When Levi Strauss & Co. observed shifting fashion trends, they leveraged data to not only analyze current patterns but also to anticipate future demands. Their success stemmed from effectively balancing data governance vs. data management. By partnering with Google Cloud, Levi’s consolidated data from retail partners, e-commerce platforms, and internal systems, ensuring robust data management processes. Concurrently, clear data governance policies maintained data consistency, security, and accuracy. This strategic approach enabled them to identify the rising popularity of looser-fit jeans, leading to a 15% increase in sales for that category.
This real-world example underscores the importance of distinguishing between data governance and data management. Many organizations mistakenly use these terms interchangeably, yet they serve distinct functions: one establishes the framework and policies, while the other executes them operationally.
In this blog, we will delve into the nuances of data governance vs. data management, exploring their differences, intersections, and the critical roles both play in fostering a data-driven organization’s success.
What is Data Governance?
Data governance is a critical aspect of data management that ensures data quality, security, consistency, and usability. Organizations can effectively manage and leverage their data assets for decision-making and operational purposes by implementing data governance policies and procedures. Moreover, data governance encompasses a range of activities, including data classification, metadata management, data access controls, data quality monitoring, and data lifecycle management. It provides a framework for establishing accountability and responsibility for data, ensuring that the right people have access to the right data at the right time.
Furthermore, data governance enables consistency and integrity across different business units and systems. It ensures that data is consistent and standardized, allowing for better integration, sharing, and analysis. Data governance also helps organizations identify and address data-related gaps and issues, enabling them to make informed decisions based on high-quality, trusted data.
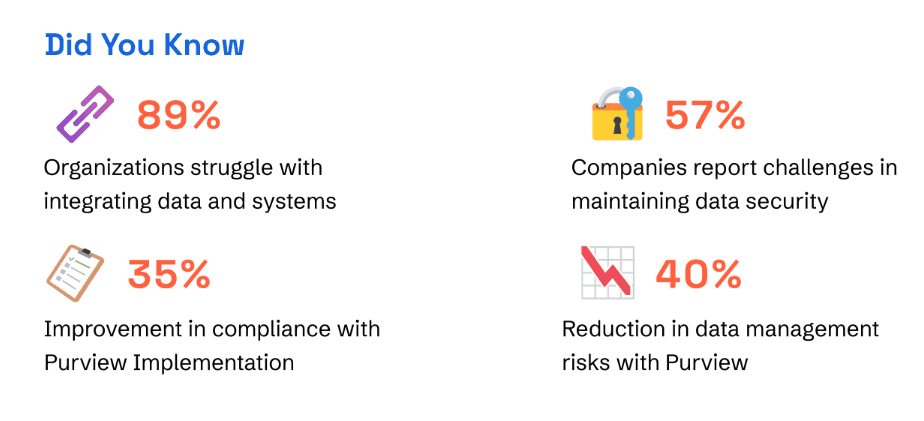
4 Pillars of Data Governance
A solid data governance framework isn’t just about setting policies — it’s about building a system that ensures data is trustworthy, secure, and usable. Below are four essential pillars that every organization must prioritize to make governance truly effective:
1. Data Quality
High-quality data is non-negotiable. If your data is inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated, even the best governance framework will fall apart. Reliable data forms the foundation for trusted insights, confident decisions, and successful analytics across the business.
2. Data Security and Compliance
Governance is closely tied to how well your data is secured and aligned with compliance standards. This involves classifying data by risk level and managing access accordingly. A good balance between accessibility and security ensures sensitive data is protected without slowing down operations.
3. Data Stewardship
Data stewards play a key role in upholding governance rules. They monitor how data is used, ensure best practices are followed, and guide teams to maintain high standards for access, quality, and security. They help create a culture of accountability and trust around data.
4. User Data Security
User Data Security ensures that all user actions are monitored and protected by systems that detect suspicious activity and prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
What is Data Management?
Data management encompasses data collection, organization, protection, and storage. It aims to improve data scalability, visibility, security, and reliability. Furthermore, it is not just the responsibility of the IT department; all employees play a role in maintaining data quality by following data management policies and procedures.
It eliminates siloed subsystems, improves data flow across business units, and enables more agile decision-making. Data management includes specialized practices such as data architecture, modeling, security, and catalogs.
Key Components of Data Management
1. Data Storage Solutions
Involves the use of systems like databases, data warehouses, data lakes, or cloud storage to safely hold structured and unstructured data. Proper storage ensures performance, scalability, and backup.
