Did you know Capital One spent eight years and mobilized over 11,000 people to completely exit its physical data centers? They became the first U.S. bank to report a complete move from legacy on-premises data centers to the public cloud, while most companies still struggle with migrations that drag on for years. More than 80% of data migration projects fail to meet deadlines or exceed budgets, yet Capital One pulled off one of the largest financial sector migrations in history.
Shifting data from one system to another may sound simple, but it is often one of the toughest tasks businesses face. The process demands speed, accuracy, and minimal disruption, yet even small mistakes can lead to costly downtime or compliance risks. That is where the right data migration tools come in. They not only streamline the transfer but also reduce manual work and errors. Whether it is a global bank consolidating its systems or a startup upgrading to modern platforms, having dependable tools can save time and money. So which ones stand out as the most reliable? Let’s look at the 10 best data migration tools.
Key Takeaways
- Data migration is no longer a backend IT activity but a business-critical initiative that impacts cost, compliance, scalability, and long-term digital growth.
- Most migration failures stem from poor planning, data quality issues, and manual execution, making the right tools and automation essential for success.
- Modern data migration tools handle complex tasks such as ETL, schema mapping, validation, security, and real-time synchronization, significantly reducing risk and downtime.
- Different tools serve different needs, from open-source flexibility and cloud-native services to enterprise-grade automation platforms designed for large-scale modernization.
- Selecting the right migration tool depends on data volume, system complexity, security requirements, budget, and internal technical expertise.
- Kanerika’s FLIP automation accelerates legacy-to-modern platform migrations by preserving business logic, reducing manual effort, and delivering faster, secure, and scalable outcomes.
What is Data Migration?
Data migration is the transfer of data from one system, storage device, or format to another. It is an essential move for businesses interested in upgrading IT infrastructure, consolidating data centers, adopting cloud-based platforms, or consolidating information from various sources. Properly implemented data migration will provide the data with accessibility, security, accuracy, and usefulness of the data both during and after the transition.
Data migration is a process for transferring structured and unstructured data, such as databases, files, applications, and documents, between environments. Such a transfer can be intra-system, such as a software version change, or inter-system, such as replacing an on-premises server with a cloud-based one. Data cleansing, transformation, validation, and testing are usually involved in the process to ensure data integrity.
Popular causes of data migration are:
- System Upgrades: Legacy systems to modern high-performance systems.
- Cloud Adoption: Moving data and applications to the cloud to be scaled, flexible, and cost-effective.
- Data Consolidation: The process of consolidating information from multiple sources to enable centralized reporting and analytics.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Applying acquired information to one platform.
Migration of data, however, may be a complex and time-consuming process, associated with risks of data loss, downtimes, and inconsistencies. This is where up-to-date data migration tools and automation platforms come in. They simplify data flow, enhance consistency, security, and compliance, minimize manual work, and facilitate quicker, more reliable migrations with minimal business dependency.
RPA for Data Migration: Best Practices and Considerations
Streamline your data migration by following RPA best practices for efficiency and precision.
What Are Data Migration Tools?
Data migration tools are programs that help you move data from one place to another without manual effort. Think of them as smart assistants that handle all the technical work. They schedule transfers, connect different systems, change data formats when needed, double-check everything moved correctly, and show you what’s happening. These tools prevent costly mistakes, keep your business running smoothly during transfers, and protect your data from damage or loss.
1. On-Premise Data Migration Tools
These tools get installed directly on your company’s computers and servers. All the work happens inside your building, so your data stays on your network the entire time.
Key Features
- You control everything about how the migration works, from security rules to exactly how data gets handled.
- Great for companies with strict regulations or sensitive data that legally can’t leave their facilities.
- They plug right into your existing databases, software, and older systems without needing internet connections.
- Your IT team needs solid technical skills to install, configure, and maintain these tools properly.
Examples
- Informatica PowerCenter: A business platform that many large companies use for complex data moves that require lots of quality checking and transformation.
- IBM InfoSphere DataStage: A heavy-duty tool that processes huge amounts of data fast and handles complicated changes between very different systems.
2. Cloud Data Migration Tools
Cloud companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google offer these as online services. They focus on getting your data into the cloud or moving it between different cloud services.
