The Rise of Enterprise AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept but a business imperative for CIOs and CTOs seeking tangible business outcomes. According to a recent survey by Deloitte, 83% of enterprises believe AI is a strategic priority for their business. As AI use cases mature, they dramatically alter the enterprise landscape while raising caution in security, privacy, and ethics. From predictive analytics to intelligent automation, organizations are leveraging enterprise artificial Intelligence to innovate, optimize, and compete better–at a faster pace.
The primary goal of this comprehensive guide is to equip enterprises with the essential knowledge and actionable strategies to implement and scale AI successfully. Whether you’re a C-level executive or a technology enthusiast, this article aims to serve as your all-in-one resource for understanding the intricacies of enterprise AI, overcoming challenges, and leveraging the full potential of artificial intelligence for business growth.
Understanding the AI space
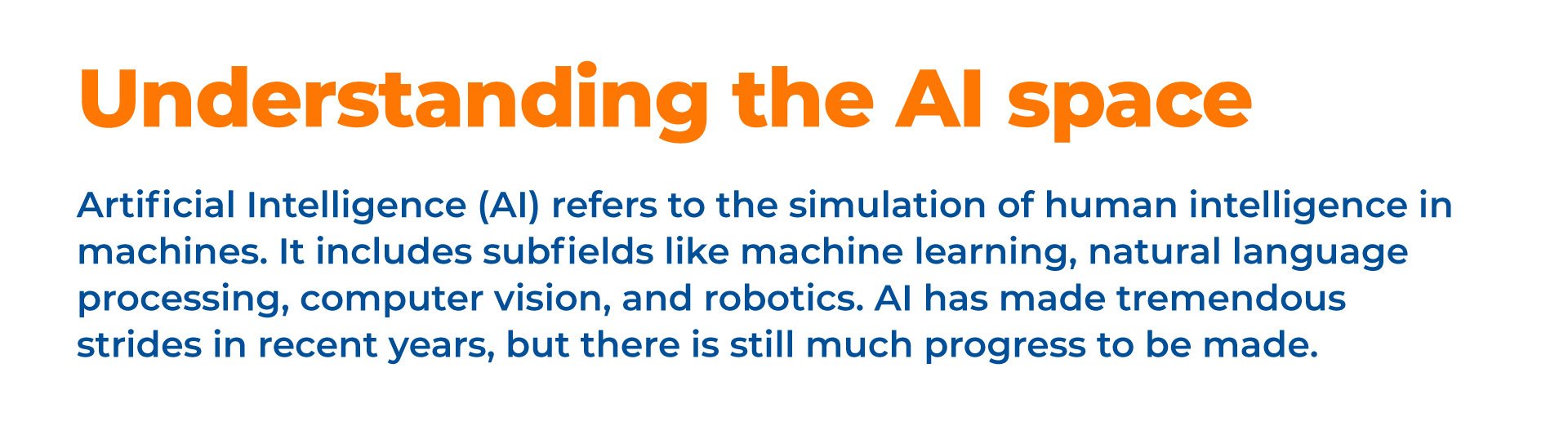
General AI
- Aims to develop human-level AI that can perform any intellectual task. This is the “holy grail” of AI, but we are still far from achieving it
- Trained on massive open datasets. Requires immense amounts of data to learn
- Focuses on developing artificial general intelligence. Seeks to replicate all facets of human cognition
- The goal is to automate human roles. Though automation can be beneficial, we must ensure it is designed ethically
- Still an emerging technology. General AI remains more theoretical than practically realizable currently
Generative AI
- Can autonomously create novel content like text, images, audio, and video, tapping into human creative abilities
- Examples include large language models like GPT-4, Claude, Falcon and image generators like DALL-E. Their outputs are impressive but imperfect
- Aims to mimic human creativity in outputs. This demonstrates new frontiers for AI
- Faces challenges around biases, lack of explainability, and unclear ROI
Enterprise AI
- Focuses on solving specific business problems and delivering ROI with a pragmatic approach
- Leverages an organization’s proprietary data. Real-world, practical datasets
- Involves narrow AI/ML models tailored to business needs. Purpose-driven, focused capabilities
- Already deployed in many industries. Proven value for businesses when done responsibly
- Provides focused capabilities and business value. Delivers useful, if narrow, objectives
General vs. Generative vs. Enterprise AI
As we can see, enterprise AI offers the most applicable capabilities for business currently, while general and generative AI represent ambitious frontiers with both promise and cautions. All the same, AI will continue rapidly evolving in the years ahead.
