Did you know60% of corporate leaders have made data governance a top priority to shield their company from data breaches and security threats. According to recent research, 62% of organizations are planning to audit their existing data governance frameworks to ensure compliance and efficiency, with many exploring a combination of corporate data governance policies to enhance their approach. This requires an in-depth understanding of the critical data governance pillars and their role in crafting a robust governance strategy.
Data governance is crucial to effectively manage, safeguard, and utilize data. It guarantees that information is correct, safe, and used in accordance with appropriate laws like HIPAA and GDPR. By establishing a strong Data Governance framework, businesses cannot only preserve data integrity and lower risks but also foster trust in data-driven decision-making processes.
The complexity of data sources, the rapidly rising volume of data, and the changing regulatory environment are the main drivers of the expanding demand for data governance. A robust governance framework is essential for protecting data and guaranteeing long-term business success as organizations depend more and more on data for operations.
Move Azure Workloads to Fabric!
Kanerika keeps your pipeline switch trouble-free.
The Five Core Data Governance Pillars
Pillar 1 – Data Quality
Accuracy and Completeness
The accuracy and completeness of the data during decision making is important. This means that no omissions or mistakes are present in the data captured and all the relevant details are there for the business to run.
Consistency Across Systems
Data should be uniform between the various distributed systems to avoid slippages. This is done by employing standard data formats and schema across different systems, hence increasing data efficiency.
Timeliness and Relevance
It’s essential that data is refreshed as often as necessary to maintain its usefulness and relevance. Current data empowers decision-makers to make accurate decisions based on the most recent business activity.
Pillar 2- Data Security and Privacy
Access Controls and Authentication
Implementing strict access controls ensures only authorized personnel can view or modify data. A multi-factor authentication methodology improves protection and assists in protecting high-risk data.
Encryption and Data Protection
Data encryption is not just a measure, it’s a necessity to keep sensitive information confidential. Whether it’s data in storage or data in transit, proper encryption is the key to ensuring no sensitive information leaks, providing a strong sense of security and confidence.
Compliance with Regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA)
Many organizations must abide by data privacy regulations, including GDPR and CCPA. These regulations include high data protection thresholds and allow individuals to have authority over their data.
Pillar 3- Data Architecture
Data Models and Structures
Formulating precise structures and tariff models enables quick storage and access to customer information. This guarantees that the data architecture is aligned with the business operations and analytics.
Integration and Interoperability
Data integration systems play a crucial role in ensuring that data can move seamlessly from one system to another, even across numerous platforms. This interoperability is not just a feature, but a necessity for modern systems, enabling multiple systems to function simultaneously and facilitating the movement and utilization of information.
Scalability and Flexibility
Once developed, the data architecture should not only be able to expand to meet growth but should also be sufficiently flexible to accommodate any changes to the existing business requirements, thus supporting future designs without any disturbance.
Pillar 4- Data Lifecycle Management
Data Creation and Acquisition
Effective data management begins at the generation stage, whether sourced from internal systems or external platforms, as it lays the foundation for maintaining quality data throughout its entire lifecycle.
Storage and Maintenance
Proper storage methods, like physical security, encryption, and regular backups, help keep the data safe. Maintenance includes regular review and editing of information to ensure truthfulness and relevance.
Archiving and Deletion
When data becomes obsolete, it should be archived in compliance with regulations and business guidelines. This ensures the safety and security of the data. After some time, it will be necessary to safely delete the old data, allowing the up-to-date data to remain within laws.
Pillar 5- Metadata Management
Data Cataloging and Classification
The first step of data management is to organize and systematically retrieve the information. It also includes applying meta-tags to information assets and creating their classifications.
Data Lineage and Traceability
Tracking the origin and movement of data (data lineage) is essential for auditing. It ensures that changes to data can be traced back to their source, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Business Glossary and Data Dictionary
A business glossary includes senior management, history, legal policies, governance documents, and other standards about the organization’s data-shared vocabulary. This minimizes department fragmentation by ensuring that all parties understand the communication regarding data in a similar manner.
