In 2025, prompt engineering has become a critical skill for businesses and individuals using ChatGPT and other large language models. OpenAI recently launched ChatGPT Enterprise, with advanced features that allow users to craft precise prompts for tasks such as summarization, content generation, and data analysis. In fact, companies like Shopify, HubSpot, and Microsoft are already leveraging prompt engineering to improve efficiency, automate workflows, and generate real-time, tailored insights. Experts say mastering prompts can be as impactful as coding when it comes to extracting value from AI.
A recent survey shows that over 65% of businesses using ChatGPT report improved productivity after training employees in prompt engineering. Furthermore, organizations that optimize prompts see up to 30% faster task completion and a 25% reduction in errors for AI-generated content. Investment in AI training, including prompt engineering workshops, is expected to exceed $1 billion globally in 2025, reflecting the growing importance of this skill in modern workplaces.
Continue reading this blog to explore what prompt engineering for ChatGPT entails, how to craft effective prompts, and practical tips for maximizing AI output in business and personal projects.
Key Takeaways
1. Prompt engineering is essential for maximizing the efficiency, accuracy, and relevance of AI outputs in business and personal tasks.
2. Engineered prompts provide context, audience, tone, structure, and examples, resulting in more precise and actionable responses than basic prompts.
3. Techniques such as zero-shot, few-shot, chain-of-thought, role-based, multi-turn, and template-based prompting improve AI performance for different use cases.
4. Understanding how large language models process prompts and selecting the right model ensures outputs align with task complexity and quality requirements.
5. Effective prompt writing focuses on clarity, context, structure, constraints, and examples to save time, maintain consistency, and produce professional results.
6. Investing in prompt engineering delivers measurable benefits, including faster task completion, reduced errors, enhanced creativity, and improved productivity across roles and industries.
Boost Your Business Growth With Smart AI Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
What Is Prompt Engineering for ChatGPT?
Prompt engineering is the deliberate practice of designing instructions that guide ChatGPT to produce precise, high-quality, and contextually relevant outputs. Unlike a simple question, prompt engineering considers the purpose of the production, the intended audience, the tone, the structure, and any constraints that affect clarity and usefulness. In 2025, prompt engineering has become a critical skill for anyone who wants to maximize the potential of AI, whether for business, research, content creation, or personal productivity.
Artificial intelligence has become a key part of modern workflows. Businesses, startups, content creators, and educators all rely on AI to save time, reduce repetitive tasks, and generate insights or creative output. However, without well-crafted prompts, even advanced models like ChatGPT can produce vague, inaccurate, or unstructured results. Consequently, mastering prompt engineering enables users to harness AI efficiently, reduce errors, and achieve actionable, professional outputs.
Why Prompt Engineering Is Important
- Improves Accuracy: Well-structured prompts guide the AI to focus on the most relevant information, reducing mistakes or irrelevant content.
- Saves Time: Instead of multiple iterations to get usable results, a precise prompt can produce high-quality output on the first attempt.
- Enhances Creativity: Clear instructions with constraints encourage the model to generate ideas or solutions aligned with the user’s goals.
- Ensures Consistency: Teams can maintain a consistent style, tone, and format across content by standardizing engineered prompts.
- Expands Usability: Prompt engineering allows AI to perform a wide variety of tasks, from content creation and coding to research and data summarization.
In short, prompt engineering turns AI from a general-purpose tool into a highly efficient assistant for specific tasks.
The Difference Between Basic and Engineered Prompts
Basic Prompts:
- Typically short and vague.
- Lack information about the audience, tone, or output format.
- Often produce generic, unstructured, or irrelevant results.
Engineered Prompts:
- Include the intended audience, context, tone, and format.
- Specify the desired length, style, and structure.
- Provide examples when necessary to guide output.
- Consistently produce structured, relevant, and actionable responses.