Key Features
- Built to work perfectly with AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and similar platforms right out of the box.
- Simple interfaces that regular business users can understand, plus connections to popular software already set up.
- Handle massive data volumes and can keep systems talking to each other continuously.
- Your data security depends on whatever the cloud provider offers, which might not fit every company’s needs.
Examples
- AWS Database Migration Service: Amazon’s service that moves databases to their cloud safely while keeping your business running normally.
- Azure Database Migration Service: Microsoft’s tool for getting databases into Azure with barely any interruption to your daily operations.
3. Open-Source Data Migration Tools
Free programs where you can look at and change the code however you want. Companies choose these to save money and get exactly what they need.
Key Features
- It costs nothing to use, and you can customize every detail to match your specific business requirements.
- Way more flexible than paid options since you can modify anything that doesn’t work for your setup.
- Require more technical knowledge to install, monitor, and troubleshoot than commercial alternatives.
- Backed by communities of programmers who constantly improve the tools and help solve problems.
Examples
- Apache Kafka: An extremely powerful real-time data streaming system that offers unlimited flexibility but needs expert developers to implement successfully.
- Airbyte: A free platform that makes building data connections simple through an easy interface, even for non-technical people.
Data Consolidation: Mastering the Art of Information Management
Optimize your information management by mastering data consolidation for clearer insights and better decision-making.
What are the Key functionalities of Data Migration Tools?
Data migration tools work like professional movers for your digital stuff. They handle the heavy lifting and make sure your information gets to its new location without getting lost or broken. These tools have gotten much better over the years because businesses need to move increasingly complex data between systems. What used to require teams of technical experts can now be done by regular business users with the right tools. Here’s what these tools actually do for you:
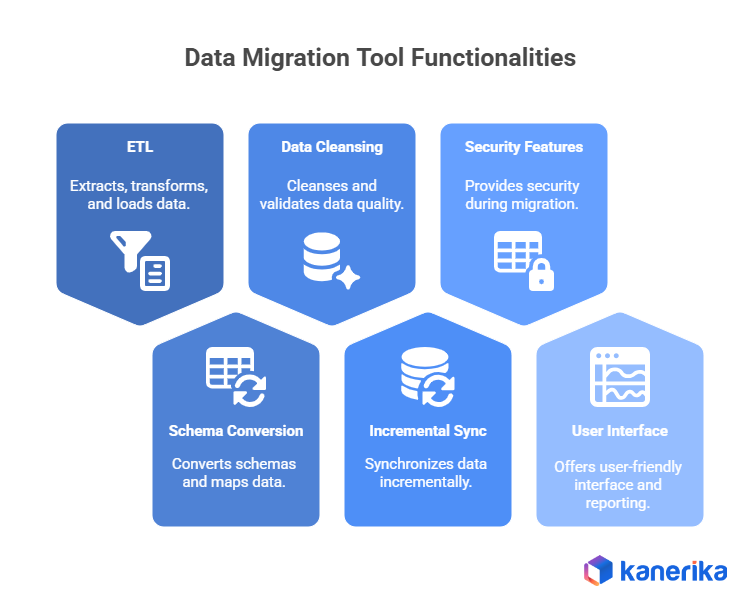
1. Data Extraction, Transformation & Loading (ETL)
ETL is the core of any data migration that actually works. It’s a three-step process that moves your data properly from where it is now to where it needs to go. Most companies discover that doing ETL right saves them weeks of fixing problems later and prevents expensive mistakes that hurt their business.
- Extraction: Tools extract data from your current system, regardless of whether it’s in databases, Excel files, or other formats. They can handle messy data structures and huge amounts of information without crashing.
- Transformation: Your raw data almost always needs changes to work in the new system. Migration tools clean things up by removing duplicates and correcting errors. They also filter out stuff you don’t want and reshape the data to fit where it’s going.
- Loading: After everything is cleaned up, the tools safely move your data into the new system. This includes figuring out where each piece of information belongs in the target system.
2. Schema Conversion & Data Mapping
Schema differences across systems are among the biggest headaches in data migration. What works perfectly in one database often won’t translate directly to another platform. Smart mapping tools have become essential for connecting these technical gaps and making sure data actually works across different systems.