Secure Your Business Future – Adopt Strong Data Governance
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Governance Solutions
How Are these 5 Data Governance Pillars Interconnected
| Pillar 1 | Pillar 2 | Interconnection |
| Data Quality | Data Security and Privacy | High-quality, accurate data makes it easier to manage and secure. Poor data quality can lead to security vulnerabilities, such as mismanaged personal information or incomplete records. |
| Data Quality | Data Architecture | A robust data architecture supports data quality by organizing data flows and models that ensure data remains consistent and accurate across systems. |
| Data Security and Privacy | Data Lifecycle Management | Ensuring security throughout the data lifecycle is essential for protecting sensitive data, from creation to deletion, helping prevent breaches at any stage of data handling. |
| Data Architecture | Metadata Management | Metadata enhances data architecture by providing context, traceability, and structure, allowing efficient organization and access to data assets within a defined architecture. |
| Data Lifecycle Management | Metadata Management | Metadata helps track data across its lifecycle, improving traceability and classification, which is critical for compliance and efficient management of data retention and deletion. |
Data Governance Examples: How Top Companies Manage Their Data
Discover how top companies excel in data governance—learn their best practices to secure, manage, and optimize your data strategy today!
Implementing the Data Governance Pillars: A Phased Approach
Using a phased approach to achieving the five pillars of data governance guarantees that each pillar is handled progressively in an orderly and organized manner to ensure that the achievement of pillars is incorporated within the organization. Here’s a subdivision of the phased implementation strategy:
Phase 1: Planning and Assessment
Objective: Establish the current status of data governance, determine data governance shortcomings, and propose actions.
Actions
- Identify any existing data governance framework and provide an in-depth analysis of any part of it.
- Reach out to the people in charge of data (owners, stewards, custodians) so that you can understand their needs and expectations.
- Set specific goals for each pillar (data quality, security, architecture, etc.).
Phase 2: Establishing Governance Roles and Policies
Objective: There should be a transparent framework for governance with defined roles and responsibilities.
Actions
- Define data owners, stewards, custodians, and possible data users.
- Develop policies for data management, security, and privacy.
- Include industry norms and policies in the business practice (GDPR, HIPAA).
- Define workflows for how data will be handled across its lifecycle.
Phase 3: Implementing Data Quality and Security Protocols
Objective: Focus on improving data accuracy, completeness, and security.
Actions
- Establish processes for data profiling, data cleansing, and data validation.
- Implement access controls, encryption, and compliance mechanisms.
- Establish metrics and tools for ongoing monitoring of data quality and security.
- Provide measures for the backup and transfer of confidential information safely.
Phase 4: Building Data Architecture and Lifecycle Management Systems
Objective: Create a precise scalability of the data architecture and provide systematic data management throughout its lifecycle.
Actions
- Develop and establish guidelines for data interfaces to enable systems interoperability.
- Develop a data creation, data storage and retrieval, and data archival system.
- Ensure that data lifecycle processes, such as retention and deletion, comply with regulations and internal policies.
Phase 5: Integrating Metadata Management
Objective: Improve data traceability, cataloging, and transparency of data.
Actions
- Develop a complete and detailed metadata catalog in the organization for appropriate classification and use of data.
- Use data lineage to show where data came from and how it has changed over time for purposes of transparency and auditing.
- We manage business terminology and data definitions using a data dictionary to ensure a consistent understanding of data within the organization.
Phase 6: Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
Objective: Assure that governance policies and practices are adhered to and revised ongoing development Office Materials.
Actions
- Develop documents containing the objectives and the location’s policies regarding data governance and compliant policies and conduct periodic evaluations of the authorities’ data governance policies and activities.
- Check indicators for regular feedback about data accuracy, safety, and structure.
- They carried out governance training and capacity building for workers and other stakeholders.
- Review the policies and procedures regularly to see if they still meet the business’s changing needs and the dictated laws.
