Every business faces challenges when it comes to making quick, informed decisions. By leveraging operational analytics, Synoptek, the IT services firm, implemented a custom business intelligence solution that analyzed operational data in real time. This approach led to a significant revenue increase by enhancing team performance and data utilization.
Yet, many organizations still overlook the power of real-time data to improve operations. Why? The idea of implementing operational analytics can feel overwhelming, especially when resources are limited. But here’s the thing: it doesn’t have to be complicated. With the right strategy, you can start seeing improvements almost immediately, making your business more responsive, cost-effective, and data-driven.
Operational analytics isn’t just a tool; it’s a game-changer. Let’s explore how to implement operational analytics effectively and start seeing improvements today.
Take Control of Your Workflows with Optimized Operational Analytics!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
What is Operational Analytics?
Operational analytics is a type of business analytics that involves continuously monitoring data and discovering insights in real-time. Its purpose is to enable teams to make quick, informed decisions on the go.
By syncing information from a data warehouse to front-end tools such as Salesforce, Marketo, or HubSpot, operational analytics allows for accurate data tracking across different platforms and tools. This facilitates streamlined business operations, improved efficiency, and enhanced collaboration among cross-functional teams.
Unlike traditional dashboard-based analytics, operational analytics goes beyond simply understanding data and focuses on taking action based on insights automatically. It ensures that all members of an organization, regardless of their technical skills, have access to the same data, thus empowering them to leverage it effectively within their daily business processes.
Why AI and Data Analytics Are Critical to Staying Competitive
AI and data analytics empower businesses to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and anticipate market trends, ensuring they maintain a strong competitive edge.
Core Principles and Methodologies of Operational Analytics
1. Real-Time Data Processing
Operational analytics prioritizes the immediate analysis of data as it’s generated. This enables organizations to respond to issues and opportunities as they arise rather than relying on historical reporting.
- Utilizes stream processing technologies to analyze data in motion
- Implements low-latency architectures that minimize the time between data creation and insight delivery
- Focuses on timely alerting and notification systems for immediate response
2. Cross-Functional Data Integration
Breaking down data silos between departments creates a unified view of operations. This principle ensures that insights reflect the interconnected nature of business processes.
- Combines data from disparate systems (ERP, CRM, supply chain, etc.)
- Creates normalized data models that standardize information across sources
- Establishes single source of truth for operational metrics
3. Process-Centric Analysis
Operational analytics examines end-to-end business processes rather than isolated functions. This approach reveals inefficiencies at handoff points and bottlenecks that might otherwise remain hidden.
- Maps data to business process steps and transitions
- Identifies process variances and execution gaps
- Measures cycle times and throughput across entire workflows
4. Actionable Insights Delivery
Analytics outputs are designed specifically for operational decision-making. This means presenting relevant information to the right people in formats that facilitate immediate action.
- Embeds insights directly into operational systems and workflows
- Delivers role-based dashboards customized to specific decision needs
- Provides clear next-best-action recommendations
5. Continuous Improvement Framework
Operational analytics establishes feedback loops that drive ongoing optimization. This iterative approach creates a self-reinforcing cycle of measurement and enhancement.
- Implements test-and-learn methodologies for operational changes
- Tracks the impact of process modifications in real-time
- Creates baselines and benchmarks to measure improvement over time
Real-Time Data Transformation: The Key To Instant Business growth
Unlock instant business growth by leveraging real-time data transformation to enable swift decision-making and optimize operational efficiency.!
Industry-Specific Operational Analytics Applications
1. Manufacturing
Production Line Optimization
Manufacturing facilities use operational analytics to maximize throughput while minimizing resource usage. Real-time monitoring identifies bottlenecks and constraints as they occur, allowing for immediate adjustments to production parameters.
- Analyzes machine cycle times to balance workload across production stages
- Identifies optimal production scheduling to reduce changeover times
- Tracks material flow to eliminate waiting and excess inventory between processes
Quality issues can be detected and addressed proactively through pattern recognition and statistical process control techniques. This shifts quality management from reactive inspection to predictive prevention.
- Implements in-line quality monitoring to catch defects before further processing
- Correlates production parameters with quality outcomes to identify root causes
- Uses image recognition and sensor data to automate quality inspection processes
Supply Chain Visibility
End-to-end visibility across the supply network enables manufacturers to optimize inventory levels and respond quickly to disruptions or demand changes.
