With Industry 5.0 on the rise, manufacturing is evolving beyond automation—shifting toward a future where humans and intelligent machines collaborate to deliver sustainable, personalized, and resilient solutions.
According to a 2024 Deloitte survey, 98% of manufacturers have started their digital transformation journey, up from just 78% in 2019. Businesses are dedicating nearly 30 percent of their operating budgets to technological investments, such as AI, cloud, 5G, and generative AI – underscoring just how important digital transformation is for their future operational success.
Continue reading to explore the top manufacturing industry trends for 2025—from smart factories and supply chains to workforce, sustainability, cybersecurity, and emerging technologies with real-world examples.
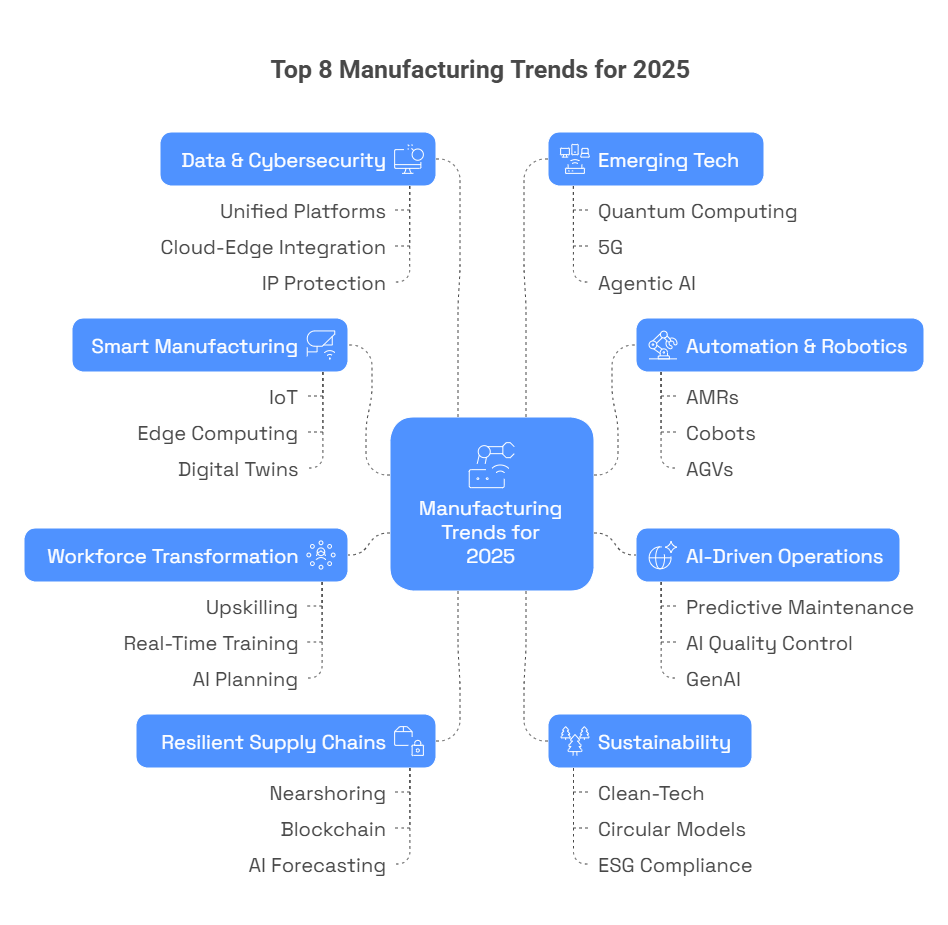
Top 8 Manufacturing Industry Trends for 2025
Trend #1 – Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing integrates IoT, edge computing, and digital twins to build intelligent factories. The focus is on real-time visibility, faster responses, and more efficient processes.
1. Industrial IoT for Real-Time Data
- Industrial IoT links together machines, sensors, and systems that gather continuous streams of data.
- This assists in the monitoring of equipment performance, energy consumption, and workflow efficiency without any manual tracking.
- Example: Bosch applies IoT across its plants, where sensors connect machines to perform machine health and energy consumption analysis. This allows predictive alerts that reduce downtime and resource wastage.
- Benefit: Faster decisions, less downtime, and more intelligent use of resources.
2. Edge Computing for Faster Decisions
- Edge computing refers to the transfer of data processing as close as possible to the machines, rather than sending everything to the cloud.
- This is important in manufacturing, where delays as short as a few seconds in deciding can result in defects or safety hazards.
- Example: Siemens, in its factories, has integrated edge computing with digital twin technology. Operators can directly respond by making instant process adjustments on the shop floor, reducing costly downtime.
- Benefit: Real-time issue resolving, improved reliability, and reduced cost on cloud bandwidth.
3. Digital Twins for Simulation and Optimization
- A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical asset or process based on real-world performance.
- Manufacturers use Digital Twins to test production changes or predict the need for maintenance without having to shut down operations.
- Example: General Electric uses digital twins for turbines, simulating performance to identify potential failures promptly. This method saves tens of millions of dollars in service expenses and uptime optimization, especially when paired with efficient ways to manufacture physical parts like when teams request a quote from RapidDirect.
- Benefit: Reduced operational risk, faster time to market, and peak system performance.
Trend #2 – Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics have moved beyond repetitive tasks—today’s intelligent machines can adapt, collaborate, and make real-time decisions, transforming how factories operate.
1. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) navigate factory floors on their own, guided by advanced sensors and AI that help them adjust to dynamic environments.
- Their primary role is to streamline material movement, take over repetitive transport tasks, and ease the workload on human workers.
- Example: Amazon Robotics’ AMRs move inventory bins around in fulfillment centers. This automation reduces the amount of walking floor workers have to do, and helps Amazon manage millions of daily orders.
- Advantages: Acceleration of logistics, reduction of manual stress, and enhanced warehouse effectiveness.
2. Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
- Cobots work side by side with humans, performing repetitive, dangerous, or precision-driven tasks.
- They are designed to be safe, easy to reprogram, and adaptable to different production needs.
- Example: Universal Robots supplies cobots to companies like Siemens, where they assist with assembly and inspection tasks. This allows workers to focus on higher-value work while cobots manage routine processes.
- Benefit: Productivity gains, improved working environment, and more capacity for production.
The Ultimate Guide to Compliance Automation for Businesses
Learn how compliance automation helps streamline regulations, reduce manual work, and ensure effective data governance.
3. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
- AGVs are programmable transport systems that use fixed paths for material transport, which allows them to flourish in well-organized factory-like environments.
- They decrease reliance on forklifts and physical material handling for added safety and efficiency.
- Example: General Motors uses AGVs in its plants to move engines and heavy components between stations. This guarantees the continuity of the material flow between work centers, reducing accident risks.
- Advantages: Optimised internal logistics, safer material handling, and reliable JIT supplies.
Trend #3 – AI-Driven Operations
AI has become the centerpiece of smarter manufacturing, driving more thoughtful decision-making and yielding savings of both time and resources, from higher-quality products to more efficient business models.
1. Predictive Maintenance Using AI
- The systems use AI to analyze machine data and anticipate malfunctions, rather than waiting for them to happen. In place of fixed maintenance schedules, it’s about predictive servicing.
- This extends equipment life and prevents costly breakdowns.
- Example: Rolls-Royce applies AI-driven predictive maintenance in its engines, helping airlines cut downtime and save millions annually in service costs.
- Benefit: Fewer disruptions, longer equipment lifespan, and reduced maintenance cost.
2. AI-Powered Quality Control
- AI-based systems rely on vision and sensor technologies to inspect products in real time.
- Better, faster, and more consistent than humans, they detect and replace faulty products more quickly, resulting in higher-quality products.
- Example: BMW uses AI-based visual inspection on its assembly lines to spot paint and component defects. This reduces rework and guarantees premium quality standards.
- Benefit: Improved defect sensitivity, reduced waste, and lower rework costs.
3. GenAI for Documentation and Training
- Generative AI rapidly generates training manuals, troubleshooting guides, and knowledge assets.
- It also provides interactive learning, which allows workers to receive answers in real-time.
- Example: Airbus leverages generative AI to write design documentation and generate training material for engineers. This reduces the time to onboard resources and guarantees that all technical information is always up to date.
- Benefit: Faster employee training, easier knowledge sharing, and reduced reliance on external experts.
Trend #4 – Workforce Transformation
As technology continues to evolve, the workforce must also adapt to the latest manufacturing industry trends. The skills required are being redefined by AI, automation, and digital platforms, which are challenging as well as creating opportunities for companies.
1. Upskilling for AI and Automation
- Employees today need to work alongside machines, robots, and AI tools. That means traditional skillsets must be complemented with digital literacy, data analysis, and automation-related skills.
- Companies are investing heavily in formalized training programs for robotics operations, AI monitoring, and advanced manufacturing tools.
- For example, Siemens has implemented worldwide training courses to retrain staff in automation and data-based decision-making.
- Benefit: Keeps employees with updated skills, reduces job dislocation, and increases productivity.
2. Real-Time Training Platforms
- Companies have transitioned from traditional, seminar-style, one-time classroom offerings to digital classrooms, which provide continuous teaching.
- These can be seen from AR/VR modules for experiential learning, simulations for application, and AI-powered recommendations for specific job roles.
- Example: Boeing has combined artificial reality with grants for training of technicians, which has cut training time by as much as 75%.
- Benefit: Faster and more effective learning and an efficient workforce.
3. AI-Based Workforce Planning
- AI helps companies predict workforce needs by analyzing trends in production, market demand, and attrition rates.
- This enables managers to allocate human and machine resources better, preventing both underutilization and overwork.
- Example: Unilever uses AI-driven platforms to analyze workforce gaps and optimize hiring strategies.
- Benefit: Helps companies maintain a balanced, future-ready workforce.
Trend #5 – Resilient Supply Chains
Recent global upheavals underscored the necessity of strong, transparent supply chains. The industry is now coming up with creative solutions to reduce risk and maintain supply chain continuity.
1. Nearshoring and Multi-Sourcing
- Instead of depending on one global supplier, companies are moving operations closer to home (nearshoring) and diversifying suppliers (multi-sourcing).
- This minimizes the risks caused by geopolitical tensions, trade restrictions, or natural disasters.
- Example: General Motors is increasingly reliant on battery materials from North America to avoid getting tripped up by overseas markets.
- Benefit: Reduces dependency on a single source and ensures supply chain continuity.
2. Blockchain for Traceability
- Blockchain technology ensures transparent tracking of products, raw materials, and shipments.
- Every transaction is securely recorded, helping detect bottlenecks, prevent fraud, and improve accountability.
- Example: Walmart uses blockchain to track food supply origins, reducing the time to trace produce from days to seconds.
- Benefit: Greater transparency, improved trust, and faster issue resolution in supply chains.
3. AI for Demand Forecasting
- AI tools analyze historical data, market patterns, and real-time signals to predict demand fluctuations.
- This helps manufacturers plan inventory levels, reduce waste, and improve order fulfillment.
- Example: Coca-Cola uses AI-driven demand forecasting to align production with consumer demand, reducing stockouts.
- Benefit: Optimizes inventory management and improves customer satisfaction.
Modernize Your Production Processes!
Kanerika guides you in adopting next-gen technologies.
Trend #6 – Sustainability and Circular Manufacturing
Sustainability is no longer optional; it is now central to how manufacturers operate. With rising environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, companies are investing in greener and more circular business models.
1. Clean-Tech Investments
- Manufacturers are increasingly turning to renewable energy, energy-efficient equipment, and low-emission technologies.
- For instance, solar power, green hydrogen, and carbon capture are gradually becoming key elements of their energy strategies. Reducing our environmental impact industrial companies are highly interested in creating sustainable packaging.
- Example: Tesla’s Gigafactories are designed to run primarily on renewable energy sources.
- Benefit: Reduces environmental impact and cuts long-term energy costs.
2. Circular Economy Models
- Instead of “take, make, waste,” the circular model emphasizes reusing, recycling, and remanufacturing products.
- Consequently, manufacturers are redesigning products for longer lifespans while also converting waste materials into valuable new resources.
- Example: Philips has a “circular lighting” service where they keep ownership of their lighting devices, refurbish them, and reuse parts—so nothing goes to waste.
- Advantage: Reduces Tubeler scraps, reduces raw material costs, and enhances resource utilization.
3. ESG Compliance and Reporting
- Governments and investors are demanding transparent environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices.
- Manufacturers are now using digital platforms to measure emissions, energy use, and supply chain sustainability.
- Example: IKEA’s take-back program and its use of FSC-certified wood contribute to its ESG goals while promoting sustainable behaviour from its own customers.
- Benefit: Positively contributes to brand trust, guarantees qualification, and will draw in environmentally conscious clientele and investors.
These are among the most impactful manufacturing industry trends driving eco-friendly operations and circular business models.
Trend #7 – Data Infrastructure and Cybersecurity
The modern manufacturing industry is becoming data-driven. From IoT sensors on machines to AI models predicting breakdowns, factories today depend heavily on reliable and secure data systems. Without a strong foundation, data remains siloed, vulnerable, or underutilized. Businesses are increasingly shifting towards integrated platforms and advanced cybersecurity to make their data an asset, not a liability.
1. Unified Data Platforms
The majority of factories continue to use fragmented systems — ERP for finance, MES for operations, CRM for customers, etc. This creates data silos where data doesn’t easily travel. Unified data platforms include all these systems, providing manufacturers to view and manage data in one place.
- Example: Microsoft Dynamics 365 is used by manufacturers to unify operations. Companies report up to 33% faster decision-making and 50% less downtime using its predictive maintenance and real-time analytics features.
- Benefit: Improves decision-making by consolidating fragmented data into one accessible platform.
2. Cloud and Edge Integration
Cloud platforms are excellent for scalability and data storage, while edge computing ensures faster decision-making closer to the machines. The integration of both is becoming crucial in factories where milliseconds matter.
- Example: GE Aviation uses edge computing to analyze aircraft engine performance mid-flight, sending only critical data to the cloud for larger trend analysis.
- Benefit: Balances speed (edge) and scalability (cloud), ensuring real-time responsiveness without overwhelming central systems.
3. Cybersecurity for IP and Systems
The more factories use digital technology, the more vulnerable they become to cyberattacks. Ransomware can shut down operations; intellectual property theft can cost companies billions. This has resulted in companies increasingly investing in robust cybersecurity for both IT (networks, data) and OT (machines, robots).
- Example: In 2021, Colonial Pipeline was the target of a ransomware attack that forced it to stop operations, resulting in a loss of millions. It’s all a learning process for manufacturers, who are making up for lost time with some layered security.
- Benefit: As part of evolving manufacturing industry trends, integrated platforms and cybersecurity measures are now crucial for protecting sensitive data and IP.
The Rise of Open-source AI agents: Key Benefits and Popular Frameworks
Explore how open-source AI agents automate tasks and boost productivity across industries.
Trend #8 – Emerging Technologies
The emergence of new technologies is changing the way factories work, transitioning away from systems based on efficiency to innovative ecosystems. Though still emerging, these technologies are quickly evolving and demonstrating enormous potential. Tools like quantum computing, 5G, and agentic AI are among the manufacturing industry trends that promise radical transformation for modern factories.
1. Quantum Computing for Simulation
Traditional computers are poorly suited to many highly complex simulations — for instance, trying thousands of material combinations to find what is most durable or most effectively evolving chemical reactions. Quantum computing enables businesses to run these simulations in minutes, rather than years.
- Example: Daimler AG collaborated with IBM for battery material research using quantum computing to find more efficient EV batteries.
- Benefit: Reduces the time required for research and fosters product design innovation.
2. 5G for Factory Connectivity
Factories today rely on interconnected robots, IOT (Internet of Things) devices, and sensors. 5G networks can support a level of ultrafast and low-lag communication that would allow machines to send and receive information in real time without lag.
- Example: Bosch launched private 5G networks in their factories for machine-to-machine communication and enhanced automation effectiveness.
- Benefit: High-speed and more reliable data transfer enables seamless connections between smart factories.
3. Agentic AI for Autonomous Workflows
Beyond predictive analytics, AI is now evolving into agentic systems— autonomous agents empowered to take action, not just provide advice. In industry, agentic AI might autonomously reroute supply chains, reconfigure production lines, or even steer robotic workflows with little to no human help.
- Example: Foxconn (Apple’s manufacturer) is exploring AI-driven robotic process automation to manage and oversee assembly line workflows by itself.
- Benefit: Boosts productivity by enabling self-managing, adaptive factory operations.
Kanerika’s Approach to Data Modernization in Manufacturing
At Kanerika, we specialize in transforming complex manufacturing data environments into scalable, business-ready ecosystems. As a certified Microsoft Data & AI Solutions partner and a strategic collaborator with Databricks, we deliver end-to-end solutions that help manufacturers unlock the full potential of modern architectures like data mesh and lakehouse platforms.
Our expertise spans data integration, advanced analytics, AI/ML, and cloud-native platform development. Using tools like Microsoft Fabric, Azure Synapse, and Databricks Lakehouse, we help manufacturers break down silos, unify data across production, supply chain, and quality systems, and enable real-time decision-making. Whether you’re starting your data modernization journey or scaling a decentralized architecture, Kanerika combines strategic consulting with deep technical delivery to ensure your data flows efficiently and delivers measurable impact.
Our solutions support security, scalability, and the latest manufacturing industry trends for measurable impact.
AI in Predictive Maintenance: Benefits, Best Implementation Strategies, and Use Cases
Discover how AI in predictive maintenance reduces downtime and boosts equipment efficiency.
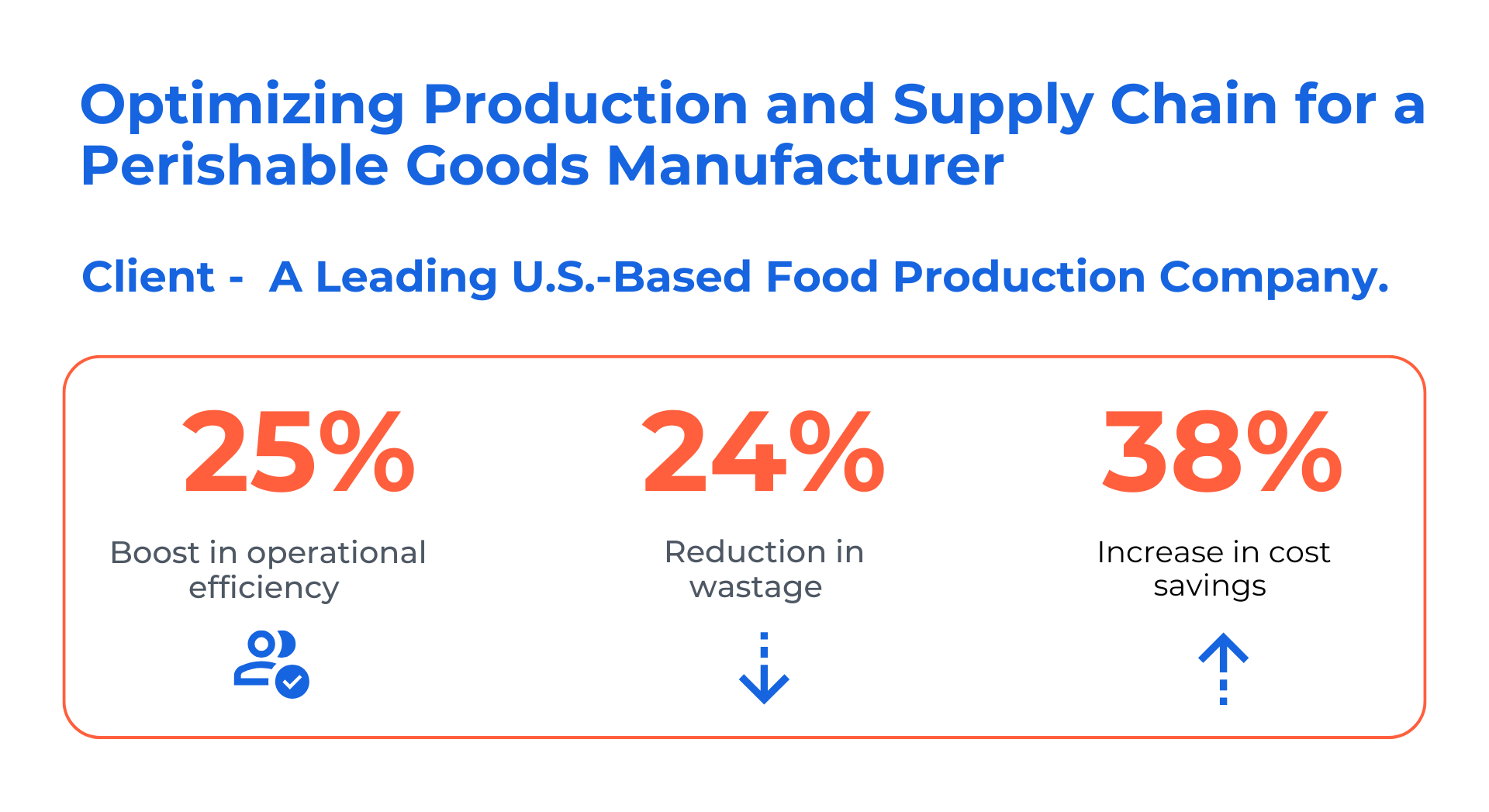
Case Study 1: Optimizing Production and Supply Chain for a Perishable Goods Manufacturer
Client: A leading U.S.-based food production company
Challenge: Inaccurate demand forecasting, production delays, and high wastage due to reliance on historical data
Solution:
- Kanerika implemented AI and ML models that factored in weather and seasonal trends
- Integrated an AI-based demand forecasting engine with the client’s ERP system
- Enabled real-time production planning and scheduling
Results:
- 25% boost in operational efficiency
- 24% reduction in wastage
- 38% increase in cost savings
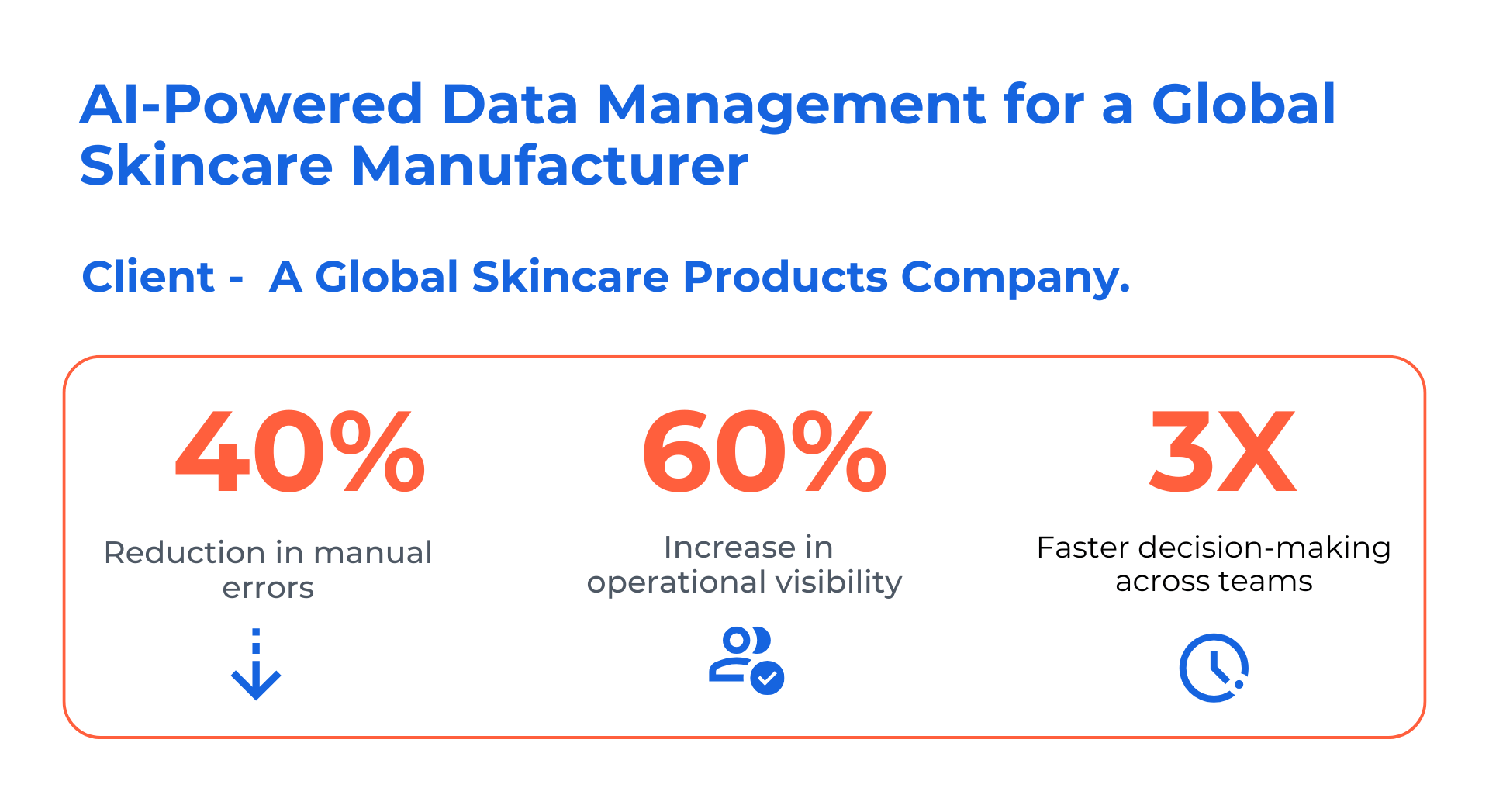
Case Study 2: AI-Powered Data Management for a Global Skincare Manufacturer
Client: A global skincare products company
Challenge: Fragmented data systems and manual reporting processes
Solution:
- Kanerika deployed AI-driven data integration and analytics tools
- Unified data sources across departments for real-time insights
- Improved quality control and production scheduling
Impact:
- 40% reduction in manual errors
- 60% increase in operational visibility
- 3x faster decision-making across teams
Partnering with Kanerika Offers Key Benefits
- Increased efficiency and agility in managing manufacturing data
- Reduced bottlenecks and silos across production and supply chain systems
- Improved data security and governance across cloud and edge environments
- Better alignment between business objectives and data strategy
- Scalable AI and automation frameworks tailored to manufacturing needs
- Real-time insights for predictive maintenance, quality control, and inventory optimization
With Kanerika as your data strategy partner, you can accelerate your journey toward a fully data-driven organization while staying ahead in the latest manufacturing industry trends.
Transform Your Factory with Modern Tech!
Partner with Kanerika to leverage cutting-edge industry trends.
FAQs
1. What are the latest manufacturing trends for 2025?
The latest manufacturing trends include smart factories, AI-driven automation, green manufacturing, digital twins, predictive maintenance, and supply chain resilience. These innovations help manufacturers cut costs, boost efficiency, and stay competitive.
2. What is the next big thing in manufacturing?
The next big thing is Industry 5.0, where humans and advanced machines collaborate. Unlike Industry 4.0’s automation focus, Industry 5.0 emphasizes personalization, sustainability, and human creativity alongside technology.
3. How is AI being used in manufacturing?
AI powers predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, quality control, robotics, and real-time supply chain monitoring. By reducing downtime and errors, AI helps manufacturers increase productivity and profit margins.
4. What is green manufacturing?
Green manufacturing focuses on reducing waste, energy use, and emissions while adopting renewable energy and recyclable materials. It not only supports sustainability but also improves brand reputation and long-term profitability.
5. How are smart factories changing the future of manufacturing?
Smart factories integrate IoT, AI, and data analytics to enable real-time decision-making. They adapt quickly to changes in demand, improve quality, and optimize operations—turning factories into connected, intelligent ecosystems.









