Enterprises have spent years unifying their data estates. Platforms like Microsoft Fabric now consolidate pipelines, warehouses, and analytics into a single environment. Yet despite this progress, a critical gap remains: AI still struggles to understand what that data actually means in business terms.
At Microsoft Ignite 2025, Microsoft addressed this challenge head-on with Fabric IQ—a semantic intelligence layer designed to transform unified data into unified intelligence. With Fabric now adopted by more than 28,000 organizations worldwide, this represents the next frontier in enterprise analytics.
This guide covers what Fabric IQ is, its current capabilities and limitations, and how enterprises can prepare for adoption.
What Is Microsoft Fabric IQ?
Microsoft Fabric IQ is a semantic intelligence layer within Microsoft Fabric that organizes data according to the language of your business—not just tables and columns, but entities, relationships, rules, and objectives.
According to Microsoft’s official documentation, “IQ (preview) is a workload for unifying data sitting across OneLake (including lakehouses, eventhouses, and semantic models) and organizing it according to the language of your business. The data is then exposed to analytics, AI agents, and applications with consistent semantic meaning and context.
Think of Microosft Fabric IQ as a metadata layer on top of data in Fabric that defines entities and their relationships so that AI can make sense of and relate the underlying data. If Fabric unifies where your data lives, Fabric IQ unifies what your data means.
Key Facts:
- Status: Public preview (announced November 2025)
- Licensing: No separate SKU—included with existing Fabric capacity
- Billing: Capacity meters for the Ontology item expected H1 2026
The Problem Fabric IQ Solves
Enterprises have unified where data lives, but the meaning of that data remains fragmented. Each team has its own definitions—”customer,” “revenue,” and “active user” mean different things across departments. Business logic lives in people’s heads, scattered reports, and inconsistent semantic models.
This creates a fundamental problem for AI. As Microsoft explains, AI agents “can read the data, but they do not understand your business. Without that grounding, AI cannot reason about cascading effects, constraints, or objectives.”
The business cost is significant: conflicting definitions cause reporting inconsistencies, AI initiatives stall after pilots, and every new project must rediscover business meaning from scratch.