- Tracks materials from suppliers through production to customer delivery
- Provides early warning systems for potential supply disruptions
- Optimizes inventory levels based on lead times and demand variability
Equipment Effectiveness Metrics
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) analytics combine availability, performance, and quality metrics to maximize the productive value of manufacturing assets.
- Monitors equipment downtime causes and durations
- Predicts maintenance needs before failures occur
- Optimizes preventive maintenance schedules based on actual usage patterns
2. Healthcare
Patient Flow Optimization
Healthcare providers use operational analytics to reduce wait times and improve patient throughput without compromising care quality.
- Predicts patient volumes by department to optimize staffing levels
- Identifies bottlenecks in the patient journey from admission to discharge
- Simulates the impact of process changes before implementation
Resource Utilization Analytics
With tight margins and limited resources, healthcare facilities analyze utilization patterns to maximize the effectiveness of staff, equipment, and facilities.
- Tracks usage patterns of high-value equipment like MRI and CT scanners
- Optimizes operating room scheduling to reduce turnover time
- Balances clinical staff workloads based on patient acuity and care requirements
Clinical Operations Improvement
Analytics help standardize clinical workflows and reduce unnecessary variation in care delivery processes.
- Identifies variations in clinical protocols and their impact on outcomes
- Analyzes length-of-stay factors to reduce unnecessary hospital days
- Optimizes medication management workflows to reduce errors and waste
Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
Healthcare organizations use operational analytics to ensure adherence to complex regulatory requirements while minimizing the administrative burden.
- Automatically tracks compliance metrics required by regulatory agencies
- Provides early warning for potential compliance issues
- Streamlines reporting processes for quality measures and patient safety indicators
4. Retail and E-commerce
Inventory Management Optimization
Retailers apply operational analytics to maintain optimal stock levels that balance inventory costs against stockout risks.
- Predicts demand fluctuations at SKU and location levels
- Optimizes replenishment timing and quantities
- Identifies slow-moving inventory for markdown or reallocation
Last-Mile Delivery Analytics
E-commerce companies analyze delivery operations to improve speed, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of getting products to customers.
- Optimizes delivery routes based on real-time traffic and order patterns
- Monitors driver performance and adherence to delivery windows
- Identifies opportunities for consolidation and shared transportation
Store Operations Efficiency
Physical retailers use analytics to optimize labor allocation, store layouts, and customer service processes.
- Matches staffing levels to customer traffic patterns
- Analyzes in-store customer journeys to improve layout and merchandising
- Optimizes checkout processes to reduce waiting times
Omnichannel Operational Insights
Modern retailers analyze operations across physical and digital channels to provide consistent customer experiences.
- Tracks inventory availability across all sales channels in real-time
- Optimizes fulfillment decisions (ship from store vs. distribution center)
- Analyzes cross-channel customer behavior to improve operational handoffs
5. Financial Services
Transaction Monitoring and Fraud Detection
Financial institutions apply operational analytics to identify suspicious patterns and prevent fraudulent activities in real-time.
- Analyzes transaction patterns to flag anomalies indicative of fraud
- Applies machine learning to reduce false positives in fraud alerts
- Tracks effectiveness of fraud prevention measures across channels
Back-Office Process Optimization
Banks and insurance companies use analytics to streamline document processing, claims handling, and other administrative operations.
- Identifies bottlenecks in document processing workflows
- Measures and reduces handling times for key processes
- Analyzes exception cases to improve straight-through processing rates
Regulatory Reporting Automation
Financial services firms apply operational analytics to streamline complex regulatory reporting requirements while ensuring accuracy.
- Automates data collection and validation for regulatory reports
- Provides audit trails for data lineage and calculation methods
- Monitors regulatory thresholds to provide early warnings of potential issues
Customer Service Operations Enhancement
Analytics improve the efficiency and effectiveness of customer service interactions across channels.
- Predicts call volumes to optimize staffing and reduce wait times
- Analyzes call content to identify common customer issues
- Routes inquiries to the most appropriate service representatives based on issue type and representative expertise
Data Profiling: A Comprehensive Guide to Enhancing Data Quality
Understand how data profiling techniques improve data quality by identifying inconsistencies and ensuring accurate, reliable information for better decision-making.
