Did you know that IoT can reduce logistics costs by up to 50% and boost overall efficiency by 30%? According to a recent report by DHL, the integration of IoT in logistics and supply chain management is not just an upgrade but a game-changer. With the global IoT market in logistics expected to reach $100 billion by 2025, the technology is proving to be a transformative force.
The integration of IoT in logistics and supply chain operations is becoming increasingly essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive. By leveraging IoT technology, companies can enhance visibility, optimize routes, and ensure the timely delivery of goods.
In this blog, we will explore how IoT is reshaping logistics and supply chain operations, providing real-world examples, key benefits, and the challenges that come with implementing this technology.
How IoT Works in Supply Chain
Integrating IoT (Internet of Things) technology into supply chain management automates and enhances various processes through real-time data collection, device communication, and intelligent analytics. Therefore, let’s look into how IoT works in the supply chain:
Device Linkage and Communication
- Networked Devices: IoT links several devices within the supply chain, such as sensors on cargo containers, RFID tags attached to products, and GPS systems within delivery vehicles. Therefore, this network continuously transmits the status and location of goods.
- Data Transmission: Connected devices transmit data to centralized cloud-based platforms, where it is then aggregated and analyzed. Various connectivity technologies, such as Wi-Fi, cellular networks, and satellite communications, facilitate this transmission, ensuring a consistent flow of information despite geographical locations.
- Improved coordination: The presence of IoT enables better coordination between various aspects involved in the supply chain. For instance, a sensor-based at a warehouse may communicate with the system management once the stock level is low, thereby automating the reordering process.

Collection and Analysis of Data
- Comprehensive Data Harvesting: IoT devices capture a wide variety of data, from temperatures and humilities in storage facilities to speed and routes used by delivery trucks. Additionally, this information helps monitor environmental conditions or handle sensitive products such as medicine or perishable food.
- Advanced Analytics: Sophisticated algorithms analyze collected data to gain actionable insights. Moreover, machine learning models can predict potential delays along the supply chain and suggest optimal vehicle routes that bypass traffic congestion.
- Decision Support: These helpful insights are produced through analysis, thus enabling quick decision-making by the logistics department’s people. Furthermore, predictive analytics can anticipate demand patterns, so managers adjust inventory levels ahead of time for higher sales.
Computerized Decision Processes
- Automation of Repetitive Activities: IoT can be utilized to automate some of the operations within a supply chain, such as inventory management, order processing, or logistics scheduling. Moreover, Sensors are also responsible for updating the system regarding inventory levels, which will include initiating new orders and adjusting storage conditions based on the characteristics of goods.
- Real-time Adjustments: An IoT system can make real-time changes to operations using current data and trends. In case a sudden weather condition disrupts planned delivery routes, the IoT system will instantly send the drivers on alternative roads, ensuring timely delivery.
- Minimized Human Error: By automating decision-making processes, IoT reduces the reliance on manual inputs and minimizes the chances of human error. Therefore, the result is a more reliable and efficient supply chain operation, which reduces waste and increases overall productivity.

The Importance of IoT in Improving Supply Chain Efficiency
1. Real-time Tracking
IoT enables real-time tracking of shipments, inventory, and assets throughout the supply chain. With sensors and GPS devices, companies can monitor the location and condition of goods at every stage, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing the risk of loss or damage. This visibility allows for proactive decision-making and swift responses to any issues that arise.
2. Optimized Inventory Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) automatically tracks inventories using predictive analytics for inventory levels. Hence, this minimizes the chances of overstocking or running out, optimizing inventory costs and space utilization.

3. Cost Efficiency and Reductions
The Internet of Things (IoT) optimizes delivery routes and schedules to reduce fuel consumption and other operational costs. Additionally, automated processes minimize reliance on human labor, lowering expenditures and reducing errors.
4. Improved Customer Satisfaction
IoT technology improves delivery accuracy. As a result, Customer-facing applications track deliveries in real-time, thus improving customer service deliverables and resulting in satisfaction.
5. Enhanced Supply Chain Agility
Market changes can be quickly responded to using IoT tools to manage demand fluctuations. Moreover, this flexibility is pertinent for staying competitive in dynamic markets.

8 Key Applications of IoT in Supply Chain Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) has several applications that improve the efficiency and responsiveness of supply chain management. Here are eight main uses where IoT is having the most effect:
1. Inventory Management
- Automated Tracking: IoT devices can automatically track inventory levels, reducing the need for manual stock counts. Moreover, they also help update records online, hence saving time.
- Predictive Analytics: Sensors combined with data analytics warn about shortages and excesses. Thus, they enable advanced ordering and optimize inventory levels.
- Enhanced Visibility: This system allows all stakeholders to monitor their stocks wherever they are distributed, leading to better planning and resource allocation.
2. Asset Tracking
- Real-time Location Data: Companies can track their assets in real-time using GPS and RFID technology that come with IoT.
- Condition Monitoring: Sensors may continuously monitor assets’ conditions, sending alarms about potential problems before they occur.
- Loss Prevention: IoT constantly monitors valuable assets, which helps reduce thefts and losses.
