Azure Cosmos DB is becoming indispensable as organizations build globally distributed, always-on applications. As of 2025, over 3,699 companies across industries—from manufacturing to software—are using Cosmos DB to power their mission-critical workloads. Traditional databases often fall short when it comes to scalability, multi-region deployment, and low latency.
Azure Cosmos DB was designed to overcome these challenges. It’s a globally distributed, multi-model database service on Azure that offers turnkey global replication, SLA-backed low latency, and seamless scalability across JSON documents, key-value pairs, graphs, and more.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of Azure Cosmos DB—exploring its powerful features, real-world applications, pricing models, and best practices—to help you unleash its full potential for your next cloud-native project.
What is Azure Cosmos DB?
Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft’s fully managed, globally distributed NoSQL database service, officially launched in 2017 as the evolution of Azure DocumentDB. It was built from the ground up to address the challenges of modern, cloud-native applications that demand global scale, low latency, and high availability.
Unlike traditional relational databases, Cosmos DB is a multi-model platform. It supports a wide variety of data models, including document, key-value, column-family, graph, and table APIs. This flexibility means developers can choose the right data model for their application without being locked into a single database type.
One of its most powerful features is global distribution. With just a few clicks, data can be replicated across multiple Azure regions, enabling applications to deliver millisecond response times to users worldwide. This is backed by comprehensive SLAs covering availability, latency, consistency, and throughput, making it a dependable choice for mission-critical applications.
Cosmos DB is also designed to simplify operations. As a fully managed service, it takes care of infrastructure, patching, scaling, and security. Developers can focus on building applications while the database automatically handles horizontal partitioning, request unit (RU) scaling, and multi-region replication.
Core Features of Azure Cosmos DB
1. Global Distribution
One of the defining features of Azure Cosmos DB is its multi-region replication. With just a few clicks, data can be distributed across any number of Azure regions worldwide. This ensures users always interact with the closest data center, reducing latency and delivering a seamless global experience. Developers can also configure regions dynamically as their applications expand.
2. Multi-Model API Support
Cosmos DB is designed as a multi-model database, supporting a wide variety of APIs:
- SQL (Core API): Document-oriented querying.
- MongoDB API: Compatibility for MongoDB workloads.
- Cassandra API: Column-family storage for large-scale data.
- Gremlin API: Graph database capabilities.
- Table API: Key-value storage, similar to Azure Table Storage.
This flexibility means developers can use their existing skills and tools while leveraging Cosmos DB’s scalability.
3. Guaranteed Low Latency
Cosmos DB is engineered for speed at scale, offering less than 10-millisecond latency for both reads and writes at the 99th percentile. This makes it ideal for real-time applications like eCommerce, gaming, and IoT solutions where milliseconds matter.
4. Elastic Scalability
With horizontal partitioning and autoscale throughput, Cosmos DB can handle workloads of any size. Developers can start small and seamlessly scale to millions of requests per second without downtime or manual intervention.
5. Consistency Models
Unlike traditional databases that offer only strong or eventual consistency, Cosmos DB provides five consistency models:
- Strong
- Bounded Staleness
- Session
- Consistent Prefix
- Eventual
This gives developers fine-grained control to balance performance, availability, and data accuracy based on application needs.
6. High Availability
Cosmos DB offers 99.999% availability SLAs when configured with multi-region writes. This ensures that mission-critical applications can continue to function even during regional outages.
7. Integration with Azure Ecosystem
Cosmos DB integrates seamlessly with the broader Azure ecosystem, including:
- Azure Functions for serverless apps.
- Azure Synapse Analytics for advanced analytics.
- Azure Event Hubs for event-driven pipelines.
This integration allows developers to build powerful, end-to-end cloud solutions without complex wiring.

Azure Cosmos DB Architecture
Azure Cosmos DB is built on a distributed, partitioned architecture designed to deliver global scalability with predictable performance.
1. Partitioning and Distribution Model
Cosmos DB uses horizontal partitioning to handle massive datasets. Data is divided into logical partitions based on a partition key (e.g., customer ID, region). These logical partitions are then mapped to physical partitions managed by the system. This design ensures workloads are evenly distributed, preventing hotspots and enabling virtually unlimited scale.
