Automation is transforming how retailers do business, and it’s just getting warmed up. Indeed, the global retail automation market size is projected to grow from $24.36 billion in 2024 to $64.09 billion by 2032. From AI-powered chatbots to robotic warehouses, automation is no longer optional, it’s becoming essential for competitiveness.
At its core, retail automation is about using technology to streamline operations, reduce manual effort, and enhance customer experience. It covers everything from self-checkout kiosks and cashier-less stores to demand forecasting and real-time inventory tracking.
The need for automation is being driven by e-commerce growth, higher consumer expectations, global supply chain disruptions, and ongoing labor shortages.
In this blog, we’ll explore the world of retail automation—examining key technologies, major benefits, real-world use cases, industry leaders, challenges, and the future outlook for retailers worldwide.
Understanding Retail Automation
Retail automation refers to the use of technology to streamline and optimize both customer-facing and back-end operations in the retail sector. At its core, it covers everything from front-end tools such as self-checkout machines, kiosks, and cashier-less stores, to back-end systems like inventory management, demand forecasting, and supply chain automation. The goal is simple: reduce manual effort, improve accuracy, and create a seamless experience for both customers and businesses.
The concept of retail automation has steadily evolved over the years. Early innovations such as barcode scanners and point-of-sale (POS) systems revolutionized checkout speed and accuracy. Over time, retailers adopted more advanced tools, including loyalty programs, e-commerce platforms, and warehouse management systems. Today, automation is powered by AI-driven chatbots, smart shelves, self-checkout technologies, and intelligent warehouses, all of which are reshaping how retailers interact with shoppers and manage their operations.
There are three primary types of retail automation:
- Front-End Automation
Tools that improve customer experience, such as kiosks, mobile payments, and cashier-less stores that make shopping faster and more convenient.
- Back-End Automation
Systems that manage operational efficiency, including real-time inventory tracking, demand forecasting, and supply chain logistics optimization.
- Omnichannel Integration
Technologies that blend online and offline shopping, enabling services like click-and-collect, same-day delivery, and personalized recommendations across platforms.
Together, these advancements illustrate how retail automation has shifted from basic transaction processing to a comprehensive ecosystem that supports efficiency, personalization, and growth.
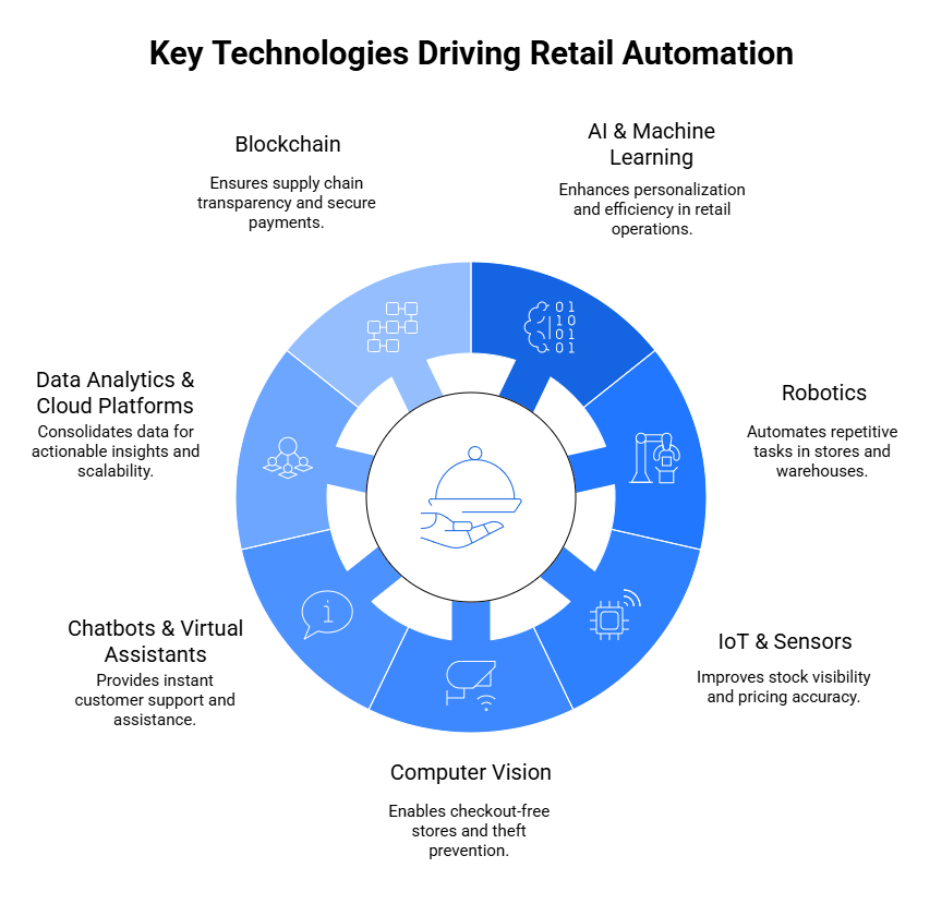
Key Technologies Driving Retail Automation
The rapid evolution of retail automation is powered by a set of advanced technologies that work together to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and streamline operations. Below are the key technologies shaping the retail landscape in 2025:
1. AI & Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence is at the heart of retail automation. Machine learning models analyze customer data to deliver personalized product recommendations, improving conversion rates and customer loyalty. Retailers also use AI for demand forecasting, enabling smarter inventory planning and reducing waste. In addition, AI-powered algorithms are applied in fraud detection, safeguarding payment systems and minimizing financial risks.
2. Robotics
Robots are increasingly used to automate repetitive tasks in both stores and warehouses. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) handle stock movement and delivery, while robotic shelf scanners monitor stock levels and pricing accuracy. In warehouses, robotic arms and sorting systems accelerate order fulfillment and reduce manual labor costs.
3. IoT & Sensors
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing stock visibility with smart shelves, RFID tags, and real-time monitoring devices. These technologies allow retailers to track product availability, reduce out-of-stock incidents, and ensure accurate pricing updates across multiple stores.
4. Computer Vision
Using cameras and AI, retailers can now operate checkout-free stores such as Amazon Go, where customers simply pick up items and leave without waiting in line. Beyond convenience, computer vision also assists with theft prevention and loss detection, safeguarding profitability.
5. Chatbots & Virtual Assistants
Customer service is being transformed by AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants that provide instant support across websites, apps, and in-store kiosks. These assistants handle common queries, assist with product searches, and escalate complex issues to human staff when needed.
6. Data Analytics & Cloud Platforms
Modern retail runs on data. Analytics platforms consolidate information from sales, customer behavior, and supply chains to generate actionable insights. When combined with cloud platforms, retailers gain scalable infrastructure to store, process, and share these insights across the organization in real time.
7. Blockchain
To ensure supply chain transparency and secure payments, blockchain is emerging as a trusted solution. By recording every transaction and product movement on immutable ledgers, retailers can guarantee authenticity, reduce fraud, and improve trust with customers.
Leading Companies in Retail Automation
The retail automation market is being shaped by a mix of technology giants, retail leaders, and specialized solution providers. Each brings unique strengths that are redefining how retailers manage operations and deliver customer experiences.
1. Amazon
Amazon has set the benchmark for front-end retail automation with its Just Walk Out technology. These checkout-free stores leverage computer vision, sensors, and AI to let customers shop without traditional checkouts. Beyond stores, Amazon also leads in warehouse automation through advanced robotics and predictive inventory systems.
2. Walmart
Walmart is investing heavily in robotics for shelf scanning and inventory tracking. Its AI-driven demand forecasting systems optimize stock levels across thousands of stores, helping the company maintain efficiency and reduce waste. Moreover, Walmart’s scale makes it a prime example of automation applied at a global retail level.
