“Artificial intelligence is the new electricity.” — Andrew Ng, Co-founder of Coursera and former Chief Scientist at Baidu. AI is powering everything from voice assistants like Siri and Alexa to recommendation engines on Netflix and Amazon, showing how different types of AI are integrated into our daily lives. These examples highlight the wide range of capabilities, from narrow AI performing specific tasks to more advanced systems that can reason and adapt.
Globally, the AI market is expected to reach $207 billion by 2025, with applications ranging from narrow AI in chatbots to more advanced general AI in autonomous systems. Experts categorize AI into three main types: narrow AI, general AI, and superintelligent AI, each with unique capabilities, limitations, and use cases across industries.
Continue reading this blog to explore the types of AI, their real-world applications, and how businesses are leveraging them to drive innovation.
Enhance Customer Experiences Using AI Technology!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
Key Takeaways
1. Generative AI is being adopted across industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, media, education, and marketing to improve speed, reduce costs, and enhance creativity.
2. Applications include drug discovery, fraud detection, personalized shopping, predictive maintenance, content creation, and customized learning experiences.
3. Businesses achieve better results by integrating AI into existing tools, maintaining quality data, creating prompt templates, and providing hands-on training to employees.
4. AI assistants enable faster decision-making by analyzing data, generating insights, automating repetitive tasks, and supporting natural language queries.
5. Kanerika provides enterprise-ready generative AI solutions and agents like DokGPT, Alan, and Jennifer to automate workflows, access knowledge quickly, and streamline business operations.
6. Adoption of generative AI helps companies save time, improve efficiency, and make operations more intelligent and data-driven.
Partner with Kanerika to Modernize Your Enterprise Operations with High-Impact Data & AI Solutions
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence refers to computer systems that perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. These systems learn from data, recognize patterns, make decisions, and solve problems without being programmed for every specific scenario. Unlike traditional software that follows fixed rules, AI adapts and improves as it processes more information.
AI works by analyzing large amounts of data to identify patterns and relationships. It uses these insights to make predictions, generate new content, or take actions. The technology continues learning from new inputs, becoming more accurate over time.
Key Capabilities of AI
1. Pattern Recognition and Prediction: AI identifies trends and anomalies in data that humans might miss. Systems predict customer behavior, detect fraud, forecast demand, and spot equipment failures before they happen.
2. Content Generation: AI creates original text, images, code, and other content based on instructions or examples. Businesses use this for writing product descriptions, designing graphics, and generating reports.
3. Natural Language Understanding: AI comprehends and responds to human language through chatbots, voice assistants, and search interfaces. It processes questions, understands context, and delivers relevant answers in conversational formats.
4. Task Automation: AI handles repetitive tasks such as data entry, document processing, scheduling, and quality checks. This frees employees to focus on strategic work requiring human judgment.
AI enables faster, more accurate decisions by processing information at scale. It reduces operational costs by automating time-consuming tasks. Companies gain competitive advantages through insights buried in their data. The technology solves problems that were previously too complex or resource-intensive to address.
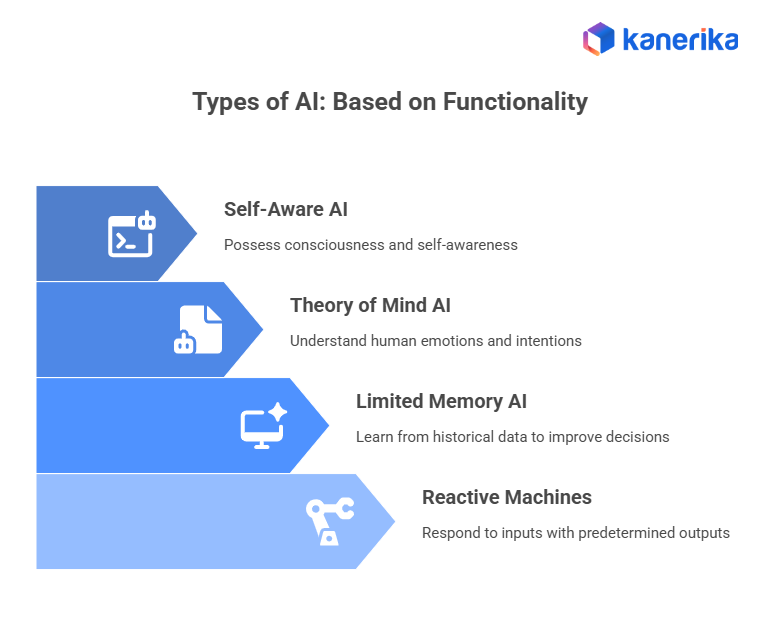
Types of AI: Based on Functionality
AI systems serve different functional purposes. Here are the main categories based on what they do.