Why Enterprises Need Artificial Intelligence

Enhanced Data Analytics
Importance of data cannot be overstated. However, raw data is rarely of use unless it can be turned into actionable insights. That’s where AI comes into play.
Advanced AI algorithms can sift through massive datasets, identifying patterns and correlations that would be impossible or incredibly time-consuming for a human to spot. This level of data analytics offers a significant competitive edge. It enables businesses to make data-driven decisions that are both timely and accurate.

Automating Routine Tasks
Every enterprise has tasks that are essential but repetitive and mundane. From data entry and customer service to inventory management, these tasks can consume a disproportionate amount of time and resources. AI can automate these processes, streamlining operations and freeing up employees for more strategic, creative endeavors. Additionally, automation not only boosts efficiency but also reduces the scope for human error, thus improving the overall quality of work.
Strategic Decision Making
Strategic decisions are the lifeblood of any enterprise, impacting its long-term success or failure. AI can contribute significantly in this area by offering predictive analytics, risk assessments, and data-driven recommendations. With AI, businesses can simulate various scenarios to predict outcomes, providing decision-makers with valuable insights that can guide strategy and planning.
Challenges and Solutions in Enterprise AI Implementation
Data Quality and Availability
One of the most significant challenges in implementing AI in an enterprise is the quality and availability of data. Inconsistent or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate insights and may even compromise the effectiveness of AI algorithms. The solution? Conduct a thorough data audit and clean-up operation. This will prepare your data for AI algorithms, ensuring the integrity of the insights generated.
Skill Gap
AI is a specialized field that requires a unique skill set, from data science to programming. Many enterprises face a skill gap when it comes to AI expertise. The solution to this is multi-fold: invest in training existing staff, hire new talent with the required skills, or partner with experts in the field.
Scalability Issues
Scalability is another hurdle many enterprises face when implementing AI. Projects often start small and then need to be expanded, which can complicate things. The solution is to adopt a staged approach. Start with pilot programs and then gradually scale up based on the results and learnings.
Ethical and Regulatory Concerns
AI can sometimes venture into ethical gray areas, such as data privacy and algorithmic bias. Regulatory compliance is another concern, especially given the ever-changing legal landscape surrounding AI. The solution? Establish an ethics committee and consult legal advisors to ensure you’re on solid ground.
Privacy and Security
Implementing AI in enterprise settings poses significant privacy and data security challenges. Data privacy concerns demand robust data encryption techniques, along with transparent user consent mechanisms. Meanwhile, cybersecurity threats are another concern. In this scenario, solutions include privacy-preserving AI techniques like federated learning and differential privacy. Additionally, it is crucial to be compliant with data regulations, ethical AI governance, and secure development practices.
Did you know?
Understanding the importance of AI governance and regulation, the UK government hosted the first-ever global AI safety summit in November 2023.
Enterprise Artificial Intelligence Use Cases
Human Resources and Talent Management
AI’s capabilities extend far beyond automating routine tasks like resume screening. Advanced algorithms can predict employee turnover, assess job fit, and even estimate the potential for career growth. This level of insight enables HR professionals to create more targeted recruitment strategies, improve employee retention, and ultimately build a more efficient and happier workforce.
Marketing and Customer Engagement
AI has revolutionized marketing strategies through data analytics and customer segmentation. But its applications don’t stop there. Advanced AI tools can predict consumer behavior, allowing businesses to anticipate customer needs before they even arise. Chatbots and virtual assistants provide real-time customer service, often indistinguishable from human interaction. Predictive analytics can also guide the timing and content of marketing campaigns, maximizing engagement and ROI.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain optimization is another area where AI shines. Algorithms can predict inventory needs down to the most minute details, like seasonal demand fluctuations or the impact of current events. AI can also optimize delivery routes, taking into account variables like traffic patterns and fuel costs, thus significantly reducing operational expenses. Moreover, automated ordering systems can ensure that inventory is always kept at optimal levels, minimizing both shortages and overstock situations.

Manufacturing and Quality Control
In the manufacturing sector, AI offers transformative potential in automating tasks and ensuring quality control. Machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data to predict machine failures, enabling proactive maintenance. This not only extends the lifespan of the machinery but also reduces downtime.
