What happens when your payment system processes transactions in seconds but your data platform takes hours to update? You lose customers to competitors who move faster. Data Migration In Fintech has become make-or-break for survival.
The numbers tell the story: McKinsey reports that digital payments will reach $10 trillion globally by 2026, with fintech companies capturing increasing market share. Yet many fintechs still run on legacy systems built before mobile banking existed.
Here’s the problem: customers expect instant everything like real-time balance updates, immediate fraud alerts, and instant loan decisions. Stripe research shows that 49% of consumers abandon purchases when payments take too long. Your data architecture determines whether you deliver speed or lose revenue.
Legacy platforms weren’t designed for this reality. They process transactions in batches overnight. They can’t handle API-driven ecosystems or real-time analytics. Additionally, they lack security controls modern regulations demand like PCI-DSS, GDPR, and SOC 2 compliance.
Successful fintechs recognize migration as strategic necessity, not IT project. The question isn’t whether to migrate as it’s whether you’ll modernize before competitors capture your customers.
Key Learnings
- Modern finance teams need faster, more flexible data platforms
Legacy ETL and reporting tools struggle to keep up with growing data volumes and real-time financial analytics demands, making modernization essential.
- Automation significantly reduces migration effort and risk
Using migration accelerators and AI-driven tooling can automate up to 70–80% of repetitive migration tasks, reducing manual errors and delivery timelines.
- Preserving financial logic is critical during migration
Successful finance migrations focus not just on moving data, but on accurately retaining business rules, calculations, and compliance logic.
- AI enhances compliance and risk operations, not just analytics
AI-powered agents can automate compliance checks, risk screening, and data discovery, enabling faster decisions with stronger governance.
- Faster insights directly improve financial decision-making
Modernized pipelines and analytics tools allow finance teams to shift from delayed, batch reporting to near real-time insights.
Migration Made Easy with Kanerika’s Accelerator
Partner with Kanerika for Seamless, Error-free Migration
Understanding Fintech Data Ecosystems
Fintech data ecosystems include multiple connected platforms handling money and customer information. This complexity makes migrations challenging and risky without proper planning.
1. Types of Fintech Data
Transaction data covers payments, money transfers, purchases, and account settlements happening constantly. Customer data stores account details, personal information, and usage history. Additionally, risk data evaluates credit scores and default probability. KYC data proves customer identities meeting legal requirements. Furthermore, fraud data tracks suspicious activities and security alerts protecting against theft.
2. Structured vs Semi-Structured Data
Structured data lives in databases like transaction amounts, account balances, customer names. This information fits neatly into rows and columns. Conversely, semi-structured data includes things like API responses, email communications, and scanned documents. Additionally, payment network messages and mobile app logs don’t follow strict database formats but still contain valuable information.
3. Interconnected System Architecture
Core banking systems handle account management and transaction processing. Payment gateways connect to credit card networks and digital wallets. Additionally, third-party services link to credit bureaus, identity checkers, and other banks. Mobile apps, websites, and merchant systems all exchange data creating complicated connections.
4. Inherent Migration Complexity
Fintech migrations face serious challenges. Systems run 24/7 without breaks. Even small errors cost money directly. Additionally, regulations demand perfect accuracy and complete audit trails. Security needs exceed most other industries. Furthermore, dozens of external partners and services must keep working throughout migrations.
Partner with Kanerika to Modernize Your Enterprise Operations with High-Impact Data & Migration Solutions
Legacy Data Migration Challenges in Fintech
Fintech legacy data migration challenges create serious obstacles for companies trying to modernize payment systems and banking platforms. These problems explain why financial technology migrations fail frequently.
1. Monolithic Core Systems and Outdated Databases
Legacy fintech systems were built as single massive applications handling everything together. Payment processing, account management, and reporting all live in one giant system. Additionally, outdated databases use old technology that modern tools can’t easily read. These platforms run on mainframes or ancient servers nobody wants to touch. Replacing them risks breaking critical money operations.