1. Reactive Machines
These systems respond to specific inputs with predetermined outputs. They don’t learn from past experiences or store memories. Reactive machines excel at narrow, well-defined tasks.
- Chess-playing computers – Systems like IBM’s Deep Blue analyze current board positions and calculate the best next move
- Spam filters – Email systems flag messages based on specific patterns and keywords
- Basic recommendation engines – Early Netflix systems that matched movies based on simple genre preferences
These systems work fast and consistently, but can’t adapt to new situations outside their programming.
2. Limited Memory AI
These systems learn from historical data and use past experiences to make better decisions. Most AI applications today fall into this category.
- Self-driving cars – Vehicles learn from millions of miles of driving data to navigate roads safely
- Chatbots – Customer service bots that improve responses based on previous conversations
- Fraud detection systems – Banks that identify suspicious transactions by learning from past fraud patterns
- Predictive maintenance – Manufacturing systems that learn normal machine behavior and flag anomalies
Limited-memory AI improves over time but retains only information relevant to its specific task.
3. Theory of Mind AI
This AI would understand human emotions, beliefs, and intentions. It doesn’t exist yet beyond research settings. The technology would recognize that people have thoughts and feelings that affect their behavior.
Companies are exploring early versions of AI for mental health support and advanced customer service, but true theory-of-mind AI remains in development.
4. Self-Aware AI
This represents AI with consciousness and self-awareness. It’s purely theoretical. No current technology comes close to this capability. Self-aware AI appears in science fiction but not in business applications.
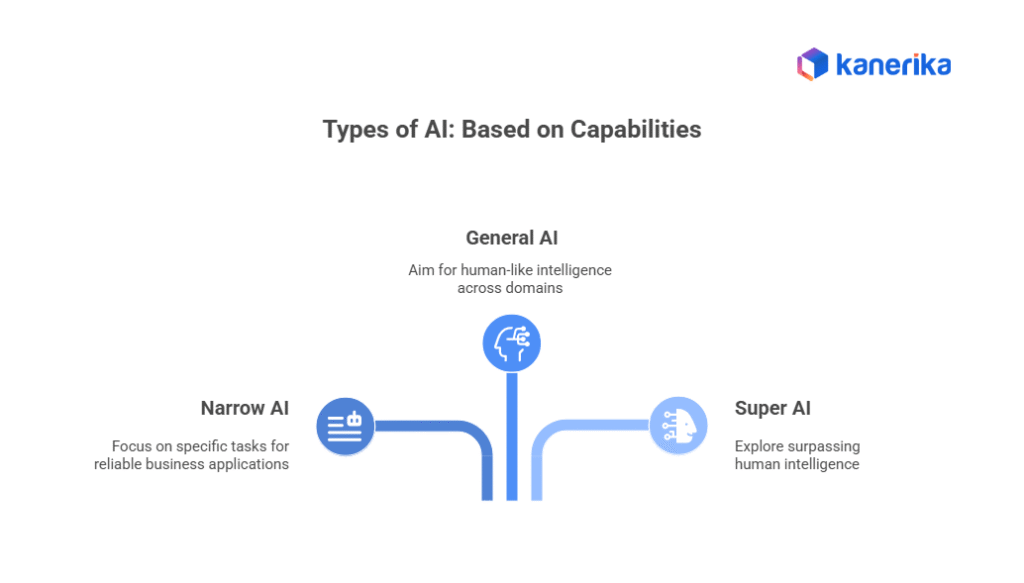
Types of AI: Based on Capabilities
AI systems also differ in their capabilities and sophistication.
1. Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI excels at one specific task but can’t transfer that knowledge to other areas. This is the only type of AI that actually exists today.
- Voice assistants – Alexa and Siri understand speech and answer questions but can’t drive cars or diagnose diseases
- Image recognition – Systems that identify objects in photos but can’t write essays
- Language translation – Tools that convert text between languages but can’t analyze financial data
- Recommendation engines – Platforms that suggest products but can’t compose music
Narrow AI dominates business use because it solves specific problems reliably. Companies deploy these systems for focused tasks where they deliver measurable value.
2. General AI (Strong AI)
General AI would match human intelligence across all domains. It could learn any intellectual task a human can learn and apply knowledge flexibly across different situations.