A Guide to Implementing Operational Analytics
Implementing operational analytics for your business can seem like a daunting task, but with the right steps, it becomes a strategic move that can lead to smarter decision-making, improved efficiency, and better customer experiences. Here’s a clear and practical guide to help you get started:
1. Assess Your Business Requirements
- What to do: Start by identifying the key areas where operational analytics can add value to your business. Are you looking to optimize supply chain operations, reduce customer service response times, or increase overall operational efficiency?
- Why it’s important: Having clear business objectives ensures that you focus your analytics efforts on areas that will deliver measurable results.
2. Collect and Prepare Your Data
- What to do: Gather data from various internal systems such as CRM, ERP, inventory management, and sales. Ensure the data is clean, accurate, and up-to-date.
- Why it’s important: Quality data is the foundation of any analytics process. Without accurate data, the insights you generate will be flawed and unreliable.
3. Choose the Right Analytics Tools
- What to do: Research and select analytics tools that best align with your business needs. This could include business intelligence platforms, machine learning tools, or specialized operational analytics software.
- Why it’s important: The right tools will allow you to process and analyze data efficiently, helping you extract actionable insights without overwhelming your team with complexity.
4. Integrate Analytics with Operational Systems
- What to do: Implement your chosen analytics tools within your operational systems, such as inventory tracking, logistics, or customer service platforms.
- Why it’s important: Integration ensures that your analytics are based on real-time, up-to-the-minute data, making your decisions more accurate and timely.
5. Monitor and Analyze Performance in Real-Time
- What to do: Set up real-time monitoring dashboards to track key metrics like delivery times, production rates, or sales conversions. Ensure these metrics align with your business objectives.
- Why it’s important: Real-time analytics allow you to make quick decisions based on current data, helping you spot potential issues and opportunities immediately.
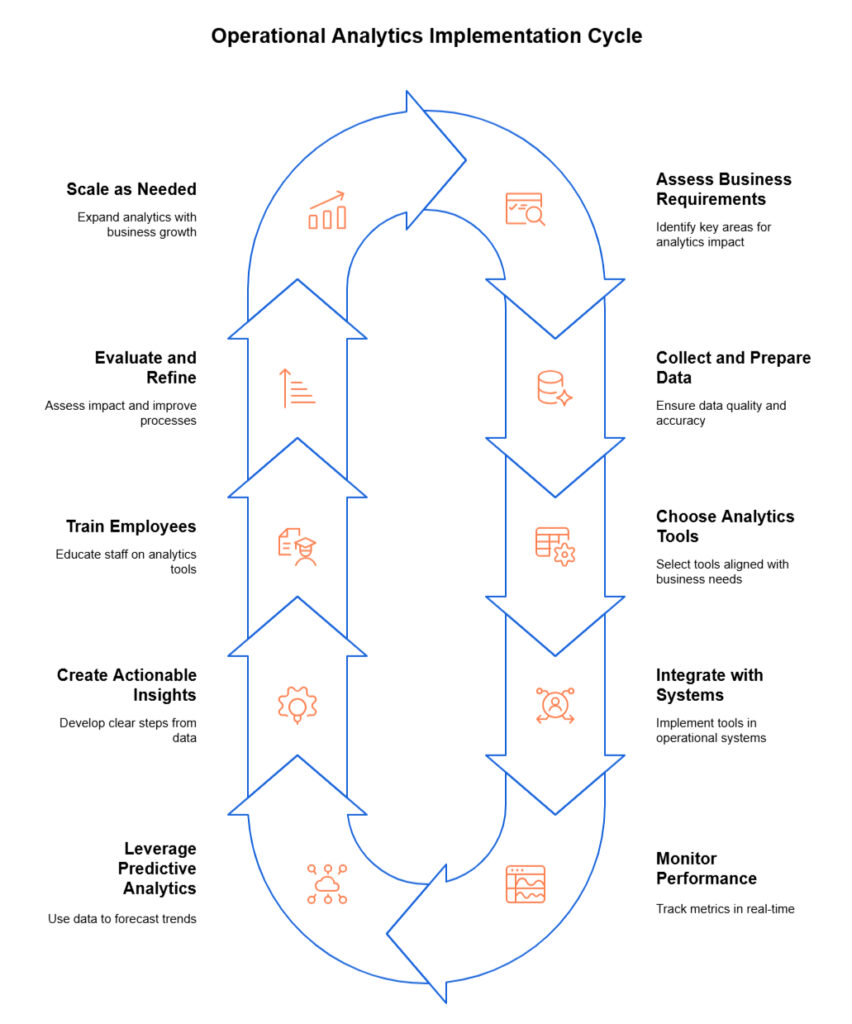
6. Leverage Predictive Analytics
- What to do: Use historical data and machine learning models to predict future trends. For example, you could predict when inventory will run low or when customer demand will peak.
