Handling data has become a daily struggle for many organisations because information now comes from more sources than ever. Companies collect data from apps, machines, websites, customer platforms, cloud tools, and internal systems, and keeping it all clean, organised, and usable is not easy. This growing pressure is why data management challenges have become a significant concern for business and IT teams.
A global report from Gartner found that 65% of organisations face issues with data quality, and poor data is responsible for an average annual loss of $ 12.9 million. In fact, studies show that a large share of companies are still not prepared for this surge in data. Poor data quality, missing standards, scattered systems, and slow processes make it hard to trust reports or build strong analytics. As a result, many teams spend more time fixing errors than analysing trends, and the gap between the data collected and the data actually used keeps widening.
In this blog, you will learn the most common data management challenges, why they slow down growth, and what steps organisations can take to build a simpler and more reliable data foundation.
Key Takeaways
- Organisations struggle with data due to poor quality, silos, rising volume, manual processes, and weak governance.
- Automated tools, unified platforms, real-time pipelines, and scalable cloud storage help fix major data issues.
- Strong security, clear ownership, and consistent standards reduce compliance risk and improve trust.
- AI boosts data quality, speeds integration, improves governance, and delivers predictive insights for better planning.
- Solving data challenges leads to faster decisions, lower costs, better customer experiences, and improved accuracy.
- Kanerika provides secure AI-driven solutions, modern data platforms, and specialised AI agents to simplify data operations.
Simplify Your Data Challenges with Kanerika’s AI Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika to unlock the full potential of your business data.
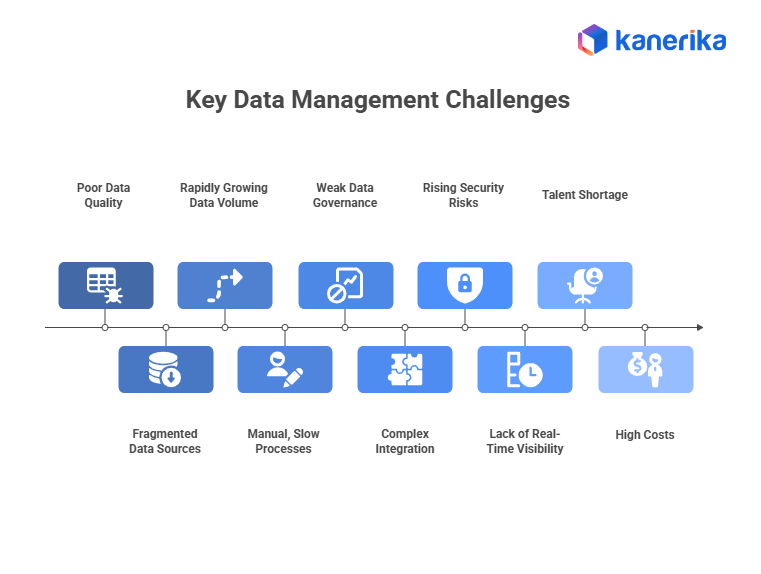
Key Data Management Challenges
1. Poor Data Quality
Poor data quality affects reporting, forecasting, customer analytics, and overall business performance. Issues like duplicate records, incomplete fields, outdated values, and inconsistent formats lead to unreliable insights. Many enterprises underestimate the impact until they face wrong decisions or operational delays. In particular, a Gartner study notes that organizations lose a significant portion of their revenue each year due to insufficient data, underscoring the cost of this challenge.
2. Fragmented Data Sources and Silos
Enterprises use dozens of tools across departments. When information stays inside isolated systems, teams cannot create a unified view of customers, operations, or performance. Silos lead to repeated work, misaligned strategies, and confusion over which dataset is the correct one. For instance, companies that successfully break silos, like Starbucks with its loyalty and app data, demonstrate how unified data improves personalization and engagement.
3. Rapidly Growing Data Volume and Variety
Organizations collect data from apps, websites, machines, IoT devices, emails, and logs. This constant increase in volume and variety overwhelms traditional storage and processing environments. Managing both structured and unstructured data becomes difficult without scalable cloud solutions. Furthermore, global data creation is rising rapidly, and businesses need modern setups to keep up.
4. Manual, Slow, and Error-Prone Processes
Many critical tasks, such as cleaning, mapping, formatting, and verifying data, are still done manually. Manual workflows slow down analytics, introduce errors, and take time away from high-value work. In fact, studies show data teams spend a large portion of their time on repetitive tasks, which limits their ability to focus on strategy and insights.
5. Weak Data Governance and Compliance Gaps
Without clear ownership, standardized policies, and defined access rules, data becomes harder to control. This creates compliance risks, especially when organizations manage sensitive customer information. Regulations like GDPR and CCPA require strict governance, and failing to meet these standards can lead to penalties and reputational damage. Therefore, strong governance ensures consistency, accountability, and protection.