3. Fleet Management
- Route Optimization: Information regarding traffic patterns and weather conditions is analyzed with the aid of IOT gadgets.
- Vehicle Maintenance: Fleet vehicles will only need repair from breakdowns when required through notifications made by IOT sensors. Therefore, it helps avoid downtime and increases vehicle life expectancy.
- Fuel Efficiency: Driving habits, along with other vehicle usage habits, can be monitored to minimize fuel consumption and decrease fuel expenses.
4. Supply Chain Visibility
- End-to-End Tracking: From raw materials to delivery, the entire supply chain is transparent due to the IoT’s improved response rate during disruptions.
- Integration with Partners: A thin line exists between suppliers and distributors, especially when receiving real-time information about some specific item directly from its manufacturer—this enhances coordination among different parties within this value chain.
- Consumer Insights: Real-time data helps companies understand what customers want before others catch up with them.
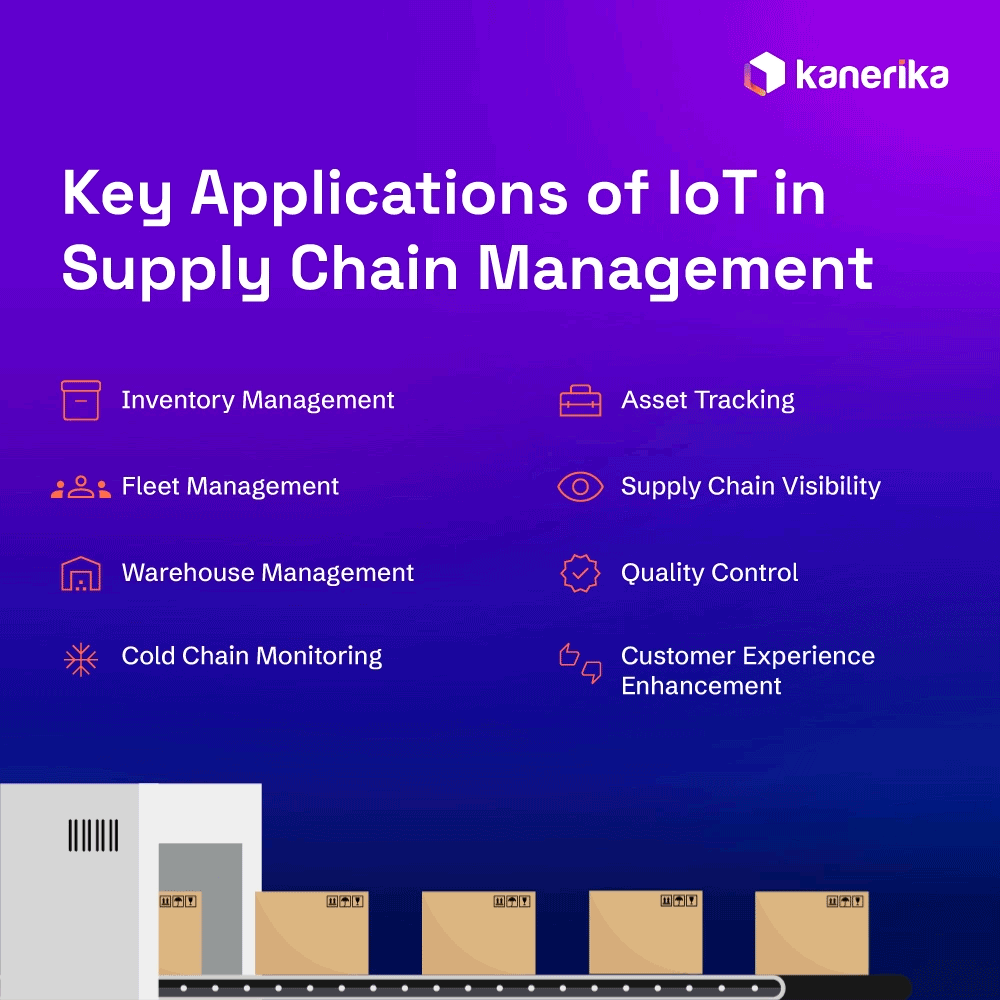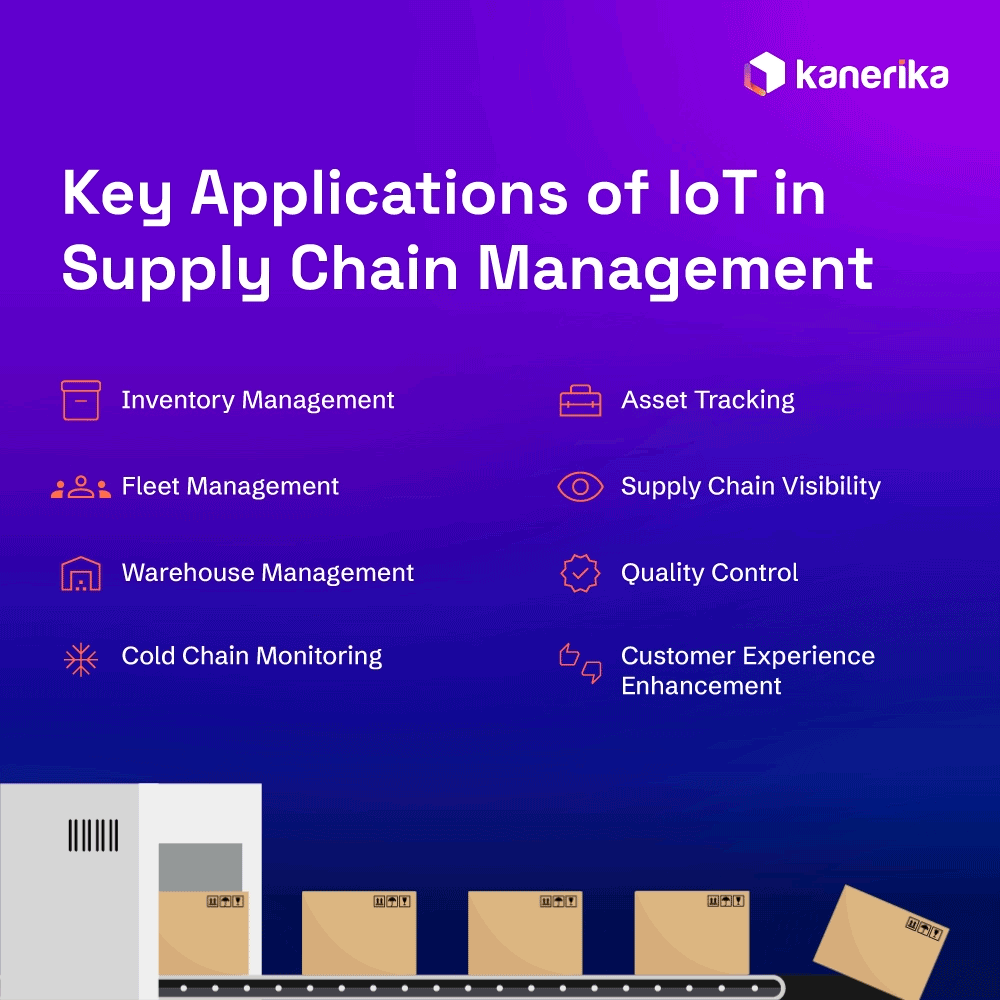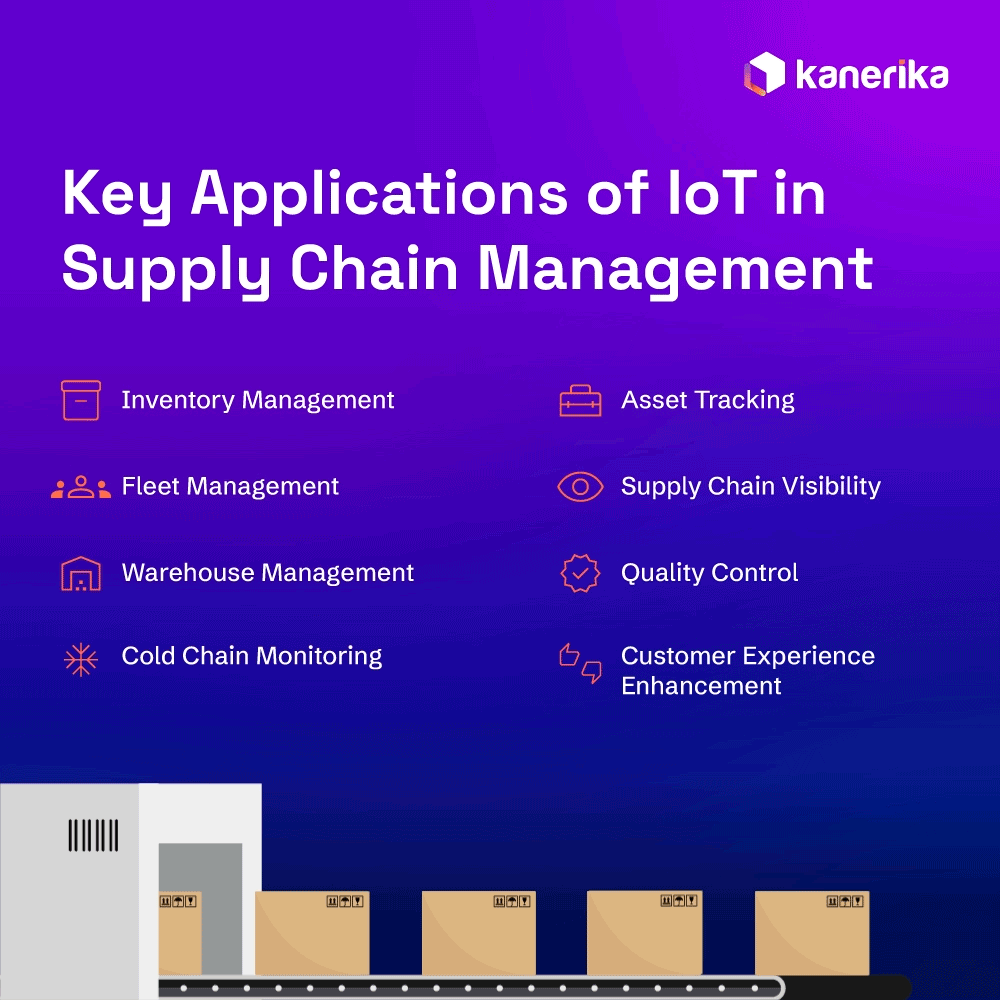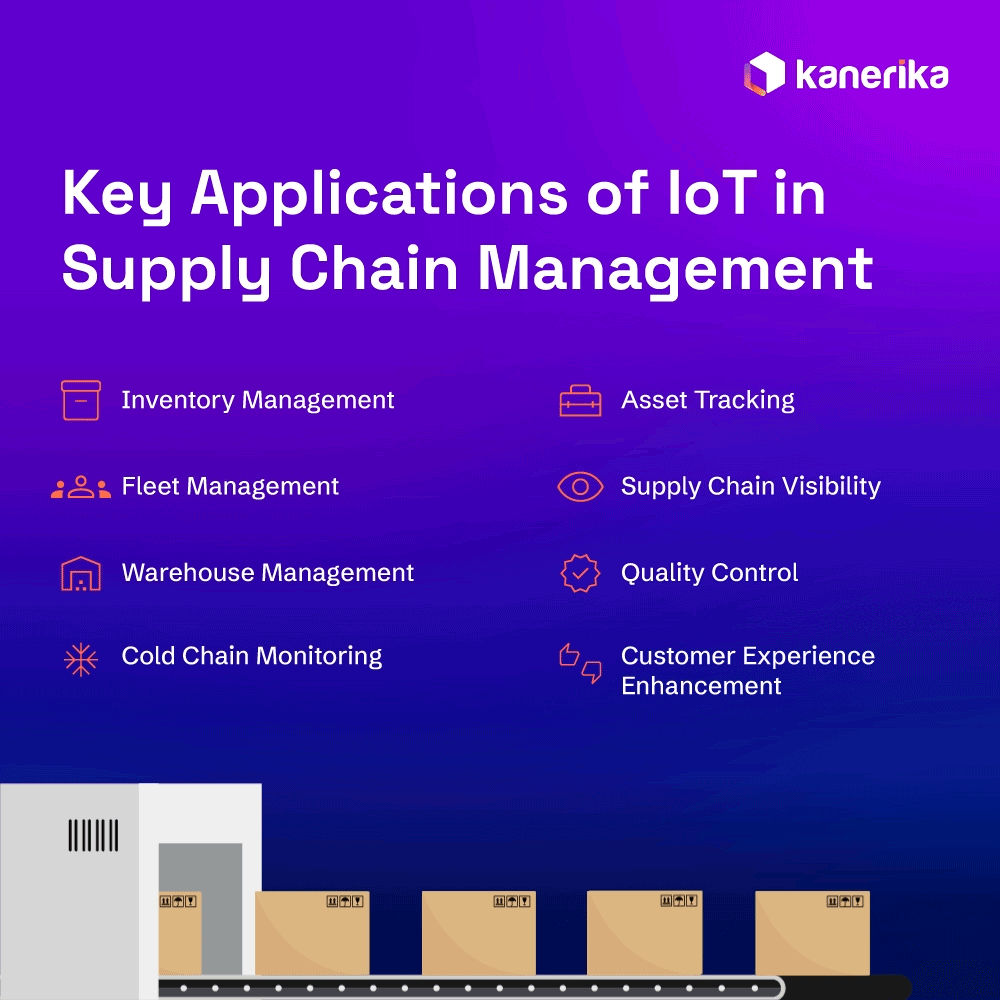
5. Warehouse Management
- Automated Warehousing: Robots and automated systems equipped with IoT technology can handle picking, packing, and storing goods more efficiently.
- Environmental Monitoring: Temperature and humidity conditions might be tracked within warehouses, thereby enabling the proper storage of goods.
- Space Optimization: These devices assist in managing warehouse layout and storage, maximizing the use of space and resources.
6. Quality Control
- Consistent Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of production lines by IoT devices aimed at identifying any variance from quality standards to enable immediate corrective actions.
- Product Authenticity: Counterfeit products can be identified using IOT, which can trace a product’s journey from manufacturer to consumer.
- Compliance Monitoring: Others ensure all their supply chains are audited and meet regulatory compliance requirements, such as labor standards or environmental protection laws.
7. Cold Chain Monitoring
- Temperature Control: In this regard, relevant IoT gadgets continuously check the temperature state of perishable products during the transportation chain.
- Alert Systems: If storage conditions deviate from preset limits, alerts are generated through IoT devices, which prevent spoilage.
- Regulatory Compliance: IoT makes compliance more accessible by ensuring that safety regulations are followed during handling and transportation.
8. Customer Experience Enhancement
- Delivery Precision: Delivery schedules become more accurate based on data received by IOT (Internet of Things), hence increasing customer satisfaction.