Moreover, AI-powered visual recognition systems can inspect products at high speed with a level of accuracy that surpasses human capabilities. These systems can identify defects or inconsistencies, ensuring that only products that meet quality standards move on to the next phase of production or get shipped. Additionally, AI can optimize the entire manufacturing process by efficiently allocating resources based on real-time data analysis, thereby reducing waste and energy consumption.
Financial Analysis and Risk Management
AI’s predictive capabilities are a boon for financial analysis. Algorithms can sift through years of financial data to predict market trends, assess investment risks, and even anticipate fluctuations in currency exchange rates. Automated trading systems can execute high-frequency trades at speeds no human could achieve, maximizing profits through real-time market analysis.
Health and Safety
In industries like manufacturing, construction, or mining, workplace safety is a critical concern. AI algorithms can monitor equipment conditions in real-time, predicting failures before they happen and thus preventing costly downtimes and potential accidents. Wearable AI devices can also monitor workers’ health stats, sending alerts in case of irregularities that could indicate a health risk.
Future of Enterprise Artificial Intelligence
Emerging Technologies
As we look toward the future, several emerging technologies are poised to take enterprise AI to the next level. Edge AI, which allows data processing on local devices, promises to make AI applications faster and more secure. Similarly, Quantum Computing holds the potential to solve complex problems that are currently beyond the reach of classical computing methods.

Ethical AI
As AI technology evolves, ethical considerations are moving to the forefront. The concept of ethical AI involves creating algorithms that are not only efficient but also fair and unbiased. Enterprises will need to pay close attention to ethical considerations as they continue to implement AI solutions.
AI Governance and Regulation
With the rapid advancement of AI, governance and regulation are also catching up. Companies can expect stricter rules around data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and AI ethics in the coming years. Being prepared for these regulatory changes is key to successfully implementing AI in the long term.
Efficient and Lean Footprint AI
One of the key trends shaping the future of enterprise AI is the development of algorithms that require less computing power and cooling. As we move towards more sustainable business practices, the efficiency of AI systems becomes crucial. Newer algorithms are being designed to perform complex tasks using a fraction of the energy that was previously required. This leaner footprint not only aligns with sustainability goals but also reduces operational costs, making AI more accessible for smaller enterprises that may not have extensive resources.

Generative AI Agents that Can Talk to Each Other
Another exciting frontier in enterprise AI is the development of generative AI agents capable of communicating with each other. These agents can collaborate to solve complex problems or manage multifaceted systems without human intervention. For example, in a supply chain scenario, one AI agent responsible for inventory could communicate with another responsible for logistics, coordinating to optimize stock levels and delivery times. This level of inter-agent communication can streamline operations and lead to more cohesive and efficient systems.
The Need for a Trustworthy Partner in Navigating Enterprise AI
Implementing Enterprise Artificial Intelligence solutions is a complex endeavor that involves a myriad of factors. From selecting the right algorithms and integrating them into existing systems to ensuring data security and regulatory compliance, the challenges are numerous. Given this complexity, the importance of having a trustworthy partner cannot be overstated.
Proven Process
A reliable partner brings a proven process to the table, a roadmap that has been refined through multiple successful implementations. This not only speeds up the deployment but also mitigates risks, ensuring that common pitfalls are avoided.
Frameworks and Tools
Having a partner with a suite of frameworks and tools can be a game-changer. These resources can streamline various stages of the implementation process, from data collection and analysis to monitoring and maintenance.
Expertise and Domain Knowledge
A trustworthy partner comes with expertise not just in AI technology but also in the specific domain in which your enterprise operates. This is critical for tailoring AI solutions to your unique challenges and opportunities.
Change Management Facilitation
Change is one of the most challenging aspects of implementing new technology. A reliable partner will provide change management facilities to ensure a smooth transition, training your staff and helping to adapt your organizational culture to embrace the new AI capabilities.

Kanerika: Your Go-To Partner for Enterprise AI and Generative AI Solutions
In the complex landscape of enterprise AI, the right partnership can make all the difference. That’s where Kanerika comes in. With an unmatched combination of technical prowess and business acumen, here’s why Kanerika is the partner you can count on:
Broad Spectrum of Expertise
Kanerika’s experience is not limited to a single industry. Their proficiency spans healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing, making them well-equipped to handle unique challenges across sectors. This wide-ranging experience brings a holistic approach to problem-solving in AI.

State-of-the-Art Technologies
Kanerika prides itself on employing the latest technologies to deliver cutting-edge AI solutions. They are committed to staying ahead of the curve, ensuring your enterprise benefits from the most advanced AI capabilities available.