- Why it’s important: Predictive analytics enables proactive decision-making, reducing the likelihood of surprises and optimizing resource allocation.
7. Create Actionable Insights and Share Them with Teams
- What to do: Turn your data insights into clear, actionable steps for your team. For example, if analytics show a delay in production, the team can immediately address the bottleneck.
- Why it’s important: Insights are only valuable if they drive action. Sharing them effectively ensures that everyone in the organization is aligned and working towards the same goals.
8. Train Employees on Using Analytics Tools
- What to do: Provide training to employees who will use operational analytics tools. This could include basic data literacy or advanced skills like data visualization and dashboard creation.
- Why it’s important: Ensuring that employees understand how to use analytics tools empowers them to make data-driven decisions and improves the overall effectiveness of your analytics efforts.
9. Evaluate and Refine the Process
- What to do: Regularly evaluate the impact of your operational analytics by measuring the improvements in efficiency, decision-making speed, and profitability.
- Why it’s important: Continuous evaluation allows you to refine your approach, address any shortcomings, and ensure that analytics are consistently providing value.
10. Scale as Needed
- What to do: As your business grows, continue scaling your analytics efforts. This might mean adding new data sources, expanding the use of analytics across departments, or upgrading your analytics tools.
- Why it’s important: Scalability ensures that your operational analytics can grow alongside your business, continuing to provide value at every stage.
Data Visualization Tools: A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right One
Explore how to select the best data visualization tools to enhance insights, streamline analysis, and effectively communicate data-driven stories.
What Are the Advantages of Operational Analytics?
1. Real-time Decision Making
Enables immediate data-driven decisions based on current conditions rather than historical reports. This reduces reaction time to emerging issues and opportunities, giving businesses a competitive edge.
2. Process Optimization
Identifies inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and improvement opportunities within operational workflows. This leads to streamlined processes, reduced waste, and improved resource allocation.
3. Predictive Capabilities
Anticipates operational problems before they occur by recognizing patterns and anomalies. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and allows for preventative measures to be implemented.
4. Enhanced Customer Experience
Provides insights into customer interactions in real-time, allowing for immediate service adjustments and personalization that improve satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Resource Allocation Efficiency
Ensures human, financial, and physical resources are deployed where they create maximum value, reducing waste and improving return on investment.
6. Performance Monitoring
Tracks operational KPIs continuously against targets, enabling swift corrective actions and creating accountability throughout the organization.
7. Data-Driven Culture
Fosters an environment where decisions at all levels are backed by evidence rather than intuition, reducing biases and improving overall decision quality.
Data Integrity Vs Data Quality: How They Impact Your Business Decisions
Understand the key differences between data integrity and data quality and discover how each critically influences informed and strategic business decision-making.
Drive Growth and Efficiency – Choose Kanerika for Next-Gen Analytics Solutions
Kanerika is a premier Data and AI solutions company dedicated to delivering innovative analytics solutions that empower businesses to unlock insights from their vast data estates quickly and accurately. As a certified Microsoft Data and AI solutions partner, we utilize Microsoft’s powerful tools, including Fabric and Power BI, to build tailored solutions that address your unique business challenges. Our expertise in these cutting-edge platforms allows us to enhance your data operations, streamline decision-making processes, and drive efficiency across your organization.
With Kanerika, you can expect solutions that not only optimize your data strategy but also foster growth and innovation. Whether you’re looking to improve reporting, streamline operations, or gain actionable insights, we ensure that your data works for you, helping you stay ahead of the competition in today’s fast-paced business landscape. Let Kanerika be your trusted partner in transforming your data into a competitive advantage.