Phase 7: Scaling and Optimization
Objective: Institutionalize governance and implement enhancement strategies to cater to future necessities.
Actions
- Change the structure of the data architecture and security policies to address the current volume of data and expectations for future expansion.
- And include new data governance technologies so that processes can be computerized and improved.
- Outline the governance structure in anticipation of additional data sources, technologies, and business growth.
Drive Innovation Through Structured Data Governance
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Governance Solutions
Case Study 1: Mastering Data Governance with Microsoft Purview – Advanced Implementation Strategies
Kanerika partnered with a top healthcare organization to implement Microsoft Purview for data governance, enabling the organization to manage and protect its data assets more effectively.
Challenges
Data consistency, compliance, and security measures were hard to achieve in the client’s multi-faceted data environment. They needed a unified data governance system that allowed for sharing current needs and addressing potential increases. Enhancing their infrastructure, the need for affordability was paramount.
Business Impact
Leveraging Kanerika’s expertise in Purview implementation, the client has established a more visible, secure, and compliant data governance structure. This has helped them become more data-driven and make more informed decisions, improve processes and operational efficiencies, and lower compliance-related risks.
Shift From SSIS To Microsoft Fabric!
Kanerika keeps your migration steady and clear.
Tools and Technologies Facilitating the Data Governance Pillars Implementation
1. Data Quality and Profiling Tools
Data Quality Management Platforms: Tools such as Talend, Informatica Data Quality, and Atacama aid in data profiling, cleansing, and validation. These platforms consult the quality of data with respect to accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Thus, encouraging business enterprises to uphold data quality within systems.
Data Profiling Tools: IBM InfoSphere and SAS Data Management go a notch higher, involving efficient profiling that undertakes the cleaning process by identifying encumbrances such as duplicates or missing variables so that decisions are made with accurate information.
2. Security and Encryption Software
Data Security Platforms: Symantec Data Loss Prevention and McAfee Total Protection are comprehensive in their approach. They offer a rich set of features that include encryption, access controls, data loss prevention, and breach monitoring. This comprehensive nature instills a sense of security and protection in the audience.
Encryption Solutions: For instance, sensitive information is ensured to be safe from First Line Protect against unauthorized access because data is fully protected by software such as Vormetric Data Security and IBM Guardium wherever the data is.
3. Metadata Management Platforms
Metadata Repositories: Tools such as Alation, Collibra, and Informatica Metadata Manager, assist organizations in organizing their metadata, increasing the accuracy of tracking, searching, and classifying their data assets.
Cataloging Solutions: Platforms like Azure Purview and Google Cloud Data Catalog automatically search for metadata and track its lineage and classification. This proactive approach is key to promoting proper data management.
4. Data Lifecycle Management Solutions
Lifecycle Management Platforms: Solutions such as IBM Tivoli Storage Manager and Veritas Data Lifecycle Management assist businesses in controlling information from its creation to its deletion, together with policies on retention and archiving.
Backup and Archiving Tools: Commvault and Veeam offer organizations powerful data backup and archiving capabilities, enabling them to maintain compliant disaster recovery plans and manage the data lifecycle.
5. Compliance Tracking Systems
Regulatory Compliance Platforms: Organizations can deploy tools like One Trust or Trust Arc to comply with regulations such as the GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. The platforms offer a range of best practices, such as auditing, reporting, and data privacy management, to meet legal requirements.
Audit and Risk Management Software: It helps businesses remain compliant with regional regulations by providing an audit trail, risk management solutions, and compliance tracking with software applications such as SAP GRC and MetricStream.
6. Integration and ETL Tools:
ETL Platforms: Tools like Talend, Apache Nifi, and Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) help extract, transform, and load (ETL) data across different systems, ensuring smooth data integration and interoperability.
Data Integration Solutions: With the likes of MuleSoft and Dell Boomi, various applications, systems, and data sources are easily integrated, which helps harness real-time information and cut down on silos.