- Schema Comparison: Tools examine both your old and new systems to find differences and potential trouble spots.
- Visual Mapping Tools: Simple interfaces let you drag and drop to show how information from your old system connects to the new one.
- Data Type Conversion: Tools change data formats like dates or money amounts to work correctly in the target system.
3. Data Cleansing & Validation
Bad data quality can ruin even the most technically perfect migration. Research shows that messy data costs businesses millions in wasted time and poor decisions. Good cleansing and validation features help companies start clean in their new systems with reliable information they can actually use.
- Identify & Remove Duplicates: Eliminate duplicate records to avoid messy data in your new system.
- Standardize Formatting: Make sure everything follows the same format, like date styles or measurement units.
- Data Validation: Tools check for missing information, incorrect entries, and quality issues before moving data.
4. Incremental Data Synchronization
Your business can’t stop running during migration, which means data keeps changing while you’re moving it. Incremental synchronization solves this problem by keeping both systems up to date throughout the process. This approach cuts down downtime and lets users keep working normally during the switch.
- Change Data Capture: Tools find what changed in your source data after the main migration finished.
- Incremental Updates: Only new or changed information gets moved over, keeping both systems in sync without starting from scratch.
- Scheduled Synchronization: Automatically grab and apply updates at regular times you choose.
5. Security Features
Data breaches during migration can expose sensitive customer information and put you in regulatory trouble. Security features are now essential for most organizations, especially those handling financial, healthcare, or personal data. Strong security controls protect both the migration process and the valuable information being moved.
- Encryption: Tools scramble your data as it moves and is stored, keeping sensitive information safe from hackers.
- Access Control: Restrict who can access the migration process and the data based on their job roles and what they’re allowed to see.
- Auditing & Logging: Track what users did and how data changed during migration for security and fixing problems later.
6. User-Friendly Interface & Reporting Tools
Complex migrations used to need teams of specialized programmers and database experts. Modern tools make the process easier with simple interfaces that business users can understand and operate. Good reporting helps project managers track progress and catch issues before they become major disasters.
- Intuitive Interface: Well-designed screens make setting up and running migrations straightforward.
- Drag-and-Drop Functionality: Visual tools let you define how data connects and flows without writing complicated code.
- Real-time Monitoring & Reporting: Watch progress, spot errors, and see how much computer power the migration is using.
- Detailed Reports: Create summaries of the migration process, data quality measurements, and any problems for future reference.
Top 10 Data Migration Tools
1. FLIP by Kanerika
FLIP takes your old systems like SSIS, SSRS, and Informatica and automatically converts them to modern platforms like Talend, Power BI, and Microsoft Fabric. No manual coding required, which saves months of developer time. The platform grabs your metadata, converts your business logic without breaking anything, and handles the entire deployment process. Your team can focus on actual business priorities instead of wrestling with technical problems that eat up budgets. Companies using FLIP report significantly faster migration times compared to manual approaches.
Best for: Companies stuck with legacy systems who want to modernize without hiring an army of expensive developers or consultants.
2. Stitch Data
Stitch Data keeps things simple with drag-and-drop features and real-time data copying. Perfect when you need to move data between cloud apps and databases without getting too complicated. The interface makes sense to non-technical users, which means you don’t need a PhD in computer science to operate it. They let you try it for free before you buy, which is always nice when you’re not sure it’ll work with your specific setup.
Best for: Straightforward cloud migrations when you don’t want to learn complicated software or spend weeks on training.
3. AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
Amazon’s dedicated tool for moving databases to its cloud platform. Works whether you’re moving between similar databases, like MySQL to MySQL, or between completely different types, like Oracle to PostgreSQL. Scales up automatically when you need more processing power and includes fault tolerance to keep your data safe if something goes wrong during transfer. Connects easily with other AWS services if you’re already using their ecosystem for storage or computing.
Best for: Getting databases into AWS infrastructure without major headaches or extended downtime periods.
4. Azure Database Migration Service
Microsoft’s version for moving databases to the Azure cloud. Supports a wide range of database types, including SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle. You can choose between fast migrations with some planned downtime or slower continuous sync options that keep your business running normally. Works particularly well if you already use other Microsoft products, such as Office 365 or Windows Server.
