Have you ever wondered why some companies move to the cloud and suddenly run faster, scale smoothly, and save money, while others struggle to see any real benefit? The answer often comes down to choosing the right cloud delivery model. Each model shapes how your data lives, how your apps run, and how easily your team can build or upgrade services.
Recent industry reports show how big this shift has become. The global cloud computing market is expected to exceed $947 billion by 2026, driven mainly by hybrid and multi-cloud deployments. Surveys also show that nearly 70% of enterprises now use a mix of public and private cloud because it gives them better control, stronger security, and smoother scaling for critical workloads.
In this blog, you will learn what each cloud delivery model offers, how they differ, and how to pick the one that supports your long-term business plans.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud delivery models define what services you get from the cloud, while deployment models define where they run.
- IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS offer different levels of control, flexibility, and management responsibilities.
- SaaS is best for ready-to-use software, PaaS for rapid development, and IaaS for full infrastructure control.
- Leading cloud providers include AWS, Azure, GCP, Oracle Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Salesforce.
- Common challenges include security concerns, vendor lock-in, compliance needs, skill gaps, and rising cloud costs.
- Real-world examples show how global companies use SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS to scale, improve performance, and drive innovation.
- Choosing the right model depends on business needs, cost structure, compliance requirements, and long-term growth plans.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud are becoming popular choices for flexibility and workload optimization.
Build Scalable Cloud Solutions Today!
Partner with Kanerika to build scalable and secure cloud solutions.
What Are Cloud Delivery Models?
Cloud delivery models describe how cloud services are delivered to users, focusing on the layers of services provided by the cloud provider. They define what you get from the cloud, whether it’s raw infrastructure, a development platform, or fully managed software.
These delivery models differ from cloud deployment models, which describe where the cloud is hosted (public, private, hybrid, multi-cloud). Delivery models focus on what is delivered, while deployment models focus on where it runs.
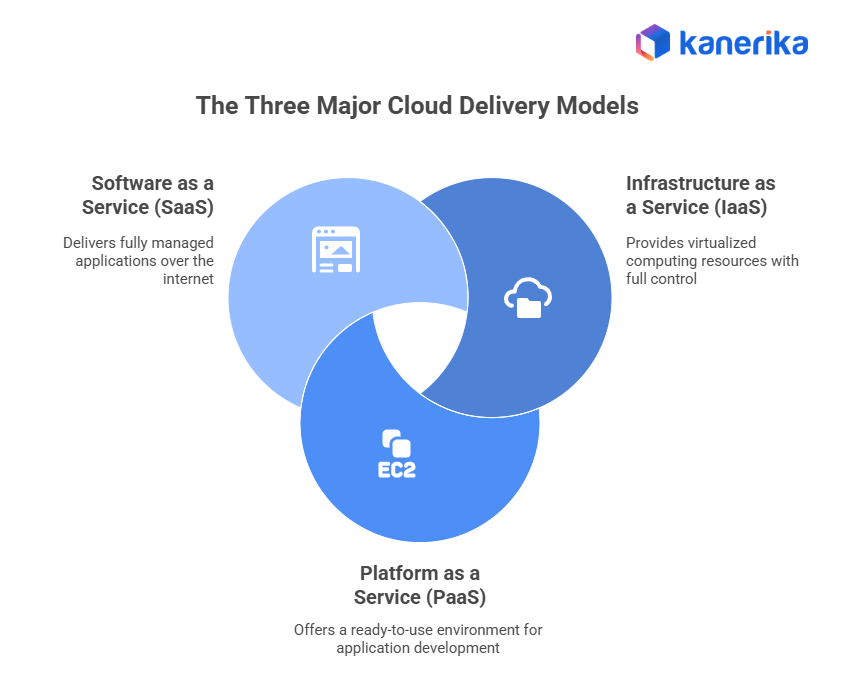
The Three Major Cloud Delivery Models
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources through the cloud, allowing businesses to provision servers, configure operating systems, install applications, and scale resources whenever needed. It includes core building blocks such as compute via virtual machines, storage systems such as object, block, or file storage, and networking components such as VPCs, load balancers, and firewalls.
IaaS offers maximum flexibility and full control over infrastructure, making it ideal for organizations moving from on-premises setups or running custom enterprise workloads. Typical use cases include website hosting, testing environments, disaster recovery systems, and large application deployments.
Example: AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a ready-to-use environment where developers can build, test, and deploy applications without managing underlying infrastructure. The provider handles servers, runtime, middleware, and scaling, allowing teams to focus only on writing and launching code.
This model simplifies development, speeds up deployment cycles, and reduces operational overhead. It is ideal for organizations looking to modernize applications, adopt DevOps workflows, or quickly build cloud-native solutions.
Example: Azure App Service, Google App Engine, AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers fully managed applications over the internet through a subscription model. Users access software directly through a browser, without worrying about installation, updates, servers, or maintenance, as everything is handled by the provider.
SaaS enables quick adoption, lower IT overhead, and consistent performance across teams. It is ideal for CRM, collaboration tools, office productivity suites, marketing platforms, and any business function that benefits from ready-to-use cloud software.
Example: Salesforce, Microsoft 365, Slack, HubSpot.
Comparing IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
Here is a clear, simple comparison table that helps readers quickly understand the differences among the three cloud delivery models.
| Feature | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| What It Provides | Virtualized compute, storage, and networking | Full development and deployment platform | Ready-to-use software applications |
| User Responsibility | Manage OS, apps, security, runtime | Manage apps and data only | No management required |
| Ideal For | Migration, custom apps, enterprise workloads | Development teams building apps faster | Businesses needing plug-and-play software |
| Level of Control | Highest | Medium | Lowest |
| Scalability | High | High | Very high |
| Maintenance | User-managed | Partially managed | Fully managed |
| Examples | AWS EC2, Azure VMs | Azure App Service, Google App Engine | Salesforce, Microsoft 365 |
Benefits of Cloud Delivery Models
Cloud delivery models bring a range of advantages to enterprises of all sizes. Here are the major benefits:
- Reduced IT Cost: Businesses avoid upfront infrastructure investments and pay only for what they use. This reduces hardware, data center, and maintenance costs.
- Improved Agility: Teams can instantly provision resources, test new ideas, and move faster without waiting for physical servers or long procurement cycles.
- Faster Time to Market: Developers can deploy applications quickly, scale environments on demand, and shorten the entire release lifecycle.
- On-Demand Scalability: Cloud resources scale automatically based on workload demand, ensuring performance and eliminating downtime risks.
- Global Accessibility: Users can access applications, data, and services from anywhere in the world, enabling remote work, international operations, and better collaboration.

Top 6 Cloud Delivery Model Companies
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is the global leader in cloud computing, offering a full range of IaaS, PaaS, and managed services. It operates the world’s largest cloud infrastructure with multiple regions and availability zones. AWS provides advanced capabilities across compute, storage, AI, analytics, DevOps, containers, and serverless. Companies like Netflix, Airbnb, Coca-Cola, and Samsung rely on AWS for high availability, global scaling, cost optimization, and fast deployment. Its ecosystem of 200-plus services makes it a top choice for startups, enterprises, and government organizations.
2. Microsoft Azure
Azure stands out for its strong enterprise adoption and seamless integration with Microsoft tools such as Office 365, Dynamics 365, Windows Server, and the Power Platform. It supports hybrid cloud environments through Azure Arc, making it ideal for businesses that need on-premises plus cloud flexibility. Companies such as Walmart, Mercedes-Benz, LinkedIn, and HSBC use Azure to modernize applications, improve security, and scale globally. Azure offers powerful AI models, analytics, and developer tools that support both traditional and cloud-native workloads.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP is known for innovation in data analytics, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-performance computing. BigQuery, Vertex AI, and Google’s global network make GCP attractive for data-driven organizations. Businesses like Spotify, PayPal, UPS, and The Home Depot depend on GCP for real-time analytics, large-scale data processing, and efficient application development. GCP’s strengths include sustainability, open-source leadership, and developer-friendly tools like Kubernetes, which originated at Google.
4. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
OCI is designed for high-performance, data-intensive, and mission-critical applications. It is a preferred choice for companies using Oracle databases, ERP systems, and financial workloads. OCI provides strong security, predictable performance, and specialized infrastructure for enterprise systems. Industries such as banking, telecom, and government rely on OCI for large-scale database migrations, secure cloud storage, and resilient operations. Companies including Zoom, 8×8, and FedEx use OCI to support their enterprise-grade workloads.
5. IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud focuses on secure hybrid cloud environments and is widely used in industries that require strict compliance, such as banking, healthcare, insurance, and government. It combines IBM’s expertise in cybersecurity, AI with Watson, and enterprise-grade infrastructure. Organizations choose IBM Cloud for workloads that require strong governance, data privacy, and regulatory compliance. Companies like American Airlines, Lufthansa, and Crédit Mutuel use IBM Cloud for critical applications, advanced analytics, and modernization of legacy systems.
6. Salesforce Cloud
Salesforce is one of the most influential SaaS and PaaS platforms in the world. It provides cloud solutions for CRM, sales, marketing, customer service, analytics, and application development. Salesforce Platform and AppExchange enable businesses to build custom apps and automate complex workflows without the heavy infrastructure management required by traditional systems. More than 150,000 companies, including Toyota, Adidas, Unilever, and Canon, use Salesforce to streamline customer engagement, manage operations, and scale their digital experience. Its strong ecosystem makes it a leader for customer-facing cloud solutions.
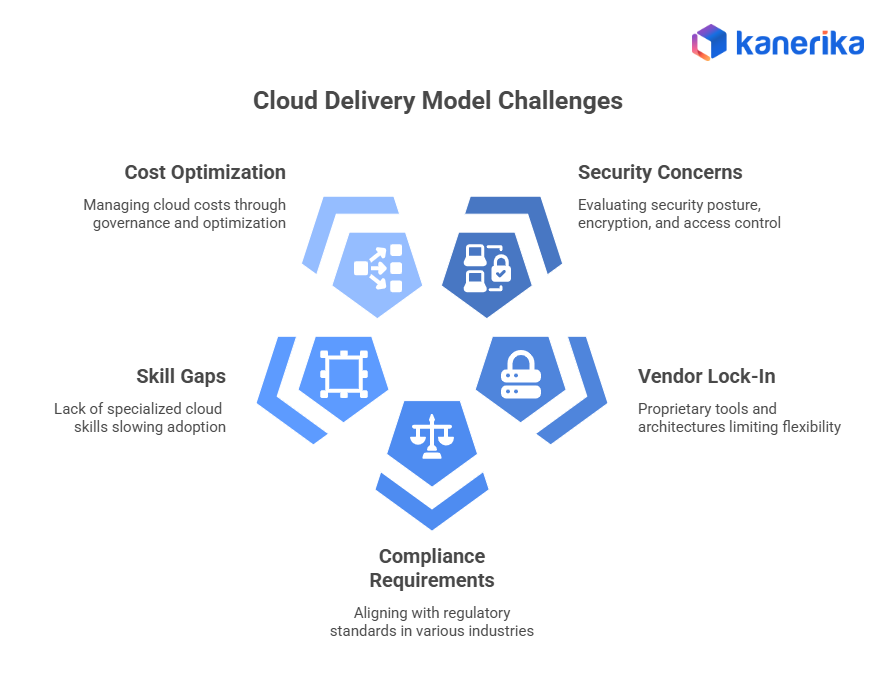
Challenges in Choosing a Cloud Delivery Model
While cloud delivery models offer major benefits, choosing the right model can be challenging. Here are the common obstacles organizations face:
- Security Concerns: Different models offer different levels of control and shared responsibility. Companies must evaluate security posture, encryption, access control, and data protection before choosing a model.
- Vendor Lock-In: Moving from one cloud provider to another can be complex. Proprietary tools, APIs, or architectures sometimes limit the flexibility to switch.
- Compliance Requirements: Industries such as BFSI, healthcare, and government require strict compliance. Each cloud model offers different compliance capabilities that must align with regulatory standards.
- Skill Gaps: Teams need specialized cloud skills, especially when managing IaaS environments. Lack of expertise can slow adoption and increase risk.
- Cost Optimization Challenges: Cloud costs can grow quickly if not monitored. Each model requires proper governance, rightsizing, and usage optimization to avoid overspending.
AI Adoption and Business Transformation Explained
Discover how AI adoption transforms businesses through automation, smarter decisions, and improved efficiency across every department.
Real-World Use Cases
1. How SaaS Is Used by Modern Businesses
Use Case:
SaaS is used when businesses need ready-to-use applications without installing software or managing infrastructure. Companies rely on SaaS for CRM, marketing automation, HR management, accounting, email, and collaboration tools. It helps organizations scale quickly, reduce IT workload, and pay only for what they use.
Real Company Examples:
- Salesforce helps global enterprises like Toyota streamline customer relationship management using SaaS CRM.
- Zoom became a global communication backbone for companies like Capital One, enabling instant remote meetings in the cloud.
- HubSpot provides marketing automation for brands like ClassPass, helping them run marketing campaigns without any on-prem setup.
2. How PaaS Accelerates Application Development
Use Case:
PaaS is used by businesses that want to build, test, deploy, or manage applications without handling servers, databases, or runtime environments. Developers use PaaS for rapid application development, API creation, microservices, and integration workflows.
Real Company Examples:
- Netflix uses AWS Elastic Beanstalk (a PaaS) to deploy and scale microservices-based applications behind its streaming platform.
- Unilever uses Google App Engine to build and run digital marketing applications across multiple global markets.
- Coca-Cola used Heroku (PaaS) to develop its “Freestyle” vending machine mobile app faster and with fewer infrastructure overheads.
3. How IaaS Powers Large-Scale, Flexible Infrastructure
Use Case:
IaaS is chosen when organizations need complete control over computing resources like virtual machines, storage, servers, networking, and security. It supports workloads such as large-scale data processing, hosting high-traffic applications, disaster recovery, and dynamic capacity scaling.
Real Company Examples:
- Airbnb relies heavily on AWS EC2 and S3 for scalable infrastructure that handles fluctuating global traffic.
- NASA uses Microsoft Azure to store and process massive datasets from space missions, leveraging IaaS for high-performance computing.
- Spotify moved its backend infrastructure to Google Cloud Platform, leveraging IaaS to scale storage and performance for millions of users.
How Cloud Application Development Powers Digital Transformation
Innovative cloud application development services are scalable, secure, and future-ready with Kanerika.
How To Choose the Right Cloud Delivery Model for Your Business
1. Map Your Business Needs to the Right Model
Start by identifying what your business truly needs: speed, control, scalability, or cost-efficiency.
- If you want quick deployment with minimal IT involvement, SaaS is the best option.
- If you need to build custom applications without managing infrastructure, choose PaaS.
- If flexibility and full control over computing resources matter, IaaS is ideal.
2. Evaluate Cost, Security, and Compliance Requirements
Each cloud model comes with a different cost structure and security responsibility.
- SaaS reduces operational costs but offers less customization.
- PaaS optimizes development cost but requires strong governance.
- IaaS provides maximum control but needs higher security oversight.
Check compliance needs (GDPR, HIPAA, ISO) before finalizing the model.
3. Consider Scalability and Long-Term Growth
Choose a model that supports your business roadmap.
- If you expect rapid scale, IaaS or PaaS provides flexibility to grow without hardware limits.
- If the focus is standard business functions (CRM, HR, finance), SaaS solutions scale effortlessly.
Many modern businesses also adopt a hybrid or multi-cloud approach to match different workloads with suitable models.
Kanerika: Delivering Intelligent Cloud Solutions for Modern Enterprises
Kanerika helps organizations adopt cloud delivery models that bring agility, scalability, and automation to their operations. Our expertise covers cloud-native application development, workflow automation, and integration with AI and RPA technologies. This approach reduces manual effort, improves efficiency, and ensures cost-effective solutions that align with business goals.
We design cloud strategies that go beyond basic migration. Our solutions focus on eliminating repetitive tasks, seamlessly integrating systems, and maintaining compliance with industry standards. Using microservices architecture and DevOps practices, we build applications that are secure, resilient, and ready for future growth.
Kanerika provides continuous optimization and real-time monitoring to keep your cloud environment performing at its best. We combine AI-driven automation with intelligent orchestration to help businesses adapt quickly to changing demands. Our cloud delivery model is built for evolution, ensuring your technology scales as your business grows.
With Kanerika, you gain a partner who understands that automation is not just about saving time, it’s about creating a foundation for innovation. We help enterprises stay competitive by delivering solutions that are agile, secure, and designed for long-term success.
Modernize Your Business with Cloud Technology!
Partner with Kanerika for Advanced Cloud-Based Solutions.
FAQs
What are the three cloud delivery models?
There are three main cloud delivery models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) gives you the building blocks – servers, storage, networking – like renting raw land; Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a pre-built platform for your applications, like renting a house with utilities included; and Software as a Service (SaaS) offers complete applications ready to use, like renting a fully furnished apartment. Each model offers different levels of control and flexibility, allowing you to choose the best fit for your needs.
What are the 4 types of cloud models?
The four main cloud models are: public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud. Public clouds are shared resources accessible to anyone, private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, hybrid clouds combine public and private for flexibility, and multi-cloud uses multiple public cloud providers for redundancy and cost optimization.
Which of the following are cloud delivery models?
Cloud delivery models describe how cloud services are offered and accessed. Think of them like different ways to “rent” computing resources. The three main models are: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), where you rent raw computing power; Platform as a Service (PaaS), where you rent a platform to develop and run applications; and Software as a Service (SaaS), where you rent a complete software application.
What are the three types of cloud deployment models in AWS?
AWS offers three main cloud deployment models: Public Cloud, where AWS manages all infrastructure, Private Cloud, where you own and manage the infrastructure within your own data center, and Hybrid Cloud, combining the benefits of both by seamlessly integrating public and private clouds for optimal flexibility and control.
What are the 3 types of cloud services AWS has?
AWS offers three main types of cloud services: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), like EC2 instances, which provide raw computing power and storage; Platform as a Service (PaaS), like Elastic Beanstalk, which offer a platform for developing and deploying applications; and Software as a Service (SaaS), like Amazon S3, which provide ready-to-use software applications over the internet.
Is AWS IaaS or PaaS?
AWS is often described as both IaaS and PaaS. While it provides the fundamental infrastructure like servers, storage, and networking (IaaS), it also offers managed services like databases, messaging queues, and serverless computing (PaaS). Essentially, AWS offers a spectrum of options, allowing you to choose the level of abstraction and control that best suits your needs.
What is IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS?
Think of it like building a house. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) gives you the bricks and mortar (servers, storage, networking). PaaS (Platform as a Service) provides the framework (operating system, programming languages) to build the house. SaaS (Software as a Service) is the finished house (ready-to-use applications like email or CRM) you can move into.
What are the 4 models of cloud computing?
The four main cloud computing models describe how clouds are deployed. They are Public Cloud (shared and open), Private Cloud (exclusive to one company), Hybrid Cloud (a mix of public and private), and Community Cloud (shared by specific organizations).
What are the 4 types of clouds in cloud computing?
There are four main types of clouds in cloud computing: Public Cloud: Services offered over the internet, shared among many users. Private Cloud: Dedicated infrastructure for a single organization’s exclusive use. Hybrid Cloud: A mix of public and private clouds that work together. Community Cloud: Shared infrastructure used by a specific group of organizations with common interests.
What are the three types of cloud deployment models?
The three main cloud deployment models are: Public cloud, where services are shared over the internet by a provider. Private cloud, dedicated solely to one organization. Hybrid cloud, which combines both public and private options to work together.
What are the three main cloud delivery models?
The three main ways cloud services are delivered are: 1. Software as a Service: You use complete applications over the internet, like web-based email. 2. Platform as a Service: You get tools and an environment to build and run your own software. 3. Infrastructure as a Service: You rent basic computing resources such as virtual servers and storage.
What are the 7 different types of clouds?
The seven main types of cloud computing models are: 1. Public Cloud Services offered over the internet by providers like AWS or Azure. 2. Private Cloud Cloud infrastructure dedicated to a single organization. 3. Hybrid Cloud A mix of public and private clouds for flexibility. 4. Community Cloud Shared by organizations with similar goals or compliance needs. 5. Multi-Cloud Using multiple cloud providers for different services. 6. Distributed Cloud Cloud services spread across multiple physical locations. 7. Poly Cloud Combining different cloud services for specialized tasks.
What is the 7 step model of cloud computing?
There isn’t a single, universally recognized 7-step model that defines cloud computing itself. Cloud computing is typically understood through its core characteristics, service models (like software or infrastructure over the internet), and deployment options. However, many organizations follow multi-step processes for *adopting* and managing cloud services. These often include planning, assessing workloads, migration, testing, optimization, and ongoing operations. This helps businesses effectively utilize cloud technology.
What are the 4 main cloud services?
The four main types of cloud services, offering different levels of control, are: 1. Software: Applications you just use over the internet, like email or word processors. 2. Platforms: Tools and environments for developers to build and run their own apps. 3. Infrastructure: Basic computing resources like virtual servers, storage, and networks. 4. Functions: Running specific pieces of code automatically, without needing to manage servers.
What are the 4 types of cloud networking?
The 4 types of cloud networking are: 1. Public Cloud Networking: Using network services from a third-party provider (like AWS, Azure). 2. Private Cloud Networking: Building and managing a cloud-like network within your own data center. 3. Hybrid Cloud Networking: Connecting your private cloud network to one or more public cloud networks. 4. Multi-Cloud Networking: Managing network connections across multiple different public cloud providers.
What is the cloud model?
The cloud model is a way to deliver computing services like servers, storage, and software over the internet. Instead of buying and maintaining your own hardware, you access these resources from a third-party provider. You only pay for what you use, offering flexibility and scalability.
What is 4 cloud computing?
Cloud computing means delivering computer services like storage and processing power over the internet. Instead of owning your own hardware and software, you rent these resources from a provider as you need them. You only pay for what you use, offering great flexibility and cost-efficiency.
What are the four types of cloud storage?
The four main types of cloud storage are: Personal: For individual users to store their own data. Public: Shared by many customers and managed by a third-party provider. Private: A dedicated system for a single organization’s exclusive use. Hybrid: Combines both public and private storage solutions.
What are SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS examples?
SaaS (Software as a Service): Ready-to-use software over the internet, like Gmail or Salesforce. PaaS (Platform as a Service): A platform for building and running your own apps, such as Google App Engine. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Virtual computers, storage, and networks, like Amazon EC2 or Microsoft Azure VMs.
What is a cloud computing model?
A cloud computing model is a way to deliver computing resources like servers, storage, and applications over the internet. Instead of owning and maintaining your own hardware, you access these services from a provider. You simply pay for what you use, offering flexibility and scalability without large upfront costs.