Transform Your Business with Data & AI!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data, Analytics, & AI implementation Services
Core Components of Microsoft Fabric IQ
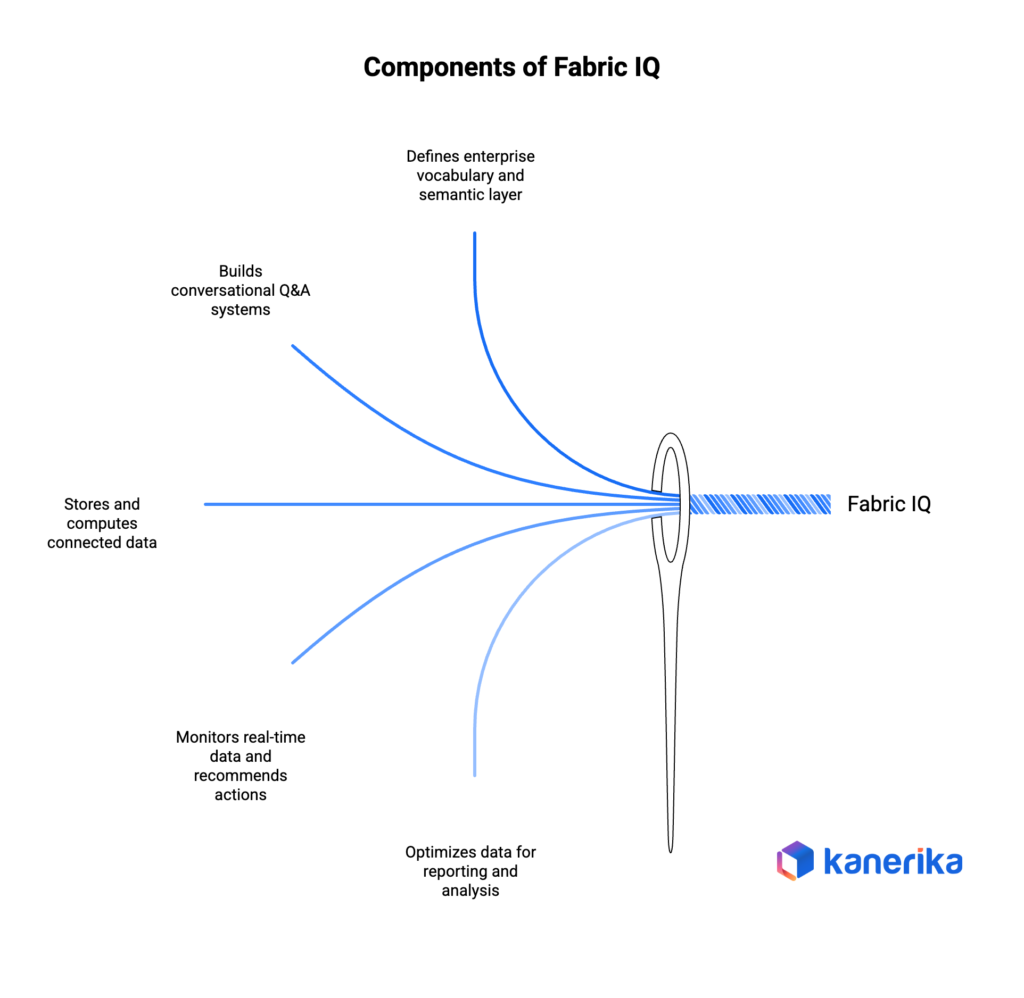
Ontology—The Semantic Foundation
The ontology is the heart of Fabric IQ. According to Microsoft documentation, “An ontology is a shared, machine-understandable vocabulary of your business. It’s made up of the things in your environment (represented as entity types), their facts (represented as properties on entity types), and the ways they connect (represented as relationships).”
Key capabilities:
- Connects to OneLake data—lakehouses, eventhouses, semantic models
- No-code visual tools allow business experts to build and evolve ontologies
- Organizations can bootstrap ontologies from existing Power BI semantic models
- Supports versioning, validation, and governance of definitions
Jumpstart Capability:
Organizations can generate an ontology directly from existing Power BI semantic models. “When your data is in a semantic model, you can generate an ontology directly from that semantic model.”
How to Create Direct Lake Semantic Models in Power BI
Explore how to turn on the Direct Lake feature, connect multiple lakehouses in a single model, create calculated measures, and build Power BI reports
Operational Agents—Autonomous Decision-Making
Operational Agents represent a new class of enterprise AI. According to Microsoft, these agents “monitor the business in real time, reason over live conditions, evaluate trade-offs, and take actions automatically to advance business outcomes.”
Unlike traditional automation, Operational Agents are context-aware and grounded in shared business semantics.
Use Case Example: A logistics company models delivery operations in the ontology. When real-time data shows traffic congestion, the Operational Agent automatically reroutes trucks while considering SLAs, delivery priorities, and cost constraints.
Data Agents—Conversational Analytics
Data Agents (previously called AI Skills) allow users to ask questions and get answers in real time using natural language. They use data from OneLake while maintaining roles and permissions.
Graph in Microsoft Fabric
Native graph storage and compute enables multi-hop reasoning. As Microsoft notes, “Ontology declares which things connect and why. Graph in Microsoft Fabric stores and computes traversals, like ‘Find shipments exposed to risky routes and related breaches.’
