Did you know the healthcare industry generates more data than any other sector in the world? Healthcare data takes many forms, including MRI scans, genetic reports, fitness tracker data, and online prescriptions. With this exponential growth, cloud-based healthcare enables efficient management and secure storage of data.
In 2025, global healthcare data is expected to reach 10.8 zettabytes, growing rapidly from 2.3 zettabytes in 2020. This surge is driven by advancements in medical imaging, genomics, wearable technology, and electronic health records. According to a report by L.E.K. Consulting, healthcare data is growing at an annual rate of 36%, making it one of the fastest-expanding data sources worldwide.
This data explosion is overwhelming traditional IT systems, making it harder for healthcare providers to gain insights, share information, and respond to patients quickly. Cloud-based healthcare helps by enabling secure, efficient, and collaborative data management, improving diagnostics, and streamlining hospital operations. It’s transforming healthcare delivery.
Let’s keep reading to explore how this digital transformation is shaping the future of healthcare.
Digital Transformation in Healthcare: Improving Quality of Life
Discover how digital transformation is improving healthcare with smarter tech and better patient outcomes.
What is Cloud-Based Healthcare?
Cloud-based healthcare is the implementation of cloud computing resources, such as data storage, remote servers, and other digital tools, for managing the applications and services of a healthcare organization. Rather than relying solely on the physical servers located in the hospital, cloud-based systems enable healthcare providers to access and process information using secure internet-based systems. The cloud storage reduces the barriers to data storage, advanced computing analyses, and remote healthcare delivery.
Why is it Significant?
A recent report by MarketsandMarkets in 2023 suggests that the worldwide cloud computing in healthcare is projected to grow to $89.4 billion by 2027, with a 17.2% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). The need for better access and increased telehealth services has led to a more accessible infrastructure paradigm. The move to cloud-based infrastructure and services is not just a technology adoption. It is a tactical response to advanced healthcare that improves clinical outcomes and operational efficiency.
Consider a rural outpatient clinic. A neurologist monitoring the imaging results of stroke treatment can upload the results of imaging tests to the cloud. A neurologist in a city hospital can access them, issue instructions, and treatment can be initiated in real-time. Cloud-based healthcare systems enable such collaborative life-saving responses.
Key Attributes of Cloud-Based Healthcare Systems
- Scalability: Adapts effortlessly to changing workloads such as increasing users and data volume.
- Accessibility: Remote consultations and telehealth services are possible as data can be accessed from any location.
- Cost Efficiency: Maintenance and hardware expenses are reduced using cloud computing systems with pay-per-use services.
- Interoperability: Allows integration of applications and enables data sharing with minimum friction across platforms from different providers.
- Security & Compliance: Fulfills HIPAA and other regulatory requirements with strong cloud security measures; proprietary cloud healthcare systems offer high protection against data breaches.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models in Healthcare
| Deployment Model | Description | Use in Healthcare | Example |
| Public Cloud | Services are offered over the internet by third-party providers. | Storing non-sensitive data, managing patient engagement apps, and telehealth platforms. | AWS HealthLake, Microsoft Azure |
| Private Cloud | Exclusive environment managed internally or by a third party. | Hosting EHRs (Electronic Health Records), ensuring high compliance and data control. | On-premise VMware, IBM Cloud |
| Hybrid Cloud | A Combination of public and private clouds. | Sharing non-sensitive data on a public cloud while keeping sensitive data private. | AWS Outposts, Azure Stack |
| Community Cloud | Shared infrastructure among organizations with similar needs. | Hospitals or clinics can share resources, collaborate on research, or adhere to standard regulations. | Google Cloud Healthcare Data Engine |
Secure, Scalable, and Smarter Healthcare!
Partner with Kanerika for Digital Health Transformation.
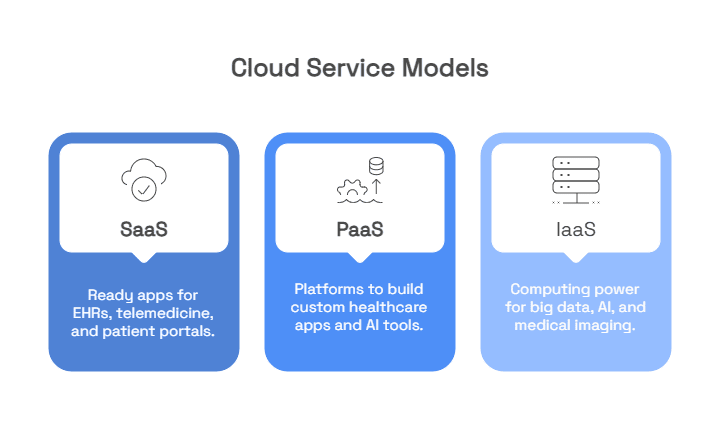
Cloud Service Models in Healthcare
Cloud computing in healthcare is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Instead, it offers three primary service models, each tailored to different operational and clinical needs. By understanding these models, healthcare organizations can better align their cloud strategy with their goals.
1. SaaS (Software as a Service)
To start with, SaaS delivers fully developed, ready-to-use applications over the internet. Healthcare providers can subscribe and start using these tools without worrying about backend infrastructure.
Common Use Cases:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs) – Platforms like Epic and Cerner help manage patient records securely and efficiently.
- Telemedicine Solutions – Tools like Zoom for Healthcare and Amwell enable virtual consultations and remote monitoring.
- Patient Portals – Allow patients to book appointments, view test results, pay bills, and communicate with their providers.
Benefits: Quick deployment, low IT maintenance, automatic updates, and cost efficiency.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Next, PaaS provides a framework for developers to build, test, and deploy healthcare applications without managing servers, storage, or network layers. This is ideal for innovation-driven organizations looking to create tailored digital health solutions.
Use Cases in Healthcare:
- Developing patient engagement apps tailored to specific populations
- Building AI diagnostic tools that analyze medical images
- Creating mobile health platforms for remote monitoring
Examples: Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform
Benefits: Speeds up development, allows easy scaling, and simplifies integration with existing systems.
3. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Finally, IaaS offers raw computing resources—like virtual servers, storage, and networking components. It’s best suited for institutions that need complete control over their environment, particularly for data-intensive tasks.
Use Cases in Healthcare:
- Running genomic data analysis for personalized medicine
- Training machine learning models for predictive diagnostics
- Storing and retrieving high-resolution medical images
Examples: AWS EC2, IBM Cloud, Google Compute Engine
Benefits: Maximum flexibility, high performance, scalable infrastructure tailored to intensive workloads.
In short, choosing between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS depends on the organization’s goals. While SaaS is best for everyday clinical tasks, PaaS supports innovation, and IaaS powers large-scale research and analytics. The right mix ensures better care, flexibility, and long-term growth.
Major Cloud Providers and Their Healthcare-Specific Solutions
Cloud computing is quietly revolutionizing healthcare. Instead of just being a place to store data, the cloud now gives hospitals and clinics the ability to access information in real time, scale up quickly when needed, and use smart tools powered by artificial intelligence. Big tech companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google aren’t just offering generic cloud services anymore—they’re designing solutions especially for medicine. These help with everything from protecting patient privacy and following strict healthcare rules to connecting different systems and making doctors’ jobs easier.
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
AWS is a leading choice for hospitals and labs moving their operations to the cloud. One major reason is that AWS provides more than 130 tools that meet healthcare privacy laws like HIPAA. Two of their key tools are:
- Amazon HealthLake: This service helps organize and clean up patient data, turning messy records into a format that’s easy to search and analyze. Doctors can see lab results, notes, and more, all in one place—making it easier to make informed decisions.
- Amazon Comprehend Medical: Reading through endless charts? This tool uses AI to automatically pull out critical details from medical documents—like diagnoses, medicines, or procedures—so nothing important gets missed.
You’ll find AWS behind telemedicine apps, in labs doing genetic research, and in hospitals using AI to help doctors diagnose faster—all around the world.
Microsoft Azure:
Azure stands out because it connects smoothly with products that many healthcare workers already use every day, like Outlook and Teams. Microsoft has created specialized healthcare options, such as:
- FHIR Server: This lets medical teams securely share and move health data between systems, whether that’s the pharmacy, billing, or lab departments.
- Azure Health Bot: When patients ask health questions online, this smart bot can help them figure out symptoms, give reliable information, and even book appointments.
- Care Coordination Tools: These features help keep tabs on each patient’s journey, making care more personal and making sure important steps never fall through the cracks.
Azure is great for hospitals moving away from old tech, adding new tools like predictive analytics, or setting up remote care, without disrupting what already works.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
GCP is known for handling huge amounts of data and offering powerful AI. Its main healthcare platform helps different medical systems work together by using shared data formats. Key features include:
- Support for HL7, FHIR, and DICOM: This means X-ray images, test results, and electronic health records from different places can all connect and communicate easily.
- Real-time data streaming: Data comes in instantly from devices and labs, letting healthcare teams spot important changes as they happen.
- Integration with Vertex AI and BigQuery: These advanced tools help experts build models that can predict patient risks, score health outcomes, and run large-scale research to improve care.
Doctors, researchers, and even public health agencies use Google Cloud for everything from finding new medicines to tracking outbreaks and improving diagnostic tools.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) Vendors Moving to Cloud
EHR vendors are increasingly migrating their systems to cloud infrastructure to improve scalability, reduce operational costs, and ensure compliance with evolving healthcare regulations. This shift allows healthcare providers to access patient data securely from anywhere, enabling better care coordination and innovation.
- In the United States, over 80% of hospital data is managed by Epic Systems and Cerner, which are both transmitted using HIPAA-compliant cloud platforms. Key features of their cloud solutions include storage, computing, and scalability, with greater interoperability and telehealth service support.
- Vendors like Allscripts and Athenahealth are adopting cloud-based, flexible deployment models, which enable faster integration with third-party applications and easier updates.
- Several cloud providers collaborate with EHR vendors to deploy functionalities like telehealth tools, remote patient monitoring solutions, AI-driven medical imaging analytics, and real-time data sharing across healthcare ecosystems.
Accelerate Healthcare Innovation with AI Expertise!
Let Kanerika guide your transformation journey.
Security and Compliance in Cloud Healthcare
Security and regulatory compliance are critical when healthcare organizations move to the cloud. Patient data is highly sensitive, and stringent standards govern its protection. Below are the key areas healthcare organizations and cloud providers must focus on:
1. HIPAA Compliance Requirements
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires healthcare entities and their partners to protect patients’ electronic health information (ePHI).
- Compliance includes signing a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with cloud providers, which legally obligates them to safeguard health data.
- Healthcare organizations must conduct regular risk assessments, implement role-based access controls, and provide staff training on HIPAA regulations.
Example: AWS signs Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with healthcare customers, ensuring shared accountability for PHI protection.
2. Data Encryption and Privacy Protection
- Data must be encrypted at rest (stored data) using strong standards like AES-256.
- Data in transit (moving between systems) must be secured using protocols such as TLS 1.2+ to prevent interception.
- Additional privacy measures include tokenization and pseudonymization to mask patient identifiers and protect data privacy.
- Segregation of protected health information (PHI) from other data helps ensure compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other laws.
Example: Mayo Clinic encrypts all patient data at rest and in transit using AES-256 and TLS 1.2+, ensuring data remains confidential and tamper-proof.
3. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- IAM systems enforce role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify patient data.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification steps.
- Fine-grained permissions and federated identity management support secure access across multiple systems and organizations.
- Leading cloud providers offer integrated IAM tools, such as AWS IAM, Azure Active Directory, and Google Cloud IAM, designed to meet healthcare security requirements.
Example: Johns Hopkins Medicine uses Azure Active Directory with role-based access control and multi-factor authentication to limit data access to authorized clinicians only.
4. Audit Trails and Monitoring
- Comprehensive audit logs track who accessed or changed data, helping detect unauthorized activity. Tools include AWS CloudTrail, Azure Activity Logs, and Google Cloud Audit Logs.
- Real-time monitoring tools alert organizations to suspicious behavior or security incidents.
- Automated compliance reporting simplifies regulatory audits and helps maintain ongoing transparency.
Example: Cleveland Clinic employs AWS CloudTrail and GuardDuty to monitor access logs and detect suspicious activity in real time, enabling fast incident response.
5. Shared Responsibility Model
- Cloud security follows a shared responsibility model in which cloud providers secure the physical infrastructure, such as data centers, hardware, and networking.
- Healthcare organizations are responsible for protecting their data, managing access controls, properly configuring services, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Misconfigurations on the customer side, such as open storage buckets or weak permissions, can cause data breaches despite a secure cloud infrastructure.
- Understanding and correctly implementing security controls on both sides is vital for protecting patient data.
From Theory To Therapy: Impact Of Automation In Healthcare
Discover how automation in healthcare streamlines workflows, elevates patient care, and accelerates innovation.
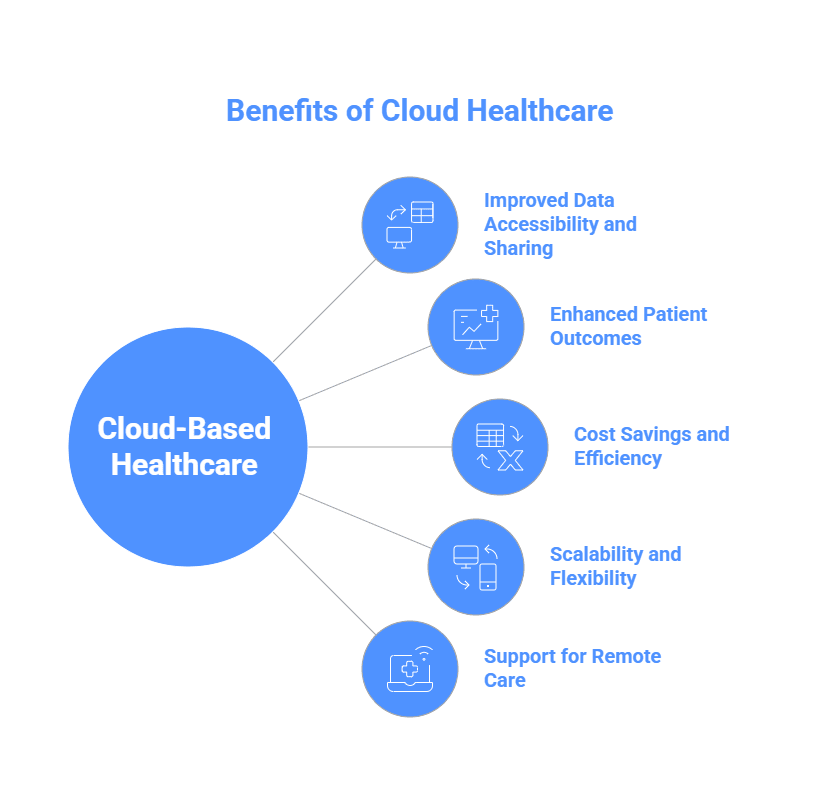
5 Benefits of Cloud-Based Healthcare
The health care industry is continuously evolving with new technologies, and the introduction of cloud computing has proven to have many advantages. The most important are listed below.
1. Enhanced Performance and Improved Accessibility
Healthcare professionals can now easily access sensitive patient data from the cloud, a significant improvement from the past when access was limited. This is vital during emergencies, remote consultations, and across multi-location hospitals. Cloud access also enables data sharing and integration with medical devices, helping speed up diagnosis and treatment in specialized care centers.
2. Improved Patient Outcomes Provided Through the Insights
With the cloud, servers can run analytics on data as it’s being ingested. This capability enables health care service specialists to monitor patient vitals in real time, detect anomalies, and respond to them in advance.
For instance, if a doctor can connect with a patient via cloud and the patient has a wearable device linked with the cloud, the doctor’s office can be notified of an abnormal heart rhythm or elevated blood sugar.
3. Cost Savings and Efficiency
Healthcare organizations no longer need to buy servers and maintain them. For health organizations, having no on-site servers to maintain also means no additional IT costs. They only pay for the resources they use, which also allows for greater flexibility in budget allocations.
4. Flexibility and Scalability
Cloud platforms can adjust easily to reimbursements in real time, like growing data volumes, new applications, or increased user demand. Whether it’s expanding a telehealth service or integrating AI diagnostics, cloud infrastructure supports rapid innovation without the need for hardware upgrades.
5. Support for Remote Care and Telehealth
Finally, cloud computing has become essential for remote care and telemedicine. It powers secure video calls, remote health monitoring, and digital prescriptions. This is especially valuable for people living in rural or hard-to-reach areas, as they can now receive quality care without the need to travel, helping make healthcare more accessible and fairer.
Key Use Cases of Cloud in Healthcare
Cloud technology is being applied across a wide range of healthcare functions. Here are some of the most transformative use cases:
1. Remote Patient Monitoring
With the help of cloud technology, glucose and blood pressure monitors, pulse oximeters, smart watches, and other health gadgets help in acquiring and sending patient data to health providers literally in real time. This real-time data acquisition aids in monitoring chronic conditions and minimizing hospital readmissions.
2. AI-Powered Diagnostics
Examination of relevant medical images, pathology slides, and even genetic data is possible thanks to the advanced algorithms that AI systems run. These algorithms, though complex, run smoothly due to the computational power cloud platforms provide. This AI technology helps radiologists and pathologists in early and accurate detection of diseases.
Example: Google’s DeepMind uses cloud-based AI to detect eye diseases from retinal scans with high accuracy.
3. Medical Image Storage and Sharing
Health providers and hospitals generate massive amounts of imaging data, from X-rays and MRIs to even CT scans. These files not only need to be stored securely but also need to be accessed easily. Cloud systems not only provide safe, scalable storage but also facilitate the sharing of files between departments or even with other institutions. This helps in acquiring second opinions and in collaborative care.
4. Disaster Recovery and Data Backup
Even with attacks from hackers, hardware failures, or natural disasters, patient data has to be continuously available and accessible during surgeries and other medical procedures. This is possible thanks to the built-in redundancy systems and backup features that cloud systems offer.
5. Collaboration Across Care Teams
With the use of cloud systems and communication tools, doctors, case nurses, consult doctors, medical specialists, and even the administrators of a health facility can work seamlessly. Shared access to patient records improves coordination, reduces errors, and enhances the overall patient experience.
Redefining Healthcare with AI Expertise!
Kanerika helps you achieve seamless, tech-enabled care.
Common Challenges and Risks
While cloud adoption in healthcare has many favorable effects, many other considerations need to be accounted for to ensure safety, compliance, and reliability.
1. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Healthcare data includes sensitive information about patients and their medical conditions, and breaches can have profound effects on patients and medical organizations. Cloud platform vendors need to have some layered security measures for data management that include:
- End-to-end encryption
- Multi-factor authentication
- Role-based access control
- Routine or cyclical vulnerability assessments
Solution: Identify cloud vendors that have industry-specific security certifications (HITRUST, ISO 27001) and implement zero-trust architecture.
2. Compliance with HIPAA and Other Regulations
Healthcare organizations must comply with regulations such as HIPAA in the USA, the GDPR in the EU, and other rules that govern privacy rights and data restrictions regarding patients. Failure to comply can result in financial deductions or even the forfeiture of reputation.
Solution: Find cloud vendors that offer compliance-ready solutions and are willing to sign Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) to provide accountability attached to compliance in establishing roles following HIPAA. Regular audits and staff training will provide additional value by addressing roadblocks that have arisen due to a lack of knowledge during compliance with regulations.
3. Vendor Lock-In and Service Reliability
Heavy reliance on a single cloud vendor can create vendor lock-in that can become difficult to change on the platform for reasons of fairness or timing, and heavily relied-upon cloud solutions also downgrade the trust in service reliability.
Solution: Implement a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy to reduce dependence on a single vendor service. Increased use of containerization and open standards can allow for portability. Track the service level agreements (SLAs) or uptime guarantees offered by your cloud vendor.
4. Internet Access and Infrastructure Gaps
Most systems rely on access to the Internet’s connectivity, and in some rural or underserved areas, that connectivity may be lacking. This may limit access to cloud-based services and telehealth services.
Solution: Implement edge computing solutions that identify end-user data access locally and synchronize data back to the cloud once a connection is achieved. Governments and NGOs can also implement capacity-building infrastructure in remote communities.
Real-World Examples of Cloud-Based Healthcare
Cloud computing is no longer a concept of the future in healthcare. It is disrupting the way that healthcare is delivered, managed, and decisions are operationalized. Let’s look at some of the real-world examples that illustrate cloud-based healthcare.
1. Mount Sinai Health System – Predictive Analytics for ICU Resource Optimization
Overview:
Mount Sinai in New York is utilizing cloud-based analytics to monitor patients’ vitals in real-time to predict deterioration. By taking information from various sources into a centralized cloud-based portal, Mount Sinai is helping clinicians to identify patients of the highest risk sooner and allocate ICU resources accordingly.
Impact:
Reduced ICU days: Improved triage and resource allocation: Improved patient outcomes by predicting care:
Technology Used:
Cloud-based predictive models, monitoring dashboards in real time, and data aggregation.
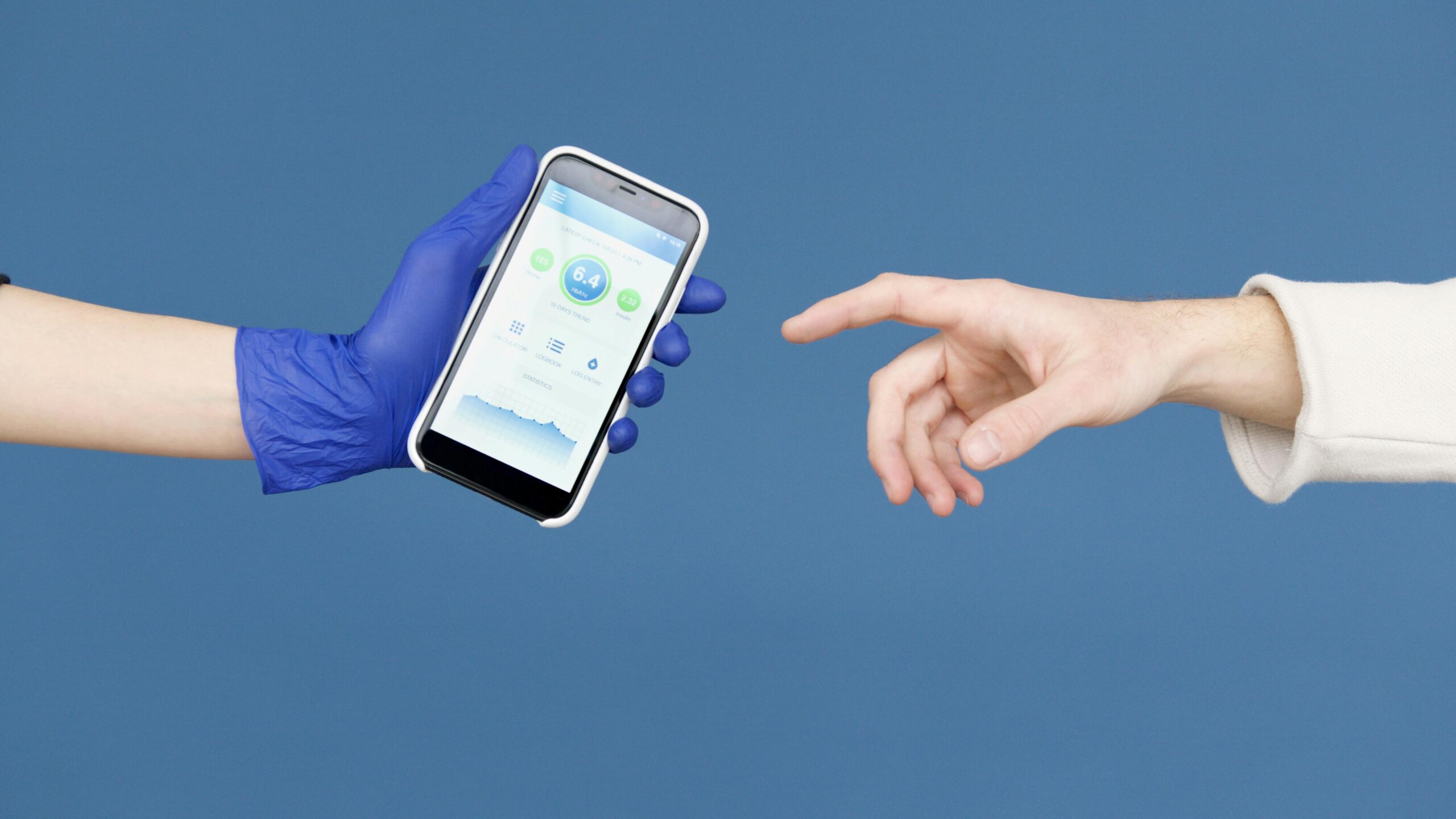
2. Babylon Health – Online Consultations, Virtual Services at scale
Overview:
Babylon Health, a UK-based startup, leverages cloud infrastructure to deliver AI-driven virtual consultations and symptom checking via its mobile app. The platform uses machine learning to triage patients and recommend next steps, making healthcare more accessible and scalable.
Impact:
- Millions of users served globally
- Reduced burden on primary care systems
- Increased access to affordable healthcare in underserved regions
Technology Used:
AWS cloud services, AI chatbot, secure video consultations.

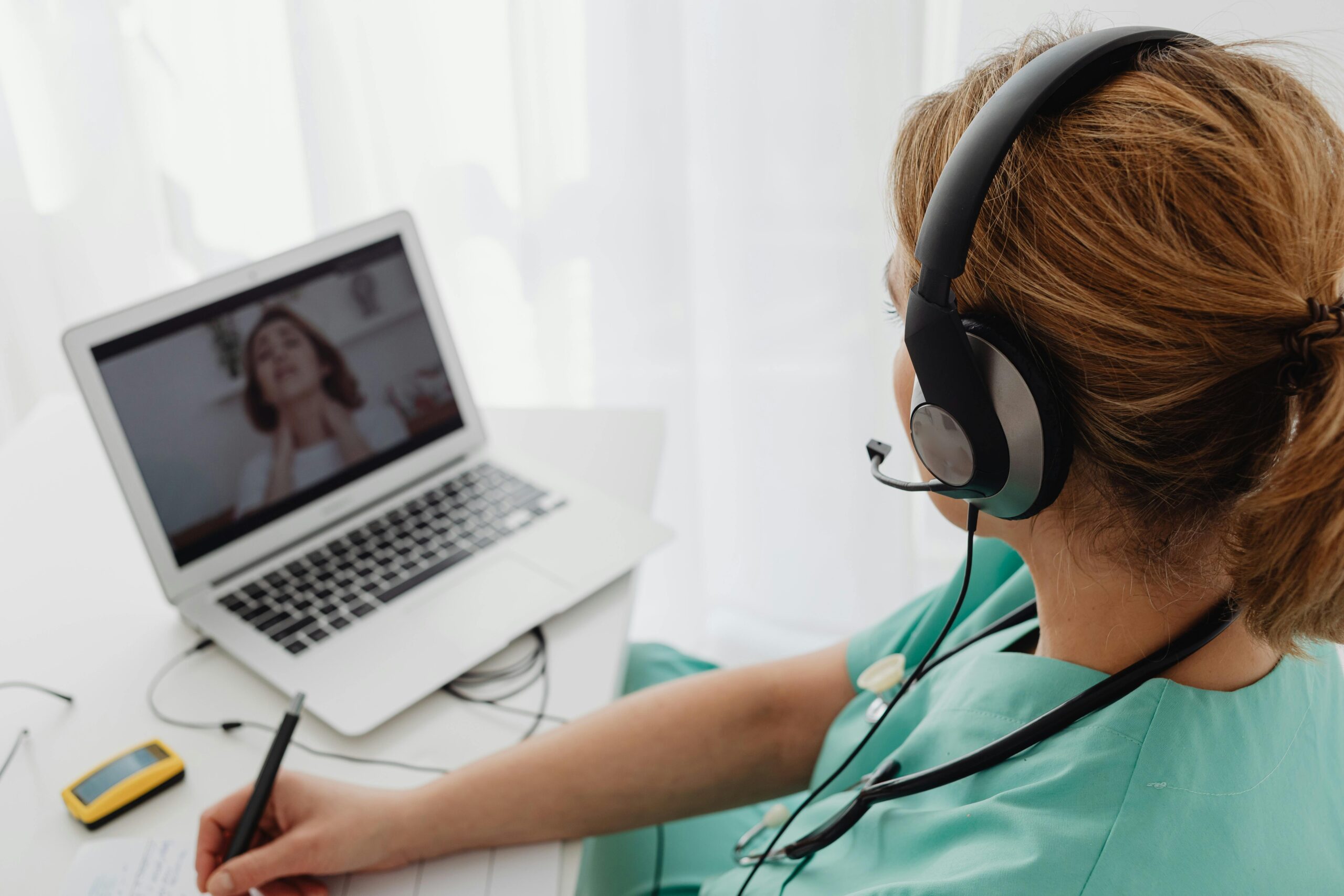
3. Philips HealthSuite – Connected Devices and Remote Monitoring
Overview:
Philips HealthSuite is a cloud-native platform that connects medical devices, apps, and patient data to enable personalized care and remote monitoring. It supports chronic disease management, telehealth, and clinical trials.
Impact:
- Improved patient adherence and engagement
- Reduced hospital readmissions
- Enhanced collaboration among care teams
Technology Used:
Cloud Foundry, HL7/FHIR APIs, real-time analytics, and secure data sharing.

These examples demonstrate how cloud-based healthcare is enabling more innovative diagnostics, scalable virtual care, and real-time decision-making across hospitals, startups, and global health systems.
4. Cleveland Clinic – AI-Powered Imaging and Diagnostics
Overview:
Cleveland Clinic uses Google Cloud’s AI tools to analyze radiology images and detect anomalies faster. The cloud infrastructure supports large-scale image storage and real-time collaboration among radiologists.
Impact:
- Faster diagnosis of conditions like cancer and stroke
- Improved accuracy in imaging interpretation
- Reduced turnaround time for radiology reports
Technology Used:
Google Cloud AI, DICOM image processing, secure cloud storage.
5. Apollo Hospitals – Cloud-Based Patient Engagement in India
Overview:
Apollo Hospitals adopted Microsoft Azure to build a cloud-based patient engagement platform. It enables appointment scheduling, teleconsultations, and access to health records via mobile apps.
Impact:
- Increased patient satisfaction and retention
- Expanded access to care in remote areas
- Streamlined hospital operations
Technology Used:
Microsoft Azure, mobile health apps, and integrated EHR systems.
Why Agentic AI in Healthcare Is the Next Big Breakthrough
Learn how agentic AI is transforming healthcare with smarter workflows, better diagnostics, and personalized care.
Kanerika’s Role in Cloud-Based Healthcare Transformation
Kanerika is a leading provider of AI, analytics, and cloud enablement services, committed to accelerating digital transformation for global enterprises—especially within healthcare. With deep expertise across data integration, governance, AI/ML, and modern cloud architectures, Kanerika helps organizations drive innovation at scale. Its strong portfolio of global certifications, including ISO 27001, ISO 27701, SOC II, CMMI Level 3, and GDPR compliance, ensures delivery excellence and data security. As a trusted partner of Microsoft, AWS, and Informatica, Kanerika empowers healthcare providers to scale securely, deliver faster insights, and achieve better patient outcomes.
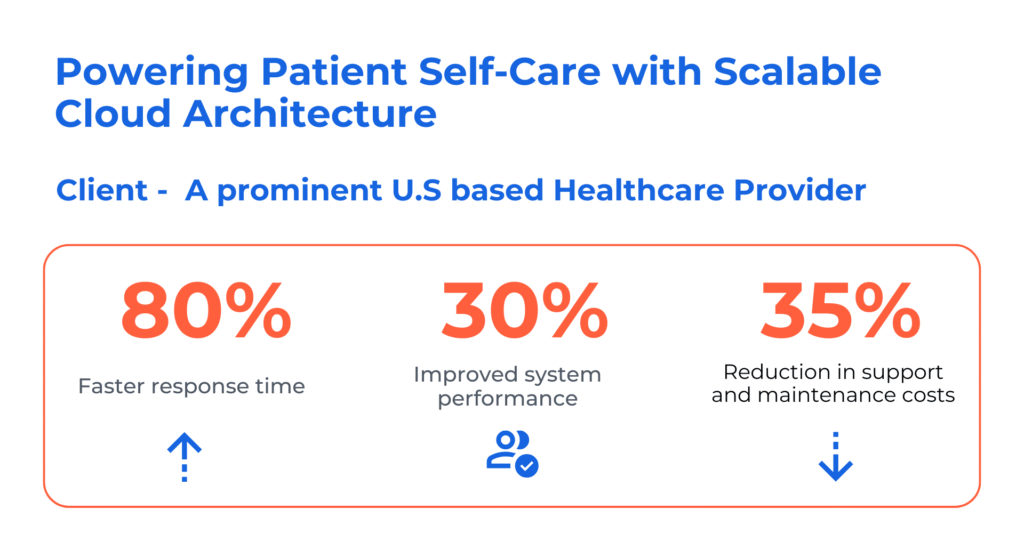
Case Study: Powering Patient Self-Care with Scalable Cloud Architecture
The Challenge
A prominent U.S.-based healthcare provider aimed to empower hypertensive patients to self-monitor their health. However, legacy systems slowed down response times, offered limited scalability, and lacked support for evolving data formats—posing serious barriers to patient care and operational agility.
Key Pain Points:
- Outdated system architecture limited patient-facing features and performance.
- Inability to support modern, complex data structures for personalized care.
- Security, compliance, and scalability gaps blocked future growth and patient engagement.
Kanerika’s Solution
Kanerika overhauled the provider’s system architecture using modern cloud technologies and data governance tools. The solution focused on:
- Architecting a scalable and secure cloud-based backend.
- Enabling faster performance and seamless integration of complex data formats.
- Empowering the internal IT team with improved analytics, lower maintenance, and rapid deployment.
Results Delivered:
- 80% faster response time, enabling near real-time insights for patients.
- 30% improvement in overall system performance.
- 35% reduction in support and maintenance costs.
- Increased security, compliance, and self-service analytics capacity.
We don’t just implement cloud solutions—we co-create digital ecosystems that empower healthcare providers to deliver smarter, faster, and more personalized care.
Turn Data into Better Decisions in Healthcare!
Partner with Kanerika for AI-powered analytics and insights.
FAQs
What is cloud in healthcare?
Cloud in healthcare refers to the use of remote, internet-based servers and services to store, manage, and process health data and applications—offering scalability, cost efficiency, and improved access to tools like EHRs, analytics, and telehealth. This model supports real-time decision-making and operational flexibility across healthcare settings.
Which cloud platform is best for healthcare?
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all “best” platform—AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are all top choices depending on needs. AWS leads in service breadth and global reach, Azure excels in integration with Microsoft tools and hybrid setups, and Google Cloud stands out in AI, analytics, and interoperability
Who are the big three providers for cloud services?
The three leading global cloud providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP)—together commanding the vast majority of the market.
Are healthcare cloud services HIPAA-compliant?
Yes. Leading providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer HIPAA-eligible services and support signing Business Associate Agreements (BAAs), making them suitable for safeguarding protected health information (PHI).
What are the main benefits of cloud computing for healthcare?
Healthcare cloud offers faster deployment, cost savings on infrastructure, enhanced collaboration, real-time data access, scalability, and advanced capabilities such as AI analytics and telehealth platforms.
How do I choose the right cloud provider for my healthcare organization?
Consider criteria like security and compliance certifications (e.g., HIPAA, HITRUST), integration with existing systems, ease of scaling, AI and analytics tools, pricing structure, and vendor support. Pilot testing can help compare options before a long-term commitment.