Enhance Business Intelligence with Comprehensive Data Governance
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Governance Solutions
Case Study 2: Implementing Modern Data Governance in a Global Bank Using Microsoft Purview
For a leading banking institution, Kanerika leveraged Microsoft Purview to revamp its data governance practices, addressing regulatory compliance and security challenges across its complex and sensitive data ecosystem.
Challenges
The institution faced fragmented data governance challenges, resulting in duplication and a huge exposure risk to non-compliance and security breaches. As a regulated organization, the bank required assistance in guaranteeing the correctness, safety, and legal compliance of customer information while making the most of internal data flows.
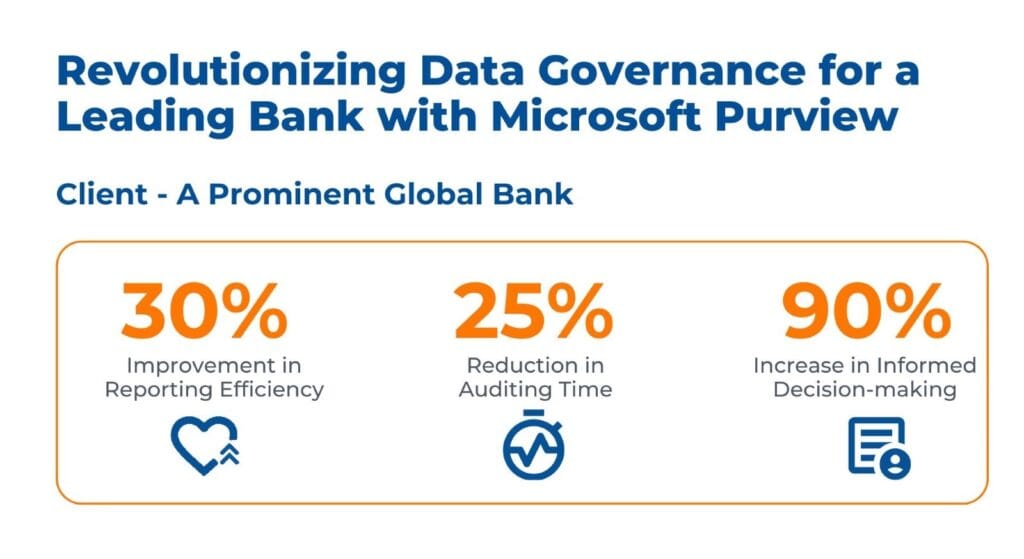
Business Impact
Microsoft Purview was deployed with the help of Kanerika to assist the bank in redefining its governance structure. Increased management and data visibility lowered the operation cost, ensured that the bank was fully compliant with changing regulatory requirements, and improved its standing in the eyes of clients and regulators.
Choose Kanerika for Advanced Data Governance Solutions
At Kanerika, we excel in delivering customized and innovative data governance solutions designed to meet your unique needs by leveraging powerful solutions such as Microsoft Purview. Our expertise is in building automated, integrated, and responsive data governance frameworks that boost data quality, enhance security, and align seamlessly with your business goals. Utilizing our proprietary consulting frameworks and composable architecture, we help you streamline operations, reduce costs, and confidently make data-driven decisions.
With a global footprint and deep industry experience, we bring proven best practices from leading brands across the world to your organization. Our unwavering focus on continuous improvement, constantly refining our solutions to meet the evolving data governance landscape and client satisfaction. Ensures your data governance initiatives are effectively implemented and refined for long-term success and growth.
Streamline Operations with Data Governance – Get Started Today
Partner with Kanerika for Expert Data Governance Solutions
FAQs
What are the 4 pillars of data governance?
Data governance rests on four keystones: accountability (who’s responsible for what data?), compliance (meeting legal and regulatory standards), data quality (ensuring accuracy and reliability), and data security (protecting data from unauthorized access). These pillars work together to ensure trustworthy and valuable data. Think of them as the foundational supports holding up the entire data ecosystem.