Fabric IQ Preview: Current Capabilities and Limitations
What’s Working Well
- Power BI integration: Can span semantic models to bridge business logic
- Microsoft ecosystem integration: Works with Real-Time Intelligence, Copilot Studio, Graph, Foundry IQ, Work IQ
- Democratized access: Visual, no-code tools lower barriers for business users
- No additional licensing: Runs on existing Fabric capacity
Current Limitations
Based on Microsoft documentation and practitioner reviews
| Limitation | Business Impact |
| DirectLake models only | Import and DirectQuery semantic models not yet supported |
| OneLake dependency | Data must reside in OneLake; external data sources require migration |
| Manual ontology building | No automated discovery; requires cross-functional workshops |
| Decimal type not supported | Fabric Graph returns null values for Decimal columns |
Analyst Sentiment
Optimistic View: Constellation Research analyst Michael Ni sees benefits including “consistent semantics, fewer one-off models, less duplicated logic, and a shared decision layer that lowers downstream maintenance.”
Cautious View: HFS Research warns that “for organizations not already invested in the Fabric ecosystem, adoption of IQ will likely take longer. Key hurdles include agreeing on shared business definitions, ensuring that data permissions are carried through to AI agents, and maintaining clean and reliable real-time data feeds.”
Vendor Lock-in Concern: Moor Insights analyst Robert Kramer notes, “The more an enterprise builds on this semantic layer, the harder it becomes to move that logic elsewhere.”
Microsoft’s Unified IQ Ecosystem
Fabric IQ doesn’t operate in isolation. It’s part of Microsoft’s broader “IQ” brand:
- Fabric IQ: Semantic layer for business data in Fabric/OneLake
- Work IQ (Microsoft 365): Semantic layer for documents, emails, Teams conversations
- Foundry IQ (Microsoft AI Foundry): Managed knowledge system for grounding custom AI agents
Together, these form a shared intelligence layer spanning business data, documents, communications, and enterprise knowledge. Developers can build agents that inherit live business context without extensive prompt engineering.
Industry Use Cases
Supply Chain & Logistics
Real-time rerouting based on traffic and weather; automatic schedule adjustments considering SLAs and costs; cross-domain queries connecting shipments, routes, sensors, and breach events.
Energy & Utilities
ENMAX Power is exploring Fabric IQ “to unify transmission and distribution grid data, overcoming the limitations of traditional relational databases that silo information and complicate real-time analysis.”
Financial Services
Unified customer views across products; risk assessment with context-aware AI; regulatory compliance with consistent definitions.
Manufacturing
Connected production planning, inventory, and supplier relationships; operational agents monitoring for supply disruptions.

Preparing for Fabric IQ: A Readiness Framework
Step 1—Assess Your Semantic Model Estate
Before building ontologies, understand your existing BI landscape:
- How many Power BI semantic models exist across workspaces?
- Which models are actively used versus dormant?
- Where do definition conflicts exist?
A BI Audit helps identify high-value models that should seed the ontology and surfaces conflicts that could undermine quality.
Step 2—Evaluate OneLake Readiness
Fabric IQ requires data in OneLake. Inventory data sources outside Fabric, assess migration complexity, and plan data movement using Fabric pipelines, Dataflows, or mirroring capabilities.
Step 3—Define Core Business Entities
Start small with 5–10 critical business concepts. Workshop core entities like Customer, Product, Order, Revenue, and Risk. Document relationships, rules, and constraints. This is harder than it sounds—definition debates have derailed many data initiatives.
Step 4—Pilot with Bounded Use Case
Choose a single business domain (one supply chain route, one product line). Build the ontology, deploy a Data Agent or Operational Agent, measure outcomes, document lessons learned, then iterate and expand.
How Kanerika Accelerates Your Fabric IQ Journey
As a Microsoft Solutions Partner for Data & AI and Fabric Featured Partner exhibiting at FabCon 2026 (March 16–20 in Atlanta), Kanerika brings deep expertise in Microsoft Fabric implementations.

BI Audit & Usage Reporting
Before building ontologies, enterprises need visibility into their semantic model landscape. Kanerika’s BI Audit service provides comprehensive inventory, usage analytics, definition conflict analysis, and ontology candidate identification.