2. Role of Request Units (RUs)
Performance in Cosmos DB is measured using Request Units (RUs), a normalized currency for throughput. Every operation—whether a read, write, or query—consumes RUs. Developers can provision throughput in terms of RUs per second, ensuring predictable performance regardless of workload complexity. Autoscale mode allows RUs to adjust dynamically with demand, avoiding under- or over-provisioning.
3. Multi-Region Architecture
Cosmos DB’s architecture is multi-master and multi-region. Applications can replicate data across any number of Azure regions worldwide. By placing data close to users, Cosmos DB guarantees sub-10ms latency for reads/writes. Multi-region writes also enable applications to accept updates from different regions simultaneously, improving responsiveness for global users.
4. Replication, Consistency, and Fault Tolerance
Replication is central to Cosmos DB’s fault tolerance. Each region hosts multiple replicas of data across fault domains. Developers can choose from five consistency models (from strong to eventual) to balance latency with data accuracy. In case of a regional failure, traffic is automatically rerouted to healthy regions, ensuring continuous availability with 99.999% SLA.

Source – Mircosoft
Benefits of Using Azure Cosmos DB
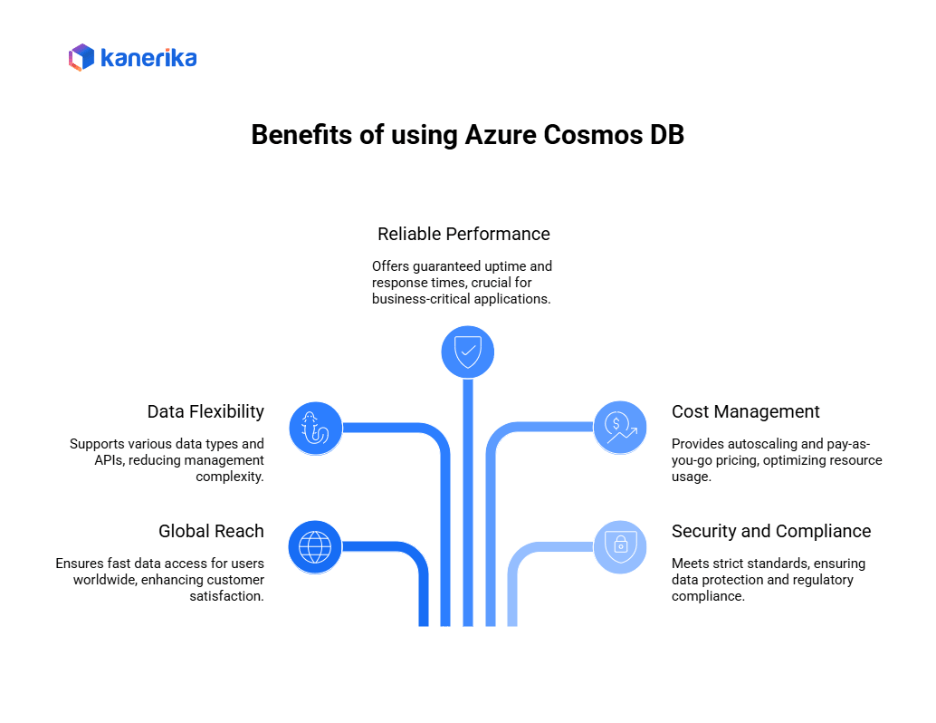
1. Serving Users Around the World
Azure Cosmos DB lets you place data close to your users no matter where they live. Customers in Japan get fast responses from servers in Tokyo, while European users access data from Amsterdam or Dublin. This global reach eliminates slow loading times that frustrate international customers.
Plus, you can add new regions with just a few clicks as your business expands. There’s no need to rebuild your application or learn new deployment processes when entering new markets.
2. Flexibility for Different Data Types
You can use the same database for different types of applications and data structures. Your web app might use the SQL API for customer profiles, while your recommendation engine uses the Graph API to track relationships between products. This flexibility means fewer databases to manage and maintain.
Teams can pick the API they already know instead of learning completely new systems. MongoDB developers keep using MongoDB syntax, while SQL experts stick with familiar queries.
