Walmart processes 2.5 petabytes of data every hour across its 20,000 stores in 28 countries, yet the retail giant’s success doesn’t come from simply collecting massive amounts of information. This can be achieved when store managers in rural Arkansas can access the same customer insights as executives in Bentonville, enabling them to make inventory decisions that directly impact their local communities.
Most businesses today face a similar challenge: they’re drowning in data but starving for actionable insights. According to Amazon Business’s 2024 State of Procurement Data Report, 95% of decision-makers say procurement has room for optimization, highlighting how even data-rich companies struggle to make information truly accessible to those who need it most.
Here’s what separates thriving companies from struggling ones: successful organizations don’t just collect data—they make it accessible to every decision-maker at every level. Data accessibility transforms raw numbers into strategic advantages, turning confusion into clarity and guesswork into informed action. When teams can quickly find, understand, and act on relevant information, everything changes.
Level Up Your Data Game With Improved Data Accessibility!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Management Solutions.
What is Data Accessibility?
Data accessibility refers to the ease with which data can be retrieved and used by users within an organization. It ensures that all employees, regardless of their technical skills, can access the data they need to perform their tasks effectively.
For instance, consider a retail company using a centralized data system where sales data, customer feedback, and inventory levels are easily accessible to marketing, sales, and operations teams.
This accessibility allows the marketing team to tailor campaigns based on real-time sales data, the sales team to adjust strategies according to customer feedback, and the operations team to manage inventory efficiently. By making data readily available, businesses can make informed decisions quickly and enhance overall productivity.
7 Critical Data Accessibility Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Businesses today face a multitude of challenges when it comes to data accessibility. Below are some of the most common ones, along with detailed insights on how to tackle them effectively.
1. Data Silos
Data stuck in separate departments can slow everything down. One team has sales figures, another has customer feedback, and no one sees the full picture. This disconnect can lead to poor planning and missed chances.
Solution: Bring teams together with integration tools that centralize your data. Encourage open data-sharing habits across departments — it’s not just an IT task, it’s a culture shift.
2. Data Quality
If your data is full of errors, duplicates, or missing values, even the most advanced dashboards won’t help. Bad data can lead to the wrong decisions and erode trust quickly.
Solution: Set up clear rules and regular checks to clean and validate data. A strong data governance plan — one that includes responsibility, review cycles, and standards — goes a long way here.
3. Lack of Technical Knowledge
Many employees avoid data tools simply because they seem too complicated. If they have to rely on IT for every small report, productivity suffers.
Solution: Make data more user-friendly. Offer basic training sessions, and invest in self-service tools that don’t need coding or technical jargon to get insights.
4. Security and Compliance Concerns
Sharing data widely is risky if you don’t control who sees what. Regulations like GDPR and HIPAA make it even more important to handle sensitive data properly.
Solution: Use role-based access, so people only see what they need. Add layers of protection with encryption, and do regular audits to keep everything in check.
5. System Scalability
As your business grows, so does your data. But older systems often can’t keep up, which means slower access and clunky performance.
Solution: Move to scalable platforms that grow with you — cloud storage and flexible databases are often more affordable and easier to scale than on-site setups.
6. Overwhelming Raw Data
Having tons of data is one thing — making sense of it is another. For many, rows of raw numbers mean nothing without a way to see patterns or trends.
Solution: Use visualization tools that turn raw figures into clear charts and dashboards. It’s much easier for teams to spot what matters when the data tells a visual story.
7. High Costs
Top-tier analytics platforms can be pricey, and smaller teams or departments often get left out. That limits who can access data and benefit from it.
Solution: Look at open-source or budget-friendly tools. You can also use tiered access, where basic insights are available to everyone, and deeper features are reserved for power users.
Data Extraction: Techniques and Best Practices for Businesses
Explore the essential data extraction techniques and best practices that businesses can implement to streamline processes and unlock valuable insights from their data.
How Can Better Data Accessibility Impact Business Performance
1. Enhanced Decision-Making:
Speed and Accuracy: With readily accessible data, employees at all levels can make quicker and more informed decisions.
Real-Time Insights: Access to real-time data enables businesses to react swiftly to market changes, improving agility and competitiveness.
2. Increased Productivity
Reduced Bottlenecks: When data is easily accessible, employees spend less time searching for information and more time on value-added activities. This streamlines workflows and enhances overall efficiency.
Empowered Workforce: Empowering employees with the right data tools foster a more proactive and engaged workforce, leading to higher productivity and job satisfaction.
3. Improved Collaboration
Unified Data View: Breaking down data silos allows for a more collaborative environment where departments can share insights and work together towards common goals.
Cross-Departmental Initiatives: Enhanced data accessibility supports cross-functional teams by providing a shared understanding of business metrics and performance.
4. Better Customer Insights
Personalized Experiences: By analyzing accessible customer data, businesses can tailor their products and services to meet specific customer needs, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Predictive Analytics: With better data access, companies can utilize predictive analytics to anticipate customer behaviors and trends, allowing for more strategic planning and marketing efforts.
5. Cost Savings
Efficiency Gains: Streamlined data processes reduce redundancies and operational costs. According to Forbes, organizations with high data accessibility see significant cost reductions due to improved efficiency and reduced need for extensive data management resources.
Optimized Resource Allocation: By having a clear view of data, businesses can better allocate resources, avoid wastage, and maximize returns on investment.
6. Compliance and Risk Management:
Regulatory Compliance: Enhanced data accessibility ensures that accurate and up-to-date information is readily available for compliance reporting, reducing the risk of penalties and fines.
Risk Mitigation: With accessible data, businesses can quickly identify and address potential risks, enhancing overall security and governance.
Navigating Data Management Challenges: Strategies for Success
Explore effective strategies for navigating data management challenges and ensuring success through streamlined processes, enhanced data governance, and robust integration solutions.
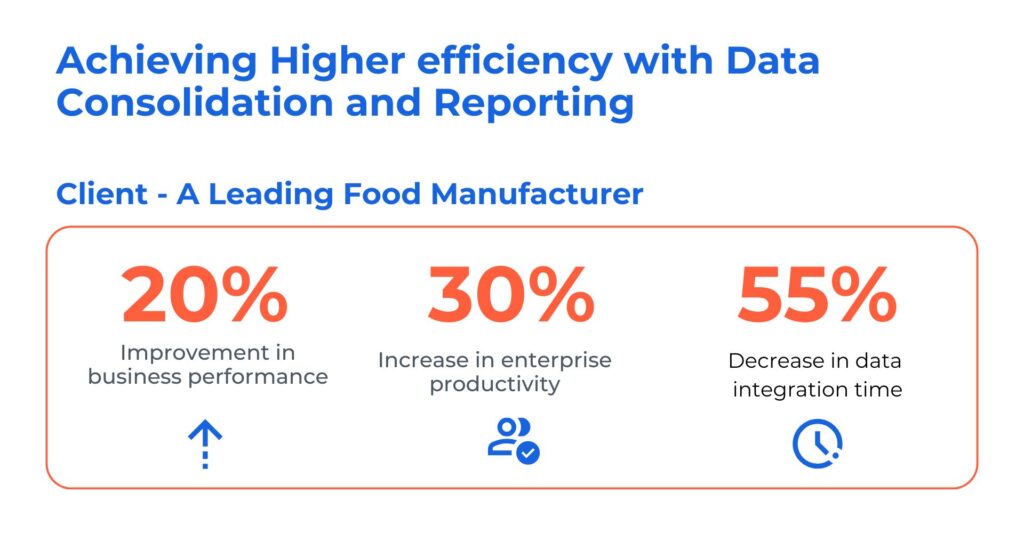
Case Study: Data Consolidation and Reporting Using Power BI
The client is an edible oil manufacturer and dealer who uses SAP systems for all major company transactions. They faced challenges with unstructured data, making real-time reporting on sales, deliveries, payments, and distribution a complex task. Inconsistent and delayed insights due to dispersed SAP and non-SAP data hindered accurate decision-making
Kanerika resolved its data management problems through the following:
- Consolidated and centralized SAP and non-SAP data sources, providing insights for accurate decision-making
- Streamlined integration of financial and HR data, ensuring synchronization enhancing overall business performance
- Automated integration processes to eliminate manual efforts and minimize error risks, saving cost and improving efficiency
Best Practices for Improving Data Accessibility
Getting data into the right hands is important — but making sure it’s usable, safe, and easy to understand is what really makes the difference. Here are some simple yet effective practices to help you do just that.
1. Use Clear, Consistent Naming Conventions
Confusing file names or cryptic column labels just slow everyone down. When data is named clearly, it’s easier to search, share, and trust.
Tips:
- Stick to a standard format (e.g.,
sales_Q1_2025.csv) - Avoid jargon or internal code words
- Use descriptive labels in dashboards and tables
2. Make Data Easy to Find
If your data is buried in folders or hidden behind permissions, people won’t use it. A central data catalog or well-organized dashboard helps teams access what they need without jumping through hoops.
Helpful ideas:
- Use folders or tags by team or use-case
- Add brief descriptions to datasets
- Keep a shared index or catalog
3. Set Role-Based Access Controls
Not everyone needs access to everything. Giving the right access to the right people keeps your data both secure and useful.
Good to keep in mind:
- Set permissions by team, role, or seniority
- Review access levels regularly
- Don’t give full access by default
4. Prioritize Data Quality Checks
Even the most accessible data is useless if it’s messy. Regular checks help catch duplicates, missing values, or out-of-date info before it causes problems.
Simple ways to improve quality:
- Schedule routine audits
- Use validation rules during data entry
- Monitor for anomalies and flag issues
5. Choose User-Friendly Tools
If your tools require advanced training just to run a basic report, most people won’t bother. Choose platforms that let non-technical users explore and analyze data confidently.
Look for tools that offer:
- Drag-and-drop dashboards
- Natural language queries
- Quick export and sharing options
6. Document Your Data
A dataset without context can be more confusing than helpful. Basic documentation helps users understand what they’re looking at and how to use it properly.
Include in your data notes:
- What each field or column means
- Where the data came from
- How often it’s updated
7. Regularly Review Accessibility Gaps
What works today might not work a few months from now. Review feedback and track how people are using your data to keep things running smoothly.
Good habits:
- Collect user feedback
- Track which datasets get the most use
- Revisit your data setup quarterly
8. Encourage a Data-Sharing Culture
Tools and rules are great — but mindset matters too. When teams understand the value of sharing and using data, accessibility improves naturally.
You can help by:
- Recognizing teams that use data well
- Hosting short sessions or demos
- Keeping communication open across departments
Key Data Accessibility Tools and Techniques
1. Open-Source Data Tools
There’s a wealth of open-source data tools available that prioritize accessibility and user-friendliness. These tools cater to various data analysis needs and often come with vibrant user communities offering support and resources. Here are a few examples:
Apache Spark: This powerful open-source framework offers robust functionalities for distributed data processing and big data analytics. Spark boasts an intuitive API and a wide range of libraries for tasks like data manipulation, machine learning, and visualization – all accessible through user-friendly interfaces.
Tableau Public: This free data visualization tool from Tableau allows users to create clear and interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards. Tableau Public prioritizes ease of use with a drag-and-drop interface and intuitive features, making data storytelling accessible to a broad audience.
OpenRefine: This open-source data wrangling tool excels at cleaning and transforming messy data sets. OpenRefine offers a user-friendly interface with features for handling duplicates, correcting inconsistencies, and standardizing data formats – all crucial steps in making data more accessible for analysis.
2. Data Storytelling Techniques
Data storytelling involves presenting complex information in a clear, concise, and engaging narrative. This technique plays a vital role in making data accessible to a wider audience. Here are some key data storytelling techniques:
Start with a clear question or problem: Frame your data analysis around a specific question or challenge that resonates with your audience. This provides context and helps them understand the significance of the data.
Use visuals effectively: Charts, graphs, and infographics can make complex data easier to understand. Choose visuals that are clear, concise, and visually appealing.
Focus on the human element: Connect the data to real-world scenarios and human experiences. Use anecdotes, case studies, or quotes to illustrate how the data impacts people.
Keep it simple: Avoid technical jargon and overwhelming the audience with too much data. Focus on the key insights and takeaways.
By using data storytelling techniques, you can transform dry statistics into a compelling narrative that fosters understanding and engagement with your data.
3. Accessibility Audits and Testing
Regular data accessibility audits and testing are crucial for ensuring your data is usable by everyone. These audits identify potential barriers for users with disabilities or those with limited technical expertise. Here’s what accessibility audits involve:
Evaluating data formats: Assess if data is available in accessible formats like audio descriptions for charts or alternative text for images.
Testing navigation: Ensure users can navigate through data sets and visualizations using a keyboard or screen reader software.
Verifying color contrast: Verify sufficient color contrast exists between text and background to ensure readability for people with visual impairments.
Data Ingestion vs Data Integration: How Are They Different?
Uncover the key differences between data ingestion and data integration, and learn how each plays a vital role in managing your organization’s data pipeline.
Emerging Trends in Data Accessibility
Data accessibility is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches emerging to make information more inclusive and usable for everyone. Here’s a look at some of the hottest trends shaping the data accessibility landscape:
1. Democratization of Data with AI and Automation:
Automated Data Cleaning and Transformation: Manual data cleaning is a time-consuming bottleneck. AI-powered tools can automate repetitive tasks, ensuring data consistency and accessibility for analysis by a wider range of users.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Data Exploration: NLP allows users to interact with data using natural language queries, making it easier for non-technical users to access and understand information.
Automated Data Visualization: AI can generate accessible data visualizations that are clear, concise, and cater to different user needs (e.g., color-blind friendly charts with audio descriptions).
2. Rise of Unstructured Data and Accessibility Solutions
Leveraging Machine Learning (ML) for Unstructured Data: Traditional methods struggle with vast amounts of unstructured data like social media posts or sensor readings. ML can analyze and extract insights from this data, making it accessible for further analysis and decision-making.
Focus on Accessibility in the Internet of Things (IoT): As IoT devices generate ever-increasing data, ensuring accessibility of this data becomes crucial. This includes developing accessible dashboards and interfaces for interacting with sensor data.
3. Accessibility through Emerging Technologies
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) for Data Exploration: AR/VR can create immersive and accessible experiences for data exploration. Imagine manipulating data visualizations in 3D space or using voice commands to navigate complex datasets.
Advanced Assistive Technologies: Advancements in screen readers, text-to-speech software, and haptic feedback technologies improve user experience for people with disabilities when interacting with data.
4. Prioritizing User-Centric Design for Accessibility
Accessibility by Design: Embedding accessibility considerations from the very beginning of data projects, not as an afterthought. This ensures new tools and platforms are inherently accessible to everyone.
Focus on User Experience (UX) for Diverse Audiences: Designing data experiences that cater to different needs and abilities, promoting inclusivity and usability. Involving people with disabilities in the design process is crucial.
5. Evolving Regulations and Standards for Data Accessibility
Global Accessibility Standards: International regulations and standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) are constantly evolving, pushing organizations to prioritize data accessibility.
Focus on Data Privacy and Security: As data accessibility expands, ensuring data privacy and security becomes paramount. Secure and accessible data platforms are essential to build trust with users.
Maximize the Value of Your Data With Innovative Analysis and Management Techniques!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
Tailoring Data Accessibility Solutions for Diverse User Needs and Challenges
1. Business Users
Challenges: Business users often lack technical expertise and find it difficult to navigate complex data systems. They require user-friendly interfaces and tools that enable them to generate reports and insights without needing deep technical knowledge.
Solutions: Implementing self-service BI tools like Tableau or Power BI can help business users create their own reports and dashboards with intuitive drag-and-drop features.
2. Intermediate Users
Challenges: Users with some technical background, such as knowledge of SQL or basic data manipulation in Python, may struggle with integrating data from multiple sources and performing advanced analyses.
Solutions: Providing SQL-based tools and data manipulation libraries can empower these users to perform more complex analyses. Training programs to enhance their skills further can also be beneficial.
3. Data Scientists
Challenges: Data scientists often face challenges related to data quality, integration, and accessibility. They need access to clean, well-structured data and powerful tools for advanced analytics and machine learning.
Solutions: Ensuring a robust data governance framework and using platforms like Jupyter Notebooks or R Studio can help data scientists work efficiently. Providing access to well-maintained data repositories and tools for data cleaning and transformation is also crucial.
4. IT and Data Engineers
Challenges: These users are responsible for maintaining data infrastructure and ensuring data security and compliance. They often struggle with managing data silos, integrating disparate data sources, and ensuring data accessibility without compromising security.
Solutions: Implementing data integration platforms and centralized data repositories can help break down silos. Role-based access controls and regular security audits can balance accessibility with data protection.
5. Executives and Decision-Makers
Challenges: Executives need high-level insights and real-time data to make strategic decisions. They often face challenges in accessing comprehensive, accurate, and timely information without getting bogged down by the technical details.
Solutions: Dashboards that provide real-time analytics and key performance indicators (KPIs) can help executives make informed decisions quickly. Ensuring that these dashboards are integrated with various data sources and provide a unified view of the organization’s performance is essential.
Why AI and Data Analytics Are Critical to Staying Competitive
AI and data analytics empower businesses to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and anticipate market trends, ensuring they maintain a strong competitive edge.
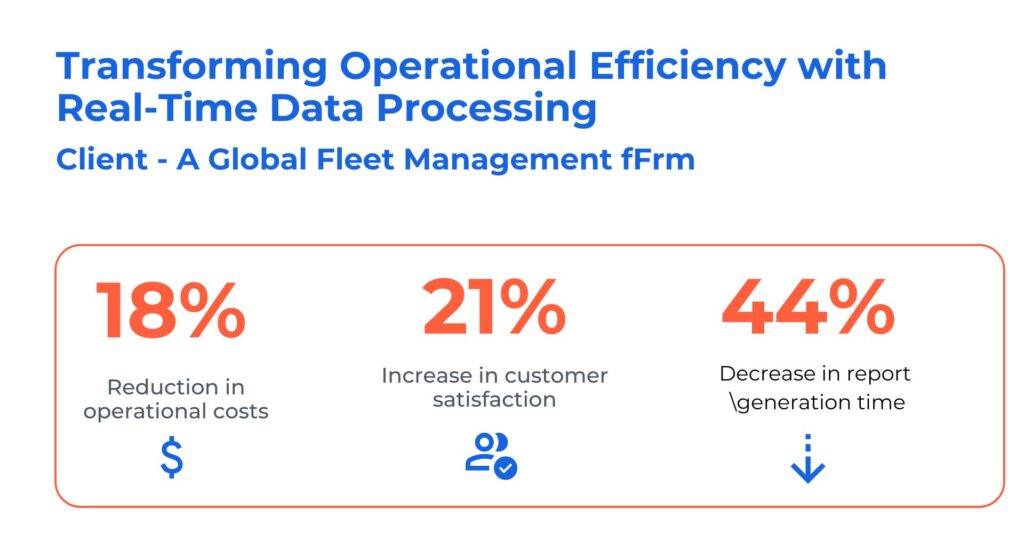
Case Study: Transforming Operational Efficiency with Real-time Data Processing
The client is a leading provider of GPS fleet tracking and management solutions. They faced challenges due to the intricate nature of real-time data integration issues associated with receiving vehicle data from various partners. They sought solutions to bolster their fleet management capabilities and increase operational efficiency.
Kanerika helped them address their problems using advanced tools and technologies like Power BI, Microsoft Azure, and Informatica. Here are the solutions we offered:
- Developed self-service analytics for proactive insights, streamlining operations, and enhancing decision-making
- Built intuitive “Report Builder” for custom KPI reports, boosting adaptability and empowering users with real-time data processing
- Reduced engineering dependency and increased process efficiency with new report-generation capabilities
Simplify Data Access Across Your Organization with Kanerika’s Advanced Solutions
Ensure seamless data accessibility with Kanerika, your expert partner in data management solutions. At Kanerika, we specialize in a comprehensive range of services designed to enhance your organization’s data capabilities. From robust data integration to insightful analytics and stunning visualizations, our advanced solutions ensure that your data is always at your fingertips.
Our data democratization strategies empower every team member, regardless of technical expertise, to access and utilize data effectively. By implementing industry-leading governance practices, we maintain the integrity and security of your data while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Kanerika’s solutions are tailored to meet the unique needs of your business, providing a unified view of your data that drives informed decision-making and fosters a data-driven culture. Whether you need to integrate disparate data sources, create intuitive dashboards, or establish a strong data governance framework, we have the expertise to transform your data management processes.
Choose Kanerika for advanced data accessibility solutions and take the first step towards simplifying data access across your organization, enhancing productivity, and achieving business excellence.
Elevate Your Business Processes with Advanced Data Management Solutions
Partner with Kanerika Today!
FAQs
What is the difference between data availability and data accessibility?
Data availability refers to whether the data exists and is ready to be used, like having a file on your computer. Data accessibility, however, refers to whether you can actually get to and use that data, like having the right permissions and tools to open the file. Think of it like having a locked box – the data is available, but you need the key (accessibility) to get to it.
How to make data accessible?
Making data accessible means ensuring it’s readily available and understandable to anyone who needs it. This involves using clear and consistent formats, providing comprehensive documentation, and using open standards to ensure compatibility across platforms. Accessibility also means considering the needs of diverse users and ensuring they can access the data in ways that are meaningful to them.
What are the two types of data access?
There are two primary ways to access data: sequential access and direct access. Sequential access, like reading a book, requires you to go through each record in order, making it slow for retrieving specific information. Direct access, like using an index in a book, allows you to jump directly to the desired data, providing faster retrieval times.
What is accessibility in data quality?
Accessibility in data quality means ensuring that data is readily available and usable by everyone, regardless of their technical skills or disabilities. It involves making data formats understandable, providing clear and concise descriptions, and using accessible tools and technologies. This allows for wider data utilization and promotes inclusivity in data analysis and decision-making.
What is data availability?
Data availability refers to the accessibility and reliability of data when you need it. It ensures that your data is readily available, even during outages or system failures. Think of it like having a backup plan for your important information, so you’re never left scrambling to recover it.
What is accessibility in data visualization?
Accessibility in data visualization means making charts and graphs understandable and usable by everyone, regardless of their abilities. It involves using clear and concise visual elements, providing alternative text descriptions, and ensuring compatibility with assistive technologies like screen readers. This ensures that everyone can access and interpret the information presented, regardless of visual impairment, cognitive differences, or other limitations.