3. NCR
NCR is a leader in self-checkout systems that are widely used by supermarkets, convenience stores, and large retailers worldwide. By reducing reliance on staffed checkouts, NCR helps retailers cut labor costs and improve customer convenience. Its focus on hardware and software integration ensures reliability and scalability.
4. Honeywell & Zebra Technologies
Both Honeywell and Zebra Technologies specialize in retail automation hardware. They provide barcode scanners, handheld devices, RFID systems, and IoT-enabled solutions that improve stock visibility, reduce shrinkage, and optimize logistics. Their technology is particularly critical in back-end supply chain operations.
5. Microsoft & Google Cloud
Tech giants Microsoft and Google Cloud are bringing their AI and cloud capabilities into retail. Microsoft’s Dynamics 365 and Azure AI solutions enable personalized recommendations, supply chain insights, and connected store experiences. As well as, Google Cloud, with its Vertex AI and retail data models, empowers retailers to forecast demand and analyze customer behavior with speed and accuracy.
6. UiPath & Blue Prism
Retailers also automate repetitive back-office tasks through robotic process automation (RPA). UiPath and Blue Prism lead this space by providing software robots that handle invoicing, order reconciliation, compliance checks, and HR workflows. This frees employees to focus on higher-value tasks and reduces operational costs.
Together, these companies showcase how retail automation is not a single technology but an ecosystem. From checkout-free shopping to predictive supply chains and robotic process automation, they are setting the stage for a smarter, more efficient future of retail.
Real-World Use Cases of Retail Automation
Retail automation is no longer a concept of the future—it is already transforming how global retailers operate and engage with customers. Leading brands across industries are adopting automation to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver seamless shopping experiences.
1. Amazon Go: Checkout-Free Shopping
Amazon’s Go stores are the most prominent example of automation in action. Using a combination of computer vision, weight sensors, and AI algorithms, customers simply walk-in, pick-up items, and leave. Also, the system automatically charges their accounts without the need for cashiers, eliminating queues and redefining convenience in physical retail.
2. Walmart: Robotic Shelf Scanning and AI Forecasting
Walmart have invested in robotic shelf scanners that patrol aisles to monitor stock levels and pricing accuracy. This ensures better product availability and fewer out-of-stock incidents. In parallel, Walmart leverages AI-driven demand forecasting to optimize supply chains across its massive global operations, minimizing waste while meeting customer demand.
3. Sephora: Virtual Try-On and AI Beauty Advisors
Sephora have embraced augmented reality and AI to create virtual try-on experiences for makeup products. Customers can test lipsticks, foundations, and eye shadows digitally before purchasing. Combined with AI-powered beauty recommendations, Sephora personalizes customer journeys and increases product discovery.
4. Nike & Adidas: Automated Inventory and Personalized Journeys
Both Nike and Adidas use automation to manage inventory and supply chains with precision, reducing stockouts and overstocking. At the customer level, they deploy AI-powered personalization engines that recommend products based on browsing history and activity, creating unique shopping experiences that drive loyalty.
5. Grocery Retailers: Self-Checkout and Omnichannel Integration
Supermarkets and grocery chains worldwide have adopted self-checkout kiosks to speed up shopping. Many also use online-to-offline integrations like “click-and-collect” or same-day delivery, supported by automated inventory updates. This blend of digital and in-store automation meets the evolving demands of modern shoppers.
6. Fashion Retail: Automated Returns and AI Stylists
Fashion retailers are tackling one of their biggest challenges—returns—through automated return processing systems that reduce operational overhead. At the same time, AI stylists and virtual fitting rooms help customers find the right styles and sizes, reducing returns while improving satisfaction.