2. Embedded Business Rules and Risk Logic
Business rules hide deep inside old code rather than documented separately. Interest calculations, credit scoring formulas, and fraud detection logic live in programs written decades ago. Additionally, risk assessment algorithms exist only in COBOL code that few people understand anymore. Extracting these rules without breaking them becomes extremely difficult and time-consuming.
3. Poor Documentation and Historical Inconsistencies
System documentation either disappeared or became useless years ago. The people who built these systems left long ago. Additionally, data inconsistencies accumulated over time duplicates customer records, wrong transaction codes, and broken account relationships. Nobody fixed these problems because changing production financial systems felt too dangerous. These issues surface during migration causing unexpected delays and errors.
The Ultimate Data Migration Checklist for Enterprises: 2026 Edition
Explore a practical, end-to-end data migration checklist that enterprises can actually follow from planning and execution to validation and post-migration success.
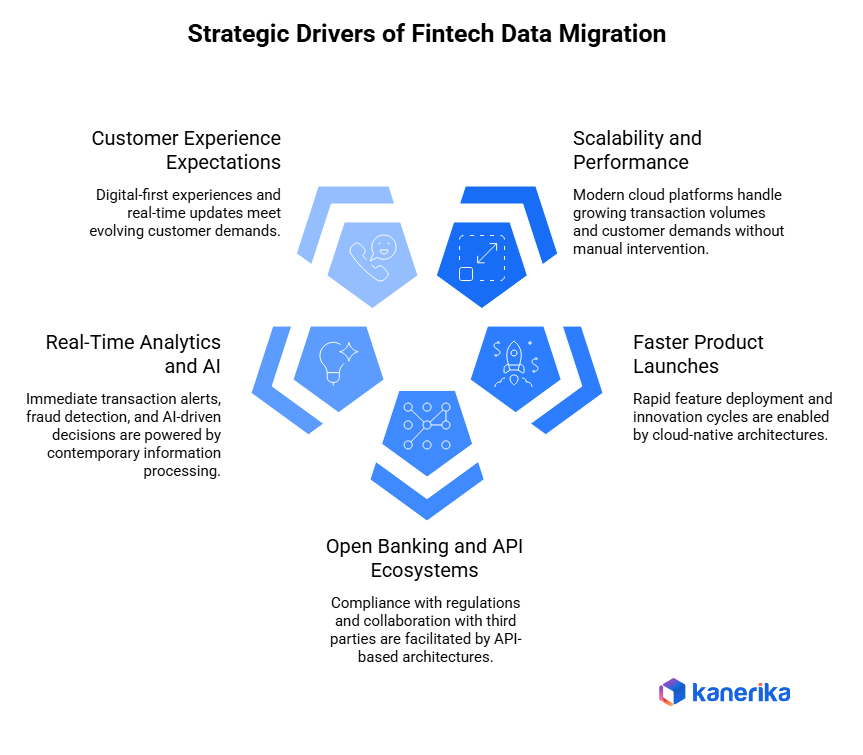
Strategic Drivers Behind Fintech Data Migration
The companies are becoming modern; hence, the fintech data migration becomes rapid as companies meet the market needs and expectations. These transformation initiatives are driven by a number of critical business factors.
1. Need for Scalability and Performance
Legacy fintech systems struggle handling growing transaction volumes during peak periods. Black Friday sales or payday processing overwhelm outdated infrastructure. Additionally, adding new customers requires expensive hardware upgrades. Modern cloud platforms scale automatically during demand spikes without manual intervention. Organizations need systems growing with their business rather than becoming bottlenecks.
2. Faster Product Launches
Modern fintech platforms enable rapid feature deployment that legacy systems can’t support. Launching new payment options, lending products, or investment services takes months on old systems. Additionally, competitors releasing innovations weekly force faster development cycles. Cloud-native architectures allow teams testing features quickly and rolling them out incrementally. Speed to market determines survival in competitive fintech markets.
