Every day, organizations generate more data than ever before, yet many struggle to turn it into information decision-makers can use. As a result, data visualization addresses this challenge by converting complex datasets into clear charts, dashboards, and interactive visuals that instantly reveal patterns, trends, and outliers. From tracking business performance to monitoring operational health, visualization has become a core part of how teams understand and act on data.
Moreover, the value of data visualization is backed by research. Studies cited by Forrester show that organizations using visual analytics are about 28% more likely to identify actionable insights faster. Additional research indicates that the human brain processes visual information significantly faster than text, making visuals far more effective for communication. Gartner also predicts that by 2026, nearly 70% of organizations will rely on visual analytics as a primary tool for enterprise decision making.
In this blog, we explore what data visualization is, why it matters, the most common techniques and tools, and best practices for presenting data to drive clarity and better decisions.
What is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is the process of representing information and data in a graphical format. By using visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps, it makes complex data easier to understand and interpret. Moreover, the goal of data visualization is to present data in a way that highlights key trends, patterns, and insights, allowing viewers to grasp information quickly.
It turns raw data into something that can be interpreted at a glance, simplifying the process of identifying important information. Additionally, data visualization is widely used in business, research, and many other fields to aid decision-making and communicate findings effectively.
Turn Raw Data Into Insights With End-to-End Analytics Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
Types of Data Visualization
Different types of data visualization are suited for different kinds of data. The right choice depends on the type of analysis you want to conduct and the audience you’re addressing.
1. Bar Charts
Bar charts are one of the most common and versatile types of data visualization. Furthermore, they are used to compare quantities across different categories, with bars of varying lengths or heights representing the values.
- Best For: Comparing discrete categories (e.g., revenue from different products, survey responses, etc.).
- How It Works: Each bar represents a category, and the length or height of the bar shows the relative size or value of that category.
- Strength: Easy to understand and interpret at a glance.
- Limitations: Not effective for showing changes over time (for that, line charts are better).
2. Line Graphs
Line graphs are used to display data points in a continuous sequence, typically over time. Connecting data points with lines makes it easy to spot trends, peaks, and dips.
- Best For: Showing trends over time, such as stock prices, temperature variations, or sales growth.
- How It Works: Data points are plotted on the graph, and a line connects these points, making the overall trend more obvious.
- Strength: Excellent for tracking changes and visualizing patterns over periods like months, years, or even hours.
- Limitations: Not ideal for comparing discrete data categories.
3. Pie Charts
Pie charts represent data as slices of a circle, where each slice shows a portion of the whole. The size of each slice is proportional to the percentage or value it represents.
- Best For: Showing proportions and part-to-whole relationships in data (e.g., market share, budget allocation).
- How It Works: The circle is divided into segments, with each segment’s size corresponding to a value. The total of all slices equals 100%.
- Strength: Visually effective for comparing parts of a whole.
- Limitations: Hard to compare many categories, as differences in slice size can be hard to interpret when there are many segments.
4. Scatter Plots
Scatter plots are used to display the relationship between two variables. Thus, each point represents a pair of values, with one variable plotted on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis.
- Best For: Analyzing the correlation between two continuous variables, such as height vs. weight, or income vs. education level.
- How It Works: Each point represents a pair of values (x, y), showing how one variable is related to the other.
- Strength: Effective at identifying trends, correlations, and outliers.
- Limitations: Can be difficult to interpret if there’s too much data or no clear relationship between the variables.
5. Heatmaps
Heatmaps use color to represent data values in a matrix format. The colors indicate the intensity of the data, helping to spot trends or patterns quickly.
- Best For: Visualizing patterns and variations in large datasets, such as website traffic or performance metrics.
- How It Works: Each cell of the heatmap is colored based on the value it represents. High values may be shown in warmer colors (red, orange) while lower values are shown in cooler colors (blue, green).
- Strength: Useful for seeing correlations or patterns across large datasets.
- Limitations: May not be effective if the data set is too small or too complex for color differentiation.
6. Dashboards
Dashboards combine multiple types of visualizations in one comprehensive view. In addition, they are often interactive, allowing users to drill down into specific data points and explore details further.
- Best For: Providing an overview of key metrics or KPIs, such as website performance, sales targets, or operational health.
- How It Works: A collection of various visualizations (charts, graphs, maps) presented together, usually with interactive options.
- Strength: Allows quick access to multiple insights and metrics in one glance.
- Limitations: Can become cluttered or overwhelming if too many metrics are displayed at once.
7. Histograms
Histograms are a type of bar chart that shows the distribution of a set of continuous data. The x-axis represents intervals or “bins,” and the y-axis represents the frequency of data within each bin.