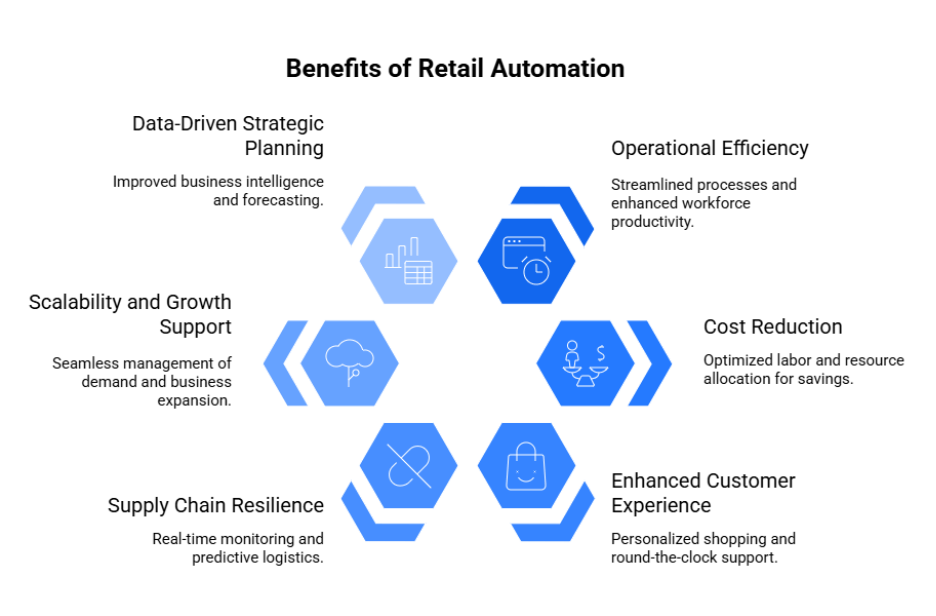
Benefits of Retail Automation
Modern retail businesses face increasing pressure to operate efficiently while delivering exceptional customer experiences. Smart automation technologies offer comprehensive solutions that address these challenges while positioning retailers for long-term success in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
1. Operational Efficiency
Streamlined Store Operations
- Faster checkout processes through self-service kiosks and automated payment systems
- Significantly fewer human errors in pricing, inventory tracking, and transaction processing
- Optimized store processes that reduce wait times and improve customer flow
- Furthermore, automated inventory management that maintains accurate stock levels
- Real-time updates on product availability and location throughout the store
Enhanced Workforce Productivity
- Staff freed from routine tasks can focus on customer service and sales assistance
- Automated scheduling systems that match staffing levels to customer demand patterns
- Moreover, streamlined employee training through interactive systems and digital guides
2. Cost Reduction
Labor Cost Optimization
- Reduced dependency on large staff numbers for routine operational tasks
- Smart scheduling that prevents overstaffing during slow periods
- Automated systems handle repetitive tasks like price updates and basic customer inquiries
- Additionally, lower training costs through standardized automated processes
Resource Allocation Efficiency
- Optimized energy usage through smart lighting and climate control systems
- Reduced waste from better inventory management and demand prediction
- Furthermore, more efficient use of physical space through data-driven layout optimization
- Lower administrative costs through automated reporting and compliance tracking
3. Enhanced Customer Experience
Personalized Shopping Journeys
- Customized product recommendations based on purchase history and preferences
- Targeted promotions and discounts delivered at the right moment
- Personalized store navigation assistance and product location guidance
- Moreover, tailored communication across multiple channels including email, mobile apps, and in-store displays
Round-the-Clock Customer Support
- 24/7 assistance through chatbots and virtual shopping assistants
- Instant answers to common questions about products, policies, and store information
- Additionally, seamless support across online and offline shopping experiences
- Self-service options that let customers resolve issues independently
4. Supply Chain Resilience
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
- Continuous tracking of inventory levels across all locations and warehouses
- Immediate alerts when stock levels reach predetermined thresholds
- Real-time visibility into supplier performance and delivery schedules
- Furthermore, automated quality control monitoring throughout the supply chain
Predictive Logistics Management
- Advanced forecasting that anticipates demand fluctuations and seasonal trends
- Optimized delivery routes and warehouse operations based on historical data
- Proactive identification of potential supply chain disruptions
- Meanwhile, automated reordering systems that maintain optimal inventory levels
5. Scalability and Growth Support
Handling Demand Fluctuations
- Seamless management of seasonal shopping spikes and promotional events
- Automated systems that scale capacity up or down based on real-time demand
- Rapid deployment of additional checkout options during peak periods
- Consequently, consistent service quality regardless of customer volume
Supporting Business Expansion
- Standardized processes that can be quickly replicated in new locations
- Centralized management systems that efficiently oversee multiple store operations
- Therefore, faster onboarding of new locations with proven operational frameworks
6. Data-Driven Strategic Planning
Improved Business Intelligence
- Comprehensive analytics on customer behavior, purchasing patterns, and preferences
- Real-time performance metrics across all aspects of retail operations
- Detailed insights into product performance and market trends
- Furthermore, integrated reporting that combines online and offline customer data
Enhanced Forecasting Capabilities
- More accurate demand predictions based on multiple data sources
- Better inventory planning that reduces both stockouts and overstock situations
- Strategic planning supported by predictive analytics and trend analysis
- Moreover, data-driven decision making that reduces guesswork and improves outcomes
Challenges of Retail Automation
While retail automation brings undeniable advantages, it also presents challenges that organizations must carefully manage to ensure sustainable adoption.