3. Open Banking and API Ecosystems
The open banking policies entail the provision of customer data to third parties via secure APIs. Old systems could not be integrated with an outside world. Also, API-based architectures allow collaborating with other fintechs, merchants, and service providers. The modern platforms open functionality via APIs which legacy monoliths are not able to readily offer. Hence, to comply with regulation and be a part of the ecosystem, migration is required.
4. Real-Time Analytics and AI
Customers want to receive immediate transaction alerts and suggestions. The real-time analytics are necessitating the use of contemporary information processing platforms. Furthermore, fraud detection and credit decisions based on AI require clean, integrated data legacy systems, which are not provided by clean data legacy systems. Machine learning models are better with increased information- modern platforms can process the information compared to legacy systems.
5. Customer Experience Expectations
Customers expect mobile-first experiences that are equal to the consumer apps such as Venmo and Cash App. The old systems developed to support branch banking are poorly suited to the new digital channels. Moreover, customers desire real-time updates and constant notifications in their accounts, as well as cross-platform experiences. To satisfy these demands, the current platforms must be digital-first oriented.
Security and Compliance in Fintech Data Migration
Fintech migration security demands exceptional protection measures throughout data transfers. Financial information attracts cybercriminals making security non-negotiable during migrations.
1. Regulatory Requirements
PCI-DSS compliance protects payment card data through strict security standards during storage and transmission. GDPR regulations govern personal financial information for European customers requiring consent and privacy controls. Additionally, SOC 2 certification demonstrates proper security controls protecting customer data. ISO 27001 standards establish comprehensive information security management systems. Violating these regulations triggers massive fines and legal consequences.
2. Encryption, Tokenization, and Access Control
Data encryption protects information both stored and moving between systems using AES-256 standards. Additionally, tokenization replaces sensitive card numbers and account details with non-sensitive substitutes during migration. Access controls limit who can view financial data as only authorized personnel with legitimate business needs. Multi-factor authentication prevents unauthorized access even if passwords get compromised. Furthermore, privileged access management tracks administrative activities throughout migrations.
3. Audit Trails and Traceability
Regulators demand complete audit logs documenting every action during migration. Track who accessed customer accounts, when data moved, and what changed. Additionally, data lineage shows exactly how financial information flowed between systems. Comprehensive traceability proves proper handling during regulatory examinations. Missing audit evidence triggers compliance violations regardless of actual security.
4. Built-In Security Planning
Security-first migration embeds protection from initial planning rather than adding it later. Threat modeling identifies risks before work begins. Additionally, security reviews happen at every phase like design, testing, and deployment. Waiting until the end creates vulnerabilities attackers to exploit. Furthermore, security teams participate in migration decisions, ensuring controls integrate properly.
5. Data Masking and Test Environments
Production data cannot be used in testing without protection. Data masking creates realistic test datasets without exposing actual customer information. Additionally, synthetic data generation produces fake but realistic financial records for development environments. This protects privacy while allowing thorough testing. Organizations violating these practices face regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
Data Quality Risks in Fintech Migrations
Data quality in fintech migration directly impacts customer trust, regulatory compliance, and business operations. Poor quality creates financial losses and reputation damage.
1. Impact on Critical Systems
Fraud detection systems fail when training data contains errors and inconsistencies. Machine learning models make wrong decisions leading to false positives blocking legitimate transactions or false negatives missing actual fraud. Additionally, credit scoring algorithms produce inaccurate risk assessments when built on flawed customer data. Wrong credit decisions cost money through bad loans or lost customers rejected incorrectly.
2. Common Quality Problems
Duplicate customer records cause confusion as same person appears multiple times with different accounts. Transaction mismatches occur when payments reference wrong accounts or customers. Additionally, reconciliation failures happen when balances don’t match between systems after migration. These errors create accounting nightmares and regulatory reporting problems. Furthermore, incorrect transaction histories destroy audit trails regulators require.
3. Profiling and Validation Importance
Pre-migration data profiling reveals quality issues before they cause problems. Identify duplicates, missing values, and format inconsistencies early when fixes cost less. Additionally, validation frameworks check data continuously during migration catching errors immediately. Waiting until after migration discovers problems too late for easy fixes.