3. Reliable Performance You Can Count On
Microsoft backs Cosmos DB performance with money-back guarantees. If response times exceed 10 milliseconds or uptime drops below 99.999%, you get service credits. This reliability matters for business-critical applications where downtime costs money and damages reputation.
These guarantees give you confidence when planning capacity and setting customer expectations. You know the database will perform consistently even during traffic spikes.
4. Smart Cost Management
You pay only for the computing power and storage you actually use. The system automatically scales resources up during busy periods and down during quiet times. This prevents paying for idle capacity while ensuring applications stay responsive when needed.
Autoscaling means you don’t need to guess future traffic patterns or over-provision resources. The database adapts to real usage automatically.
5. Security and Compliance
Cosmos DB meets strict security standards including ISO certifications, HIPAA for healthcare data, and GDPR for European privacy requirements. Data gets encrypted both in transit and at rest, with detailed access controls that track who accesses what information.
Azure Cosmos DB vs Other Databases
Azure Cosmos DB is often compared with relational and NoSQL databases. Each has unique strengths and trade-offs, so the right choice depends on your application’s requirements.
1. Cosmos DB vs Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database is a relational database designed for structured data and transactional workloads (OLTP). It excels in ACID compliance and complex joins. Cosmos DB, however, is schema-less, globally distributed, and built for large-scale NoSQL workloads.
While SQL Database offers strong relational features, Cosmos DB provides multi-region writes, lower latency, and elastic scalability across unstructured and semi-structured data.
2. Cosmos DB vs MongoDB Atlas
MongoDB Atlas is a popular NoSQL document database with a flexible schema. It supports rich queries and aggregation pipelines. Cosmos DB supports a MongoDB-compatible API, making migration easier.
Additionally, the advantage of Cosmos DB lies in its global distribution, guaranteed SLAs, and multi-model support beyond just documents (key-value, graph, etc.). However, MongoDB Atlas can be more cost-effective for single-region workloads.
3. Cosmos DB vs Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB is AWS’s flagship NoSQL database. Both DynamoDB and Cosmos DB offer global scale, millisecond latency, and high availability. DynamoDB integrates deeply with AWS services, while Cosmos DB benefits from tight Azure ecosystem integration (Functions, Synapse, Event Hubs).
Cosmos DB offers five consistency models, giving developers more flexibility, while DynamoDB provides eventual consistency by default with limited strong consistency options. Pricing is similar, though Cosmos DB’s RU-based model provides more predictable performance guarantees.
| Feature | Cosmos DB | Azure SQL DB | MongoDB Atlas | Amazon DynamoDB |
| Model | Multi-model (NoSQL) | Relational (SQL) | Document (NoSQL) | Key-Value / NoSQL |
| Latency | <10 ms global | Low, region-specific | Low (region-based) | Low (global optional) |
| Scalability | Horizontal, multi-region | Vertical + limited sharding | Horizontal, region-based | Horizontal, global tables |
| APIs | SQL, Mongo, Cassandra, Gremlin | T-SQL | MongoDB Query Language | DynamoDB API |
| Consistency | 5 models (strong → eventual) | Strong (ACID) | Strong / eventual | Eventual, limited strong |
| Best For | Global apps, multi-model workloads | Structured OLTP apps | Document-centric apps | AWS-native, high-throughput apps |
Azure Cosmos DB Pricing & Cost Optimization
1. How Cosmos DB Pricing Works
Cosmos DB charges based on three main factors. Request Units (RUs) measure the computing power your operations need – simple reads cost 1 RU while complex queries might use 50 RUs. Storage costs depend on how much data you store, including indexes and backups. Network egress charges apply when data moves between regions or leaves Azure.
Understanding RU consumption helps predict costs. A typical web application might use 10-100 RUs per user request, so you can estimate monthly costs by multiplying expected traffic by RU usage.
2. Autoscale vs Provisioned Throughput
Provisioned throughput gives you a fixed number of RUs per second at a set price. This works well for predictable workloads but you pay for unused capacity during quiet periods.
Autoscale adjusts RUs automatically based on demand, scaling from 10% to 100% of your maximum setting. You pay only for RUs actually used, but autoscale costs slightly more per RU than provisioned throughput. Choose autoscale for variable workloads and provisioned for steady traffic.