2. Data Integration
Combines data from multiple sources — CRM, ERP, third-party APIs, spreadsheets — into one consistent view. Tools like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipelines are often used to ensure data flows smoothly across systems.
3. Data Processing
Converts raw data into usable formats. This includes data cleaning, transformation, enrichment, and modeling. The goal is to make data ready for analytics, reporting, or automation.
Data Governance Vs Data Management
| Aspect | Data Governance | Data Management |
| Definition | The framework of rules, roles, and responsibilities for data use | The execution of processes to collect, store, and handle data |
| Primary Focus | Strategy, policies, accountability, compliance | Operations, tools, and data handling |
| Ownership | Led by business units, compliance teams, data stewards | Managed by IT, data engineers, and technical teams |
| Key Objective | Ensure data is secure, trusted, and used properly | Ensure data is usable, accessible, and supports daily workflows |
| Scope | Covers policies, standards, roles, and definitions | Covers infrastructure, storage, movement, and transformation of data |
| Example | Defining who can access customer data and under what conditions | Building systems that enforce those access rules and store customer data |
Key Differences Between Data Governance Vs. Data Management
1. Strategy vs. Implementation
Data Governance:
- Focuses on defining the strategy for how data is collected, stored, used, and protected.
- Establishes policies, standards, and procedures to ensure data integrity, compliance, and ethical usage.
- Acts as the blueprint or framework for managing data effectively.
- Example: Setting policies for data privacy to comply with regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
Data Management:
- Focuses on the implementation of the policies and procedures defined by governance frameworks.
- Encompasses the technical processes required to collect, store, transform, analyze, and distribute data.
- Acts as the construction phase that operationalizes governance strategies.
- Example: Using ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes to clean and store data securely.
2. Roles and Teams
Data Governance:
- Led by business-oriented roles such as Chief Data Officers (CDOs), governance councils, and legal/security teams.
- Involves decision-makers responsible for setting policies and ensuring compliance across departments.
- Focuses on accountability frameworks that define who owns and controls specific data assets.
Data Management:
- Managed by technical teams such as IT departments or database administrators.
- Involves specialists responsible for executing processes like database maintenance, analytics scaling, and system integration.
- Requires collaboration with governance teams but focuses on operational tasks.
How to Enhance Your Data Governance & Compliance with Microsoft Purview
Explore how Microsoft Purview simplifies data governance and compliance with powerful tools for managing, protecting, and securing your data effectively.
3. Metrics for Success
Data Governance:
- Evaluated using high-level Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) like regulatory compliance rates, data usage efficiency, or business value derived from data.
- Success is measured by how well policies improve trust in data across the organization.
Data Management:
- Measured using technical metrics such as system uptime, data availability, processing speed, or throughput efficiency.
- Success is determined by how effectively systems enable secure storage and seamless access to usable data.
4. Tools Used
Data Governance:
- Relies on tools for monitoring compliance, enforcing standards, and creating a common vocabulary for business-wide data descriptions.
- Examples: Metadata management platforms or governance dashboards that track adherence to policies.
Data Management:
- Utilizes technical tools for collecting, processing, enriching, storing, and distributing data across systems.
- Examples: Data warehouses (e.g., Snowflake), ETL tools (e.g., Informatica), database systems (e.g., SQL Server).
5. Scope of Activities
Data Governance:
- Focuses on the why and what of managing data—why it needs protection and what policies should govern its lifecycle.
- Includes activities like defining consent requirements for personal information use or setting retention periods for archived data.
Data Management:
- Focuses on the how—how to execute governance policies effectively using technology.
- Includes activities like cleaning datasets for analytics or scaling reporting systems to handle large volumes of real-time data.
How Do Data Governance and Data Management Collaborate?
Data governance and data management are two essential practices that work hand in hand to ensure the optimal utilization of data within organizations. These practices collaborate on various aspects to promote data integrity, accessibility, and usability.
One area where data governance and data management intersect is regulatory compliance. Data governance establishes policies and guidelines to ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards. It sets the framework for data handling, storage, and protection. On the other hand, data management is responsible for implementing and enforcing these policies to ensure that the organization meets regulatory requirements. By working together, data governance and data management ensure that the organization complies with data protection laws and maintains the security and privacy of sensitive data.
Another important collaboration between data governance and data management is role-based access. Data governance defines user roles and their data access rights based on the organization’s data governance policies.
Data management then implements and monitors role-based access controls to ensure only authorized individuals can access specific data. This collaboration helps maintain data security and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Data cataloging is another area where data governance and data management collaborate. Data governance provides the necessary context and definitions for data assets, while data management organizes and connects data sources to the cataloging tool. This collaborative effort ensures that data assets are properly documented, classified, and easily discoverable, improving accessibility and usability.