Best for: Database moves to Azure, especially for organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
5. XMigrate
Free, open-source tool that works through command-line interfaces. Good for technical folks who like having full control over every aspect of the migration process. You can customize how it transforms data, write custom scripts, and modify the source code as needed to meet specific requirements. No licensing fees ever, though you’ll need skilled developers to implement and maintain it properly.
Best for: Technical teams who prefer command-line tools and want a solution they can fully customize for unique business requirements.
6. Talend Open Studio
Another free, open-source option focused on moving and transforming data through ETL processes. Has a visual interface where you drag and drop components to build data pipelines without writing code. Works with lots of different data sources, including databases, flat files, cloud services, and APIs. Has an active community forum where users share solutions and help solve everyday problems.
Best for: ETL projects when you want free software with good community support and don’t mind learning open-source tools.
7. Fivetran
A cloud platform that’s really good at pulling data from different sources and automatically transforming it. Comes with ready-made connections to popular business software like Salesforce, HubSpot, Google Analytics, and major cloud data warehouses. Takes security seriously with encryption during transfer and storage, plus detailed access controls for sensitive data. Reduces the manual work typically required for data pipeline maintenance.
Best for: Automated moves from various business applications to cloud storage when strong security and minimal maintenance are priorities.
8. Matillion
Handles large, complex data migration projects through visual pipeline-building interfaces. Scales up for massive datasets that would choke other tools and supports complex transformations that require multiple processing steps. Built specifically for enterprise companies with demanding performance requirements and complex data relationships. Includes features for data quality monitoring and error handling throughout the migration process.
Best for: Large companies with complex data structures that need sophisticated processing and can’t afford migration failures.
9. IRI NextForm
Specializes in messy, complicated data that other tools struggle with or refuse to handle. Really shines when dealing with unstructured data, such as documents, emails, or legacy systems that store information in proprietary or outdated formats. Transforms everything into clean, standardized data for modern systems while preserving important business context. Integrates with other IRI products for comprehensive data management workflows.
Best for: Nightmare migrations involving old systems with messy data structures that need significant cleanup before they’re usable.
10. SnapLogic
Uses pre-built connectors they call “Snaps” to automate migration workflows through simple drag-and-drop interfaces. Handles real-time data integration scenarios where data needs to flow continuously between systems. Works for various migration patterns, including cloud-to-cloud transfers, on-premises-to-cloud moves, and hybrid environments. Includes monitoring tools to track data flow and catch problems before they impact business operations.
Best for: Quick migrations using ready-made connections when you need real-time data syncing and don’t want to build custom integrations from scratch.
| Tool | Features | Ideal Use Cases |
| FLIP | Automated legacy system transformation to modern platforms like Talend, Power BI, and Microsoft Fabric. | Organizations modernizing from legacy to cloud-native architectures. |
| Stitch Data | Cloud platform with drag-and-drop functionality and real-time data replication. | Simple to moderate cloud application and database migrations. |
| AWS DMS | AWS cloud service for homogeneous and heterogeneous database migrations with auto-scaling. | Database migrations to AWS cloud platform. |
| Azure Database Migration Service | Microsoft’s solution with online and offline migration options for various database sources. | Database migrations to Microsoft Azure cloud platform. |