Enhance Decision-Making with Scalable Analytics Solutions!
Partner with Kanerika Today.
FAQ
What is an example of operational analysis?
Operational analysis digs into the nuts and bolts of how a system *actually* works. For example, analyzing a call center’s wait times, agent efficiency, and call resolution rates to pinpoint bottlenecks and improve service is operational analysis in action. It’s about measuring real-world performance to find areas for optimization, not just theoretical modeling. Ultimately, it’s about making things run smoother and more effectively.
What is the difference between data analytics and operational analytics?
Data analytics is about exploring past data to understand trends and make strategic decisions; think “why did this happen?”. Operational analytics focuses on real-time data to improve current processes and efficiency; it’s about “what’s happening now and how can I fix it?”. Essentially, data analytics is retrospective, while operational analytics is proactive. They use similar methods but serve different, complementary purposes.
Which best describes operational analytics?
Operational analytics uses real-time data to monitor and improve your day-to-day business processes. It’s about understanding *what’s happening now* and making immediate adjustments, unlike strategic analytics which focuses on the future. Think dashboards showing current sales figures or customer service call volume, allowing for quick reactive decisions. It’s all about efficiency and immediate impact.
What is the meaning of operational analytics?
Operational analytics uses real-time data to monitor and improve your day-to-day business activities. It’s about understanding *what’s happening now* and using that insight to make immediate adjustments, unlike strategic analytics which focuses on the future. Think of it as the “dashboard” for your business, showing current performance and guiding immediate actions. Ultimately, it drives efficiency and effectiveness in current operations.
What are the tools of operational analysis?
Operational analysis uses various tools to dissect processes and boost efficiency. These include statistical methods like regression analysis to spot trends, process mapping to visualize workflows, and simulation modeling to predict outcomes under different scenarios. Ultimately, the goal is to identify bottlenecks and areas ripe for improvement.
What is the purpose of operations analysis?
Operations analysis helps businesses understand how their processes work, pinpoint inefficiencies, and improve performance. It’s about using data and methods to optimize everything from production flow to customer service. Ultimately, the goal is to boost efficiency, cut costs, and increase profitability. Think of it as a systematic way to make things run smoother and smarter.
What are the examples of operational data?
Operational data is the raw, real-time information your business uses daily. Think of sales transactions processed at checkout, website clicks logged each second, or a machine’s sensor readings. It’s the “doing” data, unlike the analytical data used for long-term strategy. Essentially, it’s the heartbeat of your daily operations.
What is an operations analyst?
Operations analysts are detectives of inefficiency. They use data and analytical skills to identify bottlenecks, improve processes, and boost an organization’s performance. Think of them as problem-solvers who translate complex data into actionable strategies for better efficiency and profitability. Essentially, they help companies run smoother and smarter.
What are the four types of operational reports?
Operational reports track business performance. Four key types categorize this: routine reports on regular activities, exception reports highlighting unusual events, periodic summaries covering specific timeframes, and ad-hoc reports addressing unique, immediate needs. These provide different levels of detail and serve distinct managerial purposes.
How to collect operational data?
Gathering operational data hinges on identifying your key performance indicators (KPIs). Then, strategically deploy data collection methods like automated logging, direct observation, or surveys tailored to your specific KPIs and data sources. Ensure data is consistently formatted and stored securely for accurate analysis. Finally, constantly evaluate your methods to ensure they remain efficient and effective.
What are the examples of operational processes?
Operational processes are the day-to-day activities keeping a business running. Think order fulfillment (from customer order to delivery), manufacturing a product, or even scheduling employee shifts – these are all examples. Essentially, any repeatable task directly contributing to delivering your core offering is an operational process. They form the backbone of efficiency and output.
What is the difference between business analytics and operational analytics?
Business analytics focuses on the “big picture,” using data to understand trends and make strategic decisions about the future of the company. Operational analytics, conversely, zeroes in on day-to-day operations, using data to improve efficiency and processes *right now*. Think business analytics as forecasting next quarter’s sales, while operational analytics is optimizing today’s order fulfillment. They both use data, but their goals and time horizons differ greatly.
Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter for insightful industry news, business updates and all the latest data trends online