Karl—Production-Ready Data Agent for Microsoft Fabric
While Fabric IQ’s native Data Agents continue maturing in preview, Kanerika’s Karl delivers conversational analytics capabilities today. Currently in public preview as a Microsoft Fabric workload, Karl goes GA in mid-March 2026.
Karl Capabilities:
- Natural language queries on structured data—no coding required
- Real-time data retrieval with instant visualizations
- Context-aware: Understands follow-up questions and remembers past queries
- Enterprise-ready: Role-based access, audit trails, citation-backed answers
- Multi-source integration: Works with databases, Excel, CSV, Postgres—and Fabric
Ontology Design & Implementation
Kanerika facilitates workshops to define core business entities, translates business rules into ontology constraints, and designs governance frameworks including approval workflows, version control, and Purview integration.
OneLake Migration & Data Consolidation
Using FLIP Migration Accelerators, Kanerika helps enterprises consolidate data into Fabric from Azure, on-premises, and third-party platforms.
Why Kanerika for Your Fabric IQ Journey?
Kanerika was among the first organizations worldwide to deploy Microsoft Fabric in real business environments. As a Microsoft Solutions Partner for Data & AI and Fabric Featured Partner, we’ve helped enterprises across industries build the data foundations that Fabric IQ requires.
Proven Fabric Implementation Results
Southern States Material Handling (SSMH) — Implemented a Microsoft Fabric-based Data Lakehouse unifying data across fleet management, service operations, and inventory control.

ABX Innovative Packaging Solutions — Consolidated scattered data across multiple systems into a unified framework with standardized ETL processes and custom Power BI dashboards.
“Our collaboration with Kanerika has been transformative. Their expertise has significantly enhanced our data management capabilities, empowering us to make faster, more informed decisions.
— Greg Thompson, Chief Information Officer, ABX
The semantic models you define today become the business language your AI agents speak tomorrow. Kanerika helps you build that foundation. Get started today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Microsoft Fabric IQ generally available?
No. Fabric IQ is in public preview, announced at Microsoft Ignite November 2025. No GA timeline has been announced.
Does Fabric IQ require additional licensing?
No. Fabric IQ runs on existing Fabric capacity with no separate SKU. Billing meters for the Ontology item are expected in H1 2026.
Can I use existing Power BI models with Fabric IQ?
Currently, only semantic models with tables in DirectLake mode are fully supported for data bindings. Import and DirectQuery models have limitations.
What's the difference between Fabric IQ and Copilot in Fabric?
Copilot assists users with AI-powered suggestions. Fabric IQ provides the semantic foundation—the shared business understanding—that grounds Copilot and other AI agents. They’re complementary.
How does Fabric IQ compare to Palantir Foundry?
Both provide ontology-based semantic layers. Fabric IQ’s advantage is tight Microsoft ecosystem integration and the ability to jumpstart from existing Power BI models. Palantir has deeper capabilities for complex operational scenarios and a decade head start.
What data sources does Fabric IQ support?
Fabric IQ builds on data from lakehouse tables, eventhouse streams, and existing semantic models—all within OneLake. External data must be migrated.
What's required before implementing Fabric IQ?
Key prerequisites include: data consolidated in OneLake, audit of existing semantic models, cross-functional agreement on business definitions, and a governance framework for ontology management.
What is Karl and how does it relate to Fabric IQ?
Karl is Kanerika’s Data Intelligence Agent available as a Microsoft Fabric workload. It delivers conversational analytics similar to Fabric IQ’s Data Agents but goes GA in March 2026—providing a production-ready path while native Fabric IQ agents mature.
Which industries benefit most from Fabric IQ?
Supply chain/logistics, energy/utilities, financial services, manufacturing, and retail see immediate value due to complex operational decisions requiring real-time, context-aware AI.
When is FabCon 2026?
FabCon + SQLCon are together March 16–20, 2026, in Atlanta, GA.Kanerika will be at booth 836 at the event.