6. Complex and Costly Integration
Integrating legacy systems, cloud applications, third-party tools, and modern analytics platforms is one of the most challenging data tasks. Schema differences, incompatible formats, and broken pipelines disrupt operations and slow down transformation projects. As a result, enterprises often spend significant resources on integration because it directly affects the reliability of analytics and system performance.
7. Rising Security and Privacy Risks
Cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches are increasing as businesses store more data. Protecting sensitive information is critical for building customer trust and meeting compliance requirements. Even a single breach can lead to financial loss and long-term brand damage. Consequently, strong encryption, access control, and monitoring are essential to safeguard enterprise data.
8. Lack of Real-Time Visibility
Many organizations still rely on batch-based processing, which means insights come with delays. Without real-time dashboards or alerts, teams react late to operational issues, customer activity, and market changes. Industries like finance, retail, and logistics depend heavily on real-time analytics to stay competitive. In turn, the ability to act instantly is now a key business requirement.
9. Talent and Skills Shortage
There is a growing need for skilled data engineers, builders, analysts, and AI specialists. Many organizations struggle to hire talent capable of managing modern data setups, automation tools, and cloud systems. This skills gap slows down digital transformation and increases reliance on external support or consultants.
10. High Cost of Managing Large Data Systems
Costs rise as businesses invest in storage, processing power, governance tools, security measures, and skilled teams. Cloud costs also multiply if usage is not improved. Inefficient processes and redundant tools add to expenses. Therefore, organizations now prioritize cost improvement strategies to reduce unnecessary spend and increase the return on their data investments.
How to Overcome Data Management Challenges
1. Invest in Automated Data Quality and Profiling
Deploy automated data profiling, checking, deduplication, and enrichment so issues are found before they reach reports or models. Data quality tools run scheduled checks, score datasets, and apply fixes or flags, which turns quality from an afterthought into a measurable program. As a result, this reduces rework and makes analytics trustworthy.
2. Consolidate into a Unified Data Platform or Lakehouse
Move standard data into a governed, central platform that supports both analytics and machine learning. A lakehouse or modern data platform removes duplication, provides consistent access patterns, and simplifies governance and sharing across teams, making a single source of truth practical at scale. Additionally, this approach streamlines data workflows.
3. Automate Pipelines with Modern Orchestration and CI/CD
Replace one-off scripts with versioned, observable pipelines using orchestration tools, pipeline tests, and CI/CD for data code. Automated pipelines with schema checks, retries, and drift detection reduce breaks in production and make onboarding new sources predictable and fast. Moreover, they improve reliability across the board.
4. Standardize Governance, Metadata, and a Searchable Data Catalog
Define ownership, data domains, retention rules, and access policies, and back them with a metadata catalog that shows lineage and usage. A living catalog, combined with transparent governance, makes datasets discoverable, auditable, and easier to trust for both business users and auditors. In turn, this builds confidence in data quality.
5. Use AI and ML to Speed Integration and Cleaning
Apply ML to schema mapping, semantic inference, automated data mapping, and anomaly detection, enabling the onboarding of messy or semi-structured sources faster. AI reduces manual mapping time and helps manage unstructured inputs that rule-based tools struggle with. Furthermore, it handles complex data scenarios more efficiently.
6. Adopt Scalable Cloud Storage with Cost Controls
Move heavy, variable workloads to object storage or cloud lakehouses and combine lifecycle policies, tiering, compression, and tagging to control cost. Scalability lets teams keep high-value raw data while cost controls prevent runaway bills as the data footprint grows. At the same time, performance remains high.
7. Implement Real-Time Streaming and Materialized Views for Fast Insights
Introduce streaming ingestion, event buses, and incremental materialized views for operational dashboards and alerts. Real-time streams enable fast reactions for fraud detection, personalization, and supply chain events that batch pipelines cannot support. In particular, this approach empowers immediate decision-making.
8. Harden Security: Least Privilege, Encryption, and Monitoring
Enforce least privilege access, use column-level masking for sensitive fields, encrypt data at rest and in transit, and integrate access logs into monitoring and incident workflows. Strong identity and behavior monitoring reduce the risk of breaches and help meet compliance checks. Consequently, security posture improves significantly.
9. Invest in People: Targeted Upskilling and Cross-Functional Squads
Run focused training for data engineers, analysts, and product owners, and form cross-functional squads that include domain experts. Upskilling plus team structures that combine engineering and business reduce handoffs, speed delivery, and lower reliance on external consultants. In addition, this builds internal capability.
10. Treat Data as a Product with SLOs, Contracts, and Observability
Define service level objectives for freshness, availability, and quality; use data contracts between producers and consumers; and instrument pipelines with metrics and alerts. This product mindset sets clear expectations, improves reliability, and makes it easier to prioritize engineering effort. Overall, it transforms how teams work with data.