Client-Focused Strategy
Kanerika’s approach is rooted in client satisfaction. They don’t just offer off-the-shelf solutions but work closely with you to tailor AI strategies that exceed your expectations and business goals.
Adherence to Ethical and Regulatory Standards
In a rapidly evolving regulatory landscape, Kanerika places a high priority on ethical considerations and compliance. They offer AI solutions that stand up to the most rigorous ethical and regulatory scrutiny.
Leadership in Generative AI
Generative AI is an emerging field where Kanerika has demonstrated significant expertise. Whether it’s automated content creation or AI-to-AI communication, their capabilities in generative AI are second to none.
Book a free consultation with us today to learn more about scaling business intelligence!
The Future is Now
The integration of AI into the enterprise landscape is not a trend of the future; it’s happening now. From enhancing data analytics and automating routine tasks to making strategic decisions and predicting market trends, AI’s applications within an enterprise are both transformative and multi-faceted.
As we move forward, the challenges will evolve, but with the right strategies and partnerships—like the one you can have with Kanerika—the rewards promise to be monumental.
How did Kanerika Strengthen the Business of a Leading Conglomerate by Implementing Generative AI for Reporting?
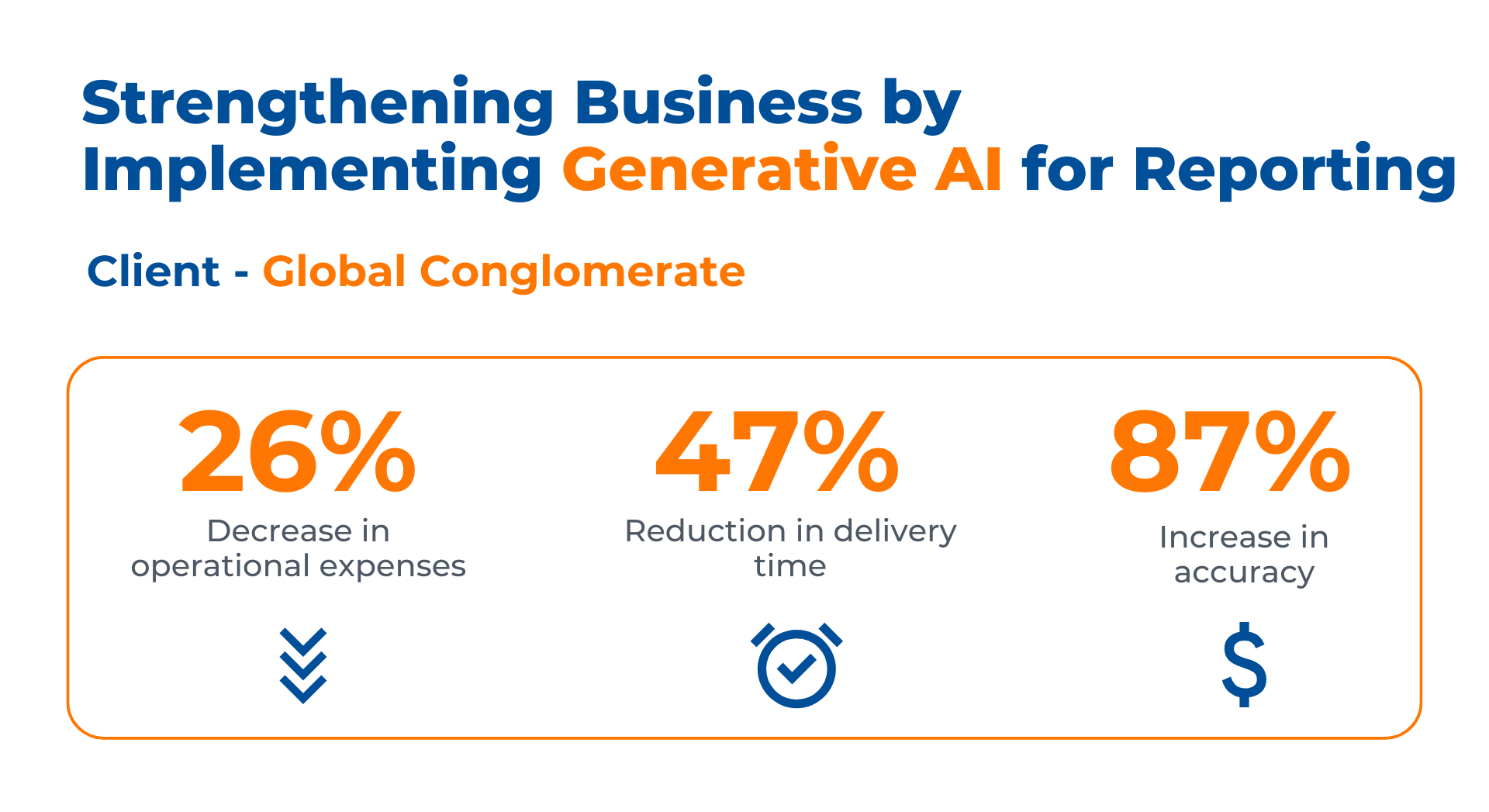
Over the years, the client had accumulated vast amounts of unstructured and qualitative data from various sources. The traditional manual approach to analyzing such data was time-consuming and prone to bias. Moreover, this approach could not effectively capture underlying trends, sentiments, and opportunities. ,
They sought a solution that harnessed the power of generative AI for reporting to automate data analysis, unlock valuable insights, and enable agile decision-making by partnering with Kanerika.