4. Trust as Business Requirement
Customer trust evaporates when account balances show wrong amounts or transactions disappear. Users switch to competitors immediately after experiencing data errors. Additionally, poor quality damages brand reputation permanently through social media complaints and negative reviews.
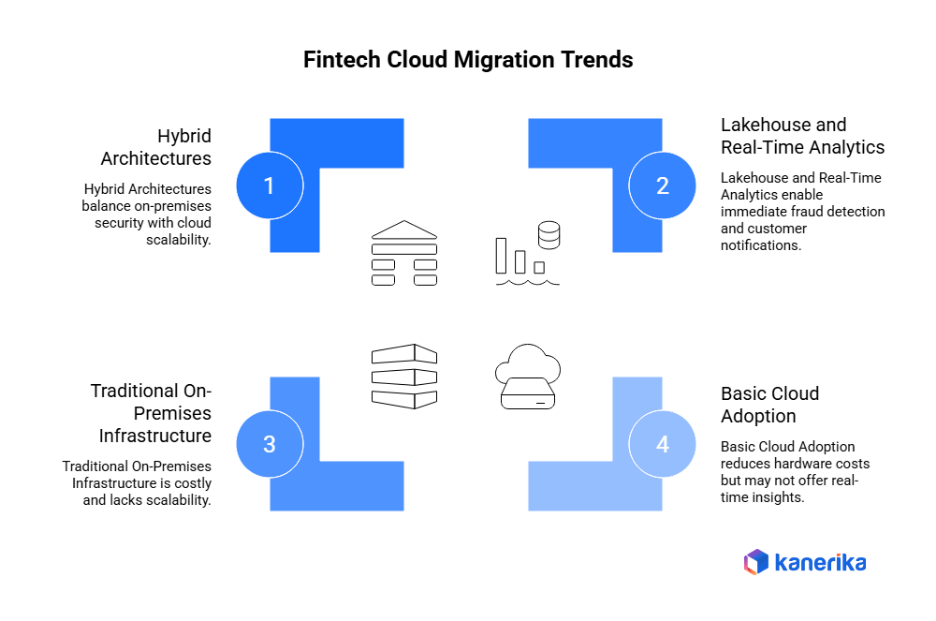
Cloud and Platform Migration Trends in Fintech
The migration to the fintech cloud is going to be faster because organizations are dropping costly on-prem infrastructure to modern platforms. The knowledge of the existing trends assists organizations in making sound decisions regarding the platform.
1. On-Premises to Cloud Adoption
Traditional fintech infrastructure required owning data centers and managing servers directly. This approach costs millions and limits scalability. Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud eliminate hardware management. Additionally, companies pay only for resources used rather than maintaining excess capacity. Security concerns previously blocking cloud adoption diminished as providers achieved certifications and compliance standards.
2. Lakehouse and Real-Time Analytics
Some Data lakehouse tools such as Snowflake and Databricks merge analytics with the flexibility of storage. Such systems process both structured data on transactions and unstructured documents simultaneously. Moreover, it has real-time analytics process streaming payment information in real-time that would allow detecting fraud immediately and informing customers. The time-consuming legacy batch processing in hours is replaced by milliseconds.
3. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Strategies
Many fintechs adopt multi-cloud approaches avoiding dependence on single vendors. Critical systems run across multiple providers ensuring continuity if one fails. Additionally, hybrid architectures keep sensitive data on-premises while moving other workloads to cloud. This balance satisfies both security requirements and scalability needs.
4. Platform Choice Implications
Different cloud platforms create varying costs and compliance complexity. AWS dominates fintech but Azure integrates better with existing Microsoft systems. Additionally, platform selection affects regulatory approval timelines and audit requirements. Wrong choices discovered mid-project cause expensive migrations between clouds.
Migration Approaches Used in Fintech
Fintech migration strategies balance speed, risk, and business continuity. Choosing appropriate approaches determines project success and customer impact.
1. Phased vs Parallel Migrations
Phased migration moves data incrementally like one product line, customer segment, or region at a time. Each phase gets validated before proceeding. Conversely, parallel migration runs old and new systems simultaneously processing identical transactions. Both platforms operate until confidence builds in new systems. Phased approaches reduce risk but extend timelines. Parallel strategies maintain business continuity but double operational costs temporarily.
2. Batch vs Near-Real-Time Migration
Batch migration transfers large data volumes during scheduled maintenance windows like nights or weekends when transaction volumes drop. This traditional approach suits historical data and completed transactions. However, near-real-time migration uses change data capture synchronizing systems continuously. New transactions flow to both platforms immediately. Real-time approaches minimize downtime but require sophisticated synchronization technology.
3. Risk-Based Migration Sequencing
Risk-based prioritization tackles low-risk systems first building team confidence and refining processes. Test accounts and internal systems migrate before customer-facing platforms. Additionally, high-value customer segments receive extra validation and testing. Critical payment processing migrates last after everything else proves stable.
4. Balancing Speed and Control
Fast migrations satisfy business pressure for quick modernization but increase error risks. Slower approaches with extensive validation protect against mistakes but frustrate stakeholders. Finding the right balance depends on organizational risk tolerance, regulatory requirements, and competitive pressure.
5. Vendor and Partner Coordination
Third-party integrations complicate fintech migrations significantly. Payment processors, credit bureaus, and banking networks need coordination and testing. Additionally, merchant partners require notifications about system changes affecting their operations. Migration timing must accommodate partner schedules and testing windows preventing service disruptions.
How BI Migration for Logistics Organizations Improves Efficiency
BI migration helps in streamline data, improve decision-making, and modernize systems for faster, clearer operations.
Automation and Accelerators in Fintech Data Migration
Fintech migration automation transforms complex transfers from manual nightmares into controlled, repeatable processes. Financial institutions cannot afford manual approaches at modern scale.
1. Why Manual Migration Fails
Manual fintech migration becomes impossible with millions of transactions and customer accounts. Hand-coding transformations for payment data takes forever. Additionally, manual validation misses errors humans cannot catch across massive datasets. Testing every scenario manually extends timelines unreasonably while increasing costly mistakes.
2. Automation’s Critical Role
Automated mapping tools analyze legacy databases suggesting modern structures quickly. Validation automation compares financial data continuously catching penny-level discrepancies immediately. Additionally, reconciliation engines verify account balances match perfectly between systems. These tools work 24/7 without fatigue or inconsistency.
3. Preserving Financial Logic
Business rule extraction identifies interest calculations, fee structures, and payment rules embedded in old code automatically. Automated conversion maintains these proven formulas without manual rewriting. This preservation protects revenue-generating logic while accelerating migration.
4. Risk Reduction Through Consistency
Standardized automation eliminates human variability causing errors. Every transaction transforms identically. Quality checks apply uniformly. Additionally, repeatable processes enable continuous improvement—lessons learned enhance future migrations automatically reducing operational risks substantially.
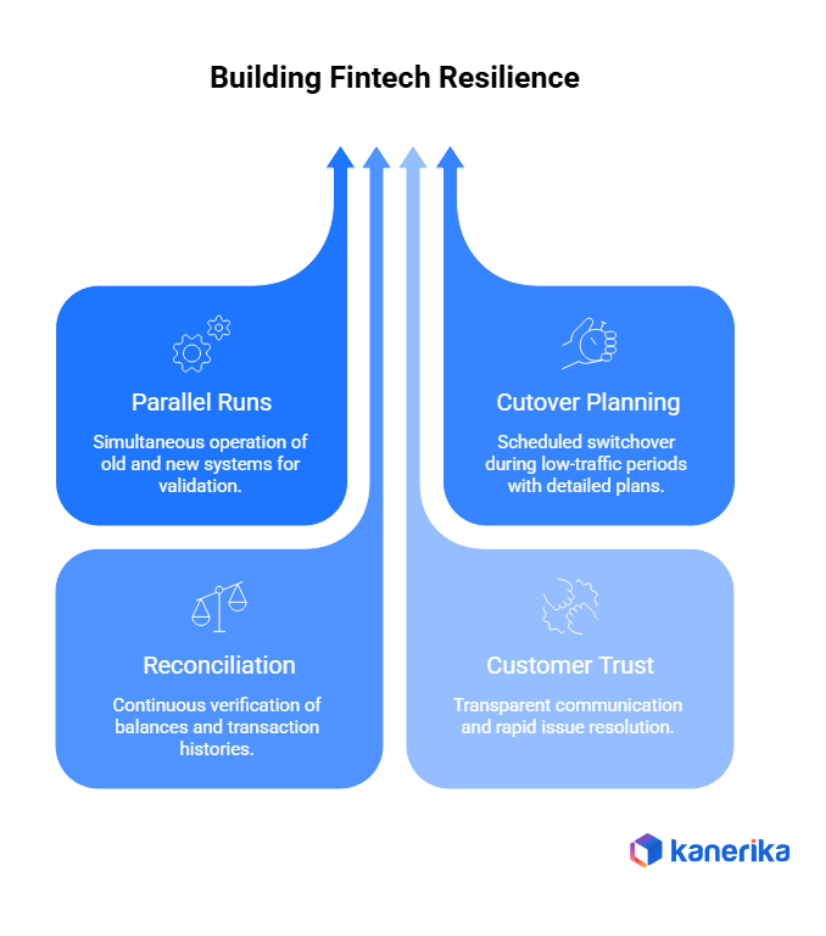
Business Continuity and Zero-Downtime Migration in Fintech
Zero-downtime fintech migration ensures payment systems stay operational throughout transitions. Interruptions cost revenue, damage reputation, and violate customer expectations immediately.
1. Uninterrupted Payment Operations
Payment systems cannot stop customers need 24/7 access to money. ATM withdrawals, online purchases, and bill payments must work continuously. Additionally, merchants depend on transaction processing for revenue. Even brief outages create angry customers switching to competitors. Therefore, fintech migrations require uninterrupted service maintaining customer access throughout transitions.
2. Parallel Runs and Cutover Planning
Parallel processing operates old and new systems simultaneously handling identical transactions. Both platforms process payments allowing comparison and validation. Additionally, cutover planning schedules final switchover during lowest-traffic periods like typically early morning hours. Detailed runbooks document exact steps, timings, and rollback procedures if problems occur.
3. Reconciliation During Coexistence
Financial reconciliation verifies balances match between systems continuously during parallel operations. Account totals must agree to the penny. Additionally, transaction histories need perfect synchronization. Discrepancies get investigated immediately before they compound. Daily reconciliation reports track data consistency throughout coexistence periods.
4. Maintaining Customer Trust
Transparent communication keeps customers informed without creating panic. Proactive notifications about planned activities build confidence. Additionally, rapid response to any issues prevents small problems becoming reputation disasters affecting long-term customer relationships.
Measuring Success in Fintech Data Migration
Fintech migration success metrics extend beyond technical completion to business value and regulatory compliance. Understanding these measures helps organizations evaluate true project outcomes.
1. Accuracy of Financial Records
Financial data accuracy represents the most critical success measure. Every account balance must match exactly not approximately. Transaction histories need perfect completeness without missing payments. Additionally, customer profiles require correct information preventing service errors. Even single-penny discrepancies trigger investigations and remediation efforts.
2. Regulatory Readiness and Audit Outcomes
Compliance validation proves migration met regulatory standards. Can you pass audits immediately after go-live? Additionally, audit trails must demonstrate proper data handling throughout migration. Regulators reviewing post-migration systems should find zero violations. Furthermore, required reports generate accurately without manual adjustments or workarounds.
3. Performance and Cost Improvements
System performance should improve measurably like faster transaction processing, quicker report generation, and reduced batch processing times. Additionally, cost efficiency includes lower infrastructure expenses, reduced manual effort, and decreased operational overhead. Quantify savings through specific metrics proving migration investment value.
4. Business Team Adoption
User acceptance determines operational success. Do risk teams trust new credit models? Can fraud analysts work effectively? Additionally, finance teams must complete reconciliations confidently. High adoption rates with minimal complaints indicate successful migration. Conversely, workarounds and shadow systems signal failure despite technical success.
Partner with Kanerika for help.
Move Your Azure Workloads to Microsoft Fabric for a Unified Setup.
Future of Data Migration in Fintech
How will fintech companies handle data migration as financial services become increasingly digital and AI-driven? The future points toward continuous modernization rather than one-time migration projects that disrupt business operations.
1. AI Transforms Migration Accuracy
AI-assisted validation and anomaly detection are revolutionizing how fintech firms move sensitive financial data. Machine learning algorithms automatically spot irregularities, validate transaction integrity, and ensure regulatory compliance during transfers. This technology reduces migration errors by 85% while maintaining audit trails.
2. Enabling Next-Generation Finance
Data migration now serves strategic purposes beyond system upgrades. Clean, accessible data enables embedded finance solutions, powers AI-driven risk models, and supports real-time fraud detection. Fintech companies use migration projects to create data foundations for machine learning applications.
3. Migration as Strategic Capability
Forward-thinking fintech organizations treat migration as a repeatable enterprise capability rather than occasional projects. Standardized processes, automated tools, and specialized teams make future migrations faster and more reliable. This approach supports rapid scaling, regulatory changes, and continuous innovation in competitive financial markets.
Microsoft Fabric Vs Databricks: A Comparison Guide
Explore key differences between Microsoft Fabric and Databricks in pricing, features, and capabilities.
Case Study 1: Informatica to Alteryx Migration for Faster Financial Analytics
A finance team relied on Informatica-based ETL for reporting and recurring analytics runs. However, as data volumes grew, reporting cycles slowed down and ETL upkeep started consuming too much time and cost. The goal was clear: migrate financial analytics workflows from Informatica to Alteryx while keeping logic consistent and improving turnaround time.
Kanerika supported the Informatica to Alteryx migration using its migration accelerators under FLIP, helping standardize workflows and reduce manual rework across pipelines. As a result, the organization saw faster reporting cycles, reduced ETL maintenance overhead, and quicker analytics delivery for finance stakeholders.
Case Study 2: AI Agent for Real-Time Compliance & Risk Detection
A global knowledge-sharing firm needed to strengthen compliance and risk screening before approving expert engagements. Yet, the process was fully manual as analysts searched the web and social platforms, compiled findings, and checked them against a rulebook. This led to backlogs, delayed approvals, and higher risk of missing critical negative news signals.
Kanerika built an AI compliance agent that automated expert profiling, ran keyword-driven discovery across public sources, and produced structured outputs mapped to compliance criteria with citations. This shifted the team from heavy research to faster review. The outcome included 3x faster expert vetting, 70% backlog reduction, and fewer delays across client-facing activities.
Kanerika Enables Seamless Fintech Data Migration with Automation and AI
Kanerika helps fintech companies and digital financial platforms modernize their data architecture and analytics through fast, secure, and intelligent data migration strategies. Fintech environments often handle massive transaction volumes, real-time payment data, customer behavior insights, fraud signals, and compliance records across multiple platforms. However, fragmented legacy systems, siloed data pipelines, and rapid product expansion can limit agility, accuracy, and regulatory readiness.
As fintech organizations scale across payments, lending, wallets, embedded finance, and digital banking services, these challenges demand a modern, cloud-first data foundation. Kanerika’s approach enables a smooth transition from legacy and semi-legacy fintech systems to modern, cloud-native platforms, without disrupting live transactions, customer experiences, or compliance workflows. Data quality, security, and regulatory alignment are embedded throughout the migration lifecycle.
Our End-to-End Fintech Data Migration Services
We provide comprehensive migration services across critical fintech data domains:
1. BI Migration
Migrate from legacy reporting tools such as Tableau, Cognos, SSRS, and Crystal Reports to Power BI, enabling real-time dashboards for transaction monitoring, fraud analytics, customer insights, financial reporting, and regulatory visibility.