Best Practices for Harmonizing Governance and Management
The data governance Vs data management debate is crucial in ensuring a well-structured and efficient data strategy. While they have distinct roles and responsibilities, data governance and data management work symbiotically to safeguard an organization’s effective utilization and management of data.
1. Establish Clear Roles and Responsibilities
- Define Governance Roles: Assign specific roles such as data stewards, governance board members, and data owners to oversee governance policies and ensure accountability.
- Integrate Management Teams: Ensure IT teams responsible for data management collaborate with governance teams to implement policies effectively.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involve stakeholders across departments (e.g., business leaders, IT professionals, security experts) to ensure governance aligns with operational needs.
2. Align Governance Policies with Business Goals
- Strategic Alignment: Data governance should support broader organizational objectives rather than operate as an isolated initiative.
- Prioritize Business Value: Focus on how governance policies improve decision-making, operational efficiency, or customer experience
- Adaptability: Ensure governance frameworks are flexible enough to evolve with changing business needs and regulatory requirements
3. Foster a Data Governance Culture
- Training Programs: Educate employees across all levels about governance policies, their roles in maintaining data integrity, and the importance of compliance.
- Ongoing Communication: Use newsletters, workshops, reports, or dashboards to keep stakeholders informed about governance progress and updates
- Promote Accountability: Encourage trust-based collaboration between business users and IT teams to reduce resistance to governance initiatives
4. Integrate Tools and Technology
- Data Discovery Tools: Use platforms like metadata management systems to gain visibility into the organization’s data landscape.
- Governance Software: Implement tools designed for managing policies, tracking compliance, and automating audits.
- Lifecycle Management Systems: Apply technologies that manage data throughout its lifecycle—from acquisition to disposal—to ensure consistency and security
5. Build Iterative Processes
- Start Small: Begin with a minimum viable deployment of governance policies and scale gradually based on feedback from stakeholders.
- Iterative Improvement: Continuously refine governance frameworks using metrics like data quality scores or compliance rates as benchmarks for success
- Break Down Complex Processes: Divide governance into smaller milestones (e.g., classification, tagging, lifecycle management) for easier implementation across departments.
Benefits of Proper Data Governance and Data Management
1. Improved Data Quality
Establishing governance policies and managing data properly ensures it is accurate, complete, and reliable — reducing errors and improving trust in reporting and analytics.
2. Regulatory Compliance
With clear governance rules and secure data management systems, organizations can meet legal and industry-specific regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX with less risk of violations or penalties.
3. Faster Decision-Making
Well-managed data that’s easy to access and trustworthy enables leaders to make informed decisions quickly, without second-guessing data accuracy.
4. Increased Operational Efficiency
Automated workflows, clear data roles, and standardized processes reduce duplication, manual corrections, and time spent searching for data.
5. Stronger Data Security
Governance defines who should access what data, and management enforces those controls — protecting sensitive information from misuse or breaches.
6. Cross-Departmental Alignment
Clear ownership and consistent definitions promote better collaboration between business and technical teams, eliminating confusion and data silos.
Kanerika: Your Trusted Partner for Implementing Robust Data Governance Solutions
At Kanerika, we understand that effective data governance is the backbone of any successful data-driven organization. As businesses increasingly rely on data to drive decision-making, it becomes crucial to manage, secure, and ensure the integrity of that data. With rising concerns over data privacy, security, and compliance, businesses need comprehensive governance strategies to protect and manage their valuable data assets.
As a trusted Microsoft Data & AI Solutions Partner, we specialize in deploying Microsoft Purview to help organizations build secure, scalable, and compliant data governance frameworks. Our expertise in implementing Microsoft Purview ensures that businesses can manage their data effectively while adhering to regulatory requirements, enhancing security, and driving operational efficiency.