| XMigrate | Open-source command-line tool with customizable data transformation for relational databases. | Command-line users migrating between relational databases. |
| Talend Open Studio | Open-source ETL platform with drag-and-drop interface and community support. | ETL processes for open-source tool users. |
| Fivetran | Cloud platform with pre-built connectors, automated transformation, and strong security features. | Automated migrations to cloud data warehouses with security focus. |
| Matillion | Visual ETL solution scaling for large datasets and complex enterprise transformations. | Complex enterprise ETL workflows requiring scalability. |
| IRI NextForm | Specialized tool for complex data formats, unstructured and legacy data transformation. | Complex data structures and legacy system migrations. |
| SnapLogic | Intelligent platform with pre-built connectors and real-time data integration capabilities. | Real-time data integration using pre-built connectors. |
What Are the Advantages of Using Data Migration Tools
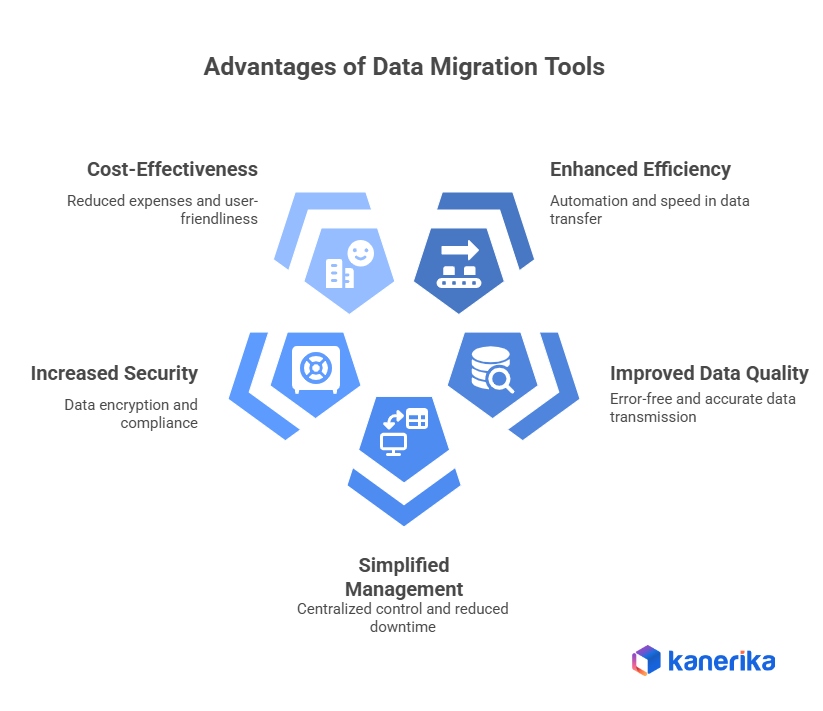
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Automation
Data migration tools excel at accelerating the process and reducing workload. They automate repetitive tasks like data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL), eliminating the need for error-prone manual scripting and coding. Additionally, these tools efficiently handle large data volumes, significantly speeding up migration times.
2. Improved Data Quality and Accuracy
By improving data quality, data migration solutions ensure error-free data transmission. Prior to migration, they fix formatting errors, find and eliminate duplicate records, and ensure data integrity. Moreover, they can alter data to conform to the structure of the target system, ensuring accurate data representation in the relocated setting.
3. Simplified Management and Reduced Risk
These tools give you a clear perspective and enable real-time monitoring by giving you a central platform to manage the entire migration process. Furthermore, automation reduces the downtime that comes with data movement, guaranteeing that your company’s operations are not adversely affected. Built-in error management and rollback features let you recover from possible problems and resume the migration process if needed, which further lowers risks.
4. Increased Security and Compliance
Data migration tools prioritize data security and compliance. They encrypt sensitive data during transfer to safeguard it, and access control mechanisms restrict unauthorized access. Furthermore, they provide detailed audit trails and logs of the migration process, ensuring compliance with data security regulations and facilitating troubleshooting if needed. Many tools even cater to specific industry regulations and compliance standards.
5. Cost-Effectiveness and User-Friendliness
Data migration tools are more affordable than manual techniques. They lower project expenses by freeing up critical IT resources through task automation and a reduction in human labor. Furthermore, a lot of tools have drag-and-drop functionality and user-friendly interfaces, making them usable even by non-technical people. The automation and data validation features offered by these tools can significantly reduce the risk of errors, leading to potential cost savings in the long run by avoiding the need to fix errors or re-migrate data due to inaccuracies.
How to Select the Right Data Migration Tool in 2026?
Selecting the right data migration tool is crucial for a smooth and successful transition of your valuable information. Some key factors to consider when making your choice include:
1. Source and Target Data Types
The compatibility between your source and target systems plays a vital role. Consider the types of data you’re migrating (databases, flat files, cloud storage) and the target system’s capabilities. Some tools specialize in migrating specific data formats, while others offer broader support for diverse data types. Choose a tool that seamlessly handles both your source and target data structures.