3. Free Tier and Development Options
Azure offers 400 RUs per second and 5GB storage free every month, which covers small applications or development work. Plus, there’s a free 12-month trial with $200 credit for new Azure accounts.
For development environments, use lower RU settings and single regions to minimize costs while testing applications.
Cost Optimization Tips
- Choose smart partition keys that distribute data evenly across partitions. Poor partitioning creates hot spots that waste RUs and hurt performance.
- Monitor RU consumption using Azure portal metrics to identify expensive queries and optimize them. Set up alerts when RU usage exceeds budgets.
- Buy reserved capacity if you plan to use Cosmos DB long-term. One-year or three-year commitments offer significant discounts compared to pay-as-you-go pricing.
- Remove unused indexes and optimize query patterns to reduce RU consumption per operation.
Optimize Your Cloud Investment for Maximum Business Impact!
Partner with Kanerika Today!
Azure Cosmos DB Real-World Use Cases
1. Retail & eCommerce
Online stores use Cosmos DB to deliver personalized shopping experiences. The database tracks what customers view, buy, and search for, then suggests relevant products in real time. Meanwhile, inventory systems update stock levels across multiple warehouses and sales channels instantly.
Order processing benefits from Cosmos DB’s global distribution. When customers place orders, the system can route them to the nearest fulfillment center while keeping payment and shipping data synchronized worldwide. This reduces delivery times and improves customer satisfaction.
2. Gaming Applications
Game developers use Cosmos DB for real-time leaderboards that update instantly as players complete levels or achieve high scores. The low latency ensures competitive rankings stay current without delays that frustrate players.
Multiplayer games store session data, player profiles, and match history in Cosmos DB. The global distribution means players from different continents can join the same game with consistent performance. Plus, the flexible data models handle different game types from simple puzzle games to complex role-playing adventures.
3. IoT Applications
Manufacturing companies and smart cities use Cosmos DB to collect data from thousands of sensors simultaneously. Temperature monitors, traffic cameras, and equipment sensors send continuous streams of data that get processed and analyzed in real time.
The database handles massive data volumes from IoT devices while providing fast queries for dashboards and alerts. When sensor readings indicate problems, operators get notified immediately so they can respond before equipment fails.
4. Financial Services
Banks use Cosmos DB for fraud detection systems that analyze transaction patterns in milliseconds. The database processes credit card purchases, wire transfers, and account activities to spot suspicious behavior instantly.
High-frequency trading systems rely on Cosmos DB’s guaranteed low latency to execute trades at optimal prices. Every millisecond matters in financial markets, so the performance guarantees provide crucial competitive advantages.
5. Healthcare Applications
Hospitals store patient records, test results, and treatment histories in Cosmos DB while meeting strict privacy regulations like HIPAA. The database encrypts sensitive medical data and provides detailed audit logs for compliance reporting.
Medical devices send patient monitoring data to Cosmos DB for real-time analysis. Doctors get alerts when vital signs indicate emergencies, enabling faster response times that save lives.
Case Study Examples
- Microsoft uses Cosmos DB internally for services like Skype, Xbox, and Office, ensuring real-time performance at global scale.
- Walmart leverages Cosmos DB for retail operations, handling vast amounts of transactional and product data.
- Jet.com adopted Cosmos DB to support its eCommerce platform, capable of processing millions of concurrent requests during peak shopping seasons.
Cloud Networking: The Future of Scalable and Secure Connectivity
Unlock scalable and secure connectivity with cloud networking, the key to future-proofing your business infrastructure.
Getting Started with Azure Cosmos DB
Azure Cosmos DB is designed to be developer-friendly, allowing you to spin up a globally distributed database in minutes. Here’s a simple walkthrough to get started:
Step 1: Create a Cosmos DB Account
Log in to the Azure Portal and search for Azure Cosmos DB. Choose “Create,” then select the subscription, resource group, and region.
Step 2: Choose API Model
Cosmos DB supports multiple APIs. Select the one that fits your workload:
- SQL (Core API) for JSON documents.
- MongoDB API for Mongo-compatible apps.