2. Data Warehouse to Data Lake Migration
Transition from rigid, on-premise data warehouses to modern data lakes or lakehouse platforms capable of handling structured and semi-structured fintech data, including transactions, customer profiles, risk indicators, event streams, and audit logs.
3. Cloud Migration
Move fintech workloads to secure, scalable cloud environments such as Azure or AWS to improve performance, elasticity, and cost efficiency while meeting strict data privacy, residency, and compliance requirements.
4. ETL and Pipeline Migration
Modernize data pipelines to support faster ingestion, transformation, and orchestration of data from payment gateways, lending systems, CRM platforms, fraud engines, KYC tools, and partner APIs, ensuring consistent data quality across fintech domains.
5. RPA Platform Migration
Upgrade automation workflows from UiPath to Microsoft Power Automate to streamline fintech processes such as transaction reconciliation, KYC checks, onboarding workflows, reporting automation, and compliance operations.
Powered by FLIP: Smart Migration Accelerators
Kanerika’s proprietary FLIP platform accelerates fintech data migration using Smart Migration Accelerators. FLIP automates up to 80% of the migration process, significantly reducing manual effort while preserving business rules, financial logic, and data accuracy.
FLIP supports complex fintech transitions such as Tableau to Power BI, SSIS to Microsoft Fabric, Informatica to Databricks, and legacy reporting to modern analytics platforms while ensuring zero data loss, strong validation, and uninterrupted fintech operations.
Security, Governance, and Compliance by Design
Throughout the migration journey, Kanerika ensures adherence to global fintech and data protection standards, including ISO 27001, ISO 27701, SOC 2, GDPR, and other industry-specific compliance requirements. Security controls, access management, audit trails, and end-to-end data lineage are enforced at every stage of migration.
By combining deep expertise in automation, AI, cloud engineering, and data governance, Kanerika enables fintech organizations to improve data quality, regulatory confidence, fraud detection accuracy, and analytics performance, while building a scalable, future-ready data foundation that supports real-time decision-making and rapid digital innovation.
Migration Made Easy with Kanerika’s Accelerator
Partner with Kanerika for Seamless, Error-free Migration
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is data migration in fintech?
Data migration in fintech involves moving financial, transactional, and customer data from legacy or fragmented systems to modern platforms. This supports faster payments, real-time analytics, and regulatory compliance. Accuracy and continuity are critical because even small errors can impact trust and revenue.
2. Why is a clear migration strategy important for fintech companies?
Fintech platforms operate at high speed and scale, often across multiple products and partners. A clear strategy defines what data to migrate, when to migrate it, and how to protect business logic. This prevents service disruptions and reduces rework.
3. How does security impact fintech data migration?
Fintech data includes sensitive financial and personal information that must remain protected during migration. Strong encryption, access controls, and monitoring are required throughout the process. Security planning ensures compliance with standards like PCI-DSS, GDPR, and SOC 2.
4. What scalability challenges do fintech organizations face during migration?
Fintech companies process growing transaction volumes and real-time data streams. Migration approaches must scale without slowing systems or increasing costs. Automation and reusable migration frameworks help manage this complexity.
5. How can fintech firms ensure data quality during migration?
Data quality is ensured through early profiling, cleansing, and validation of source data. Fintech data often contains duplicates or inconsistencies that affect fraud detection and reporting. Addressing quality before migration builds trust post go-live.
6. Can fintech data migration be done without downtime?
Yes, fintech migrations often use phased or parallel approaches to maintain live operations. Continuous synchronization and reconciliation allow systems to run without interruption. This protects customer experience and transaction processing.
7. How do fintech companies measure migration success?
Success is measured by data accuracy, system performance, regulatory readiness, and user confidence in analytics. Reduced operational overhead and faster insight generation are also key indicators. Ultimately, a successful migration enables secure growth and innovation.