1. High Implementation Costs
One of the biggest barriers is the upfront investment required for hardware, software, and infrastructure. From installing self-checkout systems to deploying warehouse robots, the initial costs can be significant, especially for small and mid-sized retailers.
2. Workforce Displacement
Automation raises concerns about job losses, as tasks once performed by staff—like checkout or stock monitoring—are taken over by machines. Moreover, retailers need to balance efficiency gains with responsible workforce management by retraining employees for higher-value roles.
3. Integration Complexity
Many retailers operate on legacy systems that do not seamlessly connect with modern platforms. Correspondingly, integrating new technologies with outdated infrastructure can be complex, time-consuming, and costly, often requiring middleware or custom solutions.
4. Data Privacy & Security
As retail automation depends heavily on customer and transaction data, privacy and cybersecurity risks are critical concerns. Breaches or misuse of sensitive data can harm customer trust and expose retailers to regulatory penalties.
5. Consumer Trust
Customers may hesitate to adopt checkout-free or AI-driven interactions due to unfamiliarity or discomfort. Building trust requires transparent communication, user-friendly design, and gradual adoption of new technologies to avoid alienating shoppers.
6. Maintenance & Scalability
Automated systems demand ongoing maintenance, software updates, and scalability planning. Without proper long-term strategies, the cost and effort of keeping these systems operational can outweigh the benefits.
Accelerate Growth and Efficiency with Enterprise-Grade Automation
Partner with Kanerika Today!
Future of Retail Automation
- The future of retail automation promises to be more intelligent, interconnected, and customer-centric. At the forefront is the rise of AI agents in retail, which will act as intelligent assistants capable of handling customer queries in real time, managing supply chain processes, and even making autonomous decisions to reduce delays and improve efficiency.
- Another major trend will be hyper-personalization, where AI uses real-time customer data to deliver individualized shopping experiences—from product recommendations to dynamic pricing tailored to each shopper.
- Omnichannel automation will also continue to mature, seamlessly blending online, mobile, and in-store experiences. Shoppers will be able to start their journey on an app, continue in-store, and complete purchases online without friction.
- In terms of logistics, the expansion of robotics will play a transformative role. Fully automated warehouses, drone-based deliveries, and robotic shelf management will dramatically reduce turnaround times and operational costs.
- Sustainability will emerge as a key focus, with automation driving greener operations through energy-efficient supply chains, optimized transportation routes, and waste reduction strategies.
- Looking ahead, the long-term outlook suggests a hybrid model—where automation doesn’t simply replace human workers but empowers them. Employees will increasingly work alongside machines, focusing on customer engagement, creativity, and problem-solving, while automation takes care of repetitive and data-heavy tasks.
- Ultimately, retail automation will evolve into a strategic advantage, helping businesses balance efficiency, sustainability, and customer satisfaction in an increasingly competitive market.