Client’s Challenges:
- Manual analysis of unstructured and qualitative data was prone to bias and unable to capture underlying trends
- Lack of automated tools hindered the extraction of valuable insights from diverse data sources
- The inability to integrate qualitative data with structured data limited the comprehensive analysis necessary for reporting
Kanerika’s Solutions:
- Deployed a generative AI for reporting solution using NLP, ML, and sentiment analysis models to process and analyze data
- Automated data collection and text analysis to extract insights from unstructured sources like market reports and industry analysis
- Integrated the new platform with structured data sources and provided user-friendly reporting and visual interfaces
Business Impact in Numbers:
- 30% Decrease in accurate decision-making time
- 37% Increase in identifying customer needs
- 55% Reduction in manual effort and analysis time
By understanding the various aspects of AI, acknowledging its challenges, and keeping an eye on future developments, enterprises can position themselves at the forefront of this technological revolution.

FAQs
What is enterprise artificial intelligence?
Enterprise AI isn’t just about adding AI to existing systems; it’s about fundamentally transforming how a business operates. It leverages AI across multiple departments, from sales and marketing to operations and finance, to improve efficiency and decision-making. This involves integrating AI tools and data strategically, often creating a network of interconnected intelligent systems. The goal is to gain a significant competitive advantage through data-driven automation and insights.
What is an example of enterprise AI?
Enterprise AI isn’t just one thing, but rather AI strategically deployed across a whole business. Think of a large company using AI for everything from predicting customer churn (using past data) to automating complex supply chains (optimizing logistics in real time). It’s about integrating intelligent systems to improve efficiency and decision-making at scale, unlike isolated AI applications. Ultimately, it’s about leveraging AI to gain a significant competitive advantage.
What is the difference between AI and enterprise AI?
AI is the broad field of making machines smart; think self-driving cars or smart assistants. Enterprise AI focuses this intelligence on solving *business* problems. It’s AI tailored for specific organizational needs, integrating with existing systems to boost efficiency and gain a competitive edge. Essentially, enterprise AI is AI with a job in a company.
What is enterprise grade AI?
Enterprise-grade AI isn’t just smart; it’s robust, reliable, and scalable. It’s built to handle the massive data and complex workflows of large organizations, ensuring high accuracy and security. Think of it as AI that’s been battle-tested for real-world business challenges, not just theoretical benchmarks. It demands rigorous governance and integration with existing systems.
What is the future of AI in enterprise?
AI’s future in enterprise is one of deep integration, not just isolated tools. We’ll see AI powering entire workflows, from customer service to supply chain management, leading to significantly improved efficiency and decision-making. Expect hyper-personalization and predictive capabilities to become the norm, reshaping how businesses operate and compete. Ultimately, AI success hinges on responsible implementation and ethical considerations.
How many enterprises use AI?
Pinpointing the exact number of enterprises using AI is tricky, as adoption varies widely by industry and definition of “AI.” Many businesses use AI components without fully embracing comprehensive AI strategies. A safe answer is “a rapidly growing and significant portion,” with adoption accelerating year by year. Precise figures are elusive due to inconsistent reporting and diverse implementation levels.
How are enterprises using AI?
Enterprises leverage AI to dramatically improve efficiency and decision-making. This spans automating routine tasks (like customer service or data entry), gaining predictive insights from complex data (for example, optimizing supply chains or identifying fraud), and personalizing customer experiences. Ultimately, AI helps businesses operate more intelligently and competitively.