- Best For: Visualizing the distribution of continuous data, such as exam scores, income distribution, or the spread of ages in a population.
- How It Works: Data is grouped into ranges (bins), and bars represent how many data points fall into each range.
- Strength: Effective for understanding how data is distributed across different intervals.
- Limitations: Not ideal for showing individual data points or comparing categories directly.
8. Bubble Charts
Bubble charts are an extension of scatter plots where each data point is represented by a bubble. The size of the bubble represents a third variable, adding a new dimension to the visual.
- Best For: Showing relationships between three variables, such as comparing GDP, population, and life expectancy across countries.
- How It Works: Each point is represented by a bubble, with the x and y axes showing two variables, and the bubble size representing a third.
- Strength: Allows for more detailed insights when analyzing three variables at once.
- Limitations: Can become hard to read if too many bubbles overlap or if the data is not well-distributed.
9. Tree Maps
Tree maps use nested rectangles to represent hierarchical data. The size and color of each rectangle indicate a data value, and the arrangement shows the relationships between categories and subcategories.
- Best For: Visualizing hierarchical data, such as the structure of a company’s departments or a portfolio’s asset allocation.
- How It Works: Data is represented in a set of nested rectangles, with each rectangle’s size representing a value and color denoting a category.
- Strength: Efficient for displaying large amounts of hierarchical data in a compact space.
- Limitations: Can be hard to interpret if the hierarchy is too complex or there are too many categories.
Data Lake vs. Data Warehouse: Which One Powers Better Business Insights?
Explore the key differences between a data lake and a data warehouse to understand which one offers better insights for your business needs.
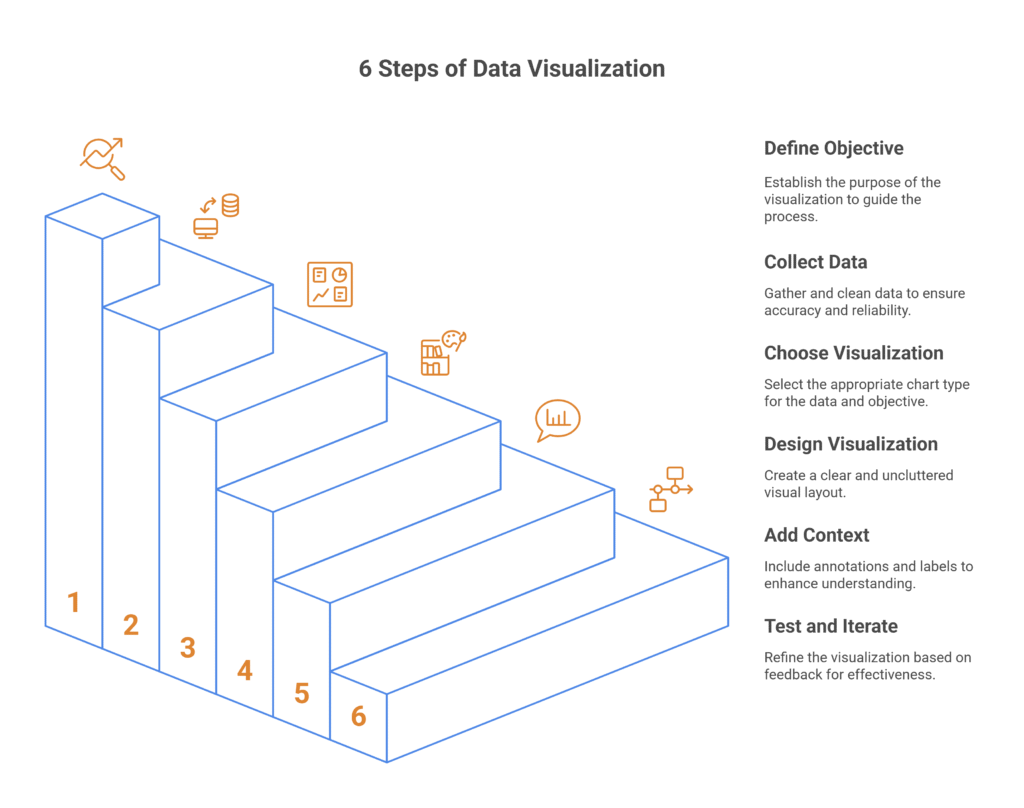
6 Steps of Data Visualization
Creating an impactful data visualization requires more than simply choosing a chart type and inserting data. Additionally, it involves a thoughtful process that ensures your visual is not only visually appealing but also functional, clear, and informative. Here’s how to create effective data visualizations, step by step:
1. Define Your Objective
The first and most crucial step in data visualization is to define the purpose behind your visual. To begin with, what story do you want the data to tell? Are you trying to show a trend, compare categories, reveal correlations, or highlight anomalies? In addition, a clear objective will guide every decision that follows, from choosing the chart type to designing the layout.