- Cassandra API, Gremlin API, or Table API for other workloads.
Step 3: Define Containers, Partitions, and Throughput
Create a database and container. Assign a partition key (e.g., /userId) to distribute data evenly. Set throughput in Request Units (RUs) or enable autoscale.
Step 4: Connect with SDKs
Cosmos DB integrates with popular SDKs, including Python, .NET, Java, and Node.js. Install the SDK of your choice to begin interacting with your database.
Step 5: Run Queries and Manage Data
Insert, update, and query data directly from your application. Cosmos DB supports SQL-like queries for JSON documents.
Sample Query (Python SDK)
from azure.cosmos import CosmosClient
# Connect to Cosmos DB
client = CosmosClient(“<COSMOS_ENDPOINT>”, “<COSMOS_KEY>”)
database = client.get_database_client(“SampleDB”)
container = database.get_container_client(“Items”)
# Query items
for item in container.query_items(
query=”SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.category=’electronics'”,
enable_cross_partition_query=True
):
print(item)
With these steps, you can quickly build, connect, and query a Cosmos DB instance, making it ready for real-world applications.
AWS Vs Azure Vs Google Cloud: How to Choose the Best Cloud Platform?
Compare AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud to determine the best cloud platform for your business needs..
Best Practices for Developers
When working with Azure Cosmos DB, following proven practices can help you achieve optimal performance, predictable costs, and seamless scalability.
1. Use the Right Partition Key
Choosing the correct partition key is crucial for performance. A well-distributed key (such as userId or regionId) ensures balanced workload distribution and avoids “hot partitions” that consume disproportionate resources.
2. Monitor RU Consumption
Since every operation consumes Request Units (RUs), monitoring usage is essential. Use Azure Monitor and alerts to track high-RU queries and adjust code or design to keep costs predictable.
3. Optimize Queries with Indexes
Cosmos DB automatically indexes data, but you can customize indexing policies to optimize queries. Avoid full scans where possible and filter/query on indexed properties to reduce RU consumption.
4. Use Session Consistency for Balance
Cosmos DB offers five consistency levels. For many apps, session consistency provides the right balance between accuracy and performance. It ensures repeatable reads for a single session while avoiding the latency of strong consistency.
5. Design for Horizontal Scaling
Applications should be built to scale horizontally. Use partitioned collections and design schemas that work effectively across distributed systems. This ensures Cosmos DB can handle millions of requests per second without bottlenecks.
6. Enable Autoscale for Cost Efficiency
Workloads often vary. Enabling autoscale throughput adjusts RU/s automatically, preventing over-provisioning during low usage and scaling up seamlessly during peak demand.

Future of Azure Cosmos DB
1. Growing Role in Smart Applications
Cosmos DB is becoming the foundation for applications that use machine learning and smart text generation. The database will store training data, model results, and real-time predictions while maintaining the fast response times these applications need. Plus, built-in vector search capabilities will make it easier to build recommendation engines and chatbots.
Companies are already using Cosmos DB to store history for conversational chatbots and user behavior data for personalization systems. This trend will accelerate as more businesses adopt smart technologies.
2. Deeper Microsoft Integration
Microsoft is connecting Cosmos DB more tightly with their analytics and business intelligence tools. Microsoft Fabric will provide seamless data pipelines between Cosmos DB and data warehouses. Synapse Analytics will offer better real-time analytics on operational data, while Power BI will create dashboards directly from Cosmos DB without complex data movement.
These integrations eliminate the need to copy data between systems, reducing costs and improving data freshness for business reporting.
3. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Support
Microsoft is expanding Cosmos DB beyond Azure with hybrid deployments that work across on-premises data centers and multiple cloud providers. This flexibility helps companies avoid vendor lock-in while maintaining consistent database experiences everywhere.
The goal is letting organizations run Cosmos DB wherever their applications need it, whether that’s Azure, AWS, on-premises, or edge computing locations.
4. Microsoft’s Vision
Microsoft envisions Cosmos DB as the backbone for globally distributed applications that adapt intelligently to changing conditions. The database will automatically optimize performance, predict capacity needs, and recover from failures without human intervention, creating truly resilient systems ready for the next generation of smart applications.