What is enterprise generative AI?
Enterprise generative AI uses powerful algorithms to create new content – text, images, code – tailored to a company’s specific needs. Unlike general-purpose AI, it’s designed for internal use, integrating with existing systems and prioritizing security and data privacy. Think of it as a custom-built AI assistant boosting productivity and innovation within a business. This means safer, more controlled and relevant results than publicly available generative AI.
What is an AI strategy for the enterprise?
An enterprise AI strategy isn’t just about adopting AI tools; it’s a roadmap for leveraging AI to achieve specific business goals. This involves identifying key problems AI can solve, prioritizing initiatives based on potential ROI, and building the necessary data infrastructure and talent. Success hinges on integrating AI ethically and responsibly into existing workflows for maximum impact. Ultimately, it’s about transforming how the business operates, not just adding a new technology.
What is responsible AI for enterprise?
Responsible AI for enterprises isn’t just about building AI; it’s about building *ethical* AI. It means proactively mitigating biases, ensuring fairness and transparency in algorithms, and prioritizing human oversight to avoid unintended consequences. This builds trust, protects reputation, and ultimately fosters a more sustainable and beneficial use of AI within the organization. It’s about aligning AI development with core business values and societal good.
What is the difference between enterprise AI and consumer AI?
Enterprise AI focuses on solving complex business problems, using data to improve efficiency and decision-making within large organizations. Consumer AI, on the other hand, targets individual users, providing personalized experiences and convenience through applications like smart assistants or recommendation engines. The key difference lies in scale and purpose: enterprise AI is about optimizing operations, while consumer AI enhances individual lives. Data privacy and security concerns also differ significantly between the two.
Can AI replace enterprise software?
No, AI won’t replace enterprise software entirely. Instead, it acts as an intelligent co-pilot, automating complex tasks, generating predictive insights, and transforming how existing systems operate. It enhances functionality and drives efficiency, evolving the software landscape rather than fully substituting its foundational role.
How big is the enterprise AI market?
The enterprise AI market is a colossal and rapidly expanding force, already valued in the high tens of billions of dollars globally. It’s less about buying a single product and more about AI becoming an essential, transformative layer across virtually every industry. We anticipate this market to soar into the hundreds of billions as businesses embed AI deeper into their core operations.
How is AI used in enterprises?
Enterprises leverage AI to fundamentally transform raw data into actionable intelligence, automating repetitive processes and optimizing complex operations for efficiency gains. It empowers smarter strategic decision-making, hyper-personalizes customer engagement, and uncovers novel growth avenues, ultimately elevating both operational performance and market responsiveness.
What are the 4 types of AI?
AI capabilities are broadly classified into four progressive types based on their thinking power. We start with Reactive Machines, which simply respond to current inputs without memory, then Limited Memory AI that uses recent past data for decision-making. Looking ahead, theoretical types include Theory of Mind AI, understanding human emotions and intentions, and ultimately Self-Aware AI, possessing consciousness and self-identity.
How is enterprise using AI?
Enterprises are strategically leveraging AI to gain a competitive edge. They’re automating complex operations, extracting predictive insights from vast data troves, and deeply personalizing customer experiences. This isn’t merely about efficiency; it’s fundamentally reshaping business models, driving innovation, and enabling smarter, faster decision-making across all functions.
How to use AI in enterprise?
Enterprises strategically embed AI to automate repetitive tasks, transforming raw data into predictive insights for smarter decision-making. It augments human potential, optimizes core business processes, and crafts personalized customer experiences. Ultimately, AI acts as a catalyst for innovation and efficiency by aligning technology directly with critical business challenges.
What are 7 types of AI?
While there isn’t one definitive list of 7 types, AI is commonly categorized using two main frameworks. By *scope*, we distinguish Narrow AI (task-specific, like current virtual assistants), General AI (human-level intellect), and Superintelligence (exceeding human capabilities). Alternatively, by *functional complexity*, AI progresses from basic Reactive Machines and Limited Memory systems towards aspirational Theory of Mind and Self-Aware AI, marking its evolution in cognitive ability.
What is the difference between generative AI and enterprise AI?
Generative AI is about *creating* novel content like text, images, or code from learned patterns. Enterprise AI, conversely, is the *application* of various AI technologies (including generative) to solve specific business problems, like optimizing operations or enhancing customer service. It’s the difference between *generating something new* and *strategically implementing AI for business value*.