Must-Know Features of The Best Accounts Payable Automation Tools
Discover the key functionalities of top-tier accounts payable automation tools to streamline your financial processes and boost organizational efficiency.
Case Studies: Kanerika’s Automation Expertise
1. Optimizing Accounts Payable Through Automation
The client is a leading fuel distribution company in the US. They faced problems in time consuming and error-prone manual invoice processing and payments to vendors, impacting the efficiency and effectiveness of the accounts payable operations
The automation specialist at Kanerika ensured that the client’s business challenges are addressed by:
- Implementing UiPath with AI/ML for automated invoice extraction, boosting efficiency
- Introducing manual review in Action Center, enhancing ML accuracy and process refinement
- Automating NetSuite entries, streamlining financial operations and cutting processing times

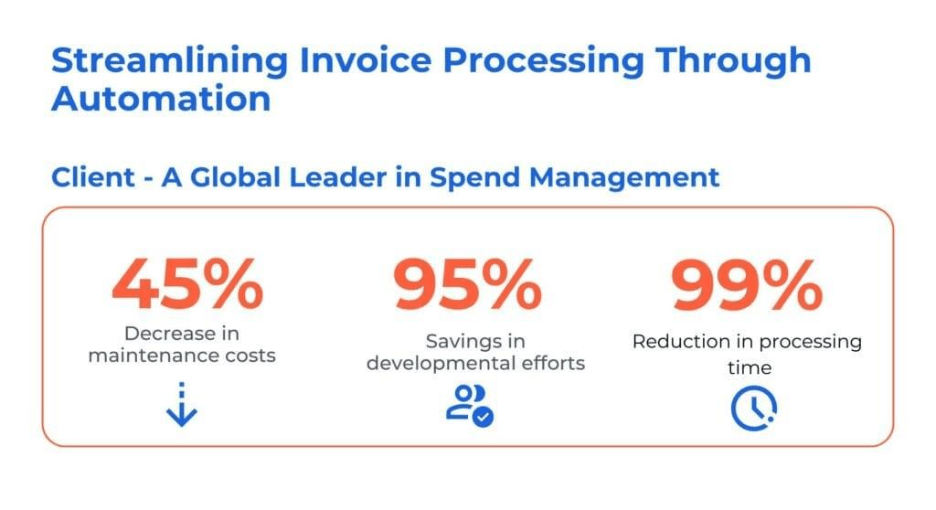
2. Streamlining Invoice Processing Automation and Rule-Based Cost Allocations
The client is a global leader in Spend Management. Delivering cost allocation services to their customers has become increasingly complex, expensive, and time-consuming. So, they sought an automated business solution to efficiently handle cost allocation and automated invoice processing across all customers.
Kanerika has resolved the client’s problems by leveraging Tools Like UiPath Kafka, and Microsoft Azure to:
- Streamlined the cost allocation process with intelligent automation, improving efficiency and time-to-market
- Implemented a rules-based engine for scalable and intelligent cost allocation, reducing custom deployment time to <5 mins
- Enabled customer-specific business rules and configurable cost allocation strategies, increasing flexibility for customer
Transform Retail Operations with Kanerika’s Advanced Automation Services
Kanerika stands at the forefront of retail automation, offering cutting-edge solutions tailored to the evolving needs of modern retailers. Leveraging deep expertise in technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML), Kanerika empowers retail businesses to optimize resources, enhance customer experiences, and increase operational agility.
Our automation strategies streamline core retail processes—ranging from inventory management and supply chain optimization to customer service and checkout operations. By automating repetitive, data-intensive tasks, we help retailers minimize errors, reduce costs, and free up skilled staff to focus on customer engagement and strategic growth.
Central to our offerings is FLIP, a low-code/no-code AI-powered DataOps platform designed to automate complex retail data workflows. FLIP accelerates decision-making by delivering accurate data insights in real time, automates the validation and cleansing of sales and inventory data, and enables secure, role-based access for retail teams. This results in seamless omnichannel operations, improved demand forecasting, and more personalized customer shopping experiences. With Kanerika, retailers can rapidly adapt to market changes, drive sustainable growth, and gain a true competitive advantage in an increasingly automated retail landscape.