2. Collect and Prepare Your Data
Before you begin creating any visual representation, ensure the data is clean and reliable. Raw data is often messy—missing values, outliers, duplicates, and inconsistencies can distort your findings and lead to inaccurate conclusions. Therefore, it’s essential to refine your data before using it in any visualization.
This step involves processes like:
- Removing or handling missing values.
- Correcting any data entry errors.
- Standardizing formats.
- Identifying and addressing outliers that could skew the results.
- Ensuring the data is current and relevant for your analysis.
3. Choose the Right Type of Visualization
Choosing the right chart or visualization is essential for delivering your message clearly. Each type of visualization has its strengths and is suited for different kinds of data and analysis.
For example:
- Bar charts are effective for comparing quantities across different categories.
- Line graphs are best for showing trends over time.
- Scatter plots are great for exploring relationships between two variables.
- Heatmaps work well for spotting patterns or correlations in large data sets.
4. Design Your Visualization
Once you’ve chosen your chart type, the next step is designing the visualization. Additionally, a well-designed chart is one that is clear, easy to read, and free from clutter. Pay attention to elements such as color schemes, labels, grid lines, and spacing to ensure that the data is presented in a way that is easy to interpret.
Good design practices include:
- Using color strategically to highlight important data points or trends.
- Ensuring your chart is not overloaded with information or extraneous elements.
- Labeling axes and adding titles that clarify what the data represents.
- Using appropriate scales and intervals to make the data easy to read and compare.
5. Add Context and Annotations
Data on its own can often be meaningless or open to misinterpretation. To guide your audience, you need to provide context. Furthermore, this might include adding labels, titles, descriptions, or annotations that explain the data, highlight key points, or describe the significance of trends or outliers.
Annotations could include:
- Explanatory notes or callouts pointing out key trends, correlations, or outliers.
- Contextual information on data sources, timeframes, or any limitations of the data.
- A brief narrative to help the viewer understand why certain data points are important.
6. Test and Iterate
Once the visualization is created, test it with others who weren’t involved in the process. Aditonally, it gathers feedback on its clarity and whether the insights are effectively communicated. This helps identify areas that may need improvement and allows you to refine the design based on feedback.
Top 10 Data Visualization Tools in Demand
1. Power BI
Power BI is a business analytics service by Microsoft, providing interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities with an easy-to-use interface. Moreover, It helps users create comprehensive reports and dashboards, and it integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft services such as Azure, Excel, and SharePoint.
- Seamless Integration: Direct integration with Microsoft products like Excel, Azure, and SharePoint, allowing for easy data import and reporting.
- Drag-and-Drop Interface: Users can easily build complex reports and dashboards with a simple drag-and-drop functionality.
- Customizable Visualizations: Power BI offers a wide range of built-in visualizations, with options for custom visuals through the marketplace.
- Real-Time Data: Enables real-time data streaming and reporting, which is especially useful for monitoring live data.
- Collaboration Features: Offers cloud-based sharing of reports and dashboards, enabling team collaboration.
2. Tableau
Tableau is one of the leading data visualization tools known for its ability to convert raw data into interactive visualizations. Moreover, with a strong focus on user experience, it allows both technical and non-technical users to design compelling reports and dashboards without needing extensive coding knowledge.
- Intuitive Drag-and-Drop Interface: Users can create visualizations without writing any code, simplifying the process of data exploration.
- Wide Range of Visualizations: Offers numerous chart types, from bar graphs to geographic maps, and custom visualizations.
- Data Blending: Ability to combine data from different sources seamlessly, without the need for complex integrations.
- Powerful Analytics: Includes advanced analytics features like forecasting, trend lines, and statistical modeling.
- Strong Community Support: Tableau’s large user community offers a wealth of resources, tutorials, and templates to assist new users.
3. Microsoft Fabric
Microsoft Fabric is an all-in-one data platform for businesses that combines various data services into a single unified solution. Moreover, it integrates data engineering, data science, business intelligence, and real-time analytics, offering a comprehensive tool for end-to-end data management and analysis.
Key Features:
- Unified Platform: Combines multiple services, such as data storage, processing, and analytics, into one seamless platform.
- AI Integration: Microsoft Fabric uses artificial intelligence to automate processes and make data more accessible for analysis.