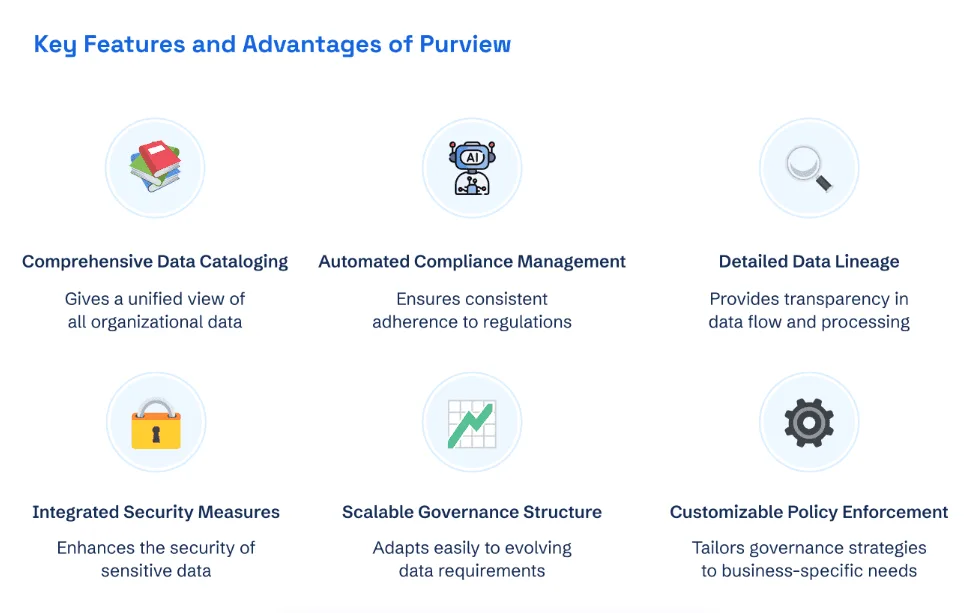
We craft customized data governance solutions that integrate industry-best practices and the latest technologies. From data privacy management to policy enforcement and data visibility, Kanerika provides the tools and expertise to ensure your data is both well-governed and strategically leveraged.
Partner with Kanerika to take control of your data governance processes. Together, we can build a future where your data is secure, compliant, and maximized for business success. Get in touch with us today to start your journey!
Strengthen Data Governance and Compliance with Microsoft Purview!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Purview implementation Services
FAQs
What are the key differences between data management and data governance?
Data management focuses on the technical aspects of handling data – storing, processing, and securing it. Data governance, conversely, is the strategic oversight and control of data, ensuring its quality, compliance, and ethical use. Think of data management as the “how,” and data governance as the “why” and “who” of data handling within an organization. They are intertwined but distinct disciplines.
What is the difference between data governance and master data management?
Data governance sets the rules of the road for how data is handled – its quality, security, and usage. Master data management (MDM) is a specific tool used to achieve data governance goals, focusing on creating a single, trusted source for critical business data like customer information. Think of governance as the overall strategy, and MDM as one key implementation method. They work together, but are distinct concepts.
What is data governance in data management?
Data governance is the overall management of data-related activities to ensure data quality, consistency, and compliance. It’s the “rules of the road” for how data is handled throughout its lifecycle, from creation to disposal. Think of it as establishing accountability and processes to ensure your organization’s data is trustworthy and useful. Good data governance prevents chaos and promotes informed decision-making.
What is the difference between data governance and DLP?
Data governance is the overall management of data throughout its lifecycle – ensuring quality, accessibility, and compliance. DLP (Data Loss Prevention) is a specific technology focused on preventing sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. Think of governance as the strategy, and DLP as one of the tools used to implement that strategy. DLP is a subset of the broader data governance framework.
What is meant by data management?
Data management is the art of organizing, storing, and accessing information effectively. It’s about ensuring data is reliable, secure, and readily available when needed, like a well-organized library for your information. This involves everything from database design to security protocols and data cleansing.
What is the difference between data management and database management?
Data management is the overarching strategy for handling all an organization’s information—its lifecycle, from creation to disposal. Database management, a subset of data management, focuses specifically on the creation, maintenance, and access of structured data within databases. Think of it as database management being a tool within the larger toolbox of data management. Essentially, databases are *how* we manage some of the data.
What is the difference between data governance and data compliance?
Data governance is how you manage your data – it’s the overall strategy for ensuring data quality, usability, and security. Data compliance, on the other hand, is *what* you must do – it’s about meeting specific legal and regulatory requirements for data handling. Governance sets the framework; compliance ensures you adhere to the rules within that framework. Think of governance as the map, and compliance as following the road.
What is the difference between data governance and data classification?
Data governance is the overall management of data, ensuring its quality, availability, and security across the entire organization. Data classification, on the other hand, is a subset of data governance, focusing specifically on categorizing data based on its sensitivity and value (e.g., public, confidential, restricted). Think of classification as a tool used within the broader framework of governance. Essentially, you classify data to effectively govern it.
What is the difference between data governance and data modeling?
Data governance is about who does what with data – the policies, processes, and accountability for data management. Data modeling, conversely, focuses on how data is structured and organized – the blueprints and diagrams defining data relationships within a system. One is about the people and rules, the other about the technical design. Think governance as the leadership, modeling as the architecture.