This technology doesn’t exist. Researchers continue working toward it, but no timeline exists for when or if it will arrive. Current AI systems are nowhere near this capability.
3. Super AI
Super AI would surpass human intelligence in every way. It remains a theoretical concept discussed in academic circles and popular media. No credible evidence suggests we’re close to developing super AI.
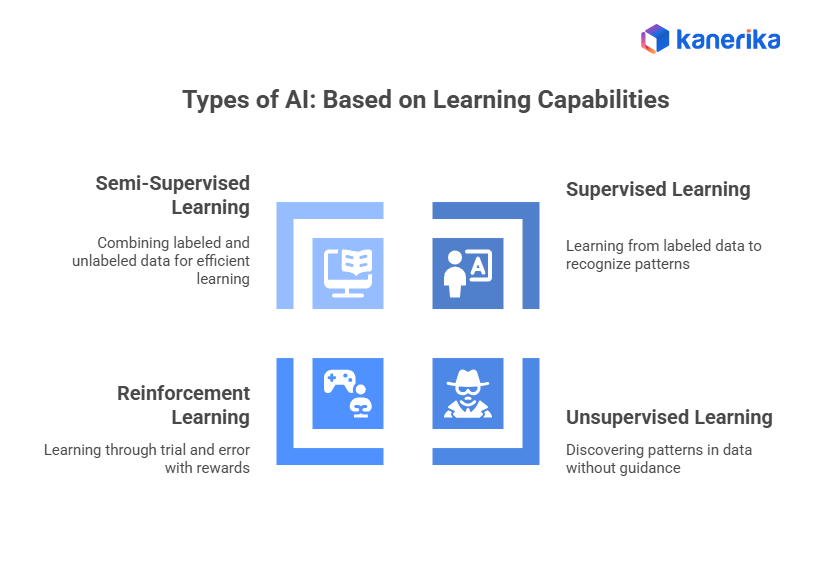
Types of AI: Based on Learning Capabilities
AI systems use different methods to learn and improve their performance.
1. Supervised Learning
The system learns from labeled training data. Humans provide examples with correct answers, and the AI learns to recognize patterns.
- Email spam detection – Systems trained on thousands of emails marked as spam or not spam
- Medical diagnosis – AI trained on labeled medical images showing diseases
- Credit scoring – Models trained on historical loan data with known outcomes
- Sales forecasting – Systems that learn from past sales data with known results
Supervised learning requires significant upfront work to label data but produces accurate results for well-defined problems.
2. Unsupervised Learning
The system finds patterns in data without being told what to look for. No labeled examples guide the learning process.
- Customer segmentation – Identifying groups of similar customers without predefined categories
- Anomaly detection – Finding unusual patterns in network traffic or financial transactions
- Market basket analysis – Discovering which products customers buy together
- Data compression – Finding efficient ways to represent information
Unsupervised learning helps discover hidden patterns that humans might miss. It works well when you don’t know what patterns exist in your data.
3. Reinforcement Learning
The system learns through trial and error, receiving rewards for good actions and penalties for bad ones. It discovers the best strategy through experimentation.
- Game playing – AI that learns to win at complex games like Go or chess
- Robot control – Industrial robots learning to assemble products efficiently
- Dynamic pricing – E-commerce systems adjust prices based on demand and competition
- Resource allocation – Cloud computing systems optimize server usage
Reinforcement learning excels at complex decision-making where the best action depends on changing circumstances.
4. Semi-Supervised Learning
This approach combines labeled and unlabeled data. The system learns from a small amount of labeled examples and a large amount of unlabeled data.
- Speech recognition – Systems trained on limited transcribed audio plus massive amounts of unlabeled speech
- Text classification – Document sorting with few labeled examples
- Medical imaging – Training diagnostic systems when labeled medical images are expensive to obtain
Semi-supervised learning reduces the cost and time needed to prepare training data while still achieving good results.