What are the 5 C's of data governance?
Data governance hinges on five key elements: Compliance ensures adherence to laws and regulations; Consistency provides standardized data definitions and processes; Completeness guarantees accurate and comprehensive data; Credibility builds trust through data quality and validation; and Confidentiality protects sensitive information through appropriate access controls. These Cs together ensure reliable and trustworthy data.
What are the 4 pillars of data structure?
Data structures aren’t built on four rigid “pillars,” but we can highlight four crucial aspects. These are: efficient storage (how data’s organized in memory), easy access (finding specific data quickly), effective manipulation (adding, deleting, updating data), and overall suitability for the task (choosing the right structure for the job). Understanding these interwoven aspects is key to mastering data structures.
What are the 3 key elements of good data governance?
Good data governance hinges on three pillars: accountability (clearly defining who’s responsible for data at each stage), compliance (ensuring data adheres to all relevant regulations and internal policies), and accessibility (making quality data readily available to authorized users for informed decision-making). These work together to build trust and value from your data assets.
What are the 3 key roles of data governance?
Data governance ensures data quality, enabling trustworthy decision-making. It establishes clear accountability for data management, preventing errors and inconsistencies. Finally, it aligns data practices with legal and regulatory requirements, minimizing risk. In short, it’s about maximizing the value and minimizing the risk of your data.
What are the 4 pillars of big data?
Big data isn’t just about massive amounts of information; it’s about handling its unique characteristics. The four pillars – Volume (sheer size), Velocity (speed of data flow), Variety (different data types), and Veracity (accuracy and trustworthiness) – highlight these key challenges and opportunities. Mastering these aspects is crucial for effectively leveraging big data’s potential. Essentially, they define what makes big data *big* and how we deal with it.
What is the McKinsey data governance framework?
McKinsey’s data governance framework isn’t a rigid, one-size-fits-all solution, but rather a flexible approach. It prioritizes establishing clear accountability for data quality and usage, ensuring data is trusted and accessible across an organization. Essentially, it’s a structured methodology for managing the entire lifecycle of data, from its origin to its eventual use in decision-making. This involves defining roles, processes, and technologies to achieve optimal data value.
What are the 4 pillars of data analysis?
Data analysis rests on four key pillars: Firstly, asking the right question—defining a clear objective. Second, data acquisition and cleaning—getting reliable, usable data. Third, analysis itself—applying appropriate methods to extract insights. Finally, communicating those findings effectively—making the results understandable and actionable. These pillars work together to ensure a robust and valuable analytical process.
What is the PWC data governance framework?
PwC’s data governance framework isn’t a single, rigid structure but a flexible approach tailored to each client’s needs. It centers on establishing clear data ownership, accountability, and policies to ensure data quality, security, and compliance. Essentially, it’s a roadmap for managing the entire data lifecycle, from creation to disposal, minimizing risk and maximizing value. This holistic approach aims to build trust and confidence in data-driven decision-making.
What are the basics of data governance?
Data governance is essentially setting the rules for how your organization handles data – who can access it, how it’s stored, and how it’s used. It’s about ensuring data quality, accuracy, and compliance with regulations. Think of it as establishing a responsible and efficient system for managing your most valuable asset: information. Ultimately, it minimizes risk and maximizes value.
What is data governance framework?
A data governance framework is essentially a roadmap for managing your organization’s data. It defines roles, responsibilities, and processes to ensure data quality, security, and compliance. Think of it as a set of rules and guidelines to keep your data organized, accurate, and trustworthy. Ultimately, it’s about maximizing the value and minimizing the risk associated with your data.
What is the core of data governance?
Data governance is fundamentally about establishing trust in your data. It’s the framework ensuring data is accurate, accessible, and used responsibly, aligning with organizational objectives. This involves defining roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing the entire data lifecycle. Ultimately, it’s about maximizing the value of data while minimizing risk.