- Personalized Interactions: Smart retailing is an excellent example of personalized interactions between companies and consumers. Consequently, it creates custom recommendations for each client, including proactive services delivered even before being asked.
- Enhanced Communication: Many businesses lack effective communication strategies, especially when it comes to updating customers about delivery times or order status, which could be changed through IoT.
Navigating the Challenges of Implementing IoT
1. Data Security and Privacy
It is a significant concern when IoT devices gather vast amounts of data, posing risks of data breach and privacy. Moreover, this risk increases if more gadgets and data points are involved.
Therefore, companies must have good security measures such as robust encryption, safe communication protocols and regular security auditing. In addition, it is important for businesses to keep the trust among their stakeholders and adhere to the rules.
2. Integration With Existing Systems
Another big challenge is integrating IoT technology with existing logistics and supply chain systems. If the existing infrastructure cannot accommodate the flood of data from IoT devices, compatibility issues may arise, which may cause potential disruptions.
Therefore, companies need scalable solutions and open standards that support seamless integration. Moreover, this may mean updating old systems or adopting middleware solutions from old technologies to new ones.

3. High Implementation Costs
The capital expenses associated with deploying IoT devices and the required infrastructural upgrades could be relatively high initially. Additionally, this includes the cost of purchasing these devices and expenditures on network enhancements, data storage means, and continuous maintenance.
Therefore, undertaking a thorough cost-benefit analysis while considering phased implementation will enable firms to manage costs successfully.
4. Data Management and Analytics
IoT generates voluminous amount of data making its management a major challenge. For one to make informed decisions out of this information, there is need for companies to have advanced analytical tools that can process it into actionable insights.
Thus, investing in big data technologies will be necessary whereas expert staff should also be hired to handle and evaluate large sets of data. Efficient data management strategies are crucial for leveraging the full potential of IoT.
5. Interoperability
One of the most challenging aspects is the diverse nature of IoT devices and platforms, which requires them to communicate with one another efficiently. Moreover, the absence of proper rules for standardizing operations may lead to fractionalization and inefficiency. Companies should choose IoT solutions that comply with industry standards and promote interoperability.

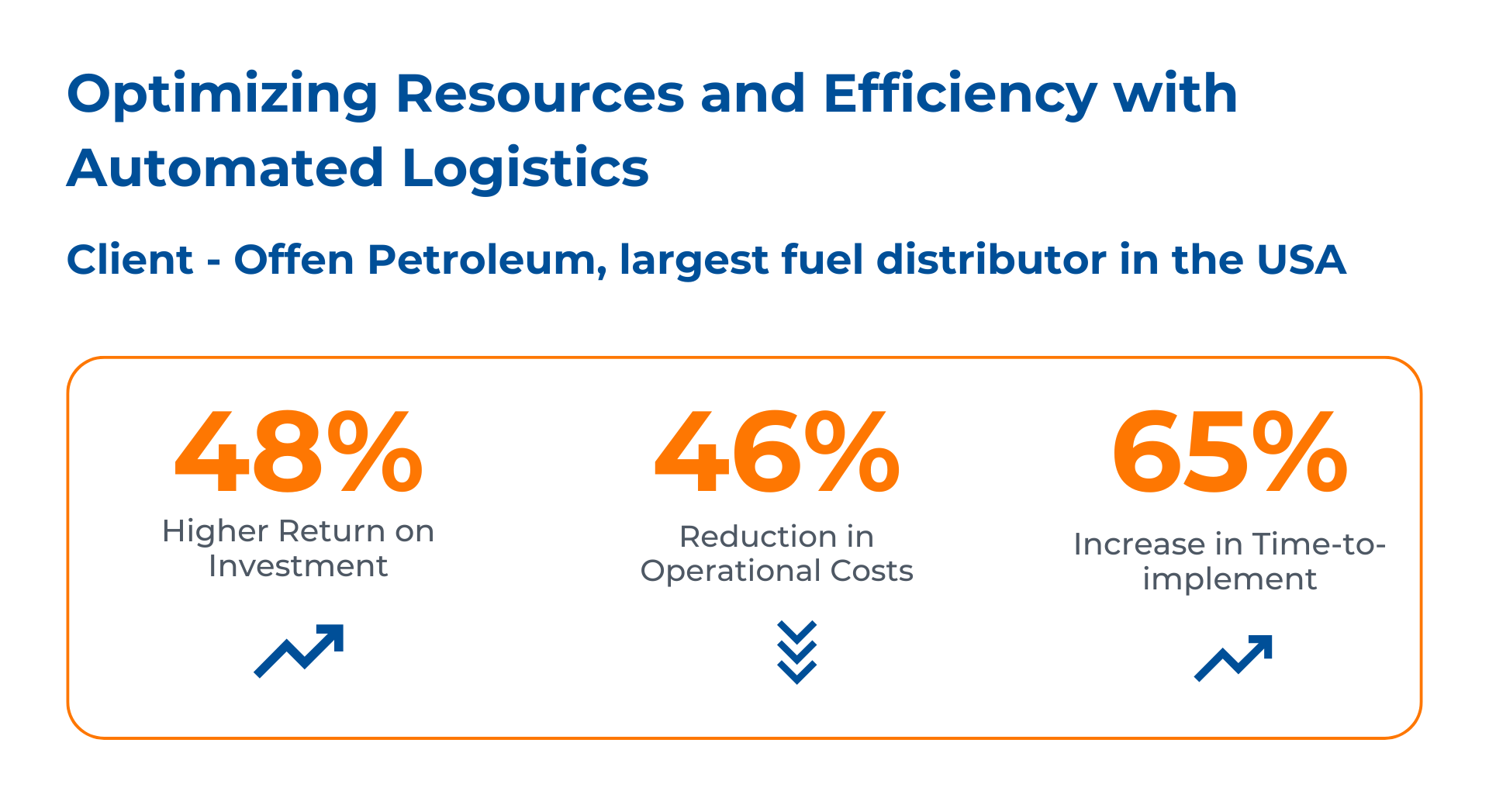
Case study: Optimizing Resources and Efficiency with Automated Logistics Operations
The client, Offen Petroleum, is one of the largest fuel distributors in the USA, specializing in logistics, warehousing, and distribution services.