2. Data Volume and Migration Complexity
The size and complexity of your data migration project significantly influence your tool selection. If you’re dealing with massive datasets or intricate migrations involving data transformation and cleansing, a robust data migration tool with scalability features is essential. Conversely, for smaller, straightforward migrations, a simpler tool might suffice.
3. Budget and Technical Expertise
Data migration tools come with varying costs and require different levels of technical knowledge for operation. Carefully evaluate your budget constraints and the technical skills available within your IT team. Some tools cater to users with limited technical expertise through user-friendly interfaces and pre-built connectors. However, more powerful tools might require advanced programming skills to configure and manage effectively.
4. Security Requirements and Compliance Regulations
Security and compliance are paramount concerns when migrating sensitive data. Ensure the tool you choose offers robust security features like encryption for data in transit and at rest, as well as access controls to restrict unauthorized access. Additionally, if your industry adheres to specific data privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), verify that the tool supports compliance with those regulations.
Data Visualization Tools: A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right One
Choose the perfect data visualization tool to transform complex data into clear, actionable insights for your business success.
Best Practices for Successful Data Migration
Ensuring a smooth and successful migration requires careful planning and execution. Below are some best practices:
1. Pre-Migration Planning and Preparation
- Define Scope and Goals: Specify what data needs to be moved (all customer information, product details, etc.), where it needs to go (new cloud storage or an updated database), and the results you hope to achieve (better data accessibility, enhanced analytics capabilities).
- Inventory and Assessment: List all the source data systems and assess their volume (gigabytes, terabytes), complexity (relational databases, flat files), and possible migration issues (inconsistencies in the data, incompatible formats).
- Tool Selection: Select a data migration tool based on its compatibility with the technical know-how, budget, and scope of your project. Think about features such as data cleansing, data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL), and security features (see previous sections for more information on features).
- Resource Allocation: Put together a committed team of people with the technical know-how (system administrators, data engineers) and data expertise to oversee the migration process.
- Communication Strategy: Create a communication strategy to inform all stakeholders (management, end users) about the migration process, schedule, and potential hiccups (e.g., system update downtime).
2. Data Quality Assessment and Cleanup
- Data Profiling: Evaluate the accuracy of your source data, identifying potential errors, missing values, and inconsistencies (e.g., inconsistent date formats and duplicate entries).
- Data Cleansing: Prior to migration, clean the source data so that it is accurate and consistent. This could entail standardizing data values (e.g., making sure consistent date formats across all records), eliminating duplicates, and fixing formatting problems.
- Data Transformation Planning: Define how data must be transformed to conform to the target system’s schema (data structure) and data types (e.g., converting text fields to numerical values for calculations).
3. Testing and Validation Procedures
- Develop a Test Plan: Create a thorough test plan that details the various migration scenarios (complete data migration, partial migration of specific data sets), as well as the features to be verified (system performance, data integrity).
- Staging Environment: To facilitate testing, set up an exact replica of the target system. This way, you can verify data integrity and evaluate the migration process without affecting the production environment, the actual system that users depend on.
- Thorough Testing: Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of every facet of the migration process, including data extraction, transformation, loading, and destination system operations. This guarantees that data is transported accurately and performs as planned.
- Data Validation: Compare the migrated data in the target system with the source data to ensure that it is accurate and complete.
4. Monitoring and Post-Migration Optimization
- Monitoring: Following the migration, monitor the target system to identify any performance problems (such as sluggish loading times or crashes) or data irregularities (such as missing data or incorrect values).
- Performance Optimization: Optimal performance after data migration can be achieved by fine-tuning the target system. This could entail scaling resources (adding additional processing power) if necessary, optimizing queries for improved efficiency, and indexing data for faster retrieval.
- Post-Migration Review: To find areas that need improvement for upcoming migrations, do a comprehensive analysis of the entire process. This involves examining probable problems that might arise, accomplishments, and lessons learnt.
Kanerika Delivers Seamless Data Platform Migration Through Automation
Kanerika can help your business seamlessly migrate to modern data platforms using our FLIP migration accelerators. We specialize in transforming data pipelines from legacy systems like Informatica to Talend, SSIS to Fabric, Tableau to Power BI, and SSRS to Power BI. Our expertise ensures your data migration is smooth and minimizes disruptions to your operations.