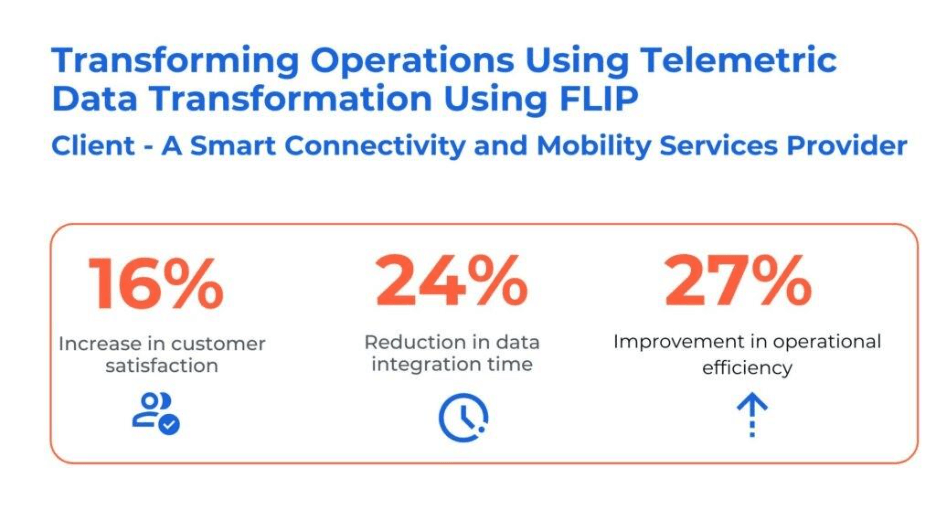
Case Study: Revolutionizing Operations through Telemetric Data Transformation Using Flip
The client excels in enabling smart connectivity and mobility services. They faced business challenges with default device message structure, which involves converting binary data received from datalogger into a proprietary message format.
Kanerika has solved their problem by leveraging the capabilities of FLIP and Kafka. Here are the solution
- Implemented FLIP for delivering a tailored message translation solution, optimizing data transformation
- Enhanced FLIP to effortlessly convert JSON/Excel/Kafka messages into diverse formats, ensuring smooth data flow
- Augmented analytics tools with personalized message transformation, enriching business insights and efficiency
Our proven track record in delivering successful automation projects is a testament to our unwavering commitment to excellence. Trust us to be your strategic partner in transforming your enterprise through intelligent automation and unlocking unprecedented growth opportunities. Choose Kanerika as your go-to automation expert and experience the power of a future-ready, automated business.
FAQs
1. What is retail automation?
Retail automation uses technology such as AI, IoT, and software platforms to streamline processes like inventory management, checkout, customer service, and marketing. The goal is to reduce manual effort, cut costs, and improve efficiency.
2. How does retail automation benefit businesses?
It improves operational efficiency, reduces errors, enhances customer experience, lowers labor costs, and provides real-time insights for better decision-making.
3. What are common examples of retail automation?
Examples include self-checkout kiosks, automated inventory tracking, AI-powered chatbots, digital price tags, robotic shelf scanners, and personalized marketing automation.
4. Does retail automation replace human workers?
Not entirely. Automation handles repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities like customer engagement, problem-solving, and strategy.
5. How does automation improve the customer experience?
Customers benefit from faster checkout, personalized recommendations, accurate stock availability, and seamless omnichannel shopping experiences.
6. Is retail automation expensive to implement?
Initial investment can be high, but the long-term savings from reduced labor costs, fewer errors, and increased efficiency often outweigh the costs. Many solutions are also scalable, making them accessible for smaller retailers.
7. What does the future of retail automation look like?
Expect wider use of AI, robotics, and predictive analytics. Smart stores, cashier-less checkout, and hyper-personalized shopping experiences will likely become more common.