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Functionality, Capabilities, and Learning Methods
| Classification | Type | What It Means | Benefits | Examples |
| Functionality | Reactive Machines | Respond to input; no memory | Fast, consistent | IBM Deep Blue, spam filters, early Netflix recommender |
| Limited Memory AI | Learns from past data | Improves accuracy | Self-driving cars, chatbots, fraud detection | |
| Theory of Mind AI | Understands emotions & intentions | Better human-AI interaction | Early mental health AI research | |
| Self-Aware AI | AI with consciousness | Hypothetical | Fiction only | |
| Capabilities | Narrow AI | Task-specific intelligence | Reliable, practical | Siri, Alexa, image recognition, translators |
| General AI | Human-level intelligence | Flexible, theoretical | Not yet developed | |
| Super AI | Surpasses human intelligence | Hypothetical | Research/concepts only | |
| Learning | Supervised | Learns from labeled data | Accurate for known tasks | Spam detection, credit scoring, medical diagnosis |
| Unsupervised | Finds patterns in unlabeled data | Reveals hidden insights | Customer segmentation, anomaly detection | |
| Reinforcement | Learns via trial & error | Good for dynamic decisions | Game AI, robot control, dynamic pricing | |
| Semi-Supervised | Mix of labeled & unlabeled data | Cost-efficient learning | Speech recognition, text classification |
Which Type of AI Do Businesses Use Most Today?
Businesses primarily use narrow AI with supervised and unsupervised learning. These technologies solve real problems with measurable ROI.
1. Retail
Retailers use AI to improve demand forecasting, inventory management, and personalized shopping experiences. Smart systems analyze sales data, local trends, and customer behavior to decide what products to stock. AI also helps match items to customers’ preferences, reducing returns and boosting satisfaction.
In real life, Stitch Fix uses AI to help stylists pick clothes that suit a customer’s taste by checking fit, past returns, and style history. Zara uses AI to forecast demand at each store and to adjust restocking levels frequently. This keeps inventory lean and speeds up turnover.
2. Healthcare
AI in healthcare supports better diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and smarter scheduling. Systems can read scans, patient history, and test results to highlight risks or recommend treatments. This helps doctors focus on care rather than paperwork or routine analysis.
For example, Mayo Clinic uses AI to scan patient images and flag early signs of heart disease that may be hard to spot manually. Tempus uses AI to analyze genetic data and patient history to match patients with suitable clinical trials, helping improve therapy outcomes.
3. Finance
In finance, AI aids risk detection, fraud prevention, and faster customer service. It can quickly scan transaction patterns, detect anomalies, and alert teams. AI also helps personalize financial advice and speed up loan or card approval processes without sacrificing security.
For example, American Express uses AI to review transactions in real time and block suspicious activity before completion. Kasisto offers AI-powered virtual banking assistants that answer detailed banking questions, reducing wait times and lightening staff workload.
4. Manufacturing
Manufacturing benefits when AI monitors machines, predicts maintenance needs, and maintains high quality. AI reviews sensor data to detect when tools are worn or when machines may fail. This reduces breakdowns, reduces waste, and improves production consistency.
For instance, General Motors uses AI to check weld quality in assembly plants by analyzing sensor data and warning operators before flaws happen. Bosch tracks wear on machining tools using AI, so tools are replaced or sharpened before they produce defective parts.
5. Logistics and Supply Chain
Logistics firms need precise timing, efficient routes, and flexible planning. AI helps predict delays, plan routes, and optimize shipping. It uses weather, traffic, and historical data to make shipping reliable and reduce costs.
In real operations, Maersk uses AI to forecast ship arrival times more accurately by considering weather, port traffic, and past routes. UPS uses AI to plan and adjust delivery routes on the go based on traffic and delivery loads, saving time and fuel.
6. Education and Learning Platforms
In education, AI helps personalize learning, adapt content to each student’s pace, and recommend courses or study plans. It analyses user performance and adjusts difficulty or content flow. This makes learning more efficient and tailored.
For example, Duolingo uses AI to adjust lesson difficulty based on learner performance, errors, and strengths. Coursera employs AI to suggest courses based on user skills and career paths, helping learners pick relevant courses without manual research.
Partner with Kanerika to Modernize Your Enterprise Operations with High-Impact Data & AI Solutions
What Are the Benefits of Each AI Type?
1. Better Accuracy Through Learning
Some AI systems learn from past data and adjust as new information comes in. This helps reduce errors in tasks like predictions, recommendations, and pattern detection. Businesses use this strength to steadily improve planning and daily operations.
2. Faster Response for Simple Tasks
Basic AI responds instantly because it does not store memory or run deep analysis. It gives the same output every time. This consistency is helpful for quick decisions, routine checks, and automated responses where reliability matters more than reasoning.
3. Support for Complex Problem Solving
More advanced systems can process large data sets and compare many scenarios in minutes. They help teams understand risks, study trends, and make informed choices. This kind of AI is helpful in research, product development, and long-term strategy.
