What if your manufacturing plant could maintain exceptional quality control and regulatory compliance, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, without human error or fatigue? This can be achieved by integrating Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in manufacturing processes. As quality standards become more stringent and regulatory landscapes more complex, RPA is revolutionizing how manufacturers approach these critical aspects of their operations.
A study by Deloitte found that 53% of organizations have already started their RPA journey. The report further states that RPA continues to surpass expectations in several key areas: enhancing compliance by 92%, improving quality and accuracy by 90%, boosting productivity by 86%, and reducing costs by 59%. The manufacturing sector, in particular, is witnessing a surge in RPA adoption, with the technology proving especially valuable in enhancing quality control and ensuring compliance. But what makes RPA so effective in these areas, and how is it transforming the manufacturing landscape? Let’s find out.
What is the Role of RPA in Modern Manufacturing Processes?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a game-changer in modern manufacturing, revolutionizing processes across the industry. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, RPA is driving unprecedented levels of efficiency and productivity.
At its core, RPA’s role in manufacturing can be broken down into several key areas:
1. Inventory Management
RPA significantly enhances inventory management by automating the monitoring and reporting of stock levels, reducing errors due to manual entry, and ensuring optimal stock levels are maintained. This automation helps in preventing both overstocking and understocking, crucial for maintaining cost efficiency and meeting customer demands promptly.
- Automated alerts for low stock levels
- Real-time inventory tracking and reporting
- Seamless integration with supply chain management systems
2. Quality Control
In the realm of quality control, RPA tools can automate data collection and analysis from various sources, including sensors and manual inspections. This ensures consistent monitoring and adherence to quality standards, improving product reliability and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Automated real-time data collection
- Consistent application of quality standards
- Proactive identification and resolution of quality issues
3. Invoice Processing
RPA simplifies the invoice processing workflow by automating the extraction and verification of data from invoices, matching them with purchase orders, and processing payments. This reduces the cycle time of accounts payable and receivable, enhancing the financial efficiency of the manufacturing processes.
- Automatic extraction and verification of invoice data
- Efficient reconciliation of invoices with purchase orders
- Streamlined payment processing

Read More – RPA Risks For Enterprises And How to Mitigate Them
4. Compliance and Reporting
Manufacturers face a complex web of regulatory requirements. RPA can handle the repetitive tasks of generating compliance documentation and reports, ensuring manufacturers meet industry standards and regulations without manual effort, which is often prone to errors.
- Automated generation of compliance reports
- Accurate data recording and document management
- Efficient resource allocation by reducing manual compliance tasks
Also Read- Grok Vs ChatGPT: Which AI Stands Out for Your Needs?
5. Customer Order Processing
RPA facilitates the automation of the entire order processing cycle, from order entry to final delivery. This results in faster processing times, reduced errors, and improved customer satisfaction by ensuring accurate and timely order fulfillment.
- Automated order entry and processing
- Integration with CRM systems for improved customer service
- Enhanced accuracy in order fulfillment
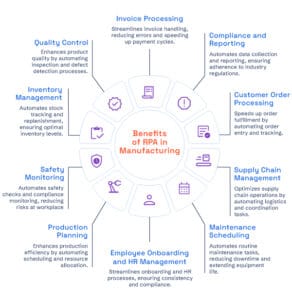
6. Supply Chain Management
RPA plays a critical role in enhancing supply chain operations by automating tasks like shipment tracking, supplier relationship management, and demand forecasting. This automation helps manufacturers optimize their supply chains, reduce lead times, and improve service levels to customers, leading to stronger relationships and increased reliability.
- Automated tracking of shipments and deliveries
- Efficient supplier relationship and contract management
- Enhanced demand forecasting accuracy
Read More – 10 Ways AI and RPA Are Shaping The Future of Automation
7. Maintenance Scheduling
RPA can automate the scheduling and monitoring of maintenance for manufacturing equipment, ensuring machines operate at optimal conditions with minimal downtime. This proactive maintenance approach helps prevent unexpected breakdowns and extends the lifespan of machinery.
- Automated scheduling of preventive maintenance
- Real-time monitoring of equipment performance
- Alerts for potential equipment failures
8. Employee Onboarding and HR Management
RPA streamlines HR processes in manufacturing by automating employee onboarding, payroll processing, and benefits management. This reduces the administrative burden on HR departments and enhances employee experience by ensuring timely and accurate handling of HR tasks.
- Automated onboarding processes for new hires
- Efficient payroll processing and benefits management
- Reduced HR administrative costs
Read More – RPA Use Cases That Will Transform Your Supply Chain Management
9. Production Planning
RPA improves production planning by integrating data across various systems to optimize production schedules based on demand forecasts, inventory levels, and workforce availability. This leads to more efficient production cycles and better resource utilization.
- Automated integration and analysis of production data
- Optimization of production schedules for maximum efficiency
- Enhanced resource allocation and utilization
10. Safety Monitoring
In the manufacturing sector, safety is paramount. RPA can enhance safety protocols by continuously monitoring workplace conditions and compliance with safety standards. This helps prevent accidents and ensures a safer working environment for employees.
- Continuous monitoring of safety conditions
- Automated alerts for safety breaches
- Compliance tracking with safety regulations
Key Technologies Enabling RPA in Manufacturing
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of RPA in manufacturing. AI enables robots to perform tasks that require decision-making, learning, and adaptation. By integrating AI, RPA systems can analyze large datasets, recognize patterns, and make intelligent decisions that mimic human reasoning. This capability allows for more sophisticated automation, extending beyond simple, repetitive tasks to more complex processes that require cognitive abilities.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI helps in predicting equipment failures before they occur, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Quality Control: AI-powered RPA can analyze images and data to detect defects in products, ensuring consistent quality.
- Process Optimization: AI algorithms can identify inefficiencies in manufacturing processes and suggest improvements, leading to optimized operations.
Read More – Navigating The Future Of Healthcare With RPA Consulting
2. Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning (ML) is another key technology that empowers RPA by enabling systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time. In manufacturing, ML algorithms can be used to analyze historical data, identify trends, and make predictions. This self-learning capability allows RPA systems to adapt to new conditions and continuously enhance their effectiveness.
- Demand Forecasting: ML models can predict future product demand based on historical sales data, helping manufacturers optimize inventory levels.
- Anomaly Detection: ML algorithms can identify unusual patterns in production data, flagging potential issues before they escalate.
- Process Improvement: By learning from past data, ML can suggest changes to manufacturing processes that increase efficiency and reduce waste.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables RPA systems to understand and interact with human language. This capability is particularly useful in automating tasks that involve unstructured data, such as emails, documents, and customer interactions. NLP allows RPA bots to interpret, analyze, and respond to text-based inputs, making it possible to automate a wide range of communication and documentation processes in manufacturing.
- Customer Service Automation: NLP-powered chatbots can handle customer inquiries, process orders, and provide support, improving customer satisfaction.
- Document Processing: NLP can extract relevant information from unstructured documents, such as invoices and purchase orders, automating data entry and validation.
- Compliance Reporting: NLP can analyze regulatory texts and ensure that manufacturing processes comply with industry standards, automating the generation of compliance reports.

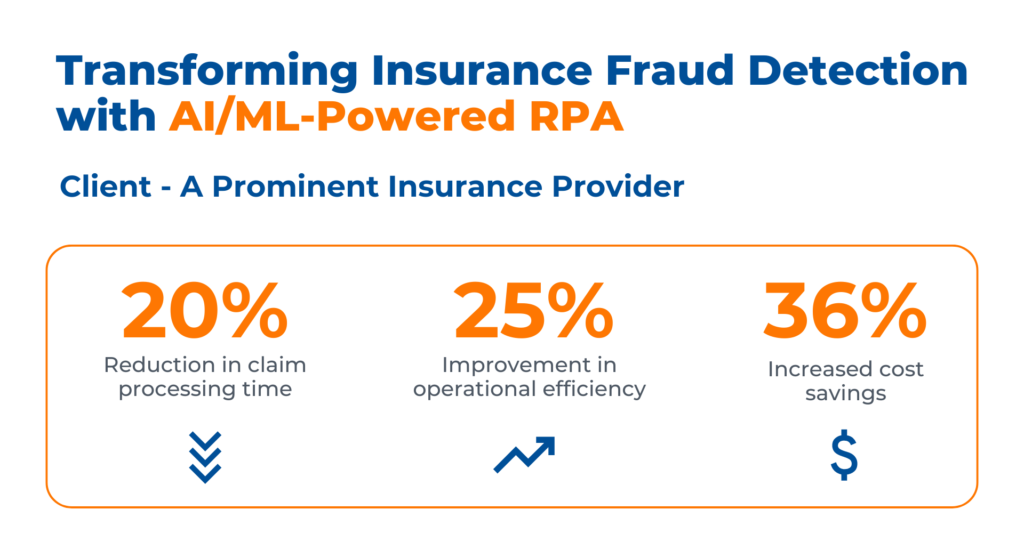
Case Study: Revolutionizing Fraud Detection in Insurance with AI/ML-Powered RPA
Business Context
A leading insurance provider, specializing in healthcare, travel, and accident coverage wanted to automate their insurance claim process solution with AI/ML to spot unusual patterns that are unnoticeable by humans. The overall goal was to use deep anomaly detection to anticipate fraud detection in insurance claims quickly, reduce the loss ratios, and fasten the claim processing.
Kanerika tackled these challenges by:
- Implementing AI RPA for fraud detection in the insurance claim process, reducing fraud-related financial losses.
- Leveraging predictive analytics, AI, NLP, and image recognition to monitor customer behavior, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Delivering AI/ML-driven RPA solutions for fraud assessment and operational excellence, resulting in cost savings.
How RPA in Manufacturing Works
1. Process Identification and Mapping
In manufacturing, RPA implementation begins with identifying repetitive, rule-based processes that are ripe for automation. This involves mapping out existing workflows, documenting steps, and understanding decision points. Processes like data entry, inventory management, and quality control checks are often prime candidates for RPA. By thoroughly analyzing these processes, manufacturers can pinpoint where RPA can make the most significant impact.
2. Bot Development and Programming
Once processes are identified, RPA developers create software bots tailored to these specific tasks. These bots are programmed to mimic human actions, interacting with digital systems just as a human worker would. In manufacturing, this might involve bots that can read and input data from production logs, generate reports, or even control certain machinery. The goal is to create bots that can perform tasks accurately and efficiently, 24/7.
3. System Integration
RPA bots in manufacturing need to integrate seamlessly with existing systems, from Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software to Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). This integration allows bots to access necessary data, update records, and trigger actions across multiple platforms. It’s crucial that this integration is robust and secure, ensuring that bots can operate effectively without compromising system integrity or data security.
4. Deployment and Monitoring
Once developed and integrated, RPA bots are deployed into the manufacturing environment. Initially, they often run alongside human workers to ensure smooth operation. Continuous monitoring is essential to track bot performance, identify any issues, and measure the impact on efficiency and quality. This monitoring allows for ongoing optimization, ensuring that the RPA solution continues to meet the evolving needs of the manufacturing process.
5. Error Handling and Exception Management
In manufacturing, where precision is critical, RPA systems must be equipped to handle errors and exceptions. Bots are programmed with predefined rules for common exceptions, allowing them to make decisions or escalate issues to human supervisors when necessary. This capability ensures that production doesn’t grind to a halt due to unexpected scenarios, maintaining the smooth flow of operations.
6. Data Collection and Analysis
One of the key strengths of RPA in manufacturing is its ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of data. Bots can continuously gather data from various sources, compile it into meaningful reports, and even perform basic analysis. This real-time data collection and analysis capability enables manufacturers to make more informed decisions, predict maintenance needs, and identify areas for process improvement.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
As manufacturing needs evolve, RPA systems can be scaled up or modified to meet new requirements. This might involve deploying more bots, expanding their capabilities, or reprogramming them for new tasks. The flexibility of RPA allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to changes in production demands, new product lines, or shifting market conditions, ensuring that automation continues to drive efficiency and competitiveness.

Case Study: Transforming Recruitment with Process Automation by RPA in HR
Business Context
The client is a distinguished service provider renowned for their unwavering commitment to timely delivery. They faced HR challenges due to the manual hiring process which had become burdensome, causing delays and inefficiencies and placing an excessive workload on the HR team.
Kanerika addressed these challenges by providing the following solutions:
- Implemented end-to-end process automation using UiPath, streamlining candidate screening and enhancing efficiency
- Deployed HR Bot to receive, filter, and consolidate resumes from various portals, improving candidate management
- Ensured accurate candidate evaluation, correct routing, and efficient candidate handling, enhancing the quality of hires with RPA services

Implementing RPA in Manufacturing
1. Assessing Automation Potential
Assessing automation potential is the crucial first step in implementing RPA in manufacturing. This process involves a thorough analysis of existing workflows to identify repetitive, rule-based tasks that are prime candidates for automation.
Key considerations include:
- Process complexity and frequency
- Current error rates and inefficiencies
- Potential ROI of automation
- Impact on existing workforce and systems
2. Choosing the Right RPA Tools and Platforms
Selecting the appropriate RPA tools and platforms is vital for successful implementation. The choice depends on the specific needs of the manufacturing process, existing IT infrastructure, and long-term automation goals.
Important factors to consider:
- Scalability and flexibility of the platform
- Ease of integration with existing systems
- Vendor support and community resources
- Total cost of ownership, including licensing and maintenance

3. Developing a Pilot Project
A pilot project serves as a proof of concept and helps identify potential challenges before full-scale implementation. It allows manufacturers to test the RPA solution in a controlled environment and gather valuable insights.
Key steps in developing a pilot:
- Select a process with high potential for immediate impact
- Set clear objectives and success metrics
- Involve key stakeholders from IT, operations, and management
- Document learnings and adjust the approach as needed

4. Scaling RPA Across the Organization
Once the pilot project proves successful, the next step is scaling RPA across the organization. This phase involves expanding automation to other processes and departments, requiring careful planning and execution.
Considerations for scaling include:
- Prioritizing processes for automation based on potential impact
- Ensuring IT infrastructure can support expanded RPA deployment
- Establishing governance structures for managing automated processes
- Continuously monitoring and optimizing RPA performance
5. Training and Change Management
Effective training and change management are critical for successful RPA implementation. This involves preparing the workforce for the changes brought by automation and ensuring they have the skills to work alongside RPA systems.
Key aspects of training and change management:
- Communicating the benefits of RPA to all employees
- Providing comprehensive training on working with RPA systems
- Addressing concerns about job security and role changes
- Fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation

Real-world Applications: How Top Manufacturing Companies Are Leveraging RPA

1. Siemens
Siemens implemented RPA in its gas turbine manufacturing process. They used RPA bots to automate the creation of technical documents, a process that previously took engineers several hours per turbine. The bots now complete this task in minutes, significantly reducing production time and allowing engineers to focus on more complex tasks.
2. Boeing
Boeing utilized RPA to streamline its supply chain management. They implemented bots to automate the process of tracking and managing thousands of parts from various suppliers. This automation improved inventory accuracy, reduced delays, and enhanced overall supply chain efficiency in their aircraft manufacturing operations.
3. Volkswagen
Volkswagen employed RPA in its financial operations related to manufacturing. They automated the process of comparing invoices with goods received notes, a task that was previously manual and time-consuming. This implementation reduced processing time by 65% and improved accuracy in their financial reconciliations.
4. Whirlpool
Whirlpool incorporated RPA into its quality control processes. They deployed bots to analyze data from IoT sensors on their production lines, automatically identifying potential quality issues. This real-time monitoring and analysis allowed for quicker response to production anomalies, reducing defects and improving overall product quality.
5. Procter & Gamble
P&G implemented RPA in its order management system. The company used bots to automate the process of receiving and processing orders from retailers, integrating this information with their production planning systems. This automation reduced order processing time and improved the accuracy of production forecasts.

6. General Electric
GE utilized RPA in its maintenance operations. They implemented bots to analyze equipment sensor data and automatically generate maintenance work orders when potential issues were detected. This predictive maintenance approach reduced unplanned downtime and extended the life of manufacturing equipment.
7. Ford Motor Company
Ford deployed RPA in its human resources department to support manufacturing operations. They automated the process of collecting and analyzing employee time and attendance data, which is crucial for production planning. This implementation improved workforce management efficiency and accuracy in payroll processing.
8. Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola implemented RPA in its inventory management system. They used bots to automate the process of monitoring stock levels across multiple warehouses and triggering reorder requests when inventory fell below certain thresholds. This automation improved inventory accuracy and reduced instances of stockouts or overstock situations.
9. Sysco
As the world’s largest food distributor, Sysco expanded its automation efforts in response to disruptions caused by the pandemic. By deploying more than 60 digital workers, Sysco was able to process 6.2 million transactions, thereby recuperating over 250,000 work hours, which significantly enhanced their customer service capabilities during critical times.
10. AGCO
A global manufacturer of agricultural equipment, AGCO has implemented RPA to manage and optimize its ERP operations, specifically in journaling tasks within their SAP systems. This automation has helped reduce overtime costs and improve accuracy in their financial operations.
Kanerika: Bridging the Gap Between Traditional Manufacturing and Industry 4.0 with RPA
At Kanerika, we excel in providing cutting-edge automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solutions tailored to elevate productivity and efficiency in manufacturing operations. Leveraging our deep expertise and industry knowledge, we implement sophisticated RPA systems that automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, thereby significantly reducing operational costs and enhancing process accuracy.
Our RPA solutions integrate advanced technologies such as AI, ML, and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to ensure seamless automation across various manufacturing processes. From predictive maintenance and quality control to inventory management and customer service, our RPA bots are designed to optimize every facet of your manufacturing operations.
By partnering with Kanerika, you benefit from our proven track record in deploying RPA systems that not only streamline your operations but also provide actionable insights through data analytics. This allows for proactive decision-making and continuous improvement in your manufacturing processes.
Our customized RPA implementations ensure that your specific business needs are met, driving substantial improvements in efficiency and productivity. Let Kanerika transform your manufacturing operations with our expert RPA solutions, enabling you to stay competitive in an increasingly automated industry.
Experience the future of manufacturing with Kanerika’s unparalleled automation expertise.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three types of RPA?
RPA isn’t neatly divided into just three types, but we can categorize it based on capabilities. There’s attended RPA, which needs human interaction; unattended RPA, running autonomously; and hybrid RPA, a blend of both, offering flexibility. These distinctions highlight the level of human involvement and automation sophistication. Essentially, the choice depends on the task’s complexity and required human oversight.
What is automation in manufacturing?
Manufacturing automation uses technology to replace or assist human workers in production processes. It streamlines operations, boosting efficiency and consistency by automating tasks like assembly, welding, or packaging. This results in lower costs, increased output, and improved product quality. Ultimately, it’s about optimizing the entire manufacturing workflow for speed and precision.
What is RPA in IT industry?
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, is essentially software robots automating repetitive, rule-based tasks in IT (and other industries). Think of it as virtual assistants handling things like data entry or report generation, freeing up human employees for more complex work. It boosts efficiency and accuracy by eliminating human error in these routine processes. Ultimately, RPA streamlines operations and reduces costs.
What are 10 amazing examples of robotic process automation in practice?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) handles repetitive digital tasks, freeing humans for more creative work. Think invoice processing, data entry, and customer service chatbots – all automated for speed and accuracy. More advanced uses include claims processing in insurance, and even robotic surgery, showcasing RPA’s versatility across industries. Essentially, RPA automates the mundane digital aspects of many jobs.
What are the three main RPA tools?
There isn’t a definitive “top three” RPA tools as the best choice depends on your specific needs. However, UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism are frequently cited as leading platforms due to their robust features and market share. Each offers different strengths in areas like scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities. Ultimately, the ideal tool will vary based on your organization’s size and automation goals.
What are the 4 types of automation?
Automation isn’t just one thing; it’s a spectrum. We broadly categorize it into process automation (streamlining tasks), robotic process automation (software bots doing repetitive digital work), machine learning automation (systems learning and adapting without explicit programming), and finally, human-in-the-loop automation (combining human intelligence with automated systems for complex decisions). Each offers a different level of intelligence and application.
What are the three examples of RPA automation?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) handles repetitive digital tasks. Think of it automating things like data entry from invoices (extracting key info and populating databases), automatically processing insurance claims based on predefined rules, or managing customer emails by routing them to the correct departments and even drafting basic replies. Essentially, RPA replaces tedious human clicks and keystrokes with software bots.
What are three benefits of RPA?
RPA streamlines repetitive tasks, freeing up human employees for more strategic work. It significantly improves accuracy by eliminating human error in mundane processes. This leads to faster processing times and increased overall efficiency, boosting productivity and potentially lowering operational costs.
How many types of robotics are there?
There’s no single definitive number of robotics types; it depends on how you categorize them. We can broadly group them by application (e.g., industrial, medical, military), functionality (e.g., mobile, collaborative, fixed), or the underlying technology (e.g., AI-powered, hydraulic). Essentially, the “types” are numerous and constantly evolving as technology advances.
What is RPA in manufacturing?
RPA in manufacturing refers to the use of robotic process automation to streamline quality control and compliance processes, such as data extraction and workflow automation, to improve production efficiency and reduce errors, ultimately enhancing overall product quality and regulatory adherence in industries like automotive and pharmaceuticals.
What does RPA mean in manufacturing?
In manufacturing, RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation, which involves using software robots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks, such as data entry and document processing, to enhance quality control, compliance, and operational efficiency, ultimately improving product quality and reducing production costs.
What are three types of RPA?
Three types of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are attended automation, unattended automation, and hybrid automation, which can be applied to manufacturing processes to enhance quality control and compliance by streamlining data extraction, workflow management, and regulatory reporting, ultimately improving operational efficiency and reducing errors.
What are the 6 types of manufacturing processes?
In manufacturing, six key processes exist: discrete, process, repetitive, job shop, batch, and continuous. These processes impact quality control and compliance, with discrete manufacturing focusing on distinct products, while process manufacturing involves continuous production of goods like chemicals or food. Understanding these processes is crucial for implementing effective RPA solutions to enhance quality and compliance in manufacturing operations.
What are the 4 types of industrial automation?
In manufacturing, industrial automation is categorized into four types: fixed automation, programmable automation, flexible automation, and integrated automation. These types enable manufacturers to streamline quality control processes, improve compliance, and increase productivity in areas like robotic process automation and machine learning, ultimately enhancing overall operational efficiency and reducing costs.
What are the 4 stages of process automation?
The four stages of process automation in manufacturing involve assessment, design, implementation, and monitoring. By automating quality control and compliance processes, manufacturers can improve product consistency, reduce errors, and increase efficiency, ultimately enhancing overall operational performance and reducing costs. This leads to better regulatory compliance and improved customer satisfaction.
What are the 5 types of industrial robots?
In manufacturing, five types of industrial robots enhance quality control and compliance: cartesian, cylindrical, polar, delta, and scara robots. These robots improve production efficiency, reduce errors, and increase precision, ultimately leading to better product quality and regulatory compliance in industries like automotive and pharmaceuticals.
What are the 4 D's of automation?
The 4 D’s of automation in manufacturing are Dematerialization, Demobilization, Densification, and Decentralization, which enable companies to streamline quality control and compliance processes, reducing errors and increasing efficiency in production lines, ultimately improving overall product quality and regulatory adherence.
What is L1, L2, and L3 in automation?
In automation, L1, L2, and L3 refer to levels of automation support. L1 is basic automation, L2 involves guided automation with human oversight, and L3 is advanced automation with minimal human intervention, often used in manufacturing quality control and compliance to improve efficiency and reduce errors.
Who are the big 4 in the industrial robotics industry?
The big 4 in the industrial robotics industry are ABB, KUKA, Fanuc, and Yaskawa, leading manufacturers of robotic automation systems that enhance quality control and compliance in manufacturing processes, particularly in robotic process automation and machine learning applications.
What skills are needed for RPA?
To implement RPA in manufacturing, professionals need programming skills in languages like Visual Basic or Java, as well as experience with automation tools and software. Knowledge of manufacturing processes and quality control procedures is also essential, allowing for effective automation of tasks and compliance with regulatory requirements, ultimately improving product quality and reducing production costs.
What robot is most commonly used in manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the most commonly used robot is the articulated robot, which enhances quality control and compliance by performing tasks such as welding, assembly, and inspection with high precision and accuracy, improving production efficiency and reducing defects, thus increasing overall product quality and regulatory adherence.
How much does RPA cost?
The cost of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in manufacturing varies depending on the scope and complexity of the implementation, with prices ranging from $5,000 to $50,000 or more per automation process, offering significant returns on investment through improved quality control, reduced labor costs, and enhanced compliance management.
How is automation used in manufacturing?
Automation in manufacturing involves using software robots to streamline processes, improving production efficiency and reducing errors. By implementing robotic process automation, manufacturers can enhance quality control, ensure compliance with regulations, and optimize supply chain management, resulting in increased productivity and cost savings. This technology helps manufacturers to improve product quality and meet customer demands more effectively.









