As data privacy regulations like GDPR and India’s DPDP Act become more stringent, companies are rethinking how they manage and protect data. In 2023, Microsoft revamped its global data governance framework to improve compliance, reliability, and decision-making—demonstrating how strong governance principles translate to measurable outcomes. According to Gartner, 80% of organizations with formal data governance see improved data usability and trust.
In this blog, we’ll explore the core principles of data governance—from accountability to access control—and how they help organizations ensure data is accurate, compliant, and secure across every function.
What are Data Governance Principles?
Data governance principles are the core guidelines that help organizations manage their data effectively and responsibly. They determine how data is collected, stored, and secured and how it is used to maintain data accuracy, consistency, and integrity across the organization.
Here are some fundamental principles:
- Accountability – Assigning clear ownership and responsibility for data assets
- Integrity – Maintaining data consistency and accuracy throughout its lifecycle.
- Compliance – Keeping pace with the law, regulations and internal rules
- Security – Protecting data from unauthorized access and use.
These values are fundamental to the Company’s success. With well-governed data, teams can make better decisions more confidently, mitigate operational risk, enhance compliance, and realize further value from their data assets.
With organizations in all sectors looking to depend on data more, the need for an organized governance framework has never been greater. Without that, companies will be liable for a lack of consistency, efficiency, and oversight. Good data governance allows clarity and effective control to handle the volume and complexity of data we face today.
Key Data Governance Principles: A Comprehensive Breakdown
1. Data Ownership and Accountability
- Understanding Data Ownership
Data ownership establishes clear responsibility for specific data assets within an organization. Moreover, owners have authority over how their data is collected, stored, processed, and shared. Additionally, effective ownership models designate both business and technical owners for each data domain.
- Implementing Accountability Frameworks
Accountability creates mechanisms to ensure data responsibilities are fulfilled consistently. Organizations should document ownership in formal matrices that specify who is responsible for what data. Regular ownership reviews ensure accountability remains relevant as organizational structures evolve.
- Business Benefits of Clear Ownership
When data responsibilities are clearly defined, decision-making bottlenecks are reduced. Issues are resolved faster because stakeholders know exactly who to approach for data-related concerns. This clarity also leads to improved strategic alignment between data management and overall business objectives.
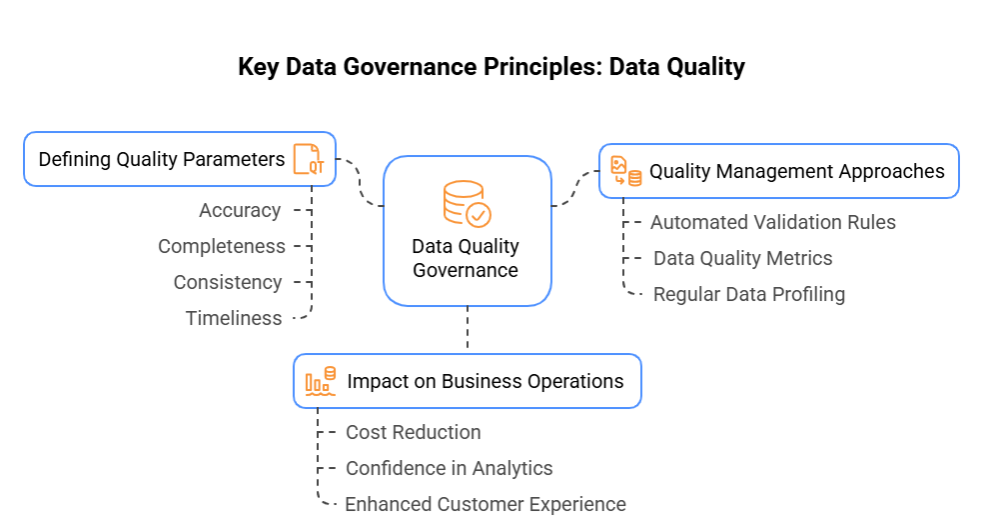
2. Data Quality
Defining Quality Parameters
- Accuracy: Data correctly represents the real-world values it aims to capture.
- Completeness: All required data elements are present and populated.
- Consistency: Data maintains uniformity across different systems and applications.
- Timeliness: Data is sufficiently current to support its intended use.
Quality Management Approaches
Implement automated validation rules to catch errors at the point of data entry. Establish data quality metrics with clear thresholds for acceptable quality levels. Conduct regular data profiling to identify quality issues before they impact business processes.
Impact of Quality on Business Operations
According to Gartner research, poor quality data costs organizations an average of $12.9 million annually. In contrast, high-quality data increases confidence in analytics and reporting outcomes. It also leads to an enhanced customer experience by ensuring accurate and consistent customer data across all touchpoints.
3. Data Security and Privacy
- Essential Security Measures: Implement role-based access controls to restrict data access based on job functions. Employ data encryption for sensitive information both in transit and at rest. Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments of data storage systems.
- Privacy Compliance Requirements: Design data collection practices with “privacy by design” principles to meet regulatory requirements. Maintain comprehensive data inventories that identify where personal information resides. Implement processes for honoring data subject rights such as access and deletion requests.
- Balancing Security and Usability: Security measures should protect data without creating undue barriers to legitimate business use. Regular security awareness training helps employees understand their role in data protection. Incident response plans should be established for addressing potential data breaches.
4. Data Accessibility and Availability
- Breaking Down Data Silos
Implement technical solutions that enable appropriate cross-departmental data sharing. Establish clear protocols for requesting access to data resources. Create centralized data catalogs that help users discover available data assets.
- Ensuring Appropriate Access
Access requirements should be defined based on legitimate business needs rather than organizational hierarchy. Time-limited access provisions must be implemented for temporary projects or specific requirements. It is also important to regularly audit access permissions to identify and remove any unnecessary access rights.
- Maximizing Data Value Through Accessibility
Greater data accessibility leads to more comprehensive business insights. Cross-functional data sharing enables new perspectives and innovative problem-solving. Reduced duplication of data collection efforts saves time and resources.
Strengthen Data Governance and Compliance with Microsoft Purview!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Purview implementation Services
5. Data Integrity
- Preserving Data Reliability involves implementing system controls that prevent unauthorized modification of critical data. This includes using checksums, digital signatures, and other technical mechanisms to verify that data hasn’t been altered. Additionally, maintaining comprehensive audit trails that record who accessed and modified data is essential.
- Validation and Error Prevention are achieved by designing input forms with validation rules that catch errors before they enter systems. Implementing referential integrity constraints in databases helps maintain relationships between data elements. Furthermore, creating automated reconciliation processes enables the identification of discrepancies between related systems.
- Building Trust Through Integrity is critical, as consistent data integrity builds confidence in reporting and analytics outputs. Reliable data reduces the time spent verifying information before making decisions. Moreover, strong integrity controls reduce the risk of financial or regulatory compliance issues.
6. Data Stewardship
- Role of Data Stewards
Data stewards serve as the operational champions of governance policies and standards. They act as bridges between IT departments and business units, translating technical requirements into business terms. Effective stewards combine domain expertise with an understanding of data management principles.
- Distributed Stewardship Model
Assign stewardship responsibilities across departments rather than centralizing them. Create stewardship communities of practice to share knowledge and address cross-functional challenges. Clearly document stewardship roles and responsibilities in formal job descriptions.
- Measuring Stewardship Effectiveness
Track resolution times for data-related issues as an indicator of stewardship performance. Monitor adoption of data standards across the organization. Measure improvements in data quality metrics over time as evidence of effective stewardship.
7. Data Lifecycle Management
Lifecycle Stages
- Creation/Acquisition: Establishing controls for how data enters the organization.
- Storage: Determining appropriate locations and formats for data retention.
- Usage: Defining how data can be utilized and by whom.
- Archiving: Moving inactive data to cost-effective storage while maintaining accessibility.
- Disposal: Securely removing data that no longer serves business or compliance purposes.
Effective Retention Policies
Define retention requirements based on business needs, regulatory obligations, and risk assessments. Clearly specify retention periods for different data types and categories. Moreover, implement automated archiving and disposal processes to ensure consistent policy enforcement.
Cost and Risk Optimization
Regular cleanup of unused data reduces storage costs and simplifies system maintenance. Also, proper archiving improves system performance while maintaining data for compliance purposes. Documented disposal procedures reduce the risk of retaining sensitive data beyond its useful life.
Top 10 Data Governance Tools for Elevating Compliance and Security
Discover the leading data governance solutions that streamline compliance management and enhance data security across enterprise environments.
8. Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
- Navigating Complex Regulations: Map regulatory requirements to specific data elements and processing activities. Maintain a comprehensive inventory of applicable regulations by geography and data type. Correspondingly, implement controls that address multiple regulatory requirements simultaneously when possible.
- Documentation and Evidence: Maintain detailed records of compliance activities and control implementations. Additionally, create clear audit trails that demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements. Document the rationale behind policy decisions to demonstrate due diligence.
- Adapting to Regulatory Changes: Establish processes for monitoring evolving regulatory landscapes. Build flexibility into governance frameworks to accommodate new requirements. Also, conduct regular compliance assessments to identify and address potential gaps.
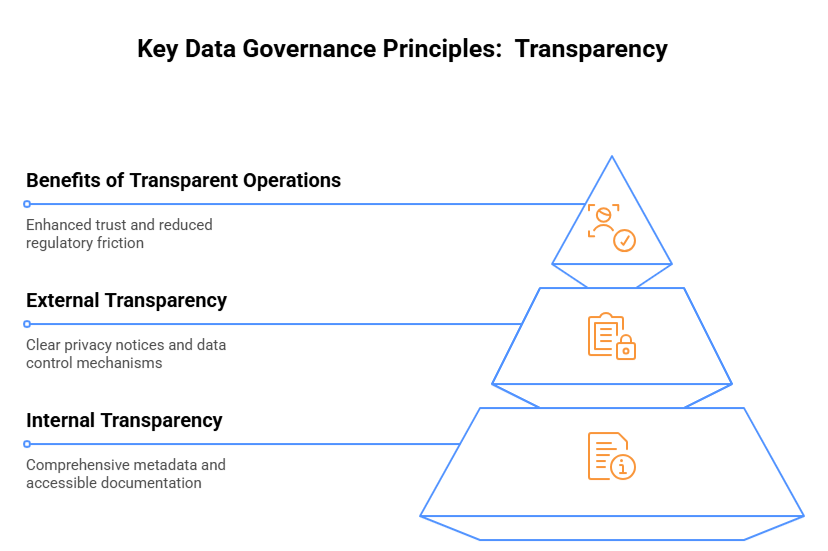
9. Transparency
- Internal Transparency Practices
Maintain comprehensive metadata that describes data origins, transformations, and usage. Create accessible documentation of governance policies and procedures. Also, provide clear visibility into decision-making processes for data-related initiatives.
- External Transparency Considerations
Develop clear, accessible privacy notices that explain data collection and usage in plain language. Additionally, provide mechanisms for customers to understand and control how their data is used. Thus, be forthcoming about data practices beyond minimum regulatory requirements.
- Benefits of Transparent Operations
Enhanced trust from customers and partners regarding data handling practices. Improved employee understanding and adoption of governance principles. Reduced friction in regulatory audits due to readily available documentation and justifications.
10. Continuous Improvement
- Regular Assessment Processes: Conduct periodic maturity assessments of governance capabilities against industry benchmarks. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure governance effectiveness. Gather feedback from stakeholders across the organization to identify improvement opportunities.
- Adaptation Strategies: Review and update policies at least annually to reflect changing business and technical environments. Create formal processes for evaluating and incorporating emerging best practices. Establish governance steering committees to oversee strategic improvements to the program.
- Building a Learning Organization: Share lessons learned from data-related incidents to prevent recurrence. Recognize and reward behaviors that align with governance principles. Invest in ongoing education to elevate data literacy throughout the organization.
Challenges in Implementing Data Governance Principles
1. Resistance to Change
Organizations encounter pushback when implementing frameworks that alter established workflows. Moreover, employees often view governance as bureaucratic rather than valuable. Departments resist surrendering control over “their” data.
2. Lack of Expertise
The field suffers from a shortage of professionals with appropriate expertise. Organizations struggle to define specific skills needed for governance roles.
3. Cost and Resource Allocation
Quantifying ROI is difficult as benefits are often preventative rather than revenue-generating. Governance initiatives frequently compete with more visible projects for resources.
4. Data Silos
Legacy systems with proprietary data structures create barriers to consistent governance. Departmentally isolated data creates redundancy and inconsistency.
5. Maintaining Compliance in a Changing Environment
Evolving regulations require constant vigilance and program adaptation. Moreover, new technologies introduce unforeseen governance challenges. Global operations face complex navigating conflicting regulatory requirements.
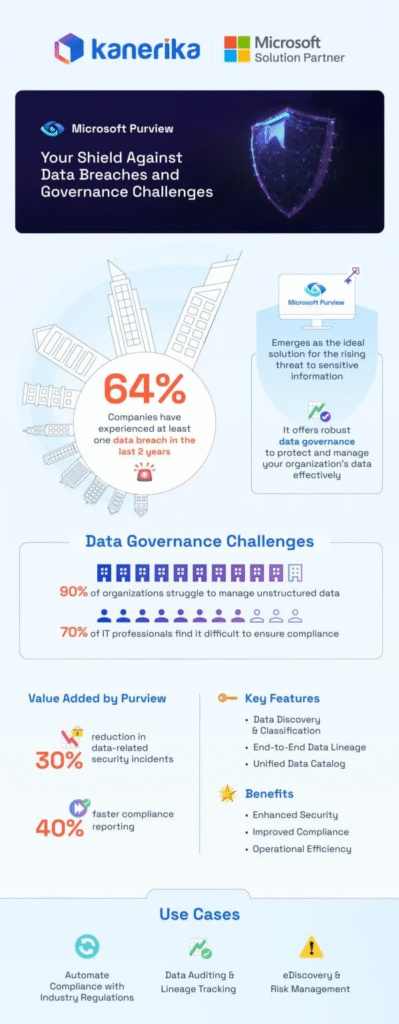
Microsoft Purview Information Protection: What You Need to Know
Explore how Microsoft Purview Information Protection safeguards your data with advanced classification, labeling, and compliance tools, ensuring secure and seamless data management.
![]() Learn More
Learn More
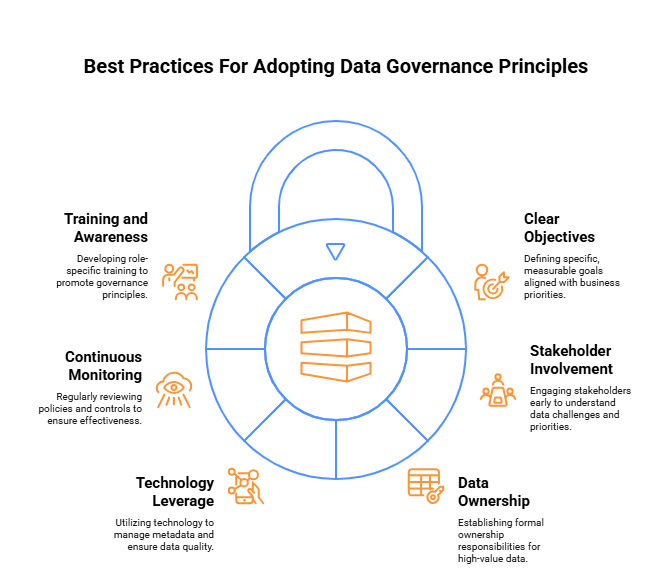
Best Practices for Adopting Data Governance Principles
1. Start with Clear Objectives
- Define specific, measurable goals aligned with business priorities.
- Identify critical data domains that will deliver the highest initial value.
- Create a roadmap with realistic milestones to track governance maturity progress.
2. Involve Stakeholders Early
- Establish a cross-functional steering committee with representation from IT, legal, and business units.
- Conduct stakeholder interviews to understand data challenges and priorities.
- Share governance benefits in terms meaningful to each stakeholder group.
3. Focus on Data Ownership
- Formally document ownership responsibilities in accessible matrices.
- Start with high-value, high-risk data to establish ownership patterns.
- Create escalation paths for resolving data issues across ownership boundaries.
4. Leverage Technology
- Implement metadata management tools to create a single source of truth.
- Utilize automated data quality monitoring to identify issues proactively.
- Deploy access management solutions that enforce governance policies.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Auditing
- Establish key performance indicators to measure governance effectiveness.
- Schedule regular reviews of policies and controls.
- Document and address compliance gaps promptly.
6. Training and Awareness
- Develop role-specific training that connects governance to daily work.
- Create easily accessible governance resources and guidelines.
- Recognize and reward behaviors that align with governance principles.
Case studies: How Kanerika Empowers Clients with Robust Data Governance Solutions
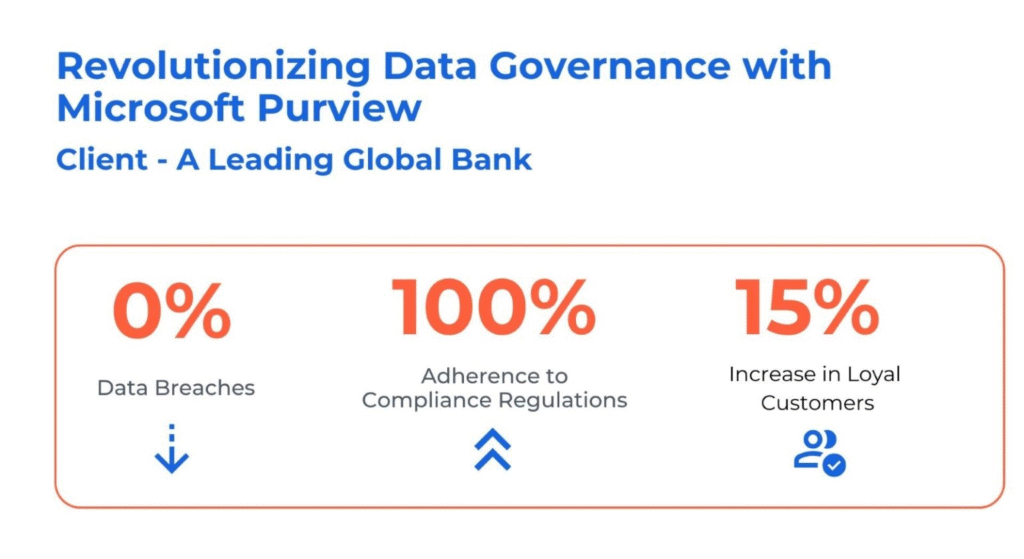
Revolutionizing Data Governance for a Leading Bank with Microsoft Purview
The client, a global banking institution with nearly 9000 branches and 22000 ATMs worldwide, faced significant challenges in managing its distributed data environment. This included data silos, operational inefficiencies, and the complexities of adhering to stringent regulatory conditions such as privacy laws. These challenges were further exacerbated by the manual and labor-intensive processes of identifying and classifying sensitive data, increasing the risk of compliance breaches.
Kanerika addressed these challenges by:
- Implementing a data discovery process using Purview’s Data Map to automatically identify and classify data assets, providing a comprehensive view of data sources and transformations.
- Enhancing data governance with Purview’s Policies, ensuring the proper classification and handling of personal data (PII, PCI, PHI), thus improving visibility and auditability.
- Automating data lineage and streamlining the flow from sources through different layers in the Lakehouse, enhancing transparency and compliance.
- Establishing data sharing rules to safeguard sensitive information and ensuring proper access to authorized stakeholders, preventing unauthorized access and data mishandling.
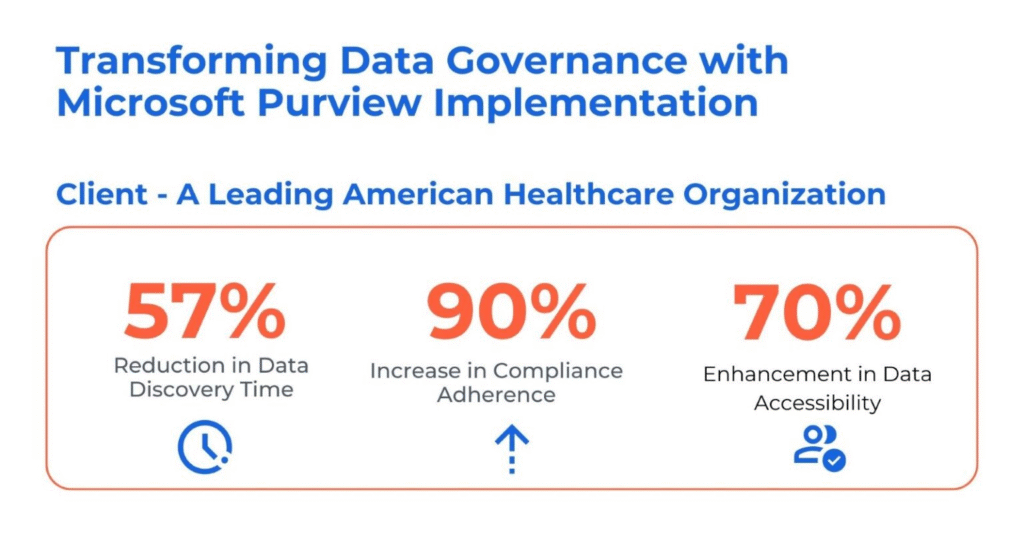
Transforming Data Governance with Microsoft Purview Implementation
The client, a leading North American healthcare organization, was facing significant data governance challenges within their complex healthcare ecosystem. Their data was dispersed across various platforms including Azure Blob Storage, SQL databases, and SaaS applications, making efficient data discovery and management difficult.
Kanerika addressed these challenges by:
- Implementing Microsoft Purview to create a centralized data catalog, enhancing data discovery and management.
- Designing a data classification framework to ensure consistent data handling and improve data quality.
- Integrating Power BI dashboards for better business insights and ongoing data governance.
- By addressing data governance issues, Kanerika helped the client improve data accuracy, streamline reporting, enhance compliance, and foster better stakeholder engagement.
Transform Your Data Governance Journey with Kanerika
As the constant data breaches and growing regulatory demands have been increased, effective data governance isn’t optional—it’s essential. At Kanerika, we make Microsoft Purview work for you, not the other way around.
We’ve seen how frustrated companies get when data governance feels like an obstacle rather than an asset. That’s why our approach focuses on making governance practical and valuable for your business. We don’t just implement technology; we transform how you manage, protect, and leverage your data.
As certified Data and AI Solutions Partner, we customize Purview to fit your unique needs. Our team works alongside yours, showing you how to classify sensitive information, monitor access, and enforce policies that matter to your organization.
We bring firsthand experience in navigating the complexities of data management across diverse systems. Our solutions are grounded in practical application, ensuring they are not only effective but also aligned with real-world business needs.
With Kanerika handling your Purview implementation, you’ll finally achieve what seemed impossible: data governance that protects your business while actually making everyone’s job easier. Because good governance shouldn’t be a headache—it should be your competitive advantage.
Strengthen Data Governance and Compliance with Microsoft Purview!
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Purview implementation Services
Frequently Asked Questions
[faq-schema id=”92001″]