Moving to modern platforms offers significant advantages, including enhanced performance, scalability, and better integration with emerging technologies such as AI and machine learning. These platforms allow for faster data processing, real-time analytics, and a more user-friendly interface, empowering your teams to make data-driven decisions with greater efficiency.
By partnering with Kanerika, businesses can streamline the migration process, reduce manual effort, and lower the risk of errors. Our tailored automation solutions are designed to meet your specific needs, ensuring that the migration is not just efficient but also aligned with your business goals. With our experience across various industries, we provide end-to-end support from planning to execution, helping you optimize costs, improve productivity, and unlock the full potential of your data in a modern, agile environment. Let us be your trusted partner in your data platform transformation.
Achieve Operational Excellence with Proven Data Migration Solutions
Partner with Kanerika Today!
FAQs
Which tool is used for data migration?
There’s no single “best” tool for data migration; the right choice depends on your specific data, source, and target systems. We typically use a combination of specialized migration software, scripting languages (like Python), and potentially ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools, tailoring the approach to each project’s unique needs. Ultimately, it’s about choosing the tools that offer the best balance of efficiency, accuracy, and security for your data.
What are the 4 types of data migration?
Data migration isn’t a one-size-fits-all process. We typically see four main approaches: big bang (all at once), phased (incremental rollouts), parallel (old and new systems run concurrently), and hybrid (a blend of these strategies). The best choice depends heavily on your system’s complexity and tolerance for downtime. Each method presents unique risks and rewards.
What is ETL in data migration?
ETL in data migration is the crucial process of getting your data ready for its new home. It involves “Extracting” data from its source, “Transforming” it into a consistent and usable format, and then “Loading” it into the target system. Think of it as a data makeover before the big move. Without ETL, your migrated data would be messy and unreliable.
What are the best ETL tools for data migration?
Choosing the “best” ETL tool depends heavily on your specific needs (data volume, complexity, budget, and existing infrastructure). Popular options range from cloud-based services like Informatica Intelligent Cloud Services or AWS Glue, offering scalability and managed services, to open-source solutions like Apache Kafka or NiFi for greater control and customization. Ultimately, the ideal tool balances ease of use with the power to handle your data’s unique characteristics.
Is Informatica a data migration tool?
Informatica is more than just a data migration tool; it’s a comprehensive data integration platform. While data migration is a key feature, it also handles data transformation, cleansing, and ongoing data management tasks within a single environment. Think of it as a Swiss Army knife for data – migration is one tool among many.
What is migration tool in AWS?
AWS migration tools are services that help you move your existing IT infrastructure and applications to the AWS cloud. They range from simple import tools for databases to complex, automated services for entire data centers. The best tool depends on your specific needs and existing systems; some offer simpler manual processes, while others provide fully managed, automated migrations. Choosing the right tool maximizes efficiency and minimizes downtime during your cloud transition.
Which tools are used to migrate files?
File migration tools vary wildly depending on the scale and type of transfer. For small jobs, simple drag-and-drop or copy-paste suffices. Larger migrations often involve specialized software like robocopy (Windows) or rsync (Linux/macOS), or even cloud-based services offering bulk file transfer. The best choice hinges on your specific needs and data volume.
What is data migration software?
Data migration software automates the complex process of moving data from one system to another. It handles everything from extraction and transformation to loading and validation, ensuring data integrity throughout the transfer. Think of it as a highly specialized moving company for your digital assets, minimizing downtime and risk. This is crucial for upgrading systems, merging databases, or simply improving data organization.
What is the difference between LSMW and LTMC?
LSMW (Legacy System Migration Workbench) is an older SAP tool for migrating data, best suited for simpler, less-structured data uploads. LTMC (Logical Data Migration Cockpit) is its modern, more powerful successor, offering improved performance, greater flexibility, and better support for complex data structures and relationships. Think of LTMC as LSMW’s refined, upgraded version. Essentially, LTMC is generally preferred for new projects.
Is Syniti an ETL tool?
Syniti isn’t solely an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tool, though it incorporates ETL capabilities. It’s more accurately described as a comprehensive data management platform. Think of ETL as a crucial feature within a broader suite for data migration, cleansing, and governance. Its strength lies in handling complex data challenges beyond simple ETL processes.