AI in Robotics: Pushing Boundaries and Creating New Possibilities
Explore how AI in robotics is creating new possibilities, enhancing efficiency, and driving innovation across sectors.
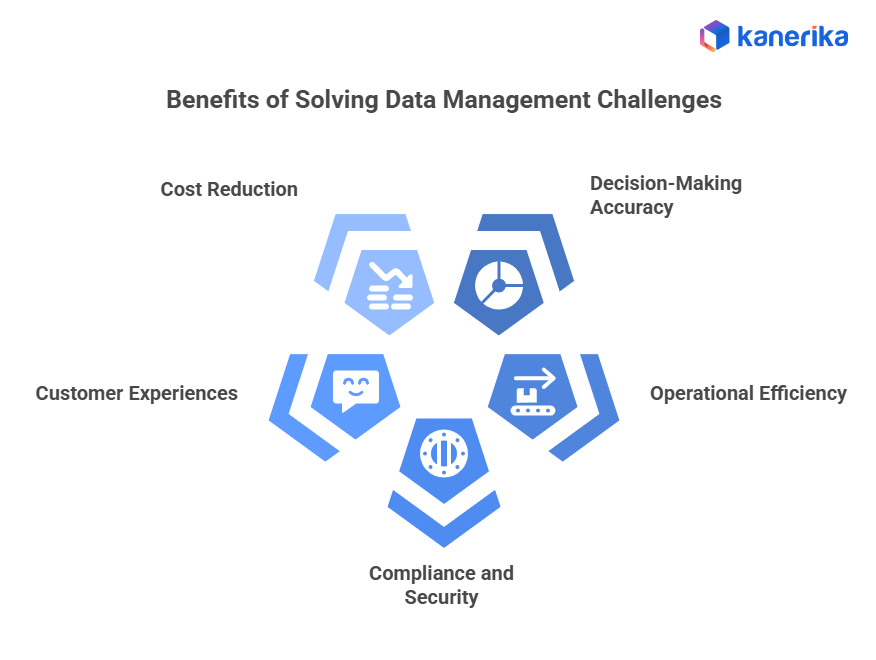
The Business Benefits of Fixing Data Management Challenges
1. Higher Decision-Making Accuracy
When data is clean, consistent, and unified across systems, decision-makers work with facts rather than assumptions. Accurate data strengthens forecasting, improves planning, and removes guesswork from strategy discussions. Teams can trust dashboards, models, and reports, which directly improve business outcomes. Furthermore, organizations that maintain high-quality data often report more substantial ROI from analytics and AI because insights reflect real business conditions.
2. Faster Operational Efficiency
Automated pipelines, standardized processes, and real-time data access reduce time spent on manual corrections and repeated checks. Workflows run more smoothly, departments collaborate easily, and information flows across tools without friction. As a result, this cuts operational delays and enables teams to act quickly on opportunities or risks. Faster data access also improves productivity for analysts, engineers, and business users.
3. Reduced Compliance and Security Risk
Strong governance, access controls, lineage tracking, and timely audits help organizations meet regulations such as GDPR, DPDP, and industry-specific rules. When sensitive data is well managed, the risk of leakage, misuse, or non-compliance drops significantly. In turn, secure data environments protect customer information, prevent unauthorized access, and build trust with stakeholders and regulators. This also reduces the financial impact of breaches or penalties.
4. Better Customer Experiences
Unified, high-quality data helps businesses better understand customer behavior, preferences, and needs. This enables personalized recommendations, faster issue resolution, and more relevant service interactions. When customer data is reliable, brands can deliver consistent experiences across channels and respond quickly to trends. Moreover, smoother experiences lead to higher satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
5. Lower Long-Term Data Costs
Efficient data infrastructure, automated quality checks, scalable cloud storage, and proper lifecycle management prevent unnecessary storage costs and manual rework. By eliminating duplicates, outdated data, and inefficient pipelines, teams reduce the total cost of ownership. Over time, improved systems require fewer resources to maintain, lowering engineering effort, cloud bills, and tool complexity. In the end, smart data management protects both budgets and performance.
Role of AI in Addressing Data Management Issues
1. AI for Quality Monitoring and Anomaly Detection
AI improves data quality by continuously scanning datasets, detecting inconsistencies, and predicting errors before they disrupt operations. For instance, companies like PayPal use machine learning to spot unusual transaction patterns in real time, preventing fraud and inaccurate reporting. Similarly, Netflix applies AI-based anomaly detection to monitor streaming performance and identify sudden drops in quality across regions. These real-world systems help teams react instantly, reduce data errors, and maintain high user satisfaction.