Example of Difference in Practice:
Basic Prompt:
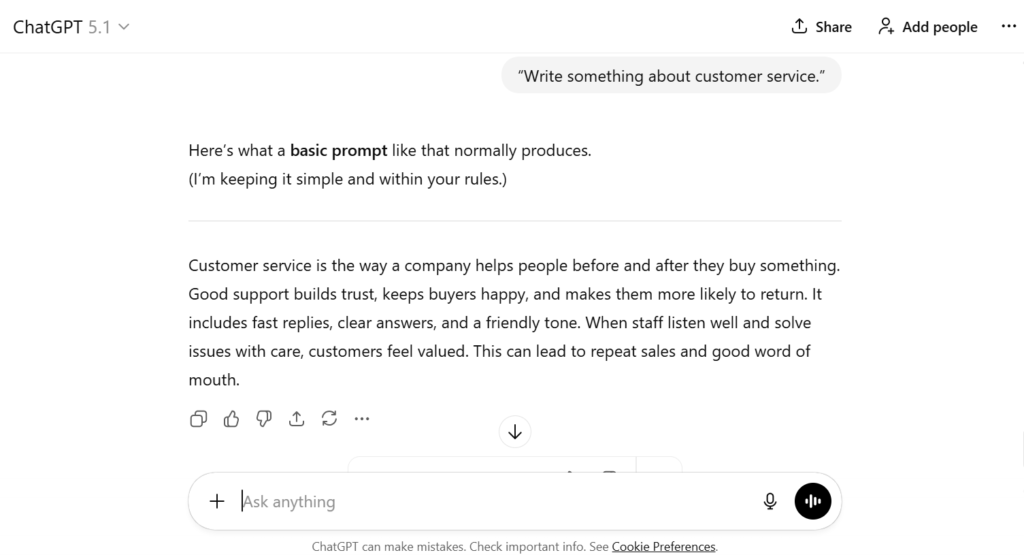
“Write something about customer service.”
What it gives:
A plain note about why customer service matters.
Engineered Prompt:
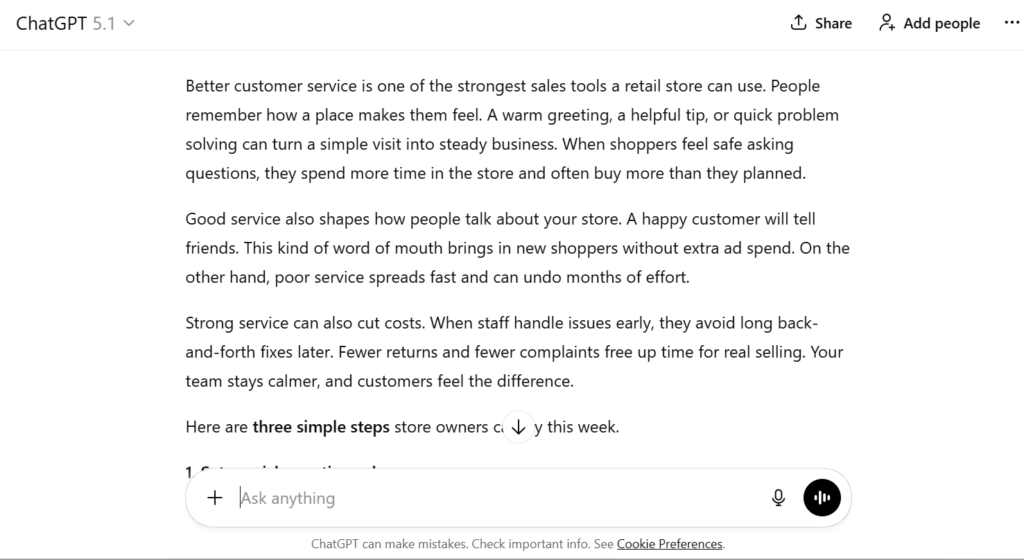
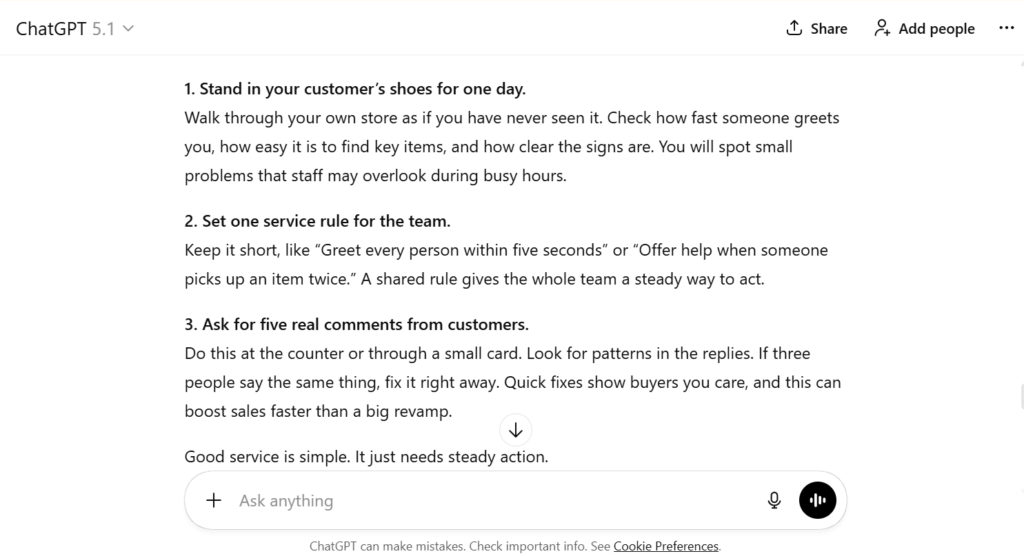
“You are a business coach. Write a 300-word note for retail store owners on how better customer service can grow sales. Add three steps that they can apply this week. Keep it clear and practical.”
What it gives:
A focused, useful guide with actions store owners can try right away.
This demonstrates that engineered prompts give the model context and direction, resulting in a far more valuable and usable response.
Who Benefits from Prompt Engineering
- Marketers: Generate targeted campaigns, social media posts, email sequences, and content calendars.
- Developers: Automate coding tasks, generate sample code, and debug efficiently.
- Writers: Produce outlines, drafts, rewritten content, and brainstorming ideas faster.
- Business Leaders: Summarize reports, create presentations, draft strategy documents, and generate client-ready content.
- Students and Researchers: Summarize complex concepts, create study guides, and generate research-based drafts.
Prompt engineering is no longer an optional skill. It is a core competency for anyone using AI to produce reliable, professional, and impactful outputs. Therefore, learning how to craft precise prompts allows users to fully leverage the potential of ChatGPT and other language models, improving both efficiency and quality across tasks.
How ChatGPT and Other LLMs Understand Prompts — Core Concepts
Understanding how ChatGPT interprets prompts is key to writing instructions that produce accurate and useful results. Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT do not “think” in a human sense. Instead, they generate responses by predicting the most likely following words based on the patterns they have learned from vast datasets. As a result, the model’s output depends heavily on the structure of the input, the context provided, and the constraints specified.
LLMs are sophisticated, but they are highly sensitive to the clarity and specificity of prompts. A well-designed prompt helps the model focus on what matters, while vague or ambiguous prompts can produce inconsistent, incomplete, or irrelevant responses. To get the best results, it is important to understand how models process instructions, how context affects their outputs, and their limitations.
How LLMs Process Prompts
- Token-based prediction: LLMs break input text into small units called tokens. Each token is analyzed, and the model predicts the next token based on probability patterns. This process continues until a complete response is generated.
- Pattern recognition: The model relies on learned patterns from billions of text examples. It does not reason like a human but simulates reasoning based on statistical correlations.
- Influence of context: The information you provide in the prompt serves as a guide. More detailed context helps the model align its outputs with your goals. Without context, responses may be generic or inaccurate.
Example:
Prompt: Explain cloud computing.
Engineered Prompt: You are a cloud technology consultant. Explain cloud computing to small business owners, covering storage, scalability, and security in simple language with examples.
The second prompt produces a focused, structured explanation by defining the audience, tone, and topics to cover.
The Role of Model Type
Different LLMs interpret prompts in different ways depending on their design:
- Reasoning-optimized models (GPT‑4, GPT‑5.1, GPT‑5.1 Codex‑Max): These models excel at multi-step reasoning, problem solving, and structured outputs. They are ideal for coding, data analysis, strategy planning, technical writing, or multi-part reasoning tasks. In particular, Codex‑Max supports longer context windows, making it suitable for large projects or complex workflows.
- General-purpose models (GPT‑3.5, GPT‑4 standard, GPT‑5.1 general): These models are flexible and perform well for conversational tasks, creative writing, summarization, and content generation. They can adapt to different tones, styles, and audiences, making them ideal for marketing content, blogs, presentations, or customer-facing communication.
- Lightweight or smaller models (GPT‑5.1 mini, GPT‑5.1 nano, earlier GPT‑3.5 variants): These are faster, cheaper, and optimized for high-volume or low-complexity tasks. They work well for internal automation, quick drafts, simple text generation, or classification tasks. However, they may produce less detailed or nuanced responses for complex instructions.
Selecting the appropriate model ensures your prompts align with the model’s strengths.
Importance of Context and Instructions
The way you provide context and instructions directly affects the output:
- Role definition: Telling the model “You are a financial analyst” or “You are a content strategist” aligns its language, tone, and focus.
- Audience specification: Clarifying the reader level (beginner, expert, general public) ensures the explanation is accessible and relevant.
- Tone and style: Formal, friendly, technical, or persuasive tones can be set through instructions.
- Format and structure: Indicating if the output should be a list, table, bullet points, steps, or a short paragraph ensures the response is usable.
Example:
Prompt: Summarize AI in healthcare.
Engineered Prompt: You are a healthcare analyst. Summarize AI applications in healthcare for hospital administrators. Use clear bullet points and keep it under 200 words.
The second prompt gives a concise, structured summary suitable for decision-making.
Common Limitations to Keep in Mind
Even advanced LLMs have boundaries that prompt engineers to consider:
- Context window limits: LLMs can process only a limited amount of text at a time. Very long conversations or documents may lead to details being missed or forgotten.
- Sensitivity to wording: Minor changes in phrasing can drastically alter the response.
- Randomness: LLMs generate outputs probabilistically. Even identical prompts may produce slightly different results.
- No real-time knowledge: Models do not access current events unless explicitly provided in the prompt.
- Ambiguity leads to inconsistency: Unclear or contradictory instructions can result in irrelevant or partially incorrect outputs.
Understanding these limitations helps users design prompts that the model can interpret correctly, reducing errors and improving consistency.
What’s Next in OpenAI’s Expansion of Apps in ChatGPT?
Discover how ChatGPT apps streamline travel planning, playlists, learning and design in-chat.
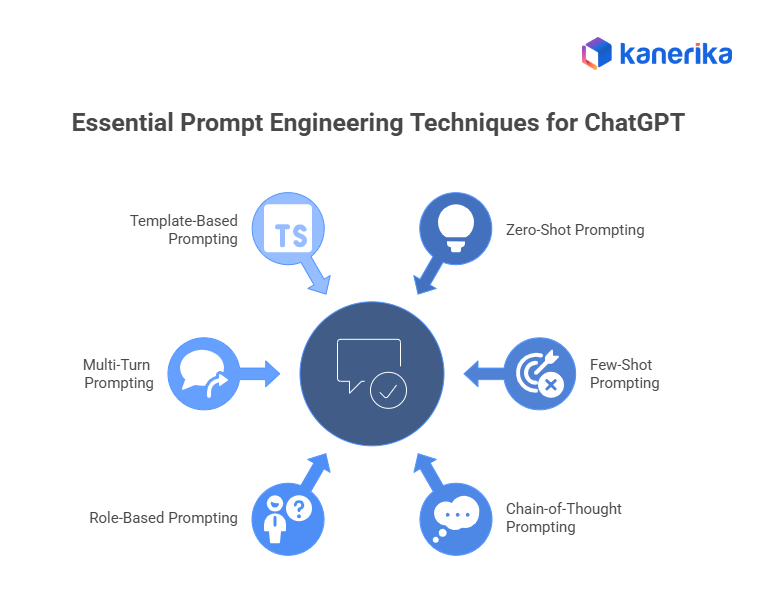
Essential Prompt Engineering Techniques for ChatGPT
Prompt engineering is a crucial skill for getting precise, structured, and actionable responses from ChatGPT. By applying the right techniques, users can effectively guide the model for content creation, problem-solving, and complex analytical tasks. The following techniques are essential for maximizing the quality of AI outputs.
1. Zero-Shot Prompting
Zero-shot prompting involves giving ChatGPT direct instructions without examples. The model relies entirely on the prompt to generate output.
- When to use: Simple and straightforward tasks where instructions are clear.
- Example: Summarize this article in three sentences.
- Best for: Quick summaries, basic explanations, and short-form content.
This technique is fast and efficient, but it requires precise wording to avoid vague or generic responses.
2. Few-Shot Prompting
Few-shot prompting provides examples along with the instruction. This helps the model recognize patterns and replicate the desired style, tone, or format.
- When to use: Tasks requiring consistency in format or repeated patterns.
- Example: Show ChatGPT two question-and-answer pairs and then ask it to answer a new, similar question.
- Best for: FAQs, structured content, standardized outputs.
Consequently, few-shot prompting reduces ambiguity and ensures more reliable, consistent responses.
3. Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Chain-of-thought prompting instructs ChatGPT to think through the steps. This technique is especially effective for multi-step logic, problem-solving, or analytical tasks.
- When to use: Complex reasoning, coding, math problems, or analytical exercises.
- Example: Solve this math problem and show your work: If a train travels 60 miles in 1.5 hours, what is its speed in miles per hour?
- Best for: Multi-step reasoning, logical problem solving, and coding tasks.
In turn, asking the model to show reasoning helps identify errors and ensures accurate outputs.
4. Role-Based Prompting
Role-based prompting assigns ChatGPT a specific persona or expertise to produce professional and audience-specific responses.
- When to use: Tasks requiring domain knowledge or specialized tone.
- Example: You are a financial advisor. Explain investment options to a beginner.
- Best for: Professional writing, consulting advice, marketing content, or educational explanations.
This technique provides context and authority, improving the relevance and credibility of outputs.
5. Multi-Turn Prompting
Multi-turn prompting uses iterative dialogue to refine responses over multiple exchanges.
- When to use: Brainstorming, editing, iterative improvements, or interactive problem solving.
- Example: User requests a blog draft, then asks ChatGPT to shorten paragraphs or add examples.
- Best for: Collaborative content creation and refining outputs to the desired quality.
This method mimics human editing and allows progressive improvement of AI-generated content.
6. Template-Based Prompting
Template-based prompting involves creating reusable prompt structures for recurring tasks.
- When to use: High-volume, repeatable content creation such as emails, reports, or social media posts.
- Example Template: You are a [role]. Write a [type of content] for [audience] about [topic]. Include [key points] and maintain [tone]. Word limit: [x] words.
- How to customize: Replace placeholders, adjust tone, and add constraints like word count or bullet points.
- Best for: Streamlining workflows and maintaining consistency across content.
Templates save time while ensuring structured, professional, and high-quality outputs.
Real-World Example — Good vs Bad Prompt (With Business Context)
In business, the effectiveness of AI outputs depends heavily on the quality of prompts. Poorly worded prompts produce generic or unusable content, while well-crafted prompts deliver actionable, professional, and department-specific results. Below are examples across five key business departments with analysis.
1. Marketing
- Bad Prompt: Write a blog about AI.
- Good Prompt: Write a 500-word blog for small business owners explaining how AI can optimize marketing campaigns. Include two case studies, break content into sections with headings, and maintain a professional yet approachable tone.
- Analysis: Clear audience, tone, structure, and examples make the output actionable for marketing teams, saving time on editing and research.
2. Sales
- Bad Prompt: Write a sales email.
- Good Prompt: Draft a 120-word email for IT managers promoting our cloud software. Highlight security features, include a call to action, and maintain a professional, persuasive tone.
- Analysis: By specifying audience, word count, and tone, the email becomes conversion-focused and ready for deployment in campaigns.
3. Human Resources
- Bad Prompt: Create an onboarding guide.
- Good Prompt: Draft a 300-word onboarding email for new employees that explains company policies, the reporting structure, and key resources. Use a friendly, welcoming tone and bullet points for clarity.
- Analysis: Structured, clear, and audience-specific prompts make internal communication more effective, reducing the need for follow-up questions.
4. Finance/Analytics
- Bad Prompt: Summarize the quarterly report.
- Good Prompt: Summarize Q3 sales and revenue data for executives in 200 words. Highlight key trends, top-performing products, and areas for improvement. Present insights in bullet points.
- Analysis: Providing audience context, format, and key focus areas ensures reports are concise, actionable, and suitable for decision-making.
5. Social Media / Brand Communications
- Bad Prompt: Write a post about marketing.
- Good Prompt: Create a 100-word LinkedIn post for marketing managers highlighting three strategies to boost Instagram engagement. Use a professional but friendly tone and include actionable tips.
- Analysis: Audience, platform, tone, and actionable content make the post ready for publishing, increasing engagement while aligning with brand strategy.
ChatGPT Atlas vs Perplexity Comet in 2025: Which Is Better?
Compare ChatGPT Atlas and Perplexity Comet to understand features pros cons and best use cases
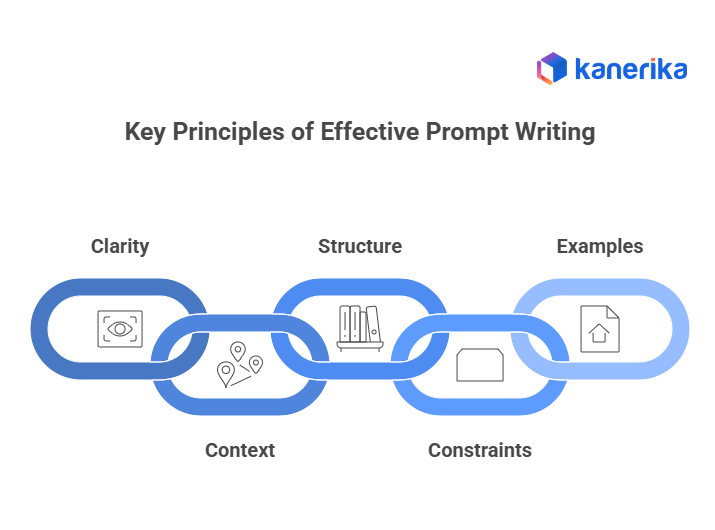
Key Principles of Effective Prompt Writing
Effective prompt writing ensures that ChatGPT delivers outputs that are accurate, structured, and immediately actionable, especially in a business context. Following key principles helps teams across marketing, sales, HR, finance, and social media consistently achieve professional results.
1. Clarity
Be precise with your instructions. Avoid vague phrases like “Write something about marketing.” Instead, specify the audience, purpose, tone, and format.
Example: Write a 400-word blog for small business owners explaining how AI improves customer service. Include two real-world examples and structure content with headings.
2. Context
Provide relevant background to guide the AI. Context ensures outputs align with your business objectives.
Example: Instead of “Draft a sales email,” specify: Draft a 120-word email for IT managers promoting our cloud software. Highlight the security benefits and include a call to action.
3. Structure
Specify the desired format to improve readability and usability. Structured prompts result in outputs that are easy to implement.
Example: Ask for bullet points, headings, or numbered lists if the output requires clarity.
4. Constraints
Limit word count, style, or scope to prevent irrelevant or overly verbose responses.
Example: Provide a 200-word LinkedIn post with three actionable tips for marketing managers.
5. Examples
Providing sample input-output pairs or few-shot examples helps maintain consistency and reduces ambiguity.
Following these principles allows teams to save time, reduce revisions, and maximize the value of AI in business workflows.
Common Prompt Engineering Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced users can make errors that reduce the effectiveness of AI outputs. Avoiding these common mistakes ensures responses are accurate, structured, and aligned with business objectives.
1. Being Too Vague or Open-Ended
Vague prompts often lead to generic or irrelevant outputs. Without clear direction, the AI may struggle to understand the intent or produce content that meets your objectives.
2. Overloading with Too Many Instructions
Providing too many instructions at once can overwhelm the model, resulting in incomplete, confusing, or inconsistent outputs. As a result, breaking complex requests into smaller, focused tasks improves clarity and quality.
3. Not Providing Enough Context
When prompts lack background information, the AI cannot tailor responses to the audience or purpose. Therefore, context is crucial for generating relevant, actionable, and professional outputs.
4. Ignoring Output Format
Failing to specify the desired format can lead to unstructured or hard-to-use content. Clear format guidance ensures outputs are easy to read, implement, and integrate into workflows.
5. Using Ambiguous Language
Unclear or subjective terms can confuse the AI, causing inconsistent results. Consequently, using precise, objective language improves accuracy and ensures the output aligns with expectations.
Kanerika: Driving Digital Transformation with Data and AI
Kanerika delivers data-driven software solutions that help businesses transform and grow. We specialize in Data Integration, Analytics, AI/ML, and Cloud Management, combining advanced technology with agile practices to deliver measurable results. Our focus is simple: to make data work for our clients by turning complexity into clarity and action.
Quality and security are at the core of everything we do. Our processes meet global standards with ISO 27701 and 27001 certifications, SOC II compliance, and GDPR adherence. Furthermore, we are also CMMi Level 3 appraised, ensuring every solution is robust, secure, and ready for enterprise-scale performance.
Our partnerships with Microsoft, AWS, and Informatica strengthen our ability to deliver innovative solutions. At Kanerika, we combine expertise, technology, and collaboration to help organizations unlock the full potential of their data and drive growth through intelligent solutions.
Upgrade Your Workflows With Intelligent AI Innovations!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
1. What is prompt engineering for ChatGPT?
Prompt engineering for ChatGPT is the practice of writing clear and structured instructions that guide the model toward accurate and helpful responses. It focuses on choosing the right words, adding context, and giving clear expectations so the output matches your goal.
2. Why is prompt engineering important?
It helps improve the quality and relevance of the answers you receive. With a well written prompt, ChatGPT understands your intent better and gives results that require fewer edits. This saves time and helps you get consistent and reliable responses.
3. How do I write an effective prompt?
Start by stating your goal clearly. Add context, define the tone or style, and specify the format such as list, paragraph or table. You can also include examples to show the exact type of output you prefer. These small details make a big difference in the final result.
4. What mistakes should I avoid in prompt engineering?
Avoid giving vague instructions, missing key details, or mixing too many ideas in one prompt. Lack of structure can confuse the model and lead to weak results. Keeping prompts clear, direct, and focused helps the AI respond more accurately.
5. Can beginners learn prompt engineering easily?
Yes. Prompt engineering does not require technical skills. It is mainly about communicating your needs clearly and learning how to structure instructions. With a little practice, anyone can improve their prompts and get better outputs from ChatGPT.