What is the difference between records management and data governance?
Records management focuses on the lifecycle of official organizational documents – their creation, storage, use, and eventual disposal, ensuring legal compliance and accessibility. Data governance is broader, encompassing the *overall strategy* for managing an organization’s data assets, including their quality, integrity, and security, to support business objectives.
What is the difference between data management and data administration?
Data management focuses on the practical handling of data – storing, accessing, and processing it efficiently. Data administration, however, is the *governance* aspect, setting policies, standards, and ensuring data quality and security across the entire organization. Think of management as the “how” and administration as the “why” and “what” of data handling. They are intertwined but distinct roles.
What is the difference between master data management and data governance?
Master Data Management (MDM) focuses on creating and maintaining a single, accurate source of truth* for critical business data (like customer or product information). Data Governance, on the other hand, is the broader framework that defines how data is managed across the entire organization*, encompassing policies, processes, and responsibilities – of which MDM is just one component. Think of MDM as a specific tool, and data governance as the overall strategy.
What is the difference between management and governance?
Management focuses on the day-to-day operations, ensuring tasks are completed and goals are met efficiently. Governance provides the overarching direction, strategy, and oversight for the organization. It ensures the organization operates ethically, responsibly, and achieves its long-term objectives. Simply put, management runs the business, while governance ensures it’s run well and for the right reasons.
What are the 4 pillars of data governance?
The four pillars of data governance are: People: Defining who is responsible for data. Processes: How data is handled and managed. Technology: The tools used to govern data effectively. Policies: The rules and standards for data use.
What comes first, data governance or data management?
Data governance sets the policies, standards, and responsibilities for how data should be handled. Data management is the act of putting those guidelines into practice, from collection to storage and use. Conceptually, governance comes first as it provides the framework that makes data management effective and compliant. They are inseparable and work hand-in-hand.
What is the difference between data governance and records management?
Data governance is the overarching framework that manages all organizational data, ensuring its quality, security, and usability. Records management is a crucial part of this, specifically focusing on information designated as official business records. It ensures these particular records are reliably maintained and accessible for compliance, legal, and historical needs.
What is the difference between data governance and data management?
Data governance defines the rules, policies, and responsibilities for how an organization uses and protects its data. It’s the what and why. Data management is the practical execution of those rules. It involves the processes and tools for collecting, storing, processing, and securing data day-to-day. Essentially, governance sets the strategy, and management executes it.
What are the 4 P's of governance?
The 4 P’s of governance outline key areas for good organizational management. They include People (roles, responsibilities, ethics), Purpose (mission, values, goals), Process (decision-making and operations), and Performance (measuring progress and accountability).
Why separate governance and management?
Separating governance (like a board) from management (day-to-day leaders) creates clear roles. Governance sets the overall direction and holds management accountable for results. Management then focuses on executing plans and running operations efficiently. This prevents conflicts of interest and strengthens oversight for better decision-making and long-term success.
What is another name for governance?
Another common term for governance is management or oversight. It refers to the overall system for directing and controlling an organization. This includes how decisions are made, implemented, and monitored to achieve its goals.
What is the difference between data governance and data asset management?
Data Governance establishes the rules, policies, and processes for managing data effectively, focusing on quality, security, and compliance. Data Asset Management is the practical work of identifying, organizing, storing, and making specific data available to maximize its value. Think of governance as setting the framework, while asset management is the operational side of handling your valuable data.
What is the difference between data governance and data analytics?
Data Governance sets the rules for how data is collected, stored, and used, ensuring it’s accurate, secure, and compliant. Data Analytics focuses on using that data to find patterns, insights, and trends to help make informed decisions. Essentially, governance ensures you have reliable data, while analytics uses it to understand and improve.
What is the difference between data governance and data strategy?
Data strategy defines what you want to achieve with your data to support business goals. Data governance then establishes how you’ll manage that data – setting the rules, standards, and responsibilities. Essentially, strategy is the what to do with data, while governance is the how to do it right and safely.
Which of the following is true for data governance and data management?
Data Governance defines the rules, policies, and responsibilities for how data should be handled, setting the what and why. Data Management is the practical execution of those rules, covering how data is collected, stored, protected, and used daily. Governance provides the oversight and framework, while management handles the operational tasks.
Should data governance be part of it?
Absolutely, data governance is vital. It ensures your data is reliable, secure, and used responsibly across the organization. This helps maintain quality, meet compliance requirements, and build trust in your information.