If you want to improve your business processes, you may have encountered the terms Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Automation (IA). While they may sound similar, there are critical differences regarding RPA vs IA.
RPA technology uses software robots to automate repetitive, rules-based tasks. These robots operate continuously without fatigue or errors, allowing human employees to concentrate on more complex work.
On the other hand, IA uses artificial intelligence (AI) technologies like machine learning and natural language processing to automate more complex processes involving unstructured data.
Understanding the differences between RPA and IA is essential when deciding which technology to implement in your organization. Choosing the right technology for your needs can improve efficiency and reduce costs in your organization.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a type of automation technology that uses software robots or bots to automate repetitive, rules-based tasks. RPA bots can mimic human actions, such as data entry, by interacting with applications as humans do.
RPA is particularly useful for mundane, repetitive tasks requiring little to no decision-making. It is also ideal for tasks that follow defined rules and can be easily automated.
RPA bots can be programmed to perform tasks much faster than humans, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. They can also work around the clock, meaning 24×7 task accomplishment without human intervention.

One of the key benefits of RPA is that it can be implemented quickly and easily. RPA bots can be deployed without extensive IT infrastructure or complex coding. This means that organizations can start reaping the benefits of RPA speedily and with minimal disruption to their existing processes.
Overall, RPA is a powerful tool for task automation that can help organizations reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve accuracy.
Exploring Intelligent Automation
Intelligent Automation (IA) is a combination of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies. It is also referred to as Intelligent Process Automation (IPA).