- Power BI Integration: Includes seamless integration with Power BI for creating interactive data visualizations directly within the platform.
- Real-Time Analytics: Provides tools for real-time analytics and streaming data, making it suitable for immediate data-driven decisions.
- Scalability: Highly scalable, enabling companies to expand their data needs as their business grows.
4. Qlik Sense
Qlik Sense is a business intelligence platform that uses an associative model to allow users to explore and visualize data. It is known for its flexibility and self-service analytics features, which allow users to analyze data without the need for technical expertise.
Key Features:
- Associative Data Model: The platform uses an associative data model that allows users to make data connections across different sources, providing more insights.
- Self-Service Analytics: Empowers users to create their own reports and dashboards without relying on IT departments.
- Smart Search: Built-in smart search functionality allows users to query data easily, finding relevant insights quickly.
- Mobile-Friendly: Qlik Sense dashboards are fully optimized for mobile devices, offering on-the-go access to analytics.
- Collaborative Features: Provides options for sharing dashboards and reports, facilitating team collaboration and decision-making.
5. Looker
Looker is a data exploration and business intelligence tool that provides an intuitive platform for exploring, analyzing, and sharing real-time data insights. Now part of Google Cloud, it is known for its flexibility in data modeling and integration with various data sources.
Key Features:
- Data Modeling Layer: Looker allows users to create custom data models using LookML, providing flexibility in how data is presented.
- Real-Time Analytics: Provides real-time data insights and reporting, which is essential for making timely decisions.
- Integrated with Google Cloud: Deep integration with Google Cloud services, providing seamless data access and powerful analytics capabilities.
- Customizable Dashboards: Offers customizable, interactive dashboards to provide meaningful insights at a glance.
- Embedded Analytics: Looker allows you to embed its dashboards and reports into external applications, facilitating easy sharing and access.
6. Domo
Domo is a cloud-based business intelligence platform that allows businesses to visualize their data in real time. Moreover, it combines data integration, visualization, and collaboration into a single platform, helping businesses make data-driven decisions faster.
Key Features:
- Real-Time Data Integration: Domo integrates data from a variety of sources, including cloud, on-premise, and third-party applications.
- Interactive Dashboards: Users can create interactive dashboards with real-time data, enabling better decision-making.
- Collaboration Tools: Built-in collaboration features allow teams to comment on reports, share insights, and discuss data in real-time.
- Pre-built Data Connectors: Domo offers numerous pre-built data connectors, making it easy to import data from popular services like Google Analytics, Salesforce, and more.
- Mobile Accessibility: Domo provides mobile-optimized dashboards, allowing users to access insights from anywhere.
7. Sisense
Sisense is a powerful business intelligence platform that simplifies complex data integration and analytics. It is known for its ability to handle large datasets and transform them into interactive visualizations and insights.
Key Features:
- In-Chip Analytics: Sisense’s in-chip technology enables fast data processing, making it ideal for big data applications.
- Custom Dashboards: Allows users to build interactive and customizable dashboards for detailed insights.
- Data Integration: Supports integration with numerous data sources, including cloud platforms, databases, and third-party applications.
- Advanced Analytics: Includes machine learning and predictive analytics capabilities to uncover hidden patterns and trends.
- Embedded Analytics: Offers embedded analytics to allow businesses to integrate data insights directly into their applications.
8. Zoho Analytics
Zoho Analytics is a self-service BI tool that allows businesses to analyze and visualize their data. It provides an easy-to-use platform for creating reports, dashboards, and visualizations from a variety of data sources.
Key Features:
- AI-Powered Insights: Zoho Analytics uses artificial intelligence to provide automated insights and trends based on the data.
- Data Integration: Easily integrates with multiple data sources, including Google Analytics, Salesforce, and other third-party services.
- Drag-and-Drop Interface: The intuitive drag-and-drop interface makes it easy for users to create reports and dashboards without needing technical expertise.
- Collaboration Features: Provides options for sharing reports and collaborating with team members on data analysis.
- Customizable Dashboards: Allows users to create personalized dashboards tailored to their needs.
9. Google Data Studio
Google Data Studio is a free, web-based tool that allows users to create interactive reports and dashboards. Additionally, it integrates easily with other Google services, making it a great option for users working within the Google ecosystem.
Key Features:
- Google Integration: Seamlessly integrates with Google services like Google Analytics, Google Ads, and Google Sheets, providing easy access to data.
- Collaborative Features: Google Data Studio allows real-time collaboration, making it easy for teams to work together on reports and dashboards.
- Customizable Reports: Users can customize the appearance of their reports using a wide range of visual elements.
- Free to Use: Unlike many other BI tools, Google Data Studio is completely free, which makes it ideal for small businesses and startups.
- Pre-Built Templates: Offers a variety of pre-built templates to help users get started quickly.
10. IBM Cognos Analytics
IBM Cognos Analytics is an AI-infused business intelligence platform that provides a range of data visualization and reporting tools. Furthermore, it’s designed to help organizations make data-driven decisions and gain insights from their data.
Key Features:
- AI-Powered Analytics: IBM Cognos uses AI to automate data preparation, report generation, and predictive analytics.
- Natural Language Queries: Users can interact with data using natural language, making it easier for non-technical users to ask questions and analyze data.
- Integrated Data Sources: Integrates with a variety of data sources, including on-premise and cloud-based platforms.
- Dashboards and Reports: Offers powerful reporting and dashboard creation tools for users to present insights clearly and effectively.
- Data Governance: Includes features to ensure that the data used for analytics is consistent and reliable, supporting compliance and governance.
Kanerika: Elevating Your Reporting and Analytics with Expert Data Solutions
At Kanerika, we help businesses move beyond basic reporting by delivering smart, scalable analytics powered by Power BI and Microsoft Fabric. As a Microsoft-certified Data and AI Solutions Partner, we specialize in turning complex data into clear, actionable insights—helping organizations make faster, better-informed decisions.
Also, our solutions are tailored to each client’s unique needs, combining advanced data visualization, predictive analytics, and intelligent automation. Whether it’s manufacturing, finance, healthcare, or retail, we design analytics ecosystems that reveal hidden patterns, improve performance, and support strategic growth.
With deep expertise in Microsoft’s analytics stack, our team builds interactive dashboards, streamlines data flows, and develops enterprise-grade data strategies that align with your business goals. Moreover, we are backed by skilled analysts and data scientists, enabling organizations to improve operations, reduce inefficiencies, and stay ahead of the competition through data they can trust.
Karl – Data Insights AI Agent for Faster Business Decisions
This AI-powered analytics agent helps teams convert structured business data into meaningful insights without the need for coding or traditional BI tools. Instead of manually creating queries or dashboards, users can ask questions in simple language and instantly receive clear summaries, charts, and visual reports. It works seamlessly with data sources such as SQL and NoSQL databases, Excel and CSV files, and cloud platforms like Microsoft Fabric, enabling easy access to insights across the organization.
Key Features & Benefits
- Query business data using natural language and get visual insights instantly
- Identify trends, patterns, and key metrics automatically
- Analyze live or uploaded data from multiple connected sources
- Continue conversations with contextual follow-up questions for deeper analysis
- Maintain data security with enterprise-grade access controls and audit trails
Therefore, this solution is ideal for teams that want quicker insights, clearer data interpretation, and less reliance on technical experts, supporting use cases like sales analysis, operational tracking, and customer behavior insights.
Turn Insights Into Visuals That Guide Business Growth And Clarity.
Partner With Kanerika To Maximize Data-Driven Success.
FAQ
What do you mean by data visualization?
Data visualization transforms complex data into easily understandable visual formats like charts and graphs. It’s essentially about telling a story with your data, revealing patterns and insights that might be hidden in raw numbers. This makes information more accessible and actionable, facilitating quicker decision-making. Think of it as translating data into a language everyone can grasp.
What are the 5 C's of data visualization?
The 5 C’s of data visualization ensure your visuals are effective. Clarity means your message is immediately understandable. Correctness guarantees accuracy; no misleading data. Completeness provides the full story, not just snippets. Conciseness avoids clutter, focusing on key insights. Finally, compelling visuals engage the audience and leave a lasting impression.
Is SQL a data visualization tool?
No, SQL is a language for managing and querying databases, not for visualizing data. Think of it as the backstage worker – it gets the data ready, but it doesn’t present it in a user-friendly format like a chart or graph. You need a separate visualization tool to display the results SQL retrieves. Essentially, SQL provides the *what*, while visualization tools provide the *how*.
What is the role of data visualization?
Data visualization translates complex data into easily understandable visuals. It helps us spot trends, patterns, and outliers that might be missed in raw numbers, allowing for quicker, more informed decision-making. Essentially, it transforms data from abstract information into actionable insights. It bridges the gap between data and understanding.
What are the benefits of data visualization?
Data visualization transforms complex data into easily digestible insights, revealing hidden patterns and trends instantly. It makes information more engaging and memorable, facilitating better understanding and quicker decision-making. Essentially, it bridges the gap between raw data and actionable knowledge, improving communication and collaboration. This leads to more effective problem-solving and strategic planning.