However, they faced multiple challenges, including heavy reliance on manual data entry and repetitive tasks within their NetSuite application, leading to data inaccuracies and significant operational delays. The lack of automated processes disrupted workflows, reduced productivity, and hindered the organization’s ability to respond quickly to increasing demands.
Kanerika solved their challenges by:
- Automating data entry, navigation, validation processes,resulting in significant improvement in operational efficiency
- Developing automated test scripts within the NetSuite application, covering critical workflows,using the programming language Java
- Mapping out end-to-end workflows for AP processes, ensuring seamless transitions from draft creation to refund handling, which eliminated bottlenecks and enhanced process visibility
How Global Brands Transform Their Supply Chains and Logistics with IoT
1. Amazon
- Robotics and Automation: Amazon has embraced IoT using advanced robotics and automated systems that speed up order processing and minimize human errors. As a result, the robots are always in contact with the store’s inventory system to update stock levels and optimize warehouse operations.
- Dynamic Routing: Real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and delivery schedules allow Amazon’s vehicles to use dynamic routing through IoT technology. Therefore, this enables them to reduce delivery times and improve customer service.
2. Walmart
- Inventory Management: Walmart uses IoT for more efficient inventory management. By using RFID tags, Walmart can follow products throughout its supply chain so that they are kept within stock limits without running out.
- Energy Efficiency: Walmart stores use IoT sensors to manage energy consumption effectively. Moreover, these sensors adjust lighting and HVAC systems based on prevailing store conditions, leading to substantial energy savings.
3. Maersk
- Container Tracking: For real-time container tracking worldwide, Maersk, one of the world’s largest shipping companies, uses IoT devices. These devices also provide location updates and condition monitoring for temperature-sensitive cargoes.
- Predictive Maintenance: Through ship-based IOT sensors, equipment condition monitoring is done, with the ability to predict when failures may occur, minimizing downtime while also extending equipment life spans.
4. DHL
- Smart Warehouses: DHL has introduced it into its logistics, making more innovative warehouses so that better picking processes can be affected inside these establishments’ premises.
- Asset Tracking: Thanks to IOT technologies, DHL operations are enhanced in security and efficiency. Moreover, IOT helps track assets’ exact locations and statuses at any moment as they move within a business environment.
5. Ford
- Supply Chain Transparency: Ford uses the Internet of Things (IoT) to monitor different parts of its supply chain and ensure that parts are delivered on time to sustain the smooth running of the production line.
- Enhanced Manufacturing Processes: IoT sensors in manufacturing equipment enable Ford to observe performance and predict when maintenance should be conducted to prevent unexpected downtimes.
6. Bosch
- Connected Industry: Bosch has come up with its own IoT Suite for linking different machines and physical infrastructure to the digital world, thus optimizing manufacturing processes while improving product quality through continuous monitoring and analysis.
- IoT-based Predictive Maintenance: Internal implementation, offering similar technology to other manufacturers, by Bosch improves efficiencies resulting in operational cost reduction.

Future Trends and Innovations
1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly converging with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), thereby transforming supply chain management through more advanced data analytics.
Moreover, these innovations enable businesses to predict future events, automate decision-making processes, and improve operational effectiveness.
2. Blockchain for Enhanced Transparency and Security
When blockchain technology is combined with IoT in supply chain management, it provides unprecedented transparency and security.
Furthermore, due to its decentralized nature, it assures a reliable system that cannot be tampered with. Moreover, this is important for industries where authenticity or compliance are significant issues, such as pharmaceuticals or luxury brands.
3. Adoption of 5G technology
Adopting 5G technology will significantly enhance the efficiency of internet-of-things devices used in supply chain management. Additionally, compared to previous technologies like 4G-LTE, etc., 5G has lower latency rates, higher speeds, and superior connectivity density, allowing smoother real-time operation.

4. IoT-Driven Autonomous Logistics
The emerging trend that is likely to revolutionize the transportation and delivery of goods is IoT-driven autonomous logistics. Moreover, self-driving trucks with IoT sensors can develop optimized routes, reducing human errors and the time needed for deliveries alongside drones and autonomous ships.
5. Edge Computing for Faster Processing
The number of IoT devices is increasing, hence the importance of edge computing. Edge computing reduces latency and speeds up response times by performing data processing at the local level rather than in a centralized cloud system.
6. Enhanced Customer Experience
IoT has become an integral part of improving customer experience by providing real-time updates and personalized services. Additionally, with this technology, customers can accurately trace their orders, receive notifications about shipping status, and even give instructions to drivers during delivery. Besides enhancing customer satisfaction, it also promotes loyalty to the brand.
Choose Kanerika for Cutting-Edge IoT-driven Logistics Transformation
Kanerika stands at the forefront of technological innovation, transforming business processes and outcomes across industries. By leveraging state-of-the-art technologies such as AI/ML, Data Analytics, IoT, Data Governance, and RPA, we help businesses tackle their challenges, fortify their market position, and gain a competitive edge.
Integrating advanced technologies like IoT in logistics can be game-changing, offering numerous benefits. These include enhanced real-time tracking, optimized route planning, streamlined operations, cost reduction, and data-driven decision-making. IoT enables precise shipment monitoring, facilitates efficient inventory management, and provides valuable insights for proactive supply chain strategies.
Partner with Kanerika to revolutionize your logistics processes, driving innovation and growth. Our customizable IoT solutions are tailored to meet your specific needs, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems. By choosing us, you’re not just adopting technology – you’re embracing a future of operational excellence, improved efficiency, and a strong competitive advantage in the ever-evolving logistics landscape.

Frequently Asked Questions
How is IoT used in logistics?
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolutionizes logistics by tracking goods in real-time using sensors and connected devices. This provides unprecedented visibility into the supply chain, optimizing routes, predicting delays, and improving overall efficiency. Essentially, IoT transforms “guesswork” into data-driven decision-making across the entire shipping process. This leads to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
How is IoT used in supply chains?
The Internet of Things (IoT) boosts supply chain efficiency by tracking goods in real-time via sensors and connected devices. This provides unparalleled visibility into location, condition, and temperature, minimizing delays and waste. Data gathered allows for predictive maintenance and optimized routing, leading to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction. Ultimately, IoT transforms supply chains from reactive to proactive systems.
What are the 4 types of IoT?
The four main types of IoT aren’t rigidly defined categories, but rather represent different deployment scales and application focuses. We see consumer IoT (smart homes, wearables), industrial IoT (smart factories, predictive maintenance), commercial IoT (retail analytics, smart buildings), and automotive IoT (connected cars, fleet management). These often overlap, and many devices span multiple types. Essentially, it’s about *where* and *how* IoT is used.
What is the future of IoT in logistics?
The future of IoT in logistics is one of hyper-efficiency and real-time visibility. Imagine a world where every package’s journey is tracked seamlessly, predicting delays and optimizing routes automatically. This means less waste, faster delivery, and a significantly improved customer experience, driven by interconnected sensors and data analysis. Ultimately, IoT will transform logistics from reactive to proactive, creating a more agile and responsive supply chain.
How Amazon uses IoT in supply chain?
Amazon leverages IoT extensively to optimize its supply chain. Sensors on packages and in warehouses track location and conditions, enabling real-time monitoring and proactive issue resolution. This data-driven approach improves delivery speed and accuracy while minimizing waste and enhancing overall efficiency. Ultimately, IoT helps Amazon deliver your packages faster and more reliably.
How to use AI in logistics?
AI revolutionizes logistics by optimizing routes and predicting demand, leading to significant cost savings and faster delivery. It automates tasks like warehouse management and inventory tracking, freeing human workers for more complex roles. AI-powered predictive analytics improve forecasting accuracy, minimizing stockouts and overstocking. Ultimately, it enhances efficiency and responsiveness across the entire supply chain.
How big is the logistics IoT market?
The logistics IoT market is massive and rapidly growing, driven by the need for real-time visibility and efficiency gains across supply chains. Its size is difficult to pinpoint exactly, varying by definition (hardware vs. software, etc.) but estimates reach tens of billions of dollars annually and are projected to expand significantly. Think of it as a constantly evolving ecosystem fueled by connected devices tracking everything from containers to individual packages.
What is an example of IoT in a warehouse?
Imagine smart shelves in a warehouse automatically tracking inventory levels and alerting staff when stock is low. This is IoT in action – sensors on the shelves relay data wirelessly to a central system, optimizing stock management and reducing waste. It’s about connecting physical items to the internet for real-time, efficient control. This boosts productivity and streamlines operations.
What is the difference between IoT and M2M?
IoT is the broader concept encompassing all interconnected devices, including those with user interaction, while M2M focuses solely on machine-to-machine communication without direct human involvement. Think of IoT as the overarching ecosystem, and M2M as a specific subset within it, like automated industrial processes. Essentially, all M2M is IoT, but not all IoT is M2M.
What are the benefits of IoT in transportation?
IoT in transportation boosts efficiency and safety by connecting vehicles and infrastructure. Real-time data improves route optimization, predictive maintenance reduces downtime, and smart traffic management eases congestion. Ultimately, this leads to lower operational costs and a smoother, safer journey for everyone. Increased security through connected vehicle communication is another key advantage.
Is IoT used in supply chain?
Yes, the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing supply chains. Sensors and connected devices track goods in real-time, providing unprecedented visibility into their location and condition. This allows for proactive issue resolution, optimized routing, and reduced waste, ultimately boosting efficiency and responsiveness. Essentially, IoT transforms a traditionally opaque system into a highly transparent and manageable one.
How is IoT used in fleet management?
IoT revolutionizes fleet management by constantly tracking vehicle location, performance, and driver behavior through sensors and GPS. This real-time data allows for optimized routing, predictive maintenance (preventing breakdowns), and improved fuel efficiency, ultimately cutting operational costs. Essentially, IoT provides a complete, connected view of your entire fleet, boosting productivity and safety.
How is IoT used in inventory management?
IoT streamlines inventory management by using sensors and trackers on items and in storage areas. This provides real-time visibility into stock levels, location, and even condition, eliminating manual counts and reducing discrepancies. Predictive analytics based on this data optimizes ordering and minimizes waste. Ultimately, IoT improves accuracy and efficiency across the entire supply chain.
What is IoT in supply chain?
IoT in supply chain uses smart sensors and devices to track products and assets in real-time. These devices gather data on their location, condition, and environment as they move. This provides enhanced visibility, improves efficiency, and helps make better decisions from manufacturing to delivery.
What are the 5 C's of IoT?
The 5 C’s of IoT describe the steps from device data to meaningful action: 1. Connect devices and Collect their raw data. 2. Communicate this data for processing, then Contextualize it to gain insights. 3. Finally, Control systems or take specific actions based on these insights.
What are the 7 C's of logistics?
The 7 C’s of logistics isn’t a single official list, but commonly refers to critical success factors. These include focusing on the Customer, optimizing Cost and Capital, maintaining Control over processes, ensuring strong Collaboration and Communication, and planning for operational Continuity. They help ensure efficient and reliable delivery of goods and services.
What are the 4 pillars of IoT?
The 4 pillars of IoT are: the devices that collect data, the connectivity that sends it, the data processing that makes sense of it, and the user applications that allow interaction. These elements work together to create smart, connected systems.
What are the 4 main components of IoT?
The 4 main components of IoT are: 1. Smart Devices: The sensors and gadgets that collect data from the physical world. 2. Connectivity: How these devices send that data over networks like Wi-Fi or cellular. 3. Data Processing: Where all that collected data is stored, analyzed, and turned into useful information. 4. User Interface: The apps and dashboards you use to see the insights and control your devices.
What are the three types of logistics?
The three main types of logistics are: Inbound Logistics: Managing the flow of materials and supplies coming into your business. Outbound Logistics: Overseeing the movement of finished products from your business to customers. Reverse Logistics: Handling product returns, repairs, and recycling.
What are IoT 5 examples?
IoT connects everyday objects to the internet. Examples include smart home devices (like thermostats and lights), wearables (such as smartwatches), connected cars for navigation and safety, smart city solutions (like intelligent traffic lights), and industrial sensors for monitoring factory equipment.
How does DHL use IoT?
DHL uses IoT for real-time tracking of packages and shipments. Sensors monitor critical conditions like temperature for sensitive goods. This data helps them optimize routes and improve overall logistics efficiency.
How big is the IoT logistics market?
The IoT logistics market is already substantial and experiencing rapid growth. It was valued at around $30-35 billion in 2022/2023. Forecasts suggest it will more than double, potentially exceeding $80 billion by 2030. This highlights its expanding use in tracking and managing goods.
How does Coca-Cola use IoT?
Coca-Cola uses IoT mainly in its smart vending machines, like the Freestyle dispensers. These machines monitor inventory levels, report maintenance needs automatically, and track popular drink choices. This helps them ensure machines are always stocked, serviced quickly, and offer the beverages customers want most efficiently.
What is the role of information technology in logistics?
Information technology optimizes logistics by providing real-time tracking of goods and vehicles. This helps companies plan routes efficiently, manage inventory precisely, and ensure timely, accurate deliveries. Ultimately, it makes the entire supply chain faster, smarter, and more cost-effective.
What are the sensors used in logistics?
Logistics uses sensors like GPS and RFID tags to track items’ locations and identify them. Temperature and humidity sensors monitor environmental conditions for sensitive goods. Barcode scanners and proximity sensors automate sorting and movement in warehouses. Accelerometers can also detect if a package experiences shock.
What is logistic technology?
Logistic technology involves digital tools and systems that help manage and optimize the flow of products from origin to destination. This includes software for tracking shipments, managing inventory, and planning the most efficient routes. Its goal is to make the entire supply chain faster, smarter, and more reliable.