IA or IPA leverages machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and other cognitive technologies to automate end-to-end processes. IA is a more advanced solution than RPA alone, as it can handle exceptions and more creative tasks that require decision-making.
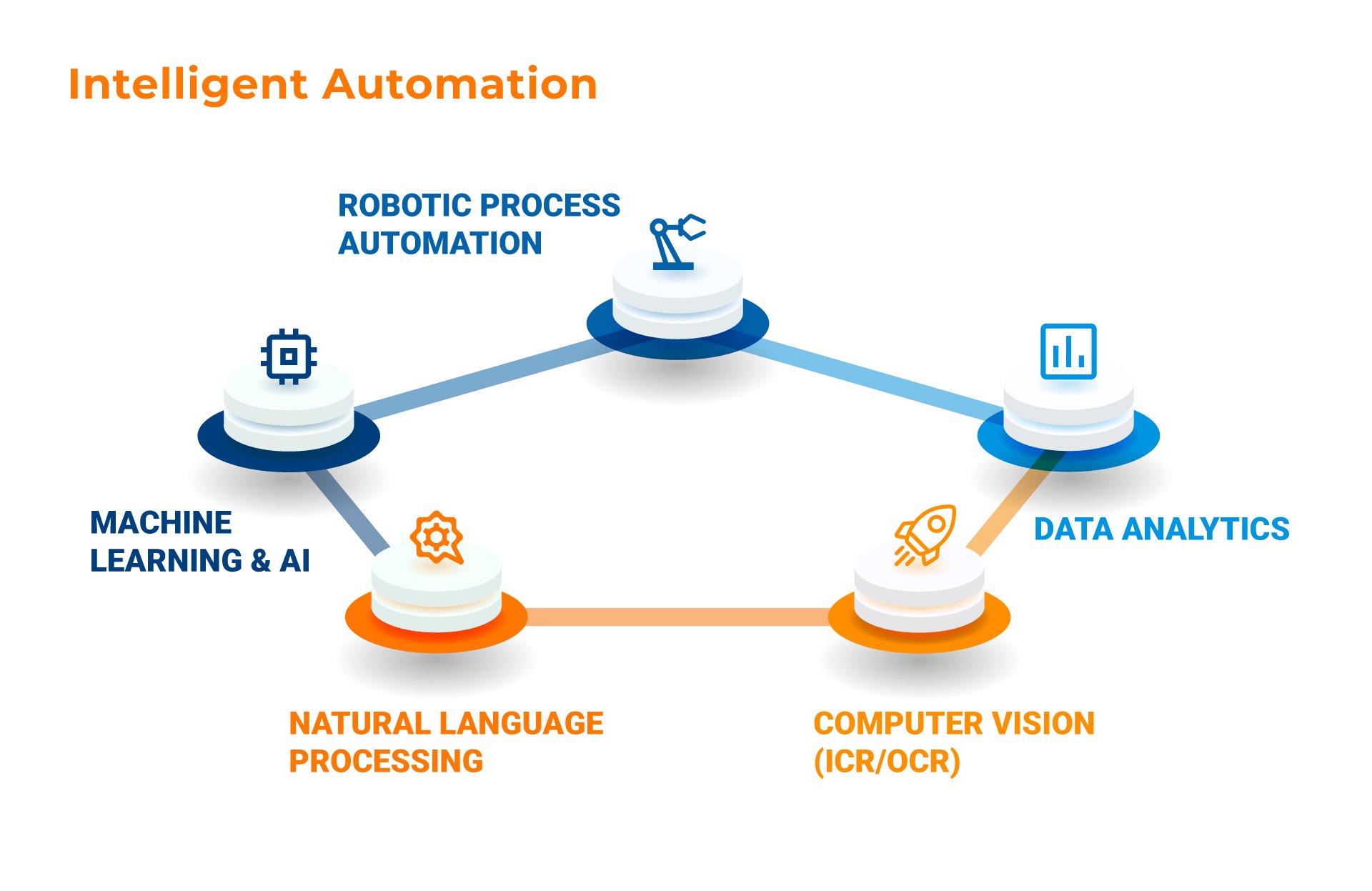
One of the key components of IA is machine learning (ML). This technology enables the system to learn from patterns and data analysis, improving its decision-making abilities. This makes IA a powerful tool for businesses seeking to improve their operations and increase efficiency.
Another essential component of IA is NLP. This technology allows the system to understand and interpret human language, automating tasks that require communication with customers or employees. Chatbots and application programming interfaces (APIs) are examples of IA solutions that leverage NLP to automate customer service and other communication-related tasks.
Also read- Understanding Intelligent Automation: An In-Depth Guide
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) is another area where IA can be applied. IDP uses optical character recognition (OCR) technology to extract data from documents and automate processes previously done manually. This technology benefits businesses that handle large documents, such as invoices or contracts.
Overall, IA solutions are designed to automate end-to-end processes that require decision-making and creative problem-solving. By leveraging advanced algorithms and cognitive technologies, IA can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and free up employees to focus on higher-level tasks.

RPA vs IA
Regarding process-centric automation, there are two main approaches: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Automation (IA). While both RPA and IA aim to automate rule-based processes, their capabilities and scope differ significantly. This section will discuss the key differences between RPA and IA.
Key Differences
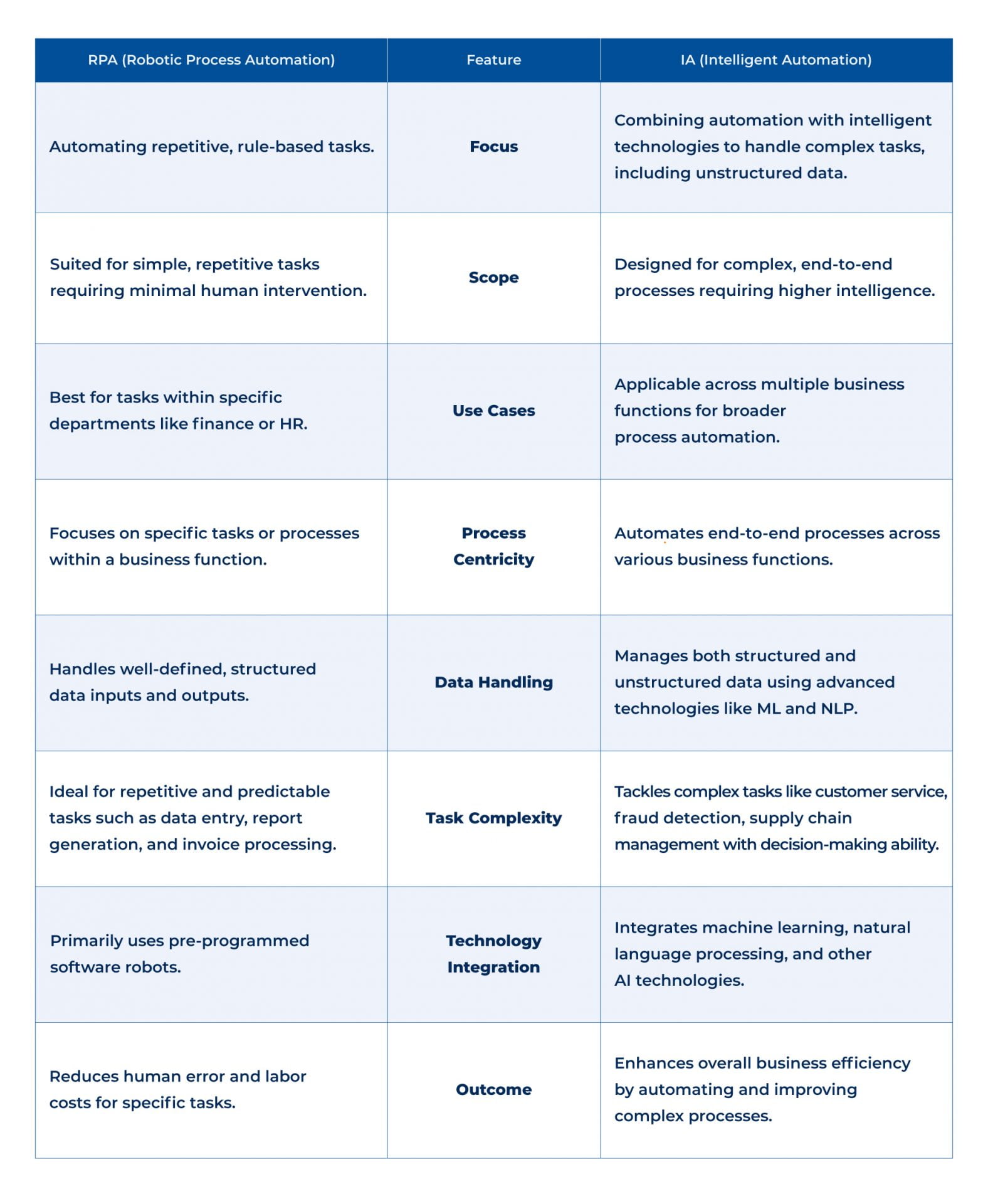
The main difference between RPA and IA is that RPA focuses more on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks. At the same time, IA combines automation with intelligent technologies to handle structured and unstructured data, make decisions, and perform high-functioning tasks. RPA is best suited for automating simple, repetitive tasks that require minimal human intervention. In contrast, IA can tackle more complex end-to-end processes requiring more intelligence.
Another significant distinction is that RPA mainly automates tasks within specific departments like finance or HR, whereas IA automates processes throughout the organization, covering various business functions.
Process-Centric Automation
RPA automates specific, rule-based tasks within a single business function, reducing errors and labor costs with programmed ‘robots. While also automating processes, IA extends across multiple functions using technologies like machine learning, handling both structured and unstructured data.
Rule-Based Processes
RPA is suitable for automating rule-based processes, where the inputs and outputs are well-defined and the tasks are repetitive and predictable. Moreover, RPA can automate data entry, report generation, and invoice processing tasks. RPA robots can follow rules and perform specific actions based on their input.
IA, on the other hand, is designed to handle both rule-based and non-rule-based processes. Additionally, IA uses machine learning and other AI technologies to analyze data and make decisions based on that data. IA can be used to automate processes such as customer service, fraud detection, and supply chain management.
Read more: Experience the Future of Operations: Kanerika’s Robotic Process Automation Services
Applications of RPA and IA
The truth is, both RPA and IA can automate tedious and repetitive tasks, streamline workflows, and reduce operational costs. RPA is particularly useful for jobs that involve structured data processing, such as invoice and payroll processing. On the other hand, IA can handle both structured and unstructured data, making it a better fit for tasks that require decision-making and interaction with natural language.
One of the key benefits of both automation technologies is a significant increase in productivity and efficiency. Automating manual processes allows employees to focus on more high-value tasks, leading to faster turnaround times and better customer service. Additionally, real-time processing and automation can help reduce errors and improve accuracy.
Another benefit of automation is cost savings. By reducing the need for manual labor, businesses can save on operational costs and reduce the risk of human error. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and improved customer experience.
In the healthcare industry, RPA and IA can process large amounts of data quickly and accurately, improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. Similarly, in supply chain management, automation can help streamline processes and reduce the risk of errors.
The ROI of implementing RPA and IA can be significant, particularly for high-volume, tedious tasks. By leveraging automation experts and collaborating with employees, businesses can identify areas where automation can be most effective and achieve the most significant cost reduction and efficiency gains. Additionally, IA can be handy for fraud detection and other tasks that require complex decision-making.

Expert Intelligent Automation Consulting Solutions
Get expert intelligent automation consulting to modernize processes, enhance performance, and implement scalable AI-driven automation solutions.
Role of AI and ML in RPA and IA
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) play a significant role in both Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Automation (IA). In RPA, use of AI and ML enables the analysis of data patterns and automates repetitive tasks. AI simulates human intelligence in machines, while RPA automates processes that use structured data and logic.
In IA, AI and ML automate complex decision-making processes and enable cognitive automation. IA combines several automation technologies, such as cognitive automation, machine learning, business process automation (BPA), and RPA. These technologies work together to automate end-to-end business processes and improve efficiency.
The use of ML in IA enables deep learning and predictive analysis. Deep learning algorithms allow machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time. Predictive analysis uses historical data to identify patterns and predict future outcomes. This helps businesses make data-driven decisions and improve their overall performance.
AI and ML in IA also enable natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision. NLP enables machines to understand and interpret human language, while computer vision enables machines to interpret and analyze visual data. These technologies automate customer service, data entry, and image recognition tasks.
Overall, AI and ML are essential components of both RPA and IA. They enable businesses to automate complex processes, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions. By leveraging these technologies, companies can stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital world.

Challenges and Solutions in Implementing RPA and IA
Deciding RPA vs IA can be challenging. However, with the right strategy and approach, these technologies can help transform your company’s operations, improving effectiveness, output, and time-to-market.
Unstructured Data
One of the challenges of implementing RPA and IA is dealing with unstructured data. Unstructured data refers to data that does not have a predefined data model or format, such as emails, social media posts, and images. To overcome this challenge, you can use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to extract relevant information from unstructured data.
Exceptions
Another challenge in implementing RPA and IA is handling exceptions. Exceptions are situations outside the normal process flow and require human intervention. To address this challenge, you can use software bots that can handle exceptions by following predefined rules or learning from previous exceptions.
Scalability
Scalability is a significant challenge when implementing RPA and IA. As your business grows, you must scale your automation processes to handle increased workload and complexity. To address this challenge, you can use AI-powered platforms that merge the swiftness and efficacy of traditional RPA with AI’s flexibility and decision-making prowess.
Case Study- Reading and Writing Shipment Information from PDF using RPA
Human Work and Thinking
RPA and IA can automate many routine tasks that humans previously performed. However, some jobs require human thinking, such as creative problem-solving and decision-making. To address this challenge, you can use RPA and IA to augment human capabilities and save time for more critical tasks.
Data Management and Integration
Data management and integration are essential when implementing RPA and IA. You must ensure that your automation processes can access accurate and up-to-date data from various sources. To address this challenge, you can use business process management (BPM) tools that provide a unified view of your data and automate data integration processes.

Automation Strategy
Developing an automation strategy is critical to the success of your RPA and IA implementation. You need to identify the right processes to automate, define clear goals and metrics, and establish a governance framework. To address this challenge, you can use an automation strategy framework that provides a step-by-step guide to developing your automation strategy.
In conclusion, implementing RPA and IA can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can overcome these challenges and reap the benefits of automation. By addressing challenges such as unstructured data, exceptions, scalability, human work and thinking, data management and integration, and automation strategy, you can ensure a successful implementation of RPA and IA.
How to Implement RPA and IA in Your Organization
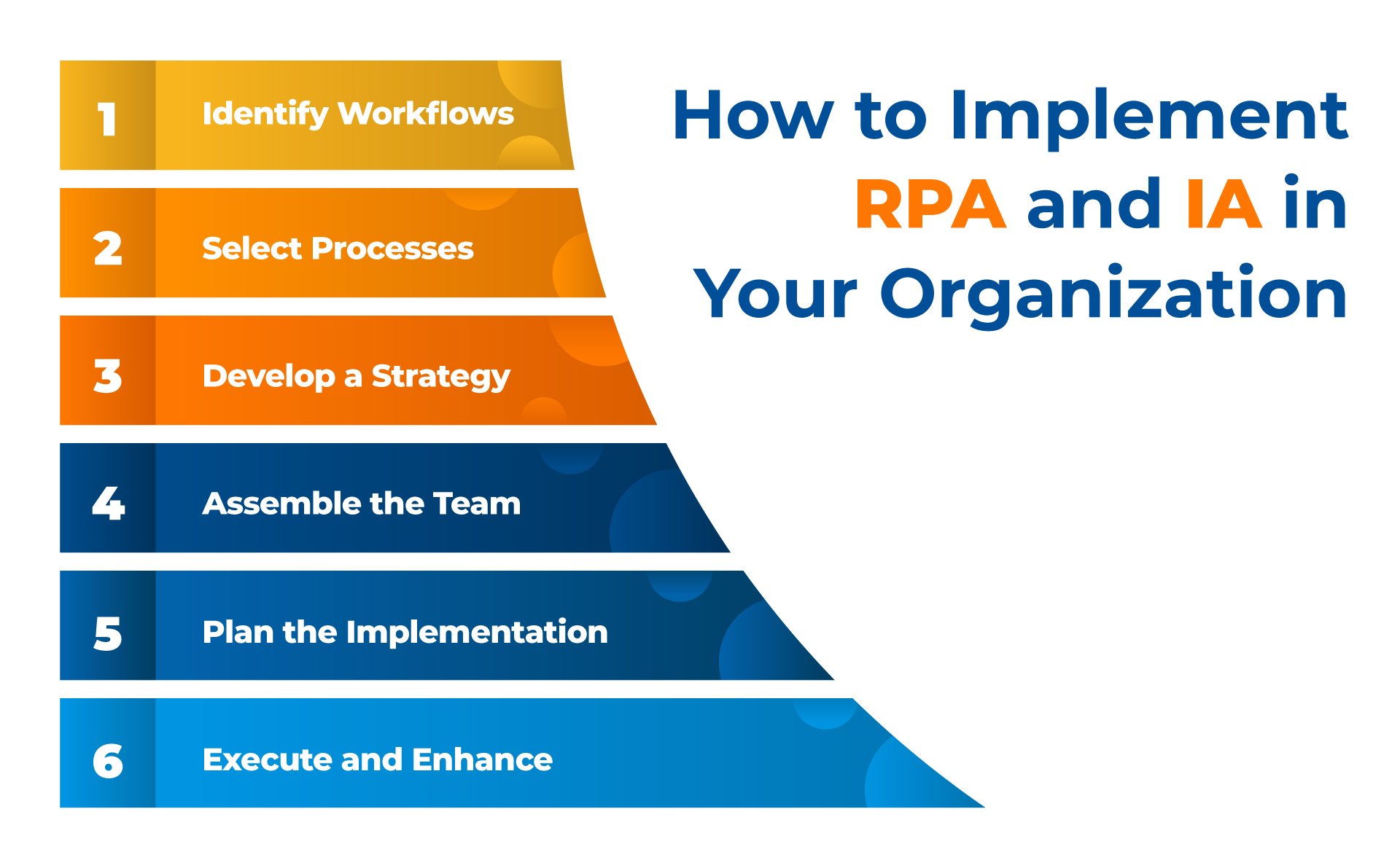
Deciding RPA vs IA for your organization can be a daunting task, but it can also be a game-changer for your business. Here are some steps you can take to implement RPA and IA in your organization:
1. Identify the Processes to Automate
The first step in implementing RPA and IA is to identify the processes that need automation. Look for repetitive, rule-based processes with a high volume of transactions. Once you have recognized these processes, you can prioritize them based on their impact on your business.
2. Evaluate the Feasibility of Automation
Once you have identified the processes to automate, you need to evaluate their feasibility for automation. This involves assessing the technical and operational feasibility of automating the process. In this assessment, you should involve the process owner, an SME, and an RPA expert.
3. Develop a Proof of Concept
After evaluating the feasibility of automation, you should develop a proof of concept to demonstrate the benefits of RPA and IA. This involves creating a prototype of the automation solution and testing it in a controlled environment. You can use the proof of concept results to convince stakeholders of the benefits of RPA and IA.
4. Choose the Right RPA and IA Tools
Once you have demonstrated the benefits of RPA and IA, you must choose the right tools to implement the automation solution. Many RPA and IA tools are available in the market, and you need to select the one that best fits your organization’s needs. Consider factors such as ease of use, scalability, and cost when selecting the tool.

5. Train Employees
The debate might be regarding RPA vs IA. But, both of them will require your employees to learn new skills. You must provide them with the necessary training to work effectively with the latest tools. This will also help improve employee morale as they feel more confident in their job performance.
6. Monitor and Optimize the Automation Solution
Finally, you must monitor and optimize the automation solution to ensure it delivers the expected benefits. This involves tracking the performance of the solution and making adjustments as necessary. You should also involve your employees in this process to ensure their engagement throughout the implementation of the automation solution.
By following these steps, you can make crucial decisions regarding RPA vs IA; and reap the benefits of increased efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
Kanerika: Your trusted Automation Strategy partner
Regarding Automation Strategy, Kanerika is the partner you can trust. With years of experience in the industry, Kanerika has helped many enterprises optimize and transform their business processes using intelligent automation technologies.
Kanerika’s approach to automation is unique. We start by understanding your business processes and identifying areas where automation can significantly impact. We then design a customized automation strategy that meets your specific needs, utilizing a combination of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies.
Kanerika’s team of experts deeply understands RPA vs IA and the latest automation technologies and stays up-to-date with the latest trends and advancements in the field. That’s why our automation solutions have been proven to deliver results.

FAQs
What is the difference between RPA and AI agent?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) bots are like digital assistants that follow pre-programmed rules to automate repetitive tasks. AI agents, however, are smarter; they learn and adapt using machine learning, making decisions and handling more complex, unpredictable situations. Think of RPA as a skilled clerk, while an AI agent is more like a problem-solving analyst. Essentially, AI can *enhance* RPA, but they’re distinct technologies.
Will RPA be replaced by AI?
No, RPA and AI are complementary, not competitive. RPA excels at automating structured, repetitive tasks, while AI handles complex, unstructured data and decision-making. Think of AI as the brain and RPA as the hands – they work best together. The future is likely to see increased integration, not replacement.
What is the difference between RPA and intelligent document processing?
RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks using pre-defined steps, like copying data between systems. Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) goes further, using AI to understand and extract information from unstructured documents (like invoices or emails) *before* RPA can process it. Think of IDP as the brainpower enabling RPA to handle more complex, variable tasks. Essentially, IDP preps the data for RPA to act upon.
What is RPA and AI?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is like having a digital worker handle repetitive computer tasks, freeing up humans for more creative work. AI (Artificial Intelligence) gives computers the ability to learn and make decisions, often without explicit programming. While RPA automates *existing* processes, AI can *improve* or even *design* new, smarter processes. They’re often used together – AI enhancing RPA’s capabilities.
How does RPA differ from IA?
RPA, or Robotic Process Automation, focuses on automating *repetitive, rule-based tasks* within existing systems, like data entry. Intelligent Automation (IA), however, leverages AI to handle more complex, unpredictable situations, including decision-making and learning from data. Essentially, IA builds upon RPA by adding cognitive capabilities. RPA is a subset of the broader IA landscape.
What is the difference between RPA and machine learning?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is like a skilled, rule-following digital worker automating repetitive tasks. Machine learning, on the other hand, is about building systems that *learn* from data to improve their performance over time – they adapt, unlike RPA’s rigid instructions. Essentially, RPA automates *what is known*, while machine learning discovers and automates *what is unknown*. They often complement each other.
What is the difference between AI agent and automation?
AI agents are proactive problem-solvers; they learn and adapt to changing situations, making decisions autonomously. Automation, conversely, simply follows pre-programmed rules without learning or adapting. Essentially, automation is a *tool* that AI agents can *use*, but they are fundamentally different in their capabilities. AI agents possess intelligence and autonomy, while automation is purely reactive execution.
What is the difference between RPA and conversational AI?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) automates *rule-based* tasks, like filling forms or moving data between systems – it’s like a tireless digital clerk. Conversational AI, on the other hand, focuses on human-like interaction, understanding natural language to handle customer service or provide information – it’s your digital assistant. They’re distinct technologies addressing different needs, though they can sometimes work together.
What is the difference between RPA and Gen AI?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) automates *pre-defined*, repetitive digital tasks like data entry, following exact instructions. Gen AI (Generative AI), on the other hand, learns from data and creates *new* things – text, images, code – exhibiting a level of understanding and adaptability RPA lacks. Think of RPA as a precise, rule-following robot, while Gen AI is a creative, learning AI. They are distinct but increasingly complementary technologies.
What is the difference between RPA and IA?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) automates repetitive, rule-based tasks, much like a digital worker following strict instructions. IA (Intelligent Automation) combines RPA with Artificial Intelligence to handle more complex processes. It allows automation to learn, understand, and make decisions, going beyond simple task execution.
Can RPA be replaced by AI?
No, AI won’t entirely replace RPA. RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by following instructions. AI, however, provides intelligence for decision-making and learning, handling complexity. Instead, they often work together, with AI making RPA systems much smarter and more capable. AI enhances RPA rather than replacing it.
What is the difference between RPA and AI agents?
RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by following exact pre-set instructions, like a digital script. AI agents, however, can understand context, learn from data, and make decisions to handle more complex or variable situations. Essentially, RPA mimics human actions, while AI agents mimic human intelligence.
Can AI replace automation?
No, AI doesn’t replace automation; it makes it much smarter. Automation is about machines performing tasks without human input. AI adds the ability to learn, adapt, and make decisions, significantly improving what automated systems can achieve.
What are the 4 types of automation?
The four main types of automation are: 1. Fixed Automation: Designed for high-volume, specific tasks with little to no change. 2. Programmable Automation: Equipment can be reprogrammed for different products or tasks, but this takes some effort. 3. Flexible Automation: Allows for quick and easy changes between different product types or operations. 4. Integrated Automation: Combines multiple machines and systems to work together seamlessly, often with computer control.
What are the 4 types of ML?
The four main types of Machine Learning are: 1. Supervised Learning: Uses examples with correct answers to learn from. 2. Unsupervised Learning: Finds patterns in data without pre-set answers. 3. Reinforcement Learning: Learns by trying actions and getting rewards or penalties. 4. Semi-Supervised Learning: Combines a small amount of answered data with a lot of unanswered data.
Which is better, artificial intelligence or robotics?
Neither is better; they are different but often work together. Robotics involves building physical machines to perform tasks. Artificial Intelligence is the brain that enables machines to learn, reason, and make decisions. AI gives robots the intelligence to act autonomously and effectively, making them a powerful duo.
Are AI and IA the same?
No, AI (Artificial Intelligence) and IA (Intelligence Amplification) are distinct concepts. AI focuses on creating machines that can perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence. IA, on the other hand, uses technology to enhance and make human intelligence more effective. One creates artificial minds, the other empowers human minds.
Is ChatGPT AI or ML?
ChatGPT is a form of Artificial Intelligence (AI). More specifically, it uses Machine Learning (ML) to learn from vast amounts of text data. So, while it’s an AI, ML is the core technology that allows it to understand and generate human-like responses.
How does RPA differ from intelligent automation?
RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by following exact instructions, like a digital worker mimicking human actions. Intelligent Automation combines RPA with AI technologies. This allows it to understand unstructured data, learn, and make decisions, handling more complex processes that require some thinking.
Does AI fall under automation?
Yes, AI often falls under the umbrella of automation. Automation is broadly about technology performing tasks without human intervention. AI takes this further by enabling systems to learn, reason, and make complex decisions, greatly expanding what can be automated. Essentially, AI powers more intelligent and adaptable forms of automation.
What is IA in artificial intelligence?
IA in Artificial Intelligence typically stands for Intelligent Agent. It’s a system that observes its surroundings, makes decisions, and takes actions to achieve specific goals. Think of it as a smart entity designed to perform tasks effectively.