4. Greater Adaptability
Some AI models adjust to new conditions without a full rebuild. They learn from recent cases and update their behavior. This helps companies stay aligned with customer habits, market shifts, and real-time data.
5. More Humanlike Interaction Potential
Research efforts aim to build AI that understands tone, emotions, and intent. If this becomes reliable, it can make communication smoother. It could support teaching, coaching, counseling, and care tasks where empathy and understanding matter.
6. Expanded Creativity and Idea Generation
Specific AI tools generate new concepts from simple inputs. They explore many possibilities at once and share options that people might overlook. This helps with design, writing, planning, and problem-solving in creative fields and technical teams.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges of AI
1. Bias in AI Models
AI systems learn from historical data, which may contain hidden biases. When this data is used to train models, the AI can produce unfair outcomes in hiring, lending, policing, or customer support. Companies must regularly audit models and diversify training data to reduce this risk.
2. Privacy and Data Security
Generative AI often requires access to sensitive information. If this data is not stored or handled correctly, it can lead to privacy violations or leaks. Strong encryption, user consent, and strict access controls are essential to protecting personal data.
3. Lack of Transparency
Many AI models operate like “black boxes,” making it hard to understand how they make decisions. This lack of clarity can lower trust among users and regulators. Businesses should prioritize explainable AI and offer clear reasoning behind automated outputs.
4. Potential Misuse of AI
AI tools can be used to create fake images, misinformation, or harmful content. Without proper guidelines, these tools may be misused by employees or external users. Companies need clear usage policies, monitoring, and safeguards to prevent misuse.
5. Impact on Workforce and Jobs
AI can automate repetitive tasks, which may change traditional roles or reduce the need for certain jobs. This creates uncertainty for employees. Businesses should invest in reskilling and upskilling programs so teams can shift to higher-value work supported by AI.
Powering Modern Enterprises with Kanerika’s AI-Driven Innovation
Artificial Intelligence comes in different forms, and Kanerika uses the right type for the right business challenge. Our expertise spans Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, and advanced Generative AI, enabling businesses to automate tasks, analyze large datasets, and deliver smarter workflows.
Kanerika’s AI agents — DokGPT, Jennifer, Alan, Susan, Karl, and Mike Jarvis — combine these AI types to solve practical problems. They handle document intelligence, risk scoring, customer analytics, voice data processing, and marketing automation. By blending predictive models, NLP, and generative capabilities, these agents help enterprises accelerate reporting, improve compliance, and enhance customer engagement without disrupting existing systems.
Beyond AI, Kanerika offers data engineering, low-code automation, and cloud management services to ensure seamless integration and scalability. Our partnerships with Microsoft, AWS, and Informatica strengthen our ability to deliver innovative solutions across platforms like Power BI, Microsoft Fabric, and Azure ML. With ISO 27001 and 27701 certifications, SOC II compliance, and GDPR adherence, we guarantee security and privacy at every step.
Whether it’s predictive analytics, conversational AI, or enterprise automation, Kanerika helps businesses harness the right AI approach and supporting technologies to drive efficiency, agility, and growth.
Boost Efficiency with AI-Driven Automation!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
1. What are the main types of AI?
AI can be classified based on functionality, capabilities, and learning methods. Functionality includes reactive machines, limited memory, theory of mind, and self-aware AI. Capabilities include narrow AI, general AI, and super AI. Learning methods include supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement, and semi-supervised learning. Most AI today falls under limited memory and narrow AI.
2. What is narrow AI and where is it used?
Narrow AI is designed for a specific task and cannot perform functions outside its scope. It is widely used in voice assistants, image recognition, recommendation engines, and chatbots. Businesses rely on narrow AI because it is reliable, practical, and delivers measurable results.
3. What is the difference between limited memory and reactive machines?
Reactive machines respond only to current inputs and cannot learn from past experiences. Limited-memory AI, on the other hand, can learn from historical data and use it to improve decision-making. Most real-world AI applications, such as self-driving cars and fraud detection systems, rely on limited memory AI.
4. What is supervised and unsupervised learning in AI?
Supervised learning involves training AI on labeled data so it can recognize patterns and make predictions. Unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data without prior instructions. Supervised learning is common in medical diagnosis or sales forecasting, while unsupervised learning is used for customer segmentation or anomaly detection.
5. Will we ever have general or super AI?
General AI would match human intelligence across all domains, and super AI would surpass it. Currently, these remain theoretical and do not exist. Researchers continue exploring these areas, but today’s AI is limited to narrow, task-specific applications.