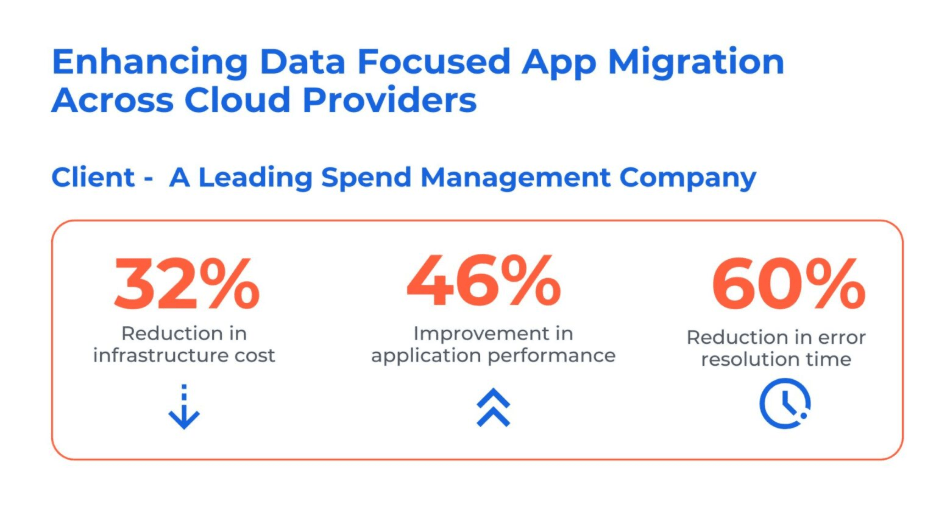
Case Study: Optimizing Data Focused App Migration Across Cloud Providers
Business Challenges: The customer is a well-known Spend Management Company. They want a smooth transition to their newly built cloud-native platform without affecting the consumer experience.
To address these issues, Kanerika has implemented the following solutions using Informatica and Kafka technologies:
- Our solution ensured a seamless transition for the client’s customers, with no break in service during the app migration to a new cloud store.
- All functionalities were preserved, and data integrity was maintained throughout the migration, thereby reducing interference with business operations.
- Our use of reconciliation to validate data integrity and contextual business rules has resulted in significant efficiency improvements, paving the way for future benefits.
Kanerika: The Ultimate Choice for All Your Cloud Management Needs
Effective cloud management is crucial for business success these days. Kanerika stands out as the number one choice for all your cloud management needs, offering unparalleled expertise and innovative solutions.
Our comprehensive cloud management services ensure seamless integration, optimized performance, and robust security across multi-cloud environments. We help businesses achieve greater flexibility, reduce costs, and enhance scalability.
Our dedicated team of cloud experts works tirelessly to tailor solutions that meet your unique requirements, providing continuous support and proactive management. Trust us to transform your cloud infrastructure into a powerhouse of efficiency and reliability. Experience the difference with Kanerika’s top-tier cloud management solutions today.
FAQs
1. What is Azure Cosmos DB?
Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft’s fully managed NoSQL database service, designed for high availability, global distribution, low latency, and elastic scalability.
2. What makes Cosmos DB different from other databases?
Unlike traditional databases, Cosmos DB offers global distribution across multiple regions, guarantees single-digit millisecond latency, and provides five consistency models to balance performance with data accuracy.
3. What data models does Azure Cosmos DB support?
Cosmos DB supports multiple APIs and data models, including SQL (Core), MongoDB API, Cassandra API, Gremlin API (graph), and Table API. This makes it highly flexible for different workloads.
4. How does Cosmos DB ensure scalability?
Cosmos DB uses a partitioning system and allows elastic scaling of throughput (RU/s) and storage independently. It can scale seamlessly across regions as application demand grows.
5. Is Azure Cosmos DB suitable for mission-critical applications?
Yes. With 99.999% availability SLA, multi-region write capability, and strong security features, Cosmos DB is built for mission-critical applications requiring reliability and resilience.
7. What are common use cases for Cosmos DB?
Popular use cases include IoT applications, e-commerce platforms, gaming backends, personalized recommendation engines, financial services, and real-time analytics.