2. AI for Metadata and Catalog Automation
Manual metadata updates are slow and incomplete, but AI automates this by tagging datasets, identifying relationships, and surfacing lineage details. Google Cloud Data Catalog uses AI to auto-classify data and detect sensitive fields, reducing documentation gaps for enterprise customers. In addition, LinkedIn employs AI-driven metadata enrichment to organize billions of profiles, job listings, and content interactions, enabling better search accuracy and recommendations. This automation speeds up and improves the reliability of data discovery.
3. AI for Predictive Insights and Forecasting
Predictive analytics powered by AI helps companies anticipate demand, customer behavior, and operational risks. Walmart uses advanced forecasting models to predict product demand at store and region levels, improving inventory placement and reducing waste. Meanwhile, Uber relies on AI to estimate rider demand, set dynamic pricing, and allocate drivers efficiently. These predictive systems enable companies to shift from reactive decision-making to proactive planning, thereby strengthening business performance.
4. AI for Governance and Policy Enforcement
AI enhances governance by tracking how data is used, identifying policy violations, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Salesforce integrates AI-driven governance checks to help enterprises enforce privacy rules and manage customer data responsibly across their cloud platform. At the same time, Capital One uses AI to monitor data access patterns and detect suspicious or unauthorized behavior within its highly regulated environment. This reduces compliance risk and protects both customers and businesses.
5. AI for Migration and Integration Automation
Data migration and integration require extensive mapping, validation, and transformation. AI automates these tasks by analyzing schemas, recommending mappings, and identifying unusual patterns during migration. Microsoft Azure Migrate uses AI to assess workloads, identify dependencies, and suggest optimal migration paths, which speeds up cloud modernization projects. Furthermore, IBM applies AI to automate data mapping and transformation during large-scale legacy-to-cloud migrations, reducing manual effort and errors. This makes transitions faster, smoother, and more cost-effective.
Kanerika: Simplifying Data Challenges with AI Solutions
Kanerika helps businesses solve complex data challenges and turn them into actionable insights using advanced AI and data management solutions. Our knowledge covers data integration, analytics, AI/ML, and cloud management, enabling organizations to build scalable systems that improve decisions and efficiency.
We ensure security and compliance with ISO 27701 and 27001 certifications, SOC II compliance, GDPR adherence, and CMMI Level 3 appraisal. These standards guarantee secure, reliable, and enterprise-ready solutions. Our partnerships with Microsoft, AWS, and Informatica allow us to deliver innovative solutions that combine modern technology with agile practices. Our mission is simple: help organizations use data to drive growth through AI-powered solutions.
To achieve this, Kanerika has built specialized AI agents — DokGPT, Jennifer, Alan, Susan, Karl, and Mike Jarvis. These agents automate tasks like document processing, risk scoring, customer analytics, and voice data analysis. They work with structured data and integrate easily into enterprise workflows, delivering faster insights and better operational efficiency.
Unlock Smarter Data Management with Kanerika’s AI-Driven Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert AI implementation Services
FAQs
What are the challenges in managing data?
Data management faces hurdles in several key areas: ensuring data quality (accuracy, completeness, consistency) across diverse sources is a constant battle. Scaling to handle ever-increasing data volumes while maintaining speed and efficiency is another major challenge. Finally, navigating complex legal and ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and security is paramount.
What are the three limitations of data management?
Data management faces limitations in three key areas: First, the sheer volume and velocity of data can overwhelm storage and processing capabilities, hindering effective analysis. Second, ensuring data quality – accuracy, completeness, and consistency – is a constant challenge, impacting decision-making reliability. Finally, maintaining data security and privacy, especially with increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, poses a persistent risk.
What are the major challenges faced in data processing?
Data processing struggles with sheer volume and velocity – handling massive datasets quickly is a constant hurdle. Inconsistent data quality (errors, missing values) requires significant cleaning and pre-processing. Finally, ensuring data security and privacy while maintaining accessibility for analysis presents a complex balancing act.
What are the four types of data management?
Data management isn’t just one thing; it’s a multifaceted approach. Think of it in four key areas: capturing and storing data (operational), analyzing it for insights (analytical), ensuring its quality and accuracy (governance), and using it securely (security). These areas work together to make data useful and trustworthy.
What is challenging in data handling?
Data handling’s biggest hurdle is managing its sheer volume, variety, and velocity – the “three Vs” of big data. Ensuring data quality, accuracy, and consistency across diverse sources is another significant challenge. Finally, effectively extracting meaningful insights and translating them into actionable knowledge requires sophisticated analytical skills and tools.
What are the challenges of handling big data?
Big data’s biggest hurdles are its sheer volume, velocity, and variety. This makes storage, processing, and analysis incredibly complex and expensive. Furthermore, extracting meaningful insights from this raw data requires sophisticated algorithms and skilled professionals. Finally, ensuring data privacy and security at this scale presents significant challenges.