. As automation grows, maintenance costs and complexity can also increase.
Enhance Your Enterprise Security With AI-Powered Surveillance
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Implementation Roadmap of Enterprise Workflow Automation
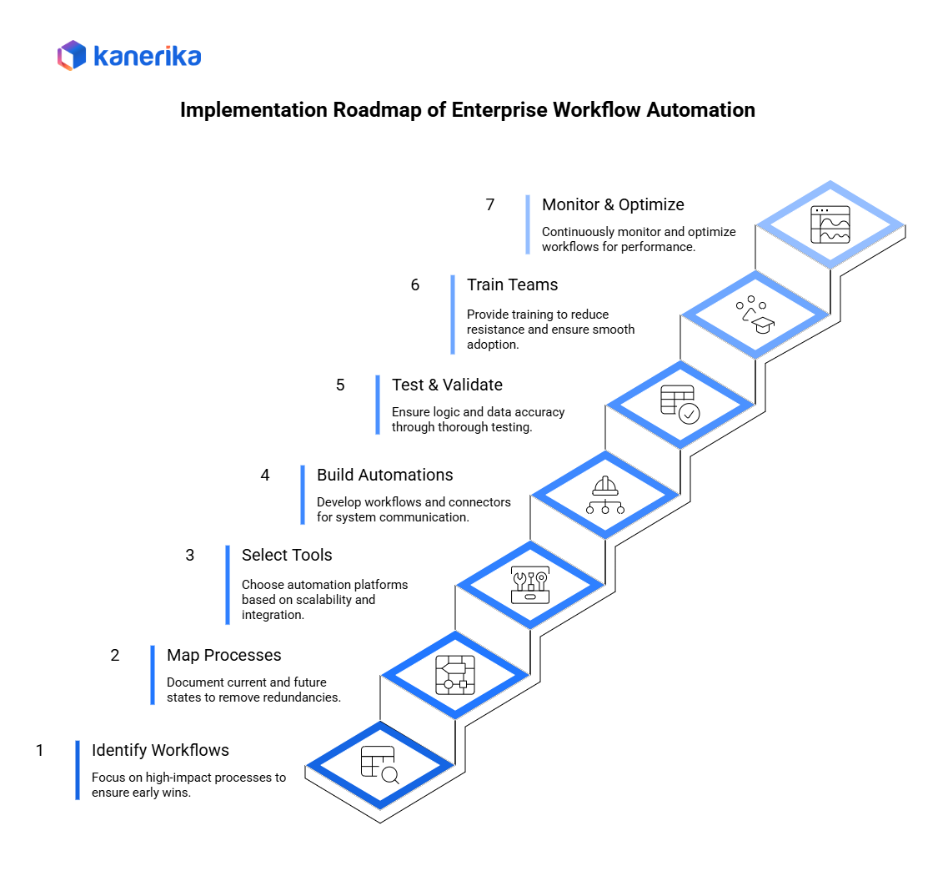
Implementing enterprise workflow automation requires a structured and well-planned approach. Below is a clear roadmap that organizations can use to ensure successful adoption.
Step 1: Identify High-Impact Workflows
To begin with, focus on processes that consume the most time, involve multiple handoffs, or frequently cause delays. Prioritising high-impact workflows ensures early wins and strong ROI.
Step 2: Map Current and Future State Processes
Next, document how each workflow currently operates. Then define the ideal future state using automation. This helps remove redundancies and avoid automating broken processes.
Step 3: Select Tools and Architecture
Choose automation platforms based on scalability, security, integrations, and ease of use. Consider whether you need BPM tools, RPA, iPaaS, or AI-driven automation.
Step 4: Build Integrations and Automations
Develop workflows, connectors, and rules. Ensure systems like ERP, CRM, HRMS, and databases can communicate through APIs or RPA bots.
Step 5: Test & Validate
Thorough testing is essential. Validate logic, data accuracy, alerts, and approval paths. Involve business users early to confirm real-world behaviour.
Step 6: Train Teams
Provide training sessions, documentation, and hands-on practice. Clear communication reduces resistance and ensures smooth adoption.
Step 7: Monitor, Optimize, Scale
Finally, monitor workflows continuously using dashboards and logs. Optimize steps based on performance data and scale automation gradually across functions.
Additional Best Practices
- Establish governance for approvals, access, and standards.
- Maintain documentation for every workflow.
- Track KPIs like cycle time, error rates, and cost savings.
- Invest in continuous improvement to keep automation relevant and efficient.
Elevate Your Enterprise Workflows with Kanerika’s Agentic AI Solutions
Kanerika brings deep expertise in AI/ML and purpose-built agentic AI to help businesses solve real challenges and drive measurable impact. From manufacturing to retail, finance to healthcare—we work across industries to boost productivity, cut costs, and unlock smarter ways to operate.
Our custom-built AI agents and GenAI models are designed to tackle specific business bottlenecks. Whether it’s streamlining inventory management, speeding up information access, or making sense of large video datasets—our solutions are built to fit your workflows.
Use cases include fast document retrieval, sales and financial forecasting, arithmetic data checks, vendor evaluation, and intelligent pricing strategies. We also enable smart video analysis and cross-platform data integration—so your teams spend less time hunting for answers and more time acting on them.
At Kanerika, we don’t just build AI. We will help you use it meaningfully.
Partner with us to turn everyday tasks into intelligent outcomes.
Boost ROI Through Data Automation – Start Your Journey Today!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Automation Services.
FAQs
1. What are Enterprise Workflow Automation Solutions?
Enterprise workflow automation solutions are systems that streamline and automate business processes using rules, integrations, AI, and RPA to reduce manual work and improve efficiency.
2. How do workflow automation solutions benefit an organization?
They reduce errors, shorten cycle times, improve compliance, increase productivity, and lower operational costs by automating repetitive and multi-step processes.
3. What technologies are used in enterprise workflow automation?
Key technologies include workflow orchestration engines, RPA, AI/LLMs, integration platforms (APIs/iPaaS), rules engines, and cloud-based monitoring tools.
4. How is enterprise workflow automation different from basic task automation?
Task automation handles simple, single actions. Enterprise workflow automation manages end-to-end processes across systems, teams, and data sources with full governance and scalability.
5. Which departments benefit the most from workflow automation?
Finance, HR, sales, IT service management, supply chain, legal, and compliance teams see major gains from faster processing, accuracy, and transparent workflows.
6. What common challenges arise during automation implementation?
Challenges include legacy system compatibility, security concerns, unclear process mapping, user resistance, vendor selection, and long-term scalability needs.
7. How can an organization get started with workflow automation?
Begin by identifying high-impact processes, mapping current workflows, selecting the right tools, building integrations, testing, training teams, and continuously optimizing